日撸 Java 三百行: DAY54-55 基于 M-distance 的推荐
0. 主题
k \textit{k} k-NN算法的变种:基于 M-distance 的推荐。
1. 基于 M-distance 的推荐
-
应用场景
该算法应用于推荐系统,例如为用户推荐一部他可能喜欢的电影。如下图所示:借助已有的观影信息来推测用户会对尚未观看过的电影打多少分。
上图中基于 M-distance 的推荐预测 u 0 u_0 u0 对 m 2 m_2 m2 打分的具体步骤如下:STEP 1. 找邻居:要求邻居必须是用户 u 0 u_0 u0 观看过的影片,且与待打分影片间的平均分差距必须小于给定阈值。即只有 m 1 m_1 m1 和 m 3 m_3 m3 能够成为邻居。
STEP 2. 打分:用户 u 0 u_0 u0 对影片 m 1 m_1 m1 和 m 3 m_3 m3 分数求均值为3,即为预测打分。 -
基于 M-distance 的推荐
基于 M-distance 的推荐是 k \textit{k} k-NN算法的变种,它和 k \textit{k} k-NN基本思路是一致的,即先找出邻居,然后根据邻居的状态来做预测,不同之处在于筛选邻居的方式以及决策机制。
由上文的例题,可以发现具体的要求如下:
找邻居
(1)邻居必须是待预测用户已打过分的项目。
(2)邻居影片的均分与待预测影片的均分差距小于给定阈值。
决策
预测得分是待预测用户对邻居影片所打分数的均值。
2.程序
程序中要注意以下几点:
- 因为数据集是稀疏矩阵,为了提升效率,所以使用压缩存储。
- 进行leave-one-out测试时,对进行测试的点,要将其数据视作未知,故需要重新计算其均分。
1.成员变量
成员变量有点多。
/**
* Default rating for 1-5 points.
*/
public static final double DEFAULT_RATING = 3.0;
/**
* The total number of users.
*/
private int numUsers;
/**
* The total number of items.
*/
private int numItems;
/**
* The total number of ratings (non-zero values)
*/
private int numRatings;
/**
* The predictions.
*/
private double[] predictions;
/**
* Compressed rating matrix. User-item-rating triples.
*/
private int[][] compressedRatingMatrix;
/**
* The degree of users (how many item he has rated).
*/
private int[] userDegrees;
/**
* The average rating of the current user.
*/
private double[] userAverageRatings;
/**
* The degree of users (how many item he has rated).
*/
private int[] itemDegrees;
/**
* The average rating of the current item.
*/
private double[] itemAverageRatings;
/**
* The first user start from 0. Let the first user has x ratings, the second user will start from x.
*/
private int[] userStartingIndices;
/**
* Number of non-neighbor objects.
*/
private int numNonNeighbors;
/**
* The radius (delta) for determining the neighborhood.
*/
private double radius;
2. 构造器
这里的作用主要是读入数据集,并且将它按我们所需要的形式进行存储,将各个成员变量根据数据集进行初始化。
/**
*************************
* Construct the rating matrix.
*
* @param paraFilename the rating filename.
* @param paraNumUsers number of users.
* @param paraNumItems number of items.
* @param paraNumRatings number of ratings.
*************************
*/
public MBR(String paraFilename, int paraNumUsers, int paraNumItems, int paraNumRatings) throws Exception {
// Step 1. Initialize these arrays.
numItems = paraNumItems;
numUsers = paraNumUsers;
numRatings = paraNumRatings;
userDegrees = new int[numUsers];
userStartingIndices = new int[numUsers + 1];
userAverageRatings = new double[numUsers];
itemDegrees = new int[numItems];
compressedRatingMatrix = new int[numRatings][3];
itemAverageRatings = new double[numItems];
predictions = new double[numRatings];
System.out.println("Reading " + paraFilename);
// Step 2. Read the data file.
File tempFile = new File(paraFilename);
if (!tempFile.exists()) {
System.out.println("File " + paraFilename + " does not exists.");
System.exit(0);
} // Of if
BufferedReader tempBufReader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(tempFile));
String tempString;
String[] tempStrArray;
int tempIndex = 0;
userStartingIndices[0] = 0;
userStartingIndices[numUsers] = numRatings;
while ((tempString = tempBufReader.readLine()) != null) {
// Each line has three values.
tempStrArray = tempString.split(",");
compressedRatingMatrix[tempIndex][0] = Integer.parseInt(tempStrArray[0]);
compressedRatingMatrix[tempIndex][1] = Integer.parseInt(tempStrArray[1]);
compressedRatingMatrix[tempIndex][2] = Integer.parseInt(tempStrArray[2]);
userDegrees[compressedRatingMatrix[tempIndex][0]]++;
itemDegrees[compressedRatingMatrix[tempIndex][1]]++;
if (tempIndex > 0) {
// Starting to read the data of a new user.
if(compressedRatingMatrix[tempIndex][0] != compressedRatingMatrix[tempIndex - 1][0]) {
userStartingIndices[compressedRatingMatrix[tempIndex][0]] = tempIndex;
} // Of of
} // Of if
tempIndex++;
} // Of while
tempBufReader.close();
double[] tempUserTotalScore = new double[numUsers];
double[] tempItemTotalScore = new double[numItems];
for (int i = 0; i < numRatings; i++) {
tempUserTotalScore[compressedRatingMatrix[i][0]] += compressedRatingMatrix[i][2];
tempItemTotalScore[compressedRatingMatrix[i][1]] += compressedRatingMatrix[i][2];
} // Of for i
for (int i = 0; i < numUsers; i++) {
userAverageRatings[i] = tempUserTotalScore[i] / userDegrees[i];
} // Of for i
for (int i = 0; i < numItems; i++) {
itemAverageRatings[i] = tempItemTotalScore[i] / itemDegrees[i];
} // Of for i
} // Of the first constructor
3. setRadius
k \textit{k} k-NN中根据选定的距离度量确定的 k \textit{k} k 个最近邻即为邻居,而基于 M-distance 的推荐则要求均值之差小于阈值才能成为邻居,阈值 δ \delta δ 与 k \textit{k} k 所起的作用类似。
/**
*************************
* Set the radius (delta).
*
* @param paraRadius The given radius.
*************************
*/
public void setRadius(double paraRadius) {
if (paraRadius > 0) {
radius = paraRadius;
} else {
radius = 0.1;
} // Of if
} // Of setRadius
4. leaveOneOutPrediction
这是核心代码,对每条数据进行了测试。其测试逻辑也就是该算法的核心逻辑如下:
Step 1. 将用户 u i u_i ui 对项目 m j m_j mj 的打分视作未知,重新计算项目 m j m_j mj 的均分。
Step 2. 遍历用户 u i u_i ui 打过分的项目,若均分与项目 m j m_j mj 的均分之差小于阈值则成为邻居,若找不到邻居,则给出默认值作为打分。
Step 3. 计算用户 u i u_i ui 对邻居项目打分的均值即为对项目 m j m_j mj 打分的预测值。
其中第 1 \text{1} 1, 2 \text{2} 2 步里的均分指所有对该项目打了分的用户给出分数的均分,而第 3 \text{3} 3 步的均分是用户 u i u_i ui 对选做邻居的项目给出分数的均分。
对每条数据都做如上测试,即为 leaveOneOutPrediction。
/**
*************************
* Leave-One-Out prediction. The predicted values are stored in predictions.
*
* @see predictions
*************************
*/
public void leaveOneOutPrediction() {
double tempItemAverageRating;
int tempUser, tempItem, tempRating;
System.out.println("\r\nLeaveOneOutPrediction for radius " + radius);
numNonNeighbors = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < numRatings; i++) {
tempUser = compressedRatingMatrix[i][0];
tempItem = compressedRatingMatrix[i][1];
tempRating = compressedRatingMatrix[i][2];
// Step 1. Recompute average rating of the current item.
tempItemAverageRating = (itemAverageRatings[tempItem] * itemDegrees[tempItem] - tempRating) / (itemDegrees[tempItem] - 1);
// Step 2. Recompute neighbors, at the same time obtain the ratings of neighbors.
int tempNeighbors = 0;
double tempTotal = 0;
int tempComparedItem;
for (int j = userStartingIndices[tempUser]; j < userStartingIndices[tempUser + 1]; j++) {
tempComparedItem = compressedRatingMatrix[j][1];
if (tempItem == tempComparedItem) {
continue;
} // Of if
if (Math.abs(tempItemAverageRating - itemAverageRatings[tempComparedItem]) < radius) {
tempTotal += compressedRatingMatrix[j][2];
tempNeighbors++;
} // Of if
} // Of for j
// Step 3. Predict as the average value of neighbors.
if (tempNeighbors > 0) {
predictions[i] = tempTotal / tempNeighbors;
} else {
predictions[i] = DEFAULT_RATING;
numNonNeighbors++;
} // Of if
} // Of for i
} // Of leaveOneOutPrediction
5. 评价
对于基于 M-distance 的推荐给出了两种评价指标,即 MAE \text{MAE} MAE 和 RSME \text{RSME} RSME 。前者是每条数据预测打分与实际打分差值的绝对值求和后计算均值,后者是每条数据预测打分与实际打分差值的平方求和后计算均值。
计算两个指标的代码如下:
/**
*************************
* Compute the MAE based on the deviation of each leave-one-out.
*************************
*/
public double computeMAE() throws Exception {
double tempTotalError = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < predictions.length; i++) {
tempTotalError += Math.abs(predictions[i] - compressedRatingMatrix[i][2]);
} // Of for i
return tempTotalError / predictions.length;
} // Of computeMAE
/**
*************************
* Compute the RSME based on the deviation of each leave-one-out.
*************************
*/
public double computeRSME() throws Exception {
double tempTotalError = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < predictions.length; i++) {
tempTotalError += (predictions[i] - compressedRatingMatrix[i][2]) * (predictions[i] - compressedRatingMatrix[i][2]);
} // Of for i
double tempAverage = tempTotalError / predictions.length;
return Math.sqrt(tempAverage);
} // Of computeRSME
6. 测试
测试代码如下:
/**
*************************
* The entrance of the program.
*
* @param args Not used now.
*************************
*/
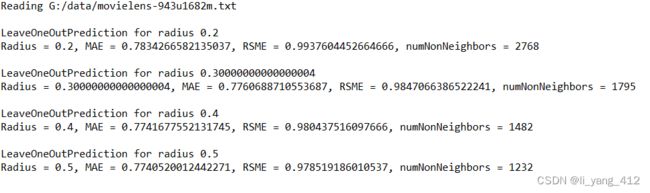
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
MBR tempRecommender = new MBR("G:/data/movielens-943u1682m.txt", 943, 1682, 100000);
for (double tempRadius = 0.2; tempRadius < 0.6; tempRadius += 0.1) {
tempRecommender.setRadius(tempRadius);
tempRecommender.leaveOneOutPrediction();
double tempMAE = tempRecommender.computeMAE();
double tempRSME = tempRecommender.computeRSME();
System.out.println("Radius = " + tempRadius + ", MAE = " + tempMAE + ", RSME = " + tempRSME + ", numNonNeighbors = " + tempRecommender.numNonNeighbors);
} // Of for tempRadius
} catch (Exception ee) {
System.out.println(ee);
} // Of try
} // Of main
3. user-based recommendation
1. 对压缩矩阵进行转置
我们处理的数据是一个矩阵,其中用户 u i u_i ui 即代表矩阵的第 i \textit{i} i 行,项目 m j m_j mj 即代表矩阵的第 j \textit{j} j 列,要预测 u i u_i ui 对 m j m_j mj 的评分,实际上就是预测矩阵中第 i \textit{i} i 行,第 j \textit{j} j 列的值。因此在以及有了基于项目的预测方法之后,要想实现基于用户的预测,自然就可以想到将矩阵进行转置。
对三元组形式存储的矩阵实现转置的方法如下:
Step 1. 用两个向量 nums \textit{nums} nums 和 pos \textit{pos} pos 分别记录矩阵中每列所含有的非零数据个数,每一列的第一个非零数据在转置后的压缩矩阵中的位置
Step 2. 遍历之前的压缩矩阵,将第 i \textit{i} i 条数据插入到新压缩矩阵的第 p \textit{p} p 个位置,在插入时要把行、列的值交换。其中 p \textit{p} p 根据这条数据的列以及向量 pos \textit{pos} pos 计算。
Step 3. 交换其他信息,比如矩阵的行列数等,这里的成员变量有点多,要细心一点。
代码如下:
/**
*************************
* Matrix transpose
*************************
*/
public void fastTransposeSMatrix() {
int[] tempStartingIndices = new int[numItems + 1];
int[][] tempMatrix = new int[numRatings][3];
// Step 1.Calculate auxiliary vector.
int[] nums = new int[numItems];
int[] pos = new int[numItems];
for (int i = 0; i < numRatings; i++) {
nums[compressedRatingMatrix[i][1]]++;
} // Of for i
pos[0] = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < numItems; i++) {
pos[i] = pos[i - 1] + nums[i - 1];
tempStartingIndices[i] = pos[i];
} // Of for i
tempStartingIndices[numItems] = numRatings;
// Step 2.Transpose the compressed matrix.
int col, position;
for (int i = 0; i < numRatings; i++) {
col = compressedRatingMatrix[i][1];
position = pos[col];
tempMatrix[position][0] = compressedRatingMatrix[i][1];
tempMatrix[position][1] = compressedRatingMatrix[i][0];
tempMatrix[position][2] = compressedRatingMatrix[i][2];
pos[col]++;
} // Of for i
// Step 3.Modify member variables.
int temp = numItems;
numItems = numUsers;
numUsers = temp;
int[] tempDegrees = userDegrees;
userDegrees = itemDegrees;
itemDegrees = tempDegrees;
double[] tempAverageRatings = userAverageRatings;
userAverageRatings = itemAverageRatings;
itemAverageRatings = tempAverageRatings;
compressedRatingMatrix = tempMatrix;
userStartingIndices = tempStartingIndices;
} // Of for fastTransposeSMatrix
2. 新的测试
测试代码如下:
/**
*************************
* The entrance of the program.
*
* @param args Not used now.
*************************
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
MBR tempRecommender = new MBR("G:/data/movielens-943u1682m.txt", 943, 1682, 100000);
tempRecommender.fastTransposeSMatrix();
for (double tempRadius = 0.2; tempRadius < 0.6; tempRadius += 0.1) {
tempRecommender.setRadius(tempRadius);
tempRecommender.leaveOneOutPrediction();
double tempMAE = tempRecommender.computeMAE();
double tempRSME = tempRecommender.computeRSME();
System.out.println("Radius = " + tempRadius + ", MAE = " + tempMAE + ", RSME = " + tempRSME + ", numNonNeighbors = " + tempRecommender.numNonNeighbors);
} // Of for tempRadius
} catch (Exception ee) {
System.out.println(ee);
} // Of try
} // Of main
4. 体会
- 顺便学了下三元组形式压缩的矩阵进行快速转置的算法。
- 成员变量多的时候,细心一点,不要漏了东西,不然出错了还得慢慢改bug。