Nacos学习笔记(四):心跳机制
一、前文回顾
在上一篇文章中我们学习了服务(以Springboot为例)是如何自动注册到Nacos中的,今天学习一些相对简单的内容,心跳。
二、心跳
1、概念
所谓的心跳也很好理解,就是心脏的跳动。在技术中心跳机制是定时发送一个自定义的结构体(心跳包),让对方知道自己还活着,以确保连接的有效性的机制。
2、客户端心跳
通过前文我们知道了Nacos中的节点分为短暂节点和持久化节点,短暂节点需要定时发送心跳包给Nacos,否则一段时间收不到心跳则会踢出该节点。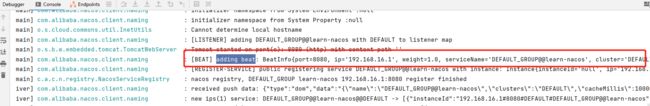
项目启动后再控制台会输出这一句话,通过搜索可以看到这句话是从com.alibaba.nacos.client.naming.beat.BeatReactor这个类输出的,由此可得该类的作用就是处理心跳的。其中发送心跳的源码如下: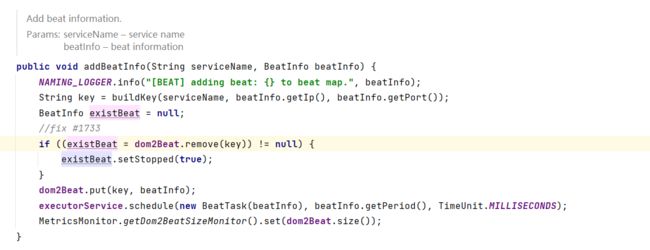
源码分析:
1、首先使用服务名、IP、端口生成一个Key,用于记录心跳。
2、将心跳信息存在名为 dom2Beat中(ConcurrentHashMap)
3、添加定时任务,默认是5秒发送一次心跳包。
心跳源码分析
在上面的源码中添加了一个类型为BeatTask的任务,源码如下:
class BeatTask implements Runnable {
BeatInfo beatInfo;
public BeatTask(BeatInfo beatInfo) {
this.beatInfo = beatInfo;
}
@Override
public void run() {
if (beatInfo.isStopped()) {
return;
}
long nextTime = beatInfo.getPeriod();
try {
JsonNode result = serverProxy.sendBeat(beatInfo, BeatReactor.this.lightBeatEnabled);
long interval = result.get("clientBeatInterval").asLong();
boolean lightBeatEnabled = false;
if (result.has(CommonParams.LIGHT_BEAT_ENABLED)) {
lightBeatEnabled = result.get(CommonParams.LIGHT_BEAT_ENABLED).asBoolean();
}
BeatReactor.this.lightBeatEnabled = lightBeatEnabled;
if (interval > 0) {
nextTime = interval;
}
int code = NamingResponseCode.OK;
if (result.has(CommonParams.CODE)) {
code = result.get(CommonParams.CODE).asInt();
}
//如果服务未发现:即第一次注册
if (code == NamingResponseCode.RESOURCE_NOT_FOUND) {
Instance instance = new Instance();
instance.setPort(beatInfo.getPort());
instance.setIp(beatInfo.getIp());
instance.setWeight(beatInfo.getWeight());
instance.setMetadata(beatInfo.getMetadata());
instance.setClusterName(beatInfo.getCluster());
instance.setServiceName(beatInfo.getServiceName());
instance.setInstanceId(instance.getInstanceId());
instance.setEphemeral(true);
try {
serverProxy.registerService(beatInfo.getServiceName(),
NamingUtils.getGroupName(beatInfo.getServiceName()), instance);
} catch (Exception ignore) {
}
}
} catch (NacosException ex) {
NAMING_LOGGER.error("[CLIENT-BEAT] failed to send beat: {}, code: {}, msg: {}",
JacksonUtils.toJson(beatInfo), ex.getErrCode(), ex.getErrMsg());
}
executorService.schedule(new BeatTask(beatInfo), nextTime, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
}
源码分析:首先可以看出该类实现了Runable接口,所以可以推断出心跳是开启了一个新的线程来处理的。
整体源码也不难可以分为以下几步:
1、判断心跳是否已经停止(因为存在移除心跳的操作,例如主动下线)。
2、发送一次心跳给Nacos。如果是首次发送则发送的注册心跳,然后将服务注册到Nacos上
3、如果不是第一次心跳,则会将心跳设置为 lightBeatEnabled(轻量级心跳),轻量级心跳不会触发注册操作,只是为了告知Nacos当前服务还活着。
4、最后以此往复,不断出重复上述的逻辑
3、服务端心跳检测
上一小节中我们简单的了解了客户端的心跳机制,既然客户端有心跳则服务端就需要有对应的心跳检测机制,通过官网中可以知道处理心跳的接口为/v1/ns/instance/beat,源码如下:
@CanDistro
@PutMapping("/beat")
@Secured(action = ActionTypes.WRITE)
public ObjectNode beat(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
ObjectNode result = JacksonUtils.createEmptyJsonNode();
result.put(SwitchEntry.CLIENT_BEAT_INTERVAL, switchDomain.getClientBeatInterval());
// 解析客户端发过来的心跳包
String beat = WebUtils.optional(request, "beat", StringUtils.EMPTY);
RsInfo clientBeat = null;
if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(beat)) {
clientBeat = JacksonUtils.toObj(beat, RsInfo.class);
}
// 集群名称
String clusterName =
WebUtils.optional(request, CommonParams.CLUSTER_NAME, UtilsAndCommons.DEFAULT_CLUSTER_NAME);
// IP
String ip = WebUtils.optional(request, "ip", StringUtils.EMPTY);
// 端口号
int port = Integer.parseInt(WebUtils.optional(request, "port", "0"));
if (clientBeat != null) {
if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(clientBeat.getCluster())) {
clusterName = clientBeat.getCluster();
} else {
// fix #2533
clientBeat.setCluster(clusterName);
}
ip = clientBeat.getIp();
port = clientBeat.getPort();
}
// 获取namespace:命名空间
String namespaceId = WebUtils.optional(request, CommonParams.NAMESPACE_ID, Constants.DEFAULT_NAMESPACE_ID);
// 服务名称
String serviceName = WebUtils.required(request, CommonParams.SERVICE_NAME);
NamingUtils.checkServiceNameFormat(serviceName);
Loggers.SRV_LOG.debug("[CLIENT-BEAT] full arguments: beat: {}, serviceName: {}, namespaceId: {}", clientBeat,
serviceName, namespaceId);
BeatInfoInstanceBuilder builder = BeatInfoInstanceBuilder.newBuilder();
builder.setRequest(request);
// 处理心跳
int resultCode =
getInstanceOperator().handleBeat(namespaceId, serviceName, ip, port, clusterName, clientBeat, builder);
result.put(CommonParams.CODE, resultCode);
result.put(SwitchEntry.CLIENT_BEAT_INTERVAL,
getInstanceOperator().getHeartBeatInterval(namespaceId, serviceName, ip, port, clusterName));
result.put(SwitchEntry.LIGHT_BEAT_ENABLED, switchDomain.isLightBeatEnabled());
return result;
}
代码并不复杂,其中核心的代码是
getInstanceOperator().handleBeat(namespaceId, serviceName, ip, port, clusterName, clientBeat,builder);
@Override
public int handleBeat(String namespaceId, String serviceName, String ip, int port, String cluster,
RsInfo clientBeat, BeatInfoInstanceBuilder builder) throws NacosException {
// 获取短暂节点
Service service = getService(namespaceId, serviceName, true);
// 获取客户端ID
String clientId = IpPortBasedClient.getClientId(ip + InternetAddressUtil.IP_PORT_SPLITER + port, true);
// 获取Client
IpPortBasedClient client = (IpPortBasedClient)clientManager.getClient(clientId);
// 如果Client为空,则返回RESOURCE_NOT_FOUND:对应的场景就是第一次注册!
if (null == client || !client.getAllPublishedService().contains(service)) {
if (null == clientBeat) {
return NamingResponseCode.RESOURCE_NOT_FOUND;
}
Instance instance = builder.setBeatInfo(clientBeat).setServiceName(serviceName).build();
// 执行注册逻辑!
registerInstance(namespaceId, serviceName, instance);
client = (IpPortBasedClient)clientManager.getClient(clientId);
}
if (!ServiceManager.getInstance().containSingleton(service)) {
throw new NacosException(NacosException.SERVER_ERROR,
"service not found: " + serviceName + "@" + namespaceId);
}
// 创建一个客户端心跳对象
if (null == clientBeat) {
clientBeat = new RsInfo();
clientBeat.setIp(ip);
clientBeat.setPort(port);
clientBeat.setCluster(cluster);
clientBeat.setServiceName(serviceName);
}
ClientBeatProcessorV2 beatProcessor = new ClientBeatProcessorV2(namespaceId, clientBeat, client);
// 健康检查
HealthCheckReactor.scheduleNow(beatProcessor);
client.setLastUpdatedTime();
return NamingResponseCode.OK;
}
代码逻辑也不复杂,并且也加了注释所以这里不在赘述,这里比较重要的就是健康检查:
HealthCheckReactor.scheduleNow(beatProcessor); 和客户端心跳一样,服务端的健康检查也是一个Runable。其中核心代码如下:
@Override
public void run() {
if (Loggers.EVT_LOG.isDebugEnabled()) {
Loggers.EVT_LOG.debug("[CLIENT-BEAT] processing beat: {}", rsInfo.toString());
}
//==================获取各种参数==================
String ip = rsInfo.getIp();
int port = rsInfo.getPort();
String serviceName = NamingUtils.getServiceName(rsInfo.getServiceName());
String groupName = NamingUtils.getGroupName(rsInfo.getServiceName());
Service service = Service.newService(namespace, groupName, serviceName, rsInfo.isEphemeral());
//===============================================
HealthCheckInstancePublishInfo instance = (HealthCheckInstancePublishInfo) client.getInstancePublishInfo(service);
if (instance.getIp().equals(ip) && instance.getPort() == port) {
if (Loggers.EVT_LOG.isDebugEnabled()) {
Loggers.EVT_LOG.debug("[CLIENT-BEAT] refresh beat: {}", rsInfo);
}
instance.setLastHeartBeatTime(System.currentTimeMillis());
if (!instance.isHealthy()) {
instance.setHealthy(true);
Loggers.EVT_LOG.info("service: {} {POS} {IP-ENABLED} valid: {}:{}@{}, region: {}, msg: client beat ok",
rsInfo.getServiceName(), ip, port, rsInfo.getCluster(), UtilsAndCommons.LOCALHOST_SITE);
NotifyCenter.publishEvent(new ServiceEvent.ServiceChangedEvent(service));
NotifyCenter.publishEvent(new ClientEvent.ClientChangedEvent(client));
NotifyCenter.publishEvent(new HealthStateChangeTraceEvent(System.currentTimeMillis(),
service.getNamespace(), service.getGroup(), service.getName(), instance.getIp(),
instance.getPort(), true, "client_beat"));
}
}
}
代码相对简单,收到心跳信息将健康状态设置为true,同时发送各种事件,之后会对这些做分析,这里暂时不做赘述。
三、总结
今天的文章相对简单也好理解,接下来还会有几篇关于Nacos源码解读的文章。希望对你有所帮助。