谷粒商城五前端技术栈vue
mvvm思想
- M:即 Model,模型,包括数据和一些基本操作
- V:即 View,视图,页面渲染结果
- VM:即 View-Model,模型与视图间的双向操作(无需开发人员干涉)
之前类似于jquery都是,jquery利用ajax请求到数据,通过各种选择器找到这个元素,然后对dom文档进行添加、删除、清空等一系列操作,才能最终在html中显示,如果元素很复杂,那么就需要我们写大量的内容。
假设html的元素发生变化,我们都需要修改相对应的jquery代码,重新找到html中的元素,整个操作其实是非常麻烦的。
而 MVVM 中的 VM 要做的事情就是把 DOM 操作完全封装起来,开发人员不用再关心 Model 和 View 之间是如何互相影响的, 只要我们 Model 发生了改变,View 上自然就会表现出来。
当用户修改了 View,Model 中的数据也会跟着改变。 把开发人员从繁琐的 DOM 操作中解放出来,把关注点放在如何操作 Model 上。
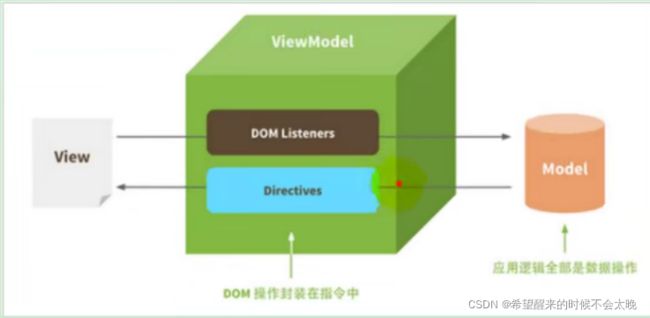
view 和 model 是通过 viewModel 绑定起来的,
此时model数据发生改变,viewModel 通过内部指令操作自动修改视图界面的值,
视图界面添加了一个内容,这个内容就会被dom listeners自动把这个内容填到model中,
开发人员只需要关注数据需要放在哪个视图,无需关注怎么放,也就是jquery选择器那一堆,
安装vue
# 将项目交给npm管理
npm init -y
# 安装vue
npm install vue@2
简单测试
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script src="./node_modules/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
<div id="app">
<h1>{{name}},非常帅</h1>
</div>
<script>
// 声明式渲染
let vm = new Vue({
el:"#app",
data:{
name: "张三"
}
});
</script>
// 双向绑定,模型变化,视图变化,反之亦然
<div id="app">
<input type="text" v-model="num">
<h1>{{name}},非常帅,有{{num}}个人为他点赞</h1>
</div>
<script>
let vm = new Vue({
// el 绑定元素 data 封装数据 methods 封装方法
el:"#app",
data:{
name: "张三",
num:1
}
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
基础指令
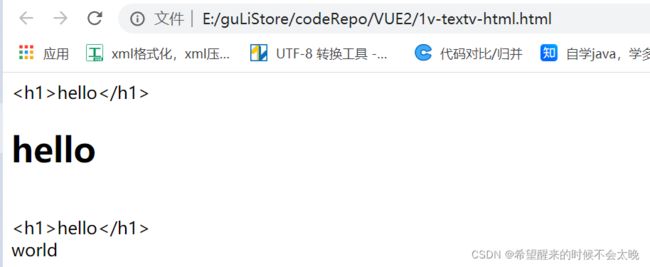
v-text v-html (插值表达式)
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Documenttitle>
head>
<body>
<script src="./node_modules/vue/dist/vue.js">script>
<div id="app">
{{msg}}<br>
<span v-html="msg">span>
<br>
<span v-text="msg">span>
<br>
{{hello()}}
div>
<script>
new Vue({
el:"#app",
data:{
msg:"hello
"
},
methods:{
hello(){
return "world"
}
}
})
script>
body>
html>
v-bind (属性绑定)
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Documenttitle>
head>
<body>
<script src="./node_modules/vue/dist/vue.js">script>
<div id="app">
<span v-bind:class="{active:isActive, 'text-danger':hasError}">
你好span>
<a v-bind:href="link">goa>
div>
<script>
new Vue({
el:"#app",
data:{
link:"http://www.baidu.com",
isActive:true,
hasError: true,
color1:'red',
size:'36px'
}
})
script>
body>
html>

上面的插值表达式,v-text,v-html,v-bind实际上都是单向绑定,
model发生变化,view会跟着变化,view发生变化,model不会发生变化
v-model(双向绑定)
v-model 是双向绑定,视图(View)和模型(Model)之间会互相影响。
既然是双向绑定,一定是在视图中可以修改数据,这样就限定了视图的元素类型。
目前 v-model 的可使用元素有:
- input
- select
- textarea
- checkbox
- radio
- components(Vue 中的自定义组件)
基本上除了最后一项,其它都是表单的输入项。
- 多个
CheckBox对应一个 model 时,model 的类型是一个数组,单个 checkbox 值默认是 boolean 类型 - radio 对应的值是 input 的 value 值
text和textarea默认对应的 model 是字符串select单选对应字符串,多选对应也是数组
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<script src="./node_modules/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
<!-- 表单项,自定义组件 -->
<!-- 一般只有他们才有双向绑定的需求 -->
<div id="app">
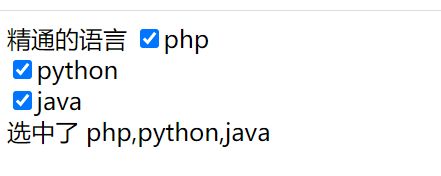
精通的语言
<input type="checkbox" v-model="language" value="php">php<br>
<input type="checkbox" v-model="language" value="python">python<br>
<input type="checkbox" v-model="language" value="java">java<br>
选中了
{{language.join(",")}}
</div>
<script>
let vm = new Vue({
el:'#app',
data:{
language:[]
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
v-on(事件绑定)
全部的按键别名:
.enter.tab.delete(捕获“删除”和“退格”键).esc.space.up.down.left.right
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Documenttitle>
head>
<body>
<script src="./node_modules/vue/dist/vue.js">script>
<div id="app">
<button v-on:click="num++">点赞button>
<button @:click="cancle($event)">取消点赞button>
<h1>有{{num}} 个赞h1>
<div style="border:1px solid red;padding:20px;" v-on:click.once="hello()">
大div
<div style="border:1px solid blue;padding:20px" v-on:click.stop="hello()">
小div<br>
<a href="http://www.baidu.com" @click.prevent.stop="hello()">去百度a>
div>
div>
<input type="text" v-model = "num" v-on:keyup.up="num+=2" @keyup.down="num-=2" @click.ctrl="num=10"><br>
提示:
div>
<script>
new Vue({
el:"#app",
data:{
num:1
},
methods:{
cancle(event){
this.num--;
console.log(event)
},
hello(){
alert("被点击了")
}
}
})
script>
body>
html>
v-for
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Documenttitle>
head>
<body>
<script src="./node_modules/vue/dist/vue.js">script>
<div id="app">
<ul>
<li v-for="(user,index) in users" :key="user.id">
当前索引:{{index}} == {{user.name}} == {{user.gender}} == {{user.age}}
<br>
对象信息:
<span v-for="(v,k,j) in user">{{v}} == {{k}} == {{j}} ; span>
li>
ul>
div>
<script>
let app = new Vue({
el:"#app",
data:{
users:[
{name:"柳岩",gender:"女",age:21},
{name:"张三",gender:"男",age:18},
{name:"周杰伦",gender:"女",age:24},
{name:"刘亦菲",gender:"女",age:18},
{name:"古力娜扎",gender:"女",age:25},
]
}
})
script>
body>
html>
v-if v-show
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Documenttitle>
head>
<body>
<script src="./node_modules/vue/dist/vue.js">script>
<div id="app">
<button @click="show = !show">点我呀!button>
<h1 v-if="show">if=看到我。。。h1>
<h1 v-show="show">show=看到我。。。h1>
div>
<script>
let app = new Vue({
el: "#app",
data:{
show: true
}
})
script>
body>
html>
v-else v-else-if
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Documenttitle>
head>
<body>
<script src="./node_modules/vue/dist/vue.js">script>
<div id="app">
<button @click="random=Math.random()">点我呀button>
<span>{{random}}span>
<h1>
<h1 v-if="random>=0.75">
看到我啦?! >=0.75
h1>
<h1 v-else-if="random>=0.5">
看到我啦?! >=0.5
h1>
<h1 v-else-if="random>=0.2">
看到我啦?! >=0.2
h1>
<h1 v-else>
看到我啦?! >0.2
h1>
h1>
div>
<script>
new Vue({
el:"#app",
data:{
random:1
}
})
script>
body>
html>
计算属性和侦听器
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Documenttitle>
head>
<body>
<script src="../node_modules/vue/dist/vue.js">script>
<div id="app">
<ul>
<li>西游记价格:{{xyjPrice}},数量:<input type="number" v-model="xyjNum">li>
<li>水浒传价格:{{shzPrice}},数量:<input type="number" v-model="shzNum">li>
<li>总价:{{totalPrice}}li>
{{msg}}
ul>
div>
<script>
// computed表示计算属性,动态计算的都可以写到这儿
// watch可以让我们监控一个值的变化,从而做出相应的反应
new Vue({
el:"#app",
data:{
xyjPrice:99.98,
shzPrice:98,
xyjNum:1,
shzNum:1
},
computed:{
totalPrice(){
// 这样会有精度的问题,这个到了项目再说
return this.xyjPrice * this.xyjNum + this.shzPrice * this.shzNum
}
},
watch:{
xyjNum: function(newVal,oldVal){
// alert("new:"+newVal + "=====" + "old" + oldVal)
if(newVal>=3){
this.msg = "库存超出限制了"
this.xyjNum = 3
}else{
this.msg = ""
}
}
}
})
script>
body>
html>
过滤器
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Documenttitle>
head>
<body>
<script src="../node_modules/vue/dist/vue.js">script>
<div id="app">
<ul>
<li v-for="user in userList">
{{user.id}} ==== {{user.name}} ==={{user.gender | gFilter}}
li>
ul>
div>
<script>
//全局过滤器
Vue.filter("gFilter",function(val){
if(val==1){
return "男"
}else{
return "女"
}
})
let vm = new Vue({
el:"#app",
data:{
userList:[
{id:1,name:'jack',gender:1},
{id:2,name:'peter',gender:0},
]
},
// filters 定义局部过滤器,只可以在当前vue实例(#app)中使用
filters:{
genderFilter(val){
if(val==1){
return "男"
}else{
return "女"
}
}
}
})
script>
body>
html>
组件化
组件化的意义在于封装、抽取和应用
在大型应用开发的时候,页面可以划分成很多部分。往往不同的页面,也会有相同的部分。 例如可能会有相同的头部导航。
但是如果每个页面都独自开发,这无疑增加了我们开发的成本。所以我们会把页面的不同部 分拆分成独立的组件,然后在不同页面就可以共享这些组件,避免重复开发。
在 vue 里,所有的 vue 实例都是组件
- 组件其实也是一个 Vue 实例,因此它在定义时也会接收:data、methods、生命周期函 数等
- 不同的是,组件不会与页面的元素绑定,否则就无法复用了,因此没有 el 属性。
- 但是组件渲染需要 html 模板,所以增加了 template 属性,值就是 HTML 模板
- 全局组件定义完毕,任何 vue 实例都可以直接在 HTML 中通过组件名称来使用组件了
- data 必须是一个函数,不再是一个对象。
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Documenttitle>
head>
<body>
<script src="../node_modules/vue/dist/vue.js">script>
<div id="ap">
<button @click="count++">我被点击了{{count}} 次button>
<counter>counter>
<counter>counter>
<counter>counter>
<button-counter>button-counter>
<button-counter>button-counter>
<button-counter>button-counter>
<button-counter>button-counter>
div>
<script>
// 全局声明注册一个组件
// 上面每一个counter组件都是独立的,每次点击不会影响其他的counter组件
Vue.component("counter",{
template:``,
data(){
return {
count:1
}
}
})
// 局部声明一个组件
const buttonCounter = {
template:``,
data(){
return {
count:1
}
}
};
new Vue({
el:"#ap",
data:{
count:1
},
components:{
"button-counter":buttonCounter
}
})
script>
body>
html>
生命周期和钩子函数
每个 Vue 实例在被创建时都要经过一系列的初始化过程 :创建实例,装载模板,渲染模 板等等。
Vue 为生命周期中的每个状态都设置了钩子函数(监听函数)。
每当 Vue 实例处于 不同的生命周期时,对应的函数就会被触发调用。
生命周期:你不需要立马弄明白所有的东西
vue实例生命周期
- new Vue(),创建vue实例,初始化事件和生命周期
- 将值注入或校验
data中,触发两个钩子函数,之前触发beforeCreate,之后触发created - 如果指定
el选项,判断是否指定template选项
否则,当调用vm.$mount(el)函数时(不知道是啥。。。),再判断是否指定template选项 - 如果指定了
template选项,将template编译到render(渲染)函数中
否则,将el外部的html作为template编译 - 将vue实例和模板挂载,触发两个钩子函数,之前触发
beforeMount,之后触发mounted,
一旦挂载完成,我们页面的数据就可以显示了 - 当data被修改的时候,虚拟dom重新渲染并应用更新,触发两个钩子函数,之前触发
beforeUpdate,之后触发updated - 当调用
vm.$destory()函数时,解除绑定,销毁子组件以及事件监听器,触发两个钩子函数,之前触发beforeDestory,之后触发destoryed
DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Documenttitle>
head>
<body>
<script src="../node_modules/vue/dist/vue.js">script>
<div id="app"> <span id="num">{{num}}span> <button v-on:click="num++">赞!button>
<h2>{{name}},非常帅!!!有{{num}}个人点赞。 h2>
div>
body>
<script> let app = new Vue({
el: "#app",
data: { name: "张三", num: 100 },
methods: {
show() { return this.name; },
add() { this.num++; }
},
beforeCreate() {
console.log("=========beforeCreate=============");
console.log("数据模型未加载:" + this.name, this.num);
console.log("方法未加载:" + this.show());
console.log("html 模板未加载: " + document.getElementById("num"));
},
created: function () {
console.log("=========created=============");
console.log("数据模型已加载:" + this.name, this.num);
console.log("方法已加载:" + this.show());
console.log("html 模板已加载: " + document.getElementById("num"));
console.log("html 模板未渲染: " + document.getElementById("num").innerText);
},
beforeMount() {
console.log("=========beforeMount=============");
console.log("html 模板未渲染: " + document.getElementById("num").innerText);
},
mounted() {
console.log("=========mounted=============");
console.log("html 模板已渲染: " + document.getElementById("num").innerText);
},
beforeUpdate() {
console.log("=========beforeUpdate=============");
console.log("数据模型已更新:" + this.num);
console.log("html 模板未更新: " + document.getElementById("num").innerText);
},
updated() {
console.log("=========updated=============");
console.log("数据模型已更新:" + this.num);
console.log("html 模板已更新: " + document.getElementById("num").innerText);
}
});
script>
html>
使用vue脚手架进行模块化开发
// 作用:将项目进行打包
npm install webpack -g
// vue项目初始化工具
npm install -g @vue/cli-init
// 或者
npm install vue-cli -g
// 初始化一个 vue项目
vue init webpack vue-demo
// 运行
npm run dev
vue项目目录结构
- build – 和打包工具webpack有关的文件夹
- config – 配置信息
- index.js – 可以配置端口号
- node_modules – 当前项目的所有依赖
- src – 编写项目的文件夹(开发关注这个就可以了)
- static – 静态资源文件(图片、字体文件等)
- .babelrc – babel 语法转义的相关配置
- index.html – 首页内容
- package.json – npm依赖包的配置信息
- package-lock.json – 每一个依赖的详细信息
项目是如何运行起来的(单文件组件)
-
HelloWorld.vue,除了上面那个v的图片之外,所有的东西都在这儿定义
-
App.vue,定义了图片,
-
index.js,设置了访问路径,引入组件
HelloWorld.vue,也就是说访问/就访问到了HelloWorld.vue页面,此时除了图片之外的所有东西在该路由都存在了 -
main.js,导入index.js使用其路由,导入
App.vue引用其图片
另一种说法
- 进入页面首先加载 index.html 和 main.js 文件。
- main.js 导入了一些模块【vue、app、router】,并且创建 vue 实例,关联 index.html 页面的
元素。使用了 router,导入了 App 组件。并且使用标签 引用了这个组件
- 第一次默认显示 App 组件。App 组件有个图片和,所以显示了图片。 但是由于代表路由的视图,默认是访问/#/路径(router 路径默认使用 HASH 模式)。在 router 中配置的/是显示 HelloWorld 组件。
- 所以第一次访问,显示图片和 HelloWorld 组件
index.html 主入口页面
DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width,initial-scale=1.0">
<title>vue-demotitle>
head>
<body>
<div id="app">div>
body>
html>
src下main.js
// The Vue build version to load with the `import` command
// (runtime-only or standalone) has been set in webpack.base.conf with an alias.
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App'
import router from './router'
Vue.config.productionTip = false
/* eslint-disable no-new */
new Vue({
el: '#app',
// 全写应该是 router:router,
router,
// 组件,全写是{App:App}
// 属性名和属性值的变量名一样的时候,可以简写
components: { App },
// 渲染,router下的index.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import Router from 'vue-router'
// 导入helloWorld组件 @src整个目录的根目录
import HelloWorld from '@/components/HelloWorld'
Vue.use(Router)
// 因为这导出模块用的是defalut,所以main.js导入的时候可以自己起名字.
export default new Router({
routes: [
{
// 路由,访问/路径 的时候,会访问HelloWorld组件
path: '/',
name: 'HelloWorld',
component: HelloWorld
}
]
})
router下的App.vue
<template>
<div id="app">
<img src="./assets/logo.png">
// 路由视图
// 意思是这个页面的上面显示的是这个图片,
// 下面显示什么由我们的访问路径动态决定
<router-view/>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'App'
}
</script>
<style>
#app {
font-family: 'Avenir', Helvetica, Arial, sans-serif;
-webkit-font-smoothing: antialiased;
-moz-osx-font-smoothing: grayscale;
text-align: center;
color: #2c3e50;
margin-top: 60px;
}
</style>
components下的HelloWorld.vue组件
<template>
<div class="hello">
<h1>{{ msg }}h1>
<h2>Essential Linksh2>
<ul>
<li>
<a
href="https://vuejs.org"
target="_blank"
>
Core Docs
a>
li>
<li>
<a
href="https://forum.vuejs.org"
target="_blank"
>
Forum
a>
li>
<li>
<a
href="https://chat.vuejs.org"
target="_blank"
>
Community Chat
a>
li>
<li>
<a
href="https://twitter.com/vuejs"
target="_blank"
>
Twitter
a>
li>
<br>
<li>
<a
href="http://vuejs-templates.github.io/webpack/"
target="_blank"
>
Docs for This Template
a>
li>
ul>
<h2>Ecosystemh2>
<ul>
<li>
<a
href="http://router.vuejs.org/"
target="_blank"
>
vue-router
a>
li>
<li>
<a
href="http://vuex.vuejs.org/"
target="_blank"
>
vuex
a>
li>
<li>
<a
href="http://vue-loader.vuejs.org/"
target="_blank"
>
vue-loader
a>
li>
<li>
<a
href="https://github.com/vuejs/awesome-vue"
target="_blank"
>
awesome-vue
a>
li>
ul>
div>
template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'HelloWorld',
data () {
return {
msg: 'Welcome to Your Vue.js App'
}
}
}
script>
<style scoped>
h1, h2 {
font-weight: normal;
}
ul {
list-style-type: none;
padding: 0;
}
li {
display: inline-block;
margin: 0 10px;
}
a {
color: #42b983;
}
style>
自己编写一个组件
components目录下创建Hello.vue
<template>
<div>
<h1>你好,Hello,{{name}}h1>
div>
template>
<script>
// 这实际上就是一个Vue实例
export default {
data() {
return {
name: '张三',
};
},
}
script>
<style>
style>
index.js添加路由
import Vue from 'vue'
import Router from 'vue-router'
import HelloWorld from '@/components/HelloWorld'
import Hello from '@/components/Hello'
Vue.use(Router)
export default new Router({
routes: [
{
path: '/',
name: 'HelloWorld',
component: HelloWorld
},
{
path:'/hello',
name:'Hello',
component:Hello
}
]
})
添加超链接在Hello页面与HelloWorld页面来回跳转
<template>
<div id="app">
<img src="./assets/logo.png">
<router-link to="/hello">去Hellorouter-link>
<router-link to="/">去首页router-link>
<router-view/>
div>
template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'App'
}
script>
<style>
#app {
font-family: 'Avenir', Helvetica, Arial, sans-serif;
-webkit-font-smoothing: antialiased;
-moz-osx-font-smoothing: grayscale;
text-align: center;
color: #2c3e50;
margin-top: 60px;
}
style>
vue整合element ui
element ui,基于vue2.0的桌面组件库
将elementui 导入到 router下的index.js
// 安装element ui
npm i element-ui
// 将elementui 导入到 router下的index.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import Router from 'vue-router'
import HelloWorld from '@/components/HelloWorld'
import Hello from '@/components/Hello'
// 导入element-ui 和 其样式文件
import ElementUI from 'element-ui';
import 'element-ui/lib/theme-chalk/index.css';
// 让vue使用element ui
// 将ElementUI 导入到这里,其他组件就都可以使用elementui了
Vue.use(ElementUI);
Vue.use(Router)
export default new Router({
routes: [
{
path: '/',
name: 'HelloWorld',
component: HelloWorld
},
{
path:'/hello',
name:'Hello',
component:Hello
}
]
})
简单测试
在Hello.vue引入elementui
<template>
<div>
<h1>你好,Hello,{{name}}</h1>
<el-radio v-model="radio" label="1">备选项1</el-radio>
<el-radio v-model="radio" label="2">备选项2</el-radio>
</div>
</template>
<script>
// 这实际上就是一个Vue实例
export default {
data() {
return {
name: '张三',
radio:"2"
};
},
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
创建vue模板
vscode
file/preferences/User Snippets/New Global Snippets File
下次在vue文件里,直接输入 vue 就可以生成这个文件了
// {
// Place your snippets for vue here. Each snippet is defined under a snippet name and has a prefix, body and
// description. The prefix is what is used to trigger the snippet and the body will be expanded and inserted. Possible variables are:
// $1, $2 for tab stops, $0 for the final cursor position, and ${1:label}, ${2:another} for placeholders. Placeholders with the
// same ids are connected.
// Example:
// "Print to console": {
// "prefix": "log",
// "body": [
// "console.log('$1');",
// "$2"
// ],
// "description": "Log output to console"
// }
// }
{
"生成 vue 模板": {
"prefix": "vue",
"body": [
"",
" ",
"",
"",
"",
""
],
"description": "生成 vue 模板"
}
}
所有内容全部来自尚硅谷视频:
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1np4y1C7Yf?p=36&spm_id_from=pageDriver