Pytorch分布式编程
当我们拥有多块显卡时,可以使用并行计算来加速,Pytorch并行计算总要用DataParallel和DistributedDataParallel两种,前者主要应用于单机多卡的情况,而后者可以应用于单机多卡和多机多卡。由于作者资源有限,因此只能用单机多卡来做总结。
这里有详细的并行计算说明。

下面这张官方截图也详细说明了为什么DistributedDataParallel优于DataParallel。

一、使用DataParallel
参考文档:https://pytorch.org/tutorials/beginner/blitz/data_parallel_tutorial.html
这种方式使用起来比较简单,只需要以下简单的几行代码即可实现。
import torch.nn as nn #导入必需的包
net = Model() #模型初始化
net = nn.DataParallel(net) #应用于分布式编程
device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu") # 查找GPU设备
net.to(device) #在GPU中运行
全部代码
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from torch.utils.data import Dataset, DataLoader
class Model(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_size, output_size):
super(Model, self).__init__()
self.fc = nn.Linear(input_size, output_size)
def forward(self, input):
output = self.fc(input)
print("\tIn Model: input size", input.size(),
"output size", output.size())
return output
class RandomDataset(Dataset):
def __init__(self, size, length):
self.len = length
self.data = torch.randn(length, size)
def __getitem__(self, index):
return self.data[index]
def __len__(self):
return self.len
input_size = 5
output_size = 2
batch_size = 30
data_size = 100
rand_loader = DataLoader(dataset=RandomDataset(input_size, data_size),
batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True)
model = Model(input_size, output_size)
if torch.cuda.device_count() > 1:
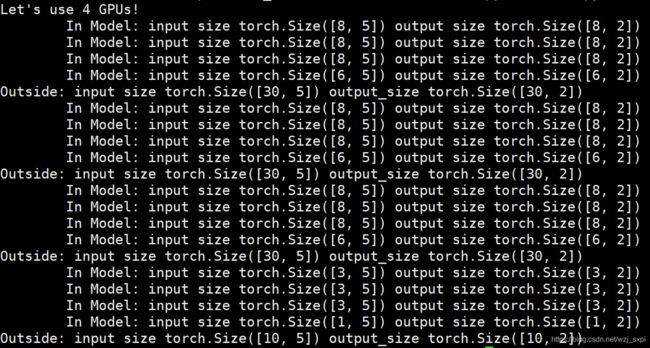
print("Let's use", torch.cuda.device_count(), "GPUs!")
#可以在添加第二个参数:device_ids=[0, 1, 2],表示只在第0,1,2块上做训练
#默认是在所有显卡上
model = nn.DataParallel(model)
device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
model.to(device)
for data in rand_loader:
input = data.to(device)
output = model(input)
print("Outside: input size", input.size(),"output_size", output.size())
二、使用DistributedDataParallel
这个正如官方所说,比较复杂但是效率更高
参考文档:https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/distributed.html#
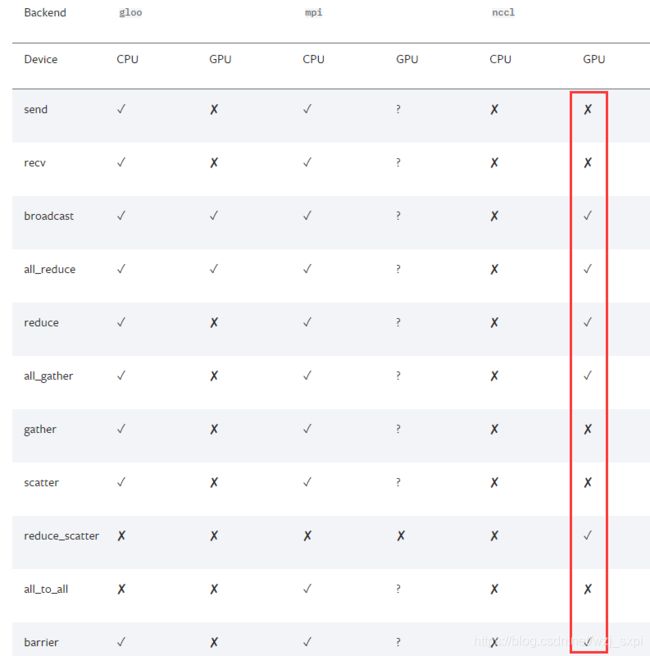
由于不同的后端通信方式的能力不同,因此这里只研究Nvidia的GPU上使用的nccl。也就是只涉及下面红框中打勾的函数。其余的遇到再进行研究。
初始化
torch.distributed.init_process_group()
在进行所有操作之前必须首先调用torch.distributed.init_process_group进行初始化
torch.distributed.init_process_group(backend, init_method=None, timeout=datetime.timedelta(0, 1800), world_size=-1, rank=-1, store=None, group_name=’’)
主要参数说明
- backend: 选择后端通信方式,这是一个str或Backend类型。根据官方文档,Nvidia推荐使用nccl,所以本博客只写有关nccl的 。
- init_method:指定如何初始化进程组。如果没有指定init_method或store, 这里则默认为env://。与
store参数互斥。如果在文件,它必须遵守如下格式
- 本地文件系统, init_method=“file:///d:/tmp/some_file”
- 共享文件系统, init_method=“file://{machine_name}/{share_folder_name}/some_file”
- world_size : Number of processes participating in the job. Required if store is specified.
- rank: Rank of the current process (it should be a number between 0 and world_size-1). Required if store is specified.
- store:一个键值对,用于交换连接与地址信息,与
init_method互斥。实在不知道3,4如何翻译,自我理解是world_size代表本机有几块GPU,而rank是说当前在哪块GPU上运算。
一句话可以概括的函数
| 函数原型 | 英文说明 | 试着翻译翻译 |
|---|---|---|
| torch.distributed.is_available() | Returns True if the distributed package is available | 返回是否支持分布式 |
| torch.distributed.get_backend(group=None) | Returns the backend of the given process group. | 返回给定给的后端通信名称 |
| torch.distributed.get_rank(group=None) | Returns the rank of current process group | 返回当前进程在哪个GPU上运行 |
| torch.distributed.get_world_size(group=None) | Returns the number of processes in the current process group | 返回当前可以运行的GPU总数 |
| torch.distributed.is_initialized() | Checking if the default process group has been initialized | 返回分布式运算是否初始化完成 |
| torch.distributed.is_nccl_available() | Checks if the NCCL backend is available. | 返回nccl是否可用 |
| torch.distributed.is_mpi_available() | Checks if the MPI backend is available. | 返回MPI是否可用 |
当前有三种初始化方式
- TCP方式
此方法指定一个rank0的IP地址,其他进行也必须手工指定rank.不支持广播地址,group_name也被废弃
import torch.distributed as dist
#Use address of one of the machines
dist.init_process_group(backend, init_method='tcp://10.1.1.20:23456',
rank=args.rank, world_size=4)
- 共享文件方式
这种共享方式要求URL以file://开头并且在共享文件系统上指定一个不存在的文件(文件所在的目录存在)。这种方式将会自动创建而不会删除此文件,因此在下一次调用相同的文件时要手动清理(必须确保文件为空或者不存在,否则会出现未知错误,不支持rank自动分配,group_name也被废除)
import torch.distributed as dist
#rank should always be specified
dist.init_process_group(backend, init_method='file:///mnt/nfs/sharedfile',
world_size=4, rank=args.rank)
- 环境变量方式
从环境变量中读取,需要设置的变量至少包含:- MASTER_PORT:rank0上的空闲端口
- MASTER_ADDR:rank0上的地址(rank0除外)
- WORLD_SIZE: 可以在这里设置,也可以在初始化函数中设置
- RANK: 可以在这里设置,也可以在初始化函数中设置
- 这种方式下rank0将被用来建立所有结点
- 这也是默认的初始化方法,意味着不必指定init_method(或者可以是env://)。
同步和异步操作集合函数
每一个集合操作函数都支持同步(Synchronous operation) 与异步(Asynchronous operation)两种操作,这依赖于async_op设置。同步操作(async_op=False)是默认的操作。

主要函数
| 函数原型 |
函数作用
|
参数
|
返回值
|
备注
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
| torch.distributed.broadcast(tensor, src, group=None, async_op=False) | 将tensor广播给同组的所有成员 | 1.tensor (Tensor) 如果src是当前的rank号,则广播出去,否则用于保存接收的数据 . 2.src (int) – Source rank. 3. group (ProcessGroup, optional) 要作用到的组. |
如果async_op设置为True,则返回异步工作操作句柄,否则返回None。 |
|
| torch.distributed.broadcast_object_list(object_list, src=0, group=None) | 广播在object_list中可picklabel的目标给整个组。 |
1. object_list((List[Any]) 要发送的可picklable列表对象,也可以包括Python对象 2. src(int) 源 |
None. If rank is part of the group, object_list will contain the broadcasted objects from src rank. | 1. 基于NCLL的通信,Tensor在通信之前必须移动到GPU设备上。通过torch.cuda.current_device()获得当前工作在哪块GPU上,通过torch.cuda.set_device()来设置当前的rank工作的GPU。2. 这个API是一个阻塞调用。 |
| torch.distributed.all_reduce(tensor, op= |
减少所有设备中的Tensor数据,使所有设备都能得到最终结果。 | 1. tensor(Tensor)-传入传出 2. op(可选) [torch.distributed.ReduceOp]()中的值。 |
Async work handle, if async_op is set to True. None, if not async_op or if not part of the group | 我的理解是计算所有设备上的数据,计算完成后清除,所以减少了 (还有待在用的过程中验证) |
| torch.distributed.reduce(tensor, dst, op= |
减少所有设备中的Tensor数据 | 1. dst(int) 目标rank | Async work handle, if async_op is set to True. None, if not async_op or if not part of the group | 和上一行的区别是只有dst的设备能得到最终结果。 |
| torch.distributed.all_gather(tensor_list, tensor, group=None, async_op=False) | 将整个组的张量收集到列表中 | 1. tensor_list(list[Tensor]) 用于集合后Tensor的输出 2.tensor(Tensor) 在当前进程中进行广播的Tensor |
Async work handle, if async_op is set to True. None, if not async_op or if not part of the group | |
| torch.distributed.all_gather_object(object_list, obj, group=None) | 收集整个组的可picklable对象加入列表(也可加入Pytorch对象) | 1.Object_list(list[Any]) 输入list对象 2.object(Any) 从当前进程中广播的Pickable Python对象。 |
None. If the calling rank is part of this group, the output of the collective will be populated into the input object_list. If the calling rank is not part of the group, the passed in object_list will be unmodified. | 1. 基于NCLL的通信,Tensor在通信之前必须移动到GPU设备上。通过torch.cuda.current_device()获得当前工作在哪块GPU上,通过torch.cuda.set_device()来设置当前的rank工作的GPU。2. 这个API是一个阻塞调用。 |
| torch.distributed.gather(tensor, gather_list=None, dst=0, group=None, async_op=False) | 在单个进程中收集Tensor | 1.tensor(Tensor) 输入Tensor 2.gather_list(list[Tensor]) 用于收集数据的Tensor(必须在 dst中指定目标设备) |
Async work handle, if async_op is set to True. None, if not async_op or if not part of the group | |
| torch.distributed.scatter(tensor, scatter_list=None, src=0, group=None, async_op=False) | 将Tensor分散到组内的所有进程,每个进程只接收一个张量 | 1. tensor(Tensor) 输出tensor 2.scatter_list(list[Tensor]) 要分散的tensor列表 3.src(int) 源rank |
Async work handle, if async_op is set to True. None, if not async_op or if not part of the group | |
| torch.distributed.scatter_object_list(scatter_object_output_list, scatter_object_input_list, src=0, group=None) | 将scatter_object_output_list列表中的可picklabel对象分散到整个组(Python对象也可加入)。每一个 rank,可分散的对象将被存储在scatter_object_output_list的第一个元素。 |
1.scatter_object_output_list(List[Any]) 非空列表,其第一个元素将存储到当前rank。 scatter_object_input_list (List[Any]) 待分散对象列表,仅 src参数上的rank会被分散,其他非rank,此项可设置为None。3. src(int) Source rank from which to scatter scatter_object_input_list。 |
None. If rank is part of the group, scatter_object_output_list will have its first element set to the scattered object for this rank. | |
| torch.distributed.reduce_scatter(output, input_list, op= |
Reduces, then scatters a list of tensors to all processes in a group. | 1. output(Tensor) 输出Tensor 2.input_list(list[Tensor]) 用来reduce和scatter的tensor列表 |
Async work handle, if async_op is set to True. None, if not async_op or if not part of the group. | |
| torch.distributed.barrier(group=None, async_op=False, device_ids=None) | 同步所有进程 | device_ids ([int]) device/GPU列表 | Async work handle, if async_op is set to True. None, if not async_op or if not part of the group | 如果async_op为False,或者在wait()上调用了异步句柄,则该集合将阻塞进程,直到整个组都进入该函数。 |
表格太丑了,后期还得学点CSS知识调调样子
启动
单节点多设备
python -m torch.distributed.launch --nproc_per_node=NUM_GPUS_YOU_HAVE
YOUR_TRAINING_SCRIPT.py (--arg1 --arg2 --arg3 and all other
arguments of your training script)
多节点多设备
- 节点1
python -m torch.distributed.launch --nproc_per_node=NUM_GPUS_YOU_HAVE
--nnodes=2 --node_rank=0 --master_addr="192.168.1.1"
--master_port=1234 YOUR_TRAINING_SCRIPT.py (--arg1 --arg2 --arg3
and all other arguments of your training script)
- 节点2
python -m torch.distributed.launch --nproc_per_node=NUM_GPUS_YOU_HAVE
--nnodes=2 --node_rank=1 --master_addr="192.168.1.1"
--master_port=1234 YOUR_TRAINING_SCRIPT.py (--arg1 --arg2 --arg3
and all other arguments of your training script)
寻找帮助
python -m torch.distributed.launch --help
提示
- 只有使用
NCCL后端才能到达最佳性能 - 必须通过命令行参数传递
--local_rank=LOCAL_PROCESS_RANK,如果用GPU训练,还要确保代码仅仅运行在LOCAL_PROCESS_RANK的GPU上,可以通过以下两种方式实现
首先解析local_rank参数
import argparse
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument("--local_rank", type=int)
args = parser.parse_args()
然后设置在当前rank上运行
方式一:在代码运行之前调用
torch.cuda.set_device(args.local_rank)
方式二:用with封装
with torch.cuda.device(args.local_rank):
#运行代码
- 应该在开始时调用以下函数来启动分布式后端。 确保
init_method使用env://,这是唯一支持的初始化方法。
torch.distributed.init_process_group(backend='YOUR BACKEND',
init_method='env://')
- 如果使用torch.nn.parallel.DistributedDataParallel()模块进行训练,则用下面的代码进行配置
model = torch.nn.parallel.DistributedDataParallel(model,
device_ids=[args.local_rank],
output_device=args.local_rank)
- 亦可以通过环境变量
LOCAL_RANK将local_rank传递给子进程,这必须在启动脚本时使用--use_env=True来激活这种方式,这时要调整示例流程,用os.environ['LOCAL_RANK']替换args.local_rank。此时将不会传递--local_rank变量。
local_rank并不是全局唯一的,它仅在设备的每个进程上是唯一的。 因此,不能使用它来决定是否应写入网络文件系统。 如果未正确执行操作,可能会出现问题(https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/12042)。
代码示例
下周再写