【零基础入门SpringBoot2】—— 原理解析
一、Profile 功能
- 为了方便多环境适配,SpringBoot简化了 profile 功能
- 主要的方式:通过创建多个配置文件,选择激活哪些环境
1、application-profile 功能
- 对于默认配置文件 application.yaml 和 application.properties 在任何时候都会加载
- 我们如何区分以及创建不同生产环境的配置文件呢?
- 文件名采用
application-(生产环境).yaml的方式即可
- 文件名采用
- 那我们如何激活指定的环境呢?
- 第一种方式:采用命令行的形式激活
java -jar xxx.jar --spring.profiles.active=环境名- 如果在我们用上面的这条指令的同时,添加了修改属性的指令,那么就会以我们新的属性值为准
- 第二种方式:采用配置文件激活
- 在我们默认的配置文件中
spring.profiles.active=环境
- 在我们默认的配置文件中
- 第一种方式:采用命令行的形式激活
- 有两点我们需要注意:
- 默认配置环境和我们指定激活的环境都会生效
- 如果出现同名配置项,那么以我们 profile 配置优先
2、@Profile条件装配功能
- 通过案例来说明:
- 我们创建一个Person接口,并定义它的两个实现类,并通过 @Profile 注解指明对应生产环境
- 在 @Profile(“prod”) 环境下,才会使用Boss类
- 在 @Profile(“test”) 环境下,才会使用Employee类
- 我们创建一个Person接口,并定义它的两个实现类,并通过 @Profile 注解指明对应生产环境
- Person 接口
package com.atguigu.boot05.bean;
/**
* @author Bonbons
* @version 1.0
*/
public interface Person {
String getName();
Integer getAge();
}
- Boss类
package com.atguigu.boot05.bean;
import lombok.Data;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Profile;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* @author Bonbons
* @version 1.0
*/
@Data
@Profile("prod")
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties("person")
public class Boss implements Person{
private String name;
private Integer age;
}
- Employee类
package com.atguigu.boot05.bean;
import lombok.Data;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Profile;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* @author Bonbons
* @version 1.0
*/
@Data
@Profile("test")
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties("person")
public class Employee implements Person{
private String name;
private Integer age;
}
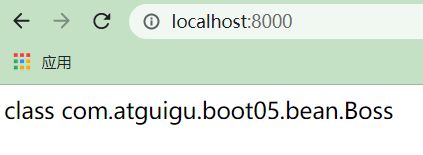
- 编写控制器的测试方法:【演示在不同环境下我们Person接口的实现类是不同的】
@Autowired
Person person;
@GetMapping("/")
public String hello(){
return person.getClass().toString();
}
- 以下为我们的三个配置文件
application.properties
person.name=boss
server.port=8080
spring.profiles.active=prod
application-prod.yaml
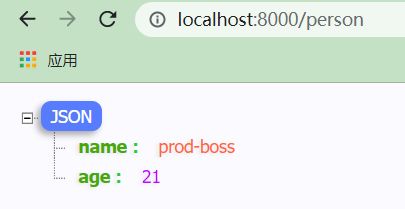
person:
name: prod-boss
server:
port: 8000
application-test.yaml
person:
name: test-boss
age: 25
server:
port: 7000
3、profile分组
- 我觉得就是可以把一个生产环境分为几个配置文件,通过数组的方式划分不同的生产环境
- 然后通过配置文件激活的时候原来指定环境名,现在替换为环境数组名
application.properties
person.name=boss
server.port=8080
spring.profiles.active=myprod
spring.profiles.group.myprod[0]=ppd
spring.profiles.group.myprod[1]=prod
spring.profiles.group.mytest[0]=test
application-ppd.yaml
person:
age: 21
- 编写一个控制器方法,处理 /person 请求,返回Person对象
- 我们prod设置了Person的name属性
- 我们ppd设置了Person的age属性
- 如果一起激活这两个环境,那么Person的数据就会正常显示
二、外部化配置
-
我们将所有的信息抽取成一个文件放在web里面集中管理——外部化配置
-
详情可以参考官方文档
-
外部化配置截图:
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-4XAodyyu-1680057177430)(attachment:cfd409b05609c96f001bbe38142151d3)]
1、外部配置源
- 配置文件常用来源:
-
Java属性文件
-
yaml文件
-
环境变量【电脑本机里面配置的】
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-o9DB5X7o-1680057177432)(attachment:39fcd3a0363be69a1f480542906580bf)]
-
命令行参数
-
2、配置文件查找位置
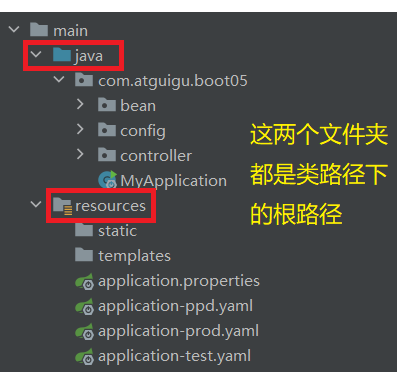
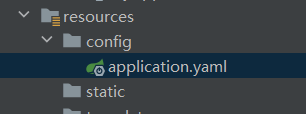
(1)classpath 根路径下
(2)classpath 根路径下的 config 目录
(3)jar 包当前目录
(4)jar 包当前目录下的 config目录
(5) /config子目录的直接子目录
这个需要在Linux服务器的根目录下进行操作
3、配置文件加载顺序
- 当前jar包内部的application.properties和application.yml
- 当前jar包内部的application-{profile}.properties 和 application-{profile}.yml
- 引用的外部jar包的application.properties和application.yml
- 引用的外部jar包的application-{profile}.properties 和 application-{profile}.yml
4、后面的可以覆盖前面的同名配置项
- 我们需要知道,上面配置文件查找位置,后给出的同名配置后覆盖先给出的同名配置
- 对于文件加载顺序,也是后加载的会覆盖先加载的同名配置
三、自定义 starter
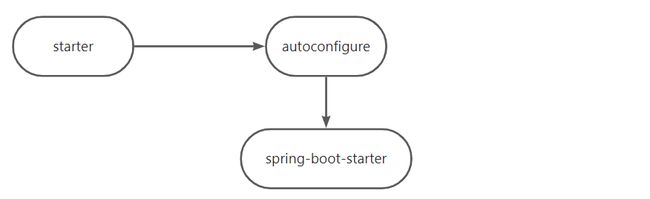
1、starter 启动原理
- starter没有任何代码,只是说明我们当前场景要引入哪些依赖,还会引入了我们当前场景真正的自动配置包 autoconfigure,
- 自动配置包就要引入我们SpringBoot最底层的、每个模块都要用到的 springboot-starter
-
autoconfigure包中配置使用 META-INF/spring.factories 中 EnableAutoConfiguration 的值,使得项目启动加载指定的自动配置类
-
编写自动配置类 xxxAutoConfiguration -> xxxxProperties
- @Configuration
- @Conditional
- @EnableConfigurationProperties
- @Bean
-
引入starter — xxxAutoConfiguration — 容器中放入组件 ---- 绑定xxxProperties ---- 配置项
2、自定义starter
- atguigu-hello-spring-boot-starter(启动器)
- atguigu-hello-spring-boot-starter-autoconfigure(自动配置包)
四、SpringBoot原理
- Spring原理、SpringMVC原理、自动配置原理、SpringBoot原理
1、SpringBoot启动过程
public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Class<?>[] primarySources, String[] args) {
return new SpringApplication(primarySources).run(args);
} // ↑ 创建SpringApplication ↑ 运行SpringApplication
(1)创建 SpringApplication
-
保存一些信息
-
判定当前应用的类型 -> ClassUtils: Servlet
// WebApplicationType类 >> 判断类型 static WebApplicationType deduceFromClasspath() { if (ClassUtils.isPresent(WEBFLUX_INDICATOR_CLASS, null) && !ClassUtils.isPresent(WEBMVC_INDICATOR_CLASS, null) && !ClassUtils.isPresent(JERSEY_INDICATOR_CLASS, null)) { return WebApplicationType.REACTIVE; // 返回响应式编程类型 } for (String className : SERVLET_INDICATOR_CLASSES) { if (!ClassUtils.isPresent(className, null)) { return WebApplicationType.NONE; } } return WebApplicationType.SERVLET; // 返回SERVLET编程类型 } -
bootstrappers: 初始启动引导器
(List: 去spring.factories 文件中找 org.springframework.boot.Bootstrapper) -
找 ApplicationContextInitializer(初始化器);去spring.factories找 ApplicationContextInitializer
List<ApplicationContextInitializer<?>> initializers
- 找 ApplicationListener (应用监听器);去spring.factories找 ApplicationListener
List<ApplicationListener<?>> listeners
- 创建 SpringApplication 完整代码
// 构造方法
public SpringApplication(ResourceLoader resourceLoader, Class<?>... primarySources) {
this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader;
Assert.notNull(primarySources, "PrimarySources must not be null");
this.primarySources = new LinkedHashSet<>(Arrays.asList(primarySources));
// WebApplicationType是枚举类 有NONE,SERVLET,REACTIVE 下行webApplicationType是SERVLET
this.webApplicationType = WebApplicationType.deduceFromClasspath();
// 初始启动引导器 去spring.factories文件中找org.springframework.boot.Bootstrapper 但我找不到实现Bootstrapper接口的类
this.bootstrappers = new ArrayList<>(getSpringFactoriesInstances(Bootstrapper.class));
// 去spring.factories找 ApplicationContextInitializer
setInitializers((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationContextInitializer.class));
// 去spring.factories找 ApplicationListener
setListeners((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class));
this.mainApplicationClass = deduceMainApplicationClass(); // 决定哪个类是我们的主程序
} // ↓
private Class<?> deduceMainApplicationClass() {
try {
StackTraceElement[] stackTrace = new RuntimeException().getStackTrace();
for (StackTraceElement stackTraceElement : stackTrace) {
// 哪个类有main方法 被找到的第1个类就是主程序类
if ("main".equals(stackTraceElement.getMethodName())) {
return Class.forName(stackTraceElement.getClassName());
}
}
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
// Swallow and continue
}
return null;
}
总结:应用创建的过程就是把一些关键的组件信息读取并保存到 SpringAppication中,作为运行SpringApplication的前置工作
(2)运行 SpringApplication
- StopWatch
- 记录应用的启动时间
- 创建引导上下文(Context环境)createBootstrapContext()
- 获取到所有之前的 bootstrappers 挨个执行 intitialize() 来完成对引导启动器上下文环境设置
```java
public interface Bootstrapper {
/**
* Initialize the given {@link BootstrapRegistry} with any required registrations.
* @param registry the registry to initialize
*/
void intitialize(BootstrapRegistry registry);
}
```
- 让当前应用进入headless模式, java.awt.headless
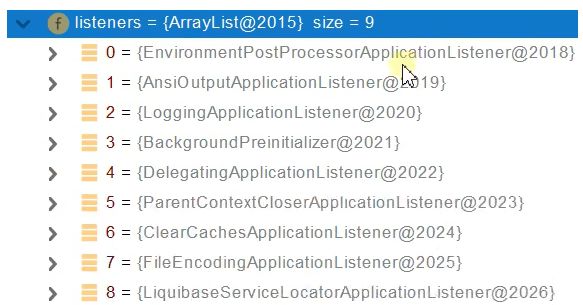
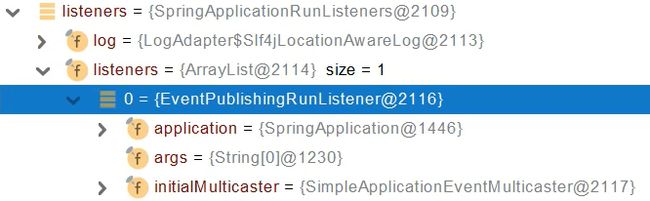
- 获取所有 RunListener(运行监听器)【为了方便所有Listener进行事件感知】
- getSpringFactoriesInstances 去spring.factories找 SpringApplicationRunListener.
- 遍历 SpringApplicationRunListener 调用 starting 方法;
- 相当于通知所有感兴趣系统正在启动过程的人,项目正在 starting。
- 保存命令行参数;ApplicationArguments
- 准备环境 prepareEnvironment();
- 返回或者创建基础环境信息对象。StandardServletEnvironment
- 配置环境信息对象。
- 读取所有的配置源的配置属性值。 - 绑定环境信息
- 监听器调用 listener.environmentPrepared();通知所有的监听器当前环境准备完成
- 创建IOC容器(createApplicationContext())
- 根据项目类型(Servlet)创建容器,
- 当前会创建 AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext
- 准备ApplicationContext IOC容器的基本信息 prepareContext()
- 保存环境信息
- IOC容器的后置处理流程。
- 应用初始化器;applyInitializers;
- 遍历所有的 ApplicationContextInitializer 。调用 initialize.。来对ioc容器进行初始化扩展功能
- 遍历所有的 listener 调用 contextPrepared。EventPublishRunListenr;通知所有的监听器contextPrepared
- 所有的监听器 调用 contextLoaded。通知所有的监听器 contextLoaded;
- 刷新IOC容器。refreshContext
- 创建容器中的所有组件(Spring注解)
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons. 使用单例模式 实例化所有剩余的(非延迟初始化)组件。 finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory); - 容器刷新完成后工作?afterRefresh
- 所有监听 器 调用 listeners.started(context); 通知所有的监听器 started
- 调用所有runners;callRunners()
- 获取容器中的 ApplicationRunner
@FunctionalInterface public interface ApplicationRunner { /** * Callback used to run the bean. * @param args incoming application arguments * @throws Exception on error */ void run(ApplicationArguments args) throws Exception; }- 获取容器中的 CommandLineRunner
@FunctionalInterface public interface CommandLineRunner { /** * Callback used to run the bean. * @param args incoming main method arguments * @throws Exception on error */ void run(String... args) throws Exception; }- 合并所有runner并且按照@Order进行排序
- 遍历所有的runner。调用 run 方法
- 如果以上有异常,
- 调用Listener 的 failed
- 调用所有监听器的 running 方法 listeners.running(context); 通知所有的监听器 running
- running如果有问题。继续通知 failed 。调用所有 Listener 的 failed;通知所有的监听器 failed
- 最终返回IOC容器 return context
- 运行SpringApplication 完整代码
// run()方法
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();//开始计时器
stopWatch.start();//开始计时
// 1.
// 创建引导上下文(Context环境)createBootstrapContext()
// 获取到所有之前的 bootstrappers 挨个执行 intitialize() 来完成对引导启动器上下文环境设置
DefaultBootstrapContext bootstrapContext = createBootstrapContext();
// 2.到最后该方法会返回这context
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
// 3.让当前应用进入headless模式
configureHeadlessProperty();
// 4.获取所有 RunListener(运行监听器)为了方便所有Listener进行事件感知
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
// 5. 遍历 SpringApplicationRunListener 调用starting方法
// 相当于通知所有感兴趣系统正在启动过程的人 项目正在starting
listeners.starting(bootstrapContext, this.mainApplicationClass);
try {
// 6.保存命令行参数 ApplicationArguments
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args);
// 7.准备环境
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, bootstrapContext, applicationArguments);
configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment);
/*
打印标志
. ____ _ __ _ _
/\\ / ___'_ __ _ _(_)_ __ __ _ \ \ \ \
( ( )\___ | '_ | '_| | '_ \/ _` | \ \ \ \
\\/ ___)| |_)| | | | | || (_| | ) ) ) )
' |____| .__|_| |_|_| |_\__, | / / / /
=========|_|==============|___/=/_/_/_/
:: Spring Boot :: (v2.4.2)
*/
Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment);
// 创建IOC容器(createApplicationContext())
// 根据项目类型webApplicationType(NONE,SERVLET,REACTIVE)创建容器,
// 当前会创建 AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext
context = createApplicationContext();
context.setApplicationStartup(this.applicationStartup);
// 8.准备ApplicationContext IOC容器的基本信息
prepareContext(bootstrapContext, context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner);
// 9.刷新IOC容器 创建容器中的所有组件 Spring框架的内容
refreshContext(context);
// 该方法没内容,大概为将来填入
afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
stopWatch.stop(); // 停止计时
if (this.logStartupInfo) { // this.logStartupInfo默认是true
new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass).logStarted(getApplicationLog(), stopWatch);
}
// 10.
listeners.started(context);
// 11.调用所有runners
callRunners(context, applicationArguments);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// 13.
handleRunFailure(context, ex, listeners);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
try {
// 12.
listeners.running(context);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// 13.
handleRunFailure(context, ex, null);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
return context;
}
2、自定义事件监听组件
-
Ctrl + O 快速批量实现接口方法
-
MyApplicationContextInitializer
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextInitializer; import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext; public class MyApplicationContextInitializer implements ApplicationContextInitializer { @Override public void initialize(ConfigurableApplicationContext applicationContext) { System.out.println("MyApplicationContextInitializer ....initialize.... "); } } -
MyApplicationListener
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationEvent; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener; public class MyApplicationListener implements ApplicationListener { @Override public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEvent event) { System.out.println("MyApplicationListener.....onApplicationEvent..."); } } -
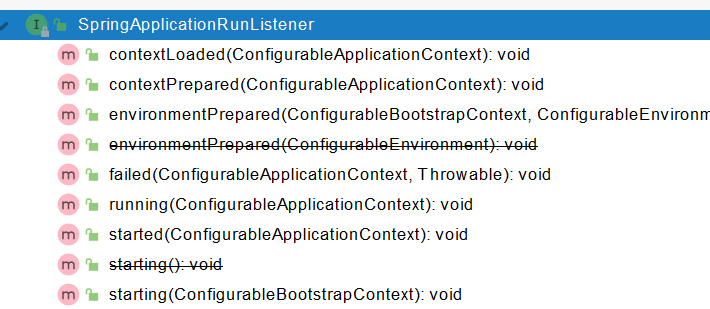
MySpringApplicationRunListener
import org.springframework.boot.ConfigurableBootstrapContext; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplicationRunListener; import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext; import org.springframework.core.env.ConfigurableEnvironment; public class MySpringApplicationRunListener implements SpringApplicationRunListener { private SpringApplication application; public MySpringApplicationRunListener(SpringApplication application, String[] args){ this.application = application; } @Override public void starting(ConfigurableBootstrapContext bootstrapContext) { System.out.println("MySpringApplicationRunListener....starting...."); } @Override public void environmentPrepared(ConfigurableBootstrapContext bootstrapContext, ConfigurableEnvironment environment) { System.out.println("MySpringApplicationRunListener....environmentPrepared...."); } @Override public void contextPrepared(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) { System.out.println("MySpringApplicationRunListener....contextPrepared...."); } @Override public void contextLoaded(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) { System.out.println("MySpringApplicationRunListener....contextLoaded...."); } @Override public void started(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) { System.out.println("MySpringApplicationRunListener....started...."); } @Override public void running(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) { System.out.println("MySpringApplicationRunListener....running...."); } @Override public void failed(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, Throwable exception) { System.out.println("MySpringApplicationRunListener....failed...."); } } -
MyApplicationRunner
import org.springframework.boot.ApplicationArguments; import org.springframework.boot.ApplicationRunner; import org.springframework.core.annotation.Order; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Order(1) // 按照Order排序 数字越大优先级越高 @Component // 放入容器 public class MyApplicationRunner implements ApplicationRunner { @Override public void run(ApplicationArguments args) throws Exception { System.out.println("MyApplicationRunner...run..."); } } -
MyCommandLineRunner
import org.springframework.boot.CommandLineRunner; import org.springframework.core.annotation.Order; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; /** * 应用启动做一个一次性事情 */ @Order(2) // 按照Order排序 @Component // 放入容器 public class MyCommandLineRunner implements CommandLineRunner { @Override public void run(String... args) throws Exception { System.out.println("MyCommandLineRunner....run...."); } } -
注册MyApplicationContextInitializer,MyApplicationListener,MySpringApplicationRunListener
- resources/META-INF/spring.factories
org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextInitializer=\ com.atguigu.boot.listener.MyApplicationContextInitializer org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener=\ com.atguigu.boot.listener.MyApplicationListener org.springframework.boot.SpringApplicationRunListener=\ com.atguigu.boot.listener.MySpringApplicationRunListener
- resources/META-INF/spring.factories