ElasticSearch 8 学习笔记总结(五)
文章目录
- 一、ElasticSearch 8 版本
- 二、ES8 集群 环境安装
-
- 1. 生成安全证书
- 2. 生成http证书
- 3. 配置第一个节点
- 4. 配置其他节点
- 三、ES集群 关联问题解决
- 四、 Kibana 安装和使用
- 五、kibana 基础操作
-
- 1. 索引操作
- 2. 文档操作
- 3. 文档搜索
- 4. 索引模板
- 六、分词器
- 七、文档评分机制
-
- 1. 什么是文档评分机制?
- 2. 分值计算 TF(词频)公式
- 3. 分值计算 IDF(逆文档频率)公式
- 4. 分值计算 评分公式
- 5. 分值计算 权重分析
一、ElasticSearch 8 版本
ES 8版本,环境是Java17的环境,jdk17号称最快的jdk。
对于升级版本如果有顾虑的话,可以考虑下载含有适配jdk的es版本。

二、ES8 集群 环境安装
1. 生成安全证书
同样,es不支持root用户进行操作。
# 新增es用户
useradd es
# 为es用户设置密码
passwd es
# 创建数据文件目录
mkdir elasticsearch-8.6.2/data
# 创建证书目录
mkdir elasticsearch-8.6.2/config/certs
# 修改文件拥有者
chown -R es:es elasticsearch-8.6.2
再第一台服务器节点es-node-1 设置集群多节点通信密钥:
# 切换用户
su es
# 签发ca证书,过程中需要按两次回车
bin/elasticsearch-certutil ca
# 用ca证书签发节点证书,过程中需按三次回车键
bin/elasticsearch-certutil cert --ca elastic-stack-ca.p12
# 将生成的证书移动到config/certs目录。
mv elastic-stack-ca.p12 elastic-certificates.p12 config/certs/
2. 生成http证书
# 生成http证书
bin/elasticsearch-certutil http
# 下面一系列的操作
[es@Test-CentOS7 elasticsearch-8.6.2]$ bin/elasticsearch-certutil cert --ca elastic-stack-ca.p12
This tool assists you in the generation of X.509 certificates and certificate
signing requests for use with SSL/TLS in the Elastic stack.
The 'cert' mode generates X.509 certificate and private keys.
* By default, this generates a single certificate and key for use
on a single instance.
* The '-multiple' option will prompt you to enter details for multiple
instances and will generate a certificate and key for each one
* The '-in' option allows for the certificate generation to be automated by describing
the details of each instance in a YAML file
* An instance is any piece of the Elastic Stack that requires an SSL certificate.
Depending on your configuration, Elasticsearch, Logstash, Kibana, and Beats
may all require a certificate and private key.
* The minimum required value for each instance is a name. This can simply be the
hostname, which will be used as the Common Name of the certificate. A full
distinguished name may also be used.
* A filename value may be required for each instance. This is necessary when the
name would result in an invalid file or directory name. The name provided here
is used as the directory name (within the zip) and the prefix for the key and
certificate files. The filename is required if you are prompted and the name
is not displayed in the prompt.
* IP addresses and DNS names are optional. Multiple values can be specified as a
comma separated string. If no IP addresses or DNS names are provided, you may
disable hostname verification in your SSL configuration.
* All certificates generated by this tool will be signed by a certificate authority (CA)
unless the --self-signed command line option is specified.
The tool can automatically generate a new CA for you, or you can provide your own with
the --ca or --ca-cert command line options.
By default the 'cert' mode produces a single PKCS#12 output file which holds:
* The instance certificate
* The private key for the instance certificate
* The CA certificate
If you specify any of the following options:
* -pem (PEM formatted output)
* -multiple (generate multiple certificates)
* -in (generate certificates from an input file)
then the output will be be a zip file containing individual certificate/key files
Enter password for CA (elastic-stack-ca.p12) :
Please enter the desired output file [elastic-certificates.p12]:
Enter password for elastic-certificates.p12 :
Certificates written to /opt/es/elasticsearch-8.6.2/elastic-certificates.p12
This file should be properly secured as it contains the private key for
your instance.
This file is a self contained file and can be copied and used 'as is'
For each Elastic product that you wish to configure, you should copy
this '.p12' file to the relevant configuration directory
and then follow the SSL configuration instructions in the product guide.
For client applications, you may only need to copy the CA certificate and
configure the client to trust this certificate.
[es@Test-CentOS7 elasticsearch-8.6.2]$ ls
bin data elastic-stack-ca.p12 lib logs NOTICE.txt README.asciidoc
config elastic-certificates.p12 jdk LICENSE.txt modules plugins
[es@Test-CentOS7 elasticsearch-8.6.2]$ mv elastic-stack-ca.p12 elastic-certificates.p12 config/certs/
[es@Test-CentOS7 elasticsearch-8.6.2]$ bin/elasticsearch-certutil http
## Elasticsearch HTTP Certificate Utility
The 'http' command guides you through the process of generating certificates
for use on the HTTP (Rest) interface for Elasticsearch.
This tool will ask you a number of questions in order to generate the right
set of files for your needs.
## Do you wish to generate a Certificate Signing Request (CSR)?
A CSR is used when you want your certificate to be created by an existing
Certificate Authority (CA) that you do not control (that is, you don't have
access to the keys for that CA).
If you are in a corporate environment with a central security team, then you
may have an existing Corporate CA that can generate your certificate for you.
Infrastructure within your organisation may already be configured to trust this
CA, so it may be easier for clients to connect to Elasticsearch if you use a
CSR and send that request to the team that controls your CA.
If you choose not to generate a CSR, this tool will generate a new certificate
for you. That certificate will be signed by a CA under your control. This is a
quick and easy way to secure your cluster with TLS, but you will need to
configure all your clients to trust that custom CA.
Generate a CSR? [y/N]N
## Do you have an existing Certificate Authority (CA) key-pair that you wish to use to sign your certificate?
If you have an existing CA certificate and key, then you can use that CA to
sign your new http certificate. This allows you to use the same CA across
multiple Elasticsearch clusters which can make it easier to configure clients,
and may be easier for you to manage.
If you do not have an existing CA, one will be generated for you.
Use an existing CA? [y/N]y
## What is the path to your CA?
Please enter the full pathname to the Certificate Authority that you wish to
use for signing your new http certificate. This can be in PKCS#12 (.p12), JKS
(.jks) or PEM (.crt, .key, .pem) format.
CA Path: certs/elastic-stack-ca.p12
Reading a PKCS12 keystore requires a password.
It is possible for the keystore's password to be blank,
in which case you can simply press <ENTER> at the prompt
Password for elastic-stack-ca.p12:
## How long should your certificates be valid?
Every certificate has an expiry date. When the expiry date is reached clients
will stop trusting your certificate and TLS connections will fail.
Best practice suggests that you should either:
(a) set this to a short duration (90 - 120 days) and have automatic processes
to generate a new certificate before the old one expires, or
(b) set it to a longer duration (3 - 5 years) and then perform a manual update
a few months before it expires.
You may enter the validity period in years (e.g. 3Y), months (e.g. 18M), or days (e.g. 90D)
For how long should your certificate be valid? [5y] 5y
## Do you wish to generate one certificate per node?
If you have multiple nodes in your cluster, then you may choose to generate a
separate certificate for each of these nodes. Each certificate will have its
own private key, and will be issued for a specific hostname or IP address.
Alternatively, you may wish to generate a single certificate that is valid
across all the hostnames or addresses in your cluster.
If all of your nodes will be accessed through a single domain
(e.g. node01.es.example.com, node02.es.example.com, etc) then you may find it
simpler to generate one certificate with a wildcard hostname (*.es.example.com)
and use that across all of your nodes.
However, if you do not have a common domain name, and you expect to add
additional nodes to your cluster in the future, then you should generate a
certificate per node so that you can more easily generate new certificates when
you provision new nodes.
Generate a certificate per node? [y/N]N
## Which hostnames will be used to connect to your nodes?
These hostnames will be added as "DNS" names in the "Subject Alternative Name"
(SAN) field in your certificate.
You should list every hostname and variant that people will use to connect to
your cluster over http.
Do not list IP addresses here, you will be asked to enter them later.
If you wish to use a wildcard certificate (for example *.es.example.com) you
can enter that here.
Enter all the hostnames that you need, one per line.
When you are done, press <ENTER> once more to move on to the next step.
linux1
linux2
linux3
You entered the following hostnames.
- linux1
- linux2
- linux3
Is this correct [Y/n]Y
## Which IP addresses will be used to connect to your nodes?
If your clients will ever connect to your nodes by numeric IP address, then you
can list these as valid IP "Subject Alternative Name" (SAN) fields in your
certificate.
If you do not have fixed IP addresses, or not wish to support direct IP access
to your cluster then you can just press <ENTER> to skip this step.
Enter all the IP addresses that you need, one per line.
When you are done, press <ENTER> once more to move on to the next step.
192.168.43.133
192.168.43.69
192.168.43.134
You entered the following IP addresses.
- 192.168.43.133
- 192.168.43.69
- 192.168.43.134
Is this correct [Y/n]Y
## Other certificate options
The generated certificate will have the following additional configuration
values. These values have been selected based on a combination of the
information you have provided above and secure defaults. You should not need to
change these values unless you have specific requirements.
Key Name: linux1
Subject DN: CN=linux1
Key Size: 2048
Do you wish to change any of these options? [y/N]n
## What password do you want for your private key(s)?
Your private key(s) will be stored in a PKCS#12 keystore file named "http.p12".
This type of keystore is always password protected, but it is possible to use a
blank password.
If you wish to use a blank password, simply press <enter> at the prompt below.
Provide a password for the "http.p12" file: [<ENTER> for none]
## Where should we save the generated files?
A number of files will be generated including your private key(s),
public certificate(s), and sample configuration options for Elastic Stack products.
These files will be included in a single zip archive.
What filename should be used for the output zip file? [/opt/es/elasticsearch-8.6.2/elasticsearch-ssl-http.zip]
Zip file written to /opt/es/elasticsearch-8.6.2/elasticsearch-ssl-http.zip
# 最后生成了一个压缩包,里面就存放了http证书。
# 解压文件
unzip elasticsearch-ssl-http.zip
# 移动到配置文件中
mv elasticsearch/http.p12 kibana/elasticsearch-ca.pem config/certs
3. 配置第一个节点
配置node-01节点的elasticsearch.yml文件:
# 设置ES集群名称
cluster.name: es-cluster
# 设置集群中当前节点名称
node.name: es-node-1
# 设置数据,日志文件路径
path.data: /opt/es/elasticsearch-8.6.2/data
path.logs: /opt/es/elasticsearch-8.6.2/logs
# 设置网络访问节点
network.host: linux1
# 设置网络访问端口
http.port: 9200
# 初始节点
discovery.seed_hosts: ["linux1"]
# 安全认证
xpack.security.enabled: true
xpack.security.enrollment.enabled: true
xpack.security.http.ssl:
enabled: true
keystore.path: /opt/es/elasticsearch-8.6.2/config/certs/http.p12
truststore.path: /opt/es/elasticsearch-8.6.2/config/certs/http.p12
xpack.security.transport.ssl:
enabled: true
verification_mode: certificate
keystore.path: /opt/es/elasticsearch-8.6.2/config/certs/elastic-certificates.p12
truststore.path: /opt/es/elasticsearch-8.6.2/config/certs/elastic-certificates.p12
# 此处需注意,es-node-1为上面配置的节点名称
cluster.initial_master_nodes: ["es-node-1"]
http.host: [_local_,_site_]
ingest.geoip.downloader.enabled: false
xpack.security.http.ssl.client_authentication: none
# 启动es服务
bin/elasticsearch
拿到密码,访问https://linux1:9200即可。
# 可以配置etc/hosts文件
192.168.43.133 linux1
192.168.43.69 linux2
192.168.43.134 linux3
访问https://linux1:9200。
4. 配置其他节点
同样上传elasticsearch8版本压缩包,然后解压。
第一步,创建es用户,配置权限。
# 新增es用户
useradd es
# 为es用户设置密码
passwd es
# 创建数据文件目录
mkdir elasticsearch-8.6.2/data
# 创建证书目录
mkdir elasticsearch-8.6.2/config/certs
# 修改文件拥有者
chown -R es:es elasticsearch-8.6.2
第二步:证书,因为第一个节点已经生成了证书,所以其他节点直接搬过来就行。
第三步:配置elasticsearch.yml配置文件,注意修改节点名称以及网络访问节点。
# 设置ES集群名称
cluster.name: es-cluster
# 设置集群中当前节点名称
node.name: es-node-2
# 设置数据,日志文件路径
path.data: /opt/es/elasticsearch-8.6.2/data
path.logs: /opt/es/elasticsearch-8.6.2/logs
# 设置网络访问节点
network.host: linux2
# 设置网络访问端口
http.port: 9200
# 初始节点
discovery.seed_hosts: ["linux1"]
# 安全认证
xpack.security.enabled: true
xpack.security.enrollment.enabled: true
xpack.security.http.ssl:
enabled: true
keystore.path: /opt/es/elasticsearch-8.6.2/config/certs/http.p12
truststore.path: /opt/es/elasticsearch-8.6.2/config/certs/http.p12
xpack.security.transport.ssl:
enabled: true
verification_mode: certificate
keystore.path: /opt/es/elasticsearch-8.6.2/config/certs/elastic-certificates.p12
truststore.path: /opt/es/elasticsearch-8.6.2/config/certs/elastic-certificates.p12
# 此处需注意,es-node-1为上面配置的节点名称
cluster.initial_master_nodes: ["es-node-1"]
http.host: [_local_,_site_]
ingest.geoip.downloader.enabled: false
xpack.security.http.ssl.client_authentication: none
第四步:依次启动集群节点,注意不要使用root用户启动。
# 后台启动服务
bin/elasticsearch -d
第五步:访问测试。

注意:可能涉及到账号密码, 忘记了,可以设置免密登录。
三、ES集群 关联问题解决
四、 Kibana 安装和使用
Kibana是es的开源分析可视化工具。
第一步:去es官方,下载对应版本的Kibana压缩包。
第二步:创建证书,移动给kibana。
# 在es服务器中生成证书,输入回车即可
bin/elasticsearch-certutil csr -name kibana -dns linux1
# 会生成一个csr-bundle.zip,并且解压它。
unzip csr-bundle.zip
# 将解压后的文件移动到kibana的config目录中
mv kibana.csr kibana.key /opt/es/kibana-8.6.2/config/
[root@Test-CentOS7 config]$ pwd
/opt/es/kibana-8.6.2/config
# 生成crt文件
[root@Test-CentOS7 config]$ openssl x509 -req -in kibana.csr -signkey kibana.key -out kibana.crt
第三步:修改配置文件:kibana.yml。
# 服务端口
server.port: 5601
# 服务主机名
server.host: "linux1"
# 国际化 - 中文
i18n.locale: "zh-CN"
# ES服务主机地址
elasticsearch.hosts: ["https://linux1:9200"]
# 访问ES服务的账号密码
elasticsearch.username: "kibana"
elasticsearch.password: "3j=JYpywv=jMtQB+XIXS"
elasticsearch.ssl.verificationMode: none
elasticsearch.ssl.certificateAuthorities: ["/opt/es/elasticsearch-8.6.2/config/certs/elasticsearch-ca.pem"]
server.ssl.enabled: true
server.ssl.certificate: /opt/es/kibana-8.6.2/config/kibana.crt
server.ssl.key: /opt/es/kibana-8.6.2/config/kibana.key
第四步:给es赋予权限。
# 切换目录
chown -R es:es /opt/es/kibana-8.6.2/
第五步:切换用户,启动软件。
# 切换用户
su es
# 启动软件
bin/kibana
访问:https://192.168.43.133:5601/ 地址查看。

五、kibana 基础操作
1. 索引操作
打开开发者工具。
左边是控制台,右边是输出结果。
2. 文档操作
文档是ES软件搜索数据的最小单位。
对数据的增删改查,实际上就是对文档的增删改查。
3. 文档搜索
4. 索引模板
索引模板就是当创建多个索引时,可能这多个索引存在共性,因此就有了一套模板,去应用这套模板。
六、分词器
集成IK分词器:
下载地址:https://github.com/medcl/elasticsearch-analysis-ik/releases
七、文档评分机制
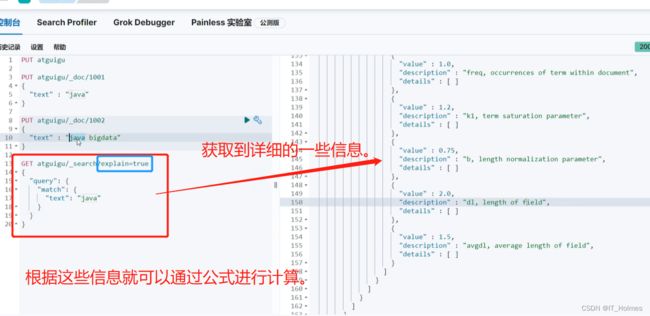
1. 什么是文档评分机制?
文档得分就是 通过计算得到的分数,根据分数考量哪些优先被返回。
2. 分值计算 TF(词频)公式
3. 分值计算 IDF(逆文档频率)公式
4. 分值计算 评分公式
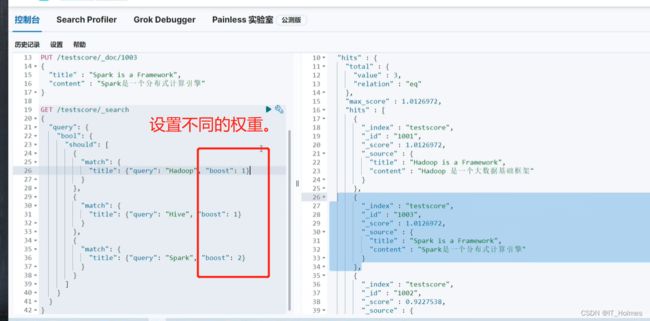
**评分公式:boost(默认为2.2)权重系数 * idf计算得到的值 * tf得到的值 **