如何理解CAS
CAS的基本概念
CAS全称Compare And Swap(比较与交换),是一种无锁编程算法,能够完全避免锁竞争带来的体统开销问题,也能够避免CPU在多个线程之间频繁切换和调度带来的开销。从某种程度上说,CAS比加锁机制具有更优的性能。
CAS能够在不阻塞的前提下,以原子性的方式来更新共享变量的数据,也就是在更新变量的数据时,能够保证现成的安全性。CAS算法一般会涉及3个操作数据,分别为:
- 要更新的内存中的变量V
- 与内存中的值进行比较的预期值X
- 要写入内存的新值N
CAS算法的总体流程为:当且仅当变量V的值与预期值X相同时,才会将V的值修改为新值N。如果V的值与X的值不相同,则说明已经有其他线程修改了V的值,当前线程不会更新V的值。最终,CAS会返回当前V的值。
CAS本质上是一种乐观锁的思想,当多个线程同时使用CAS的方式更新某个变量时,只会有一个线程更新成功,其他的线程都会因为内存中变量V的值与预期值X不相同而更新失败。与加锁方式不同的是,使用CAS更新失败的线程不会阻塞挂起,当更新失败时,可以再次尝试更新,也可以放弃更新,在处理上比加锁机制更加灵活。
在CAS的具体实现的很多场景下,进行一次CAS操作时不够的,在大部分场景下,CAS都需要伴随着自旋操作,在更新数据失败时不断尝试去重新更新数据,这种方式也被称为CAS自旋。
java中的java.util.concurrent.atomic包下提供的原子类底层基本都是通过CAS算法实现的,目前大部分的CPU内部都实现了原子化的CAS指令,java中的原子类底层都是调用JVM提供的方式实现的,JVM中的方法则是调用CPU的原子化CAS指令实现的。
例如,内存中有一个变量value的值为1,此时有多个线程通过CAS的方式更新value的值,假设,需要将value的值更新为2,CAS的操作如下: - 从内存中读取value的值
- 使用数值1与value值进行比对,如果value的值等于1,说明没有其他线程修改过value的值,就将value的值更新为2并写回内存。此时value的值为2,CAS操作成功。
- 在使用数值1与value的值进行比对时,如果发现value的值不等于1,说明有其他线程修改过value的值,此时就什么都不做,value的值仍然为被其他线程修改后的值。
- CAS操作更新失败的线程可以根据规则选择继续进行CAS自旋或者放弃更新。
CAS的核心类Unsafe
Unsafe类是java中实现CAS操作的底层核心类,提供了硬件级别的原子性操作,在Unsafe类中,提供了大量的native方法,通过JNI的方式调用JVM底层C和C++实现的函数。在java中的java.util.concurrent.atomic包下的原子类,底层都是基于Unsafe类实现的。
Unsafe类实战
使用Unsafe类获取UnsafeTest类中的静态变量staticNmae和成员变量memberVariable的偏移量,然后通过Unsafe类中的putObject()方法直接修改staticName的值,通过compareAndSwapObject()方法修改memberVariable的值
package com.lifly;
import sun.misc.Unsafe;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
/**
* @author lifly
* @description
* @date 2023-04-06 22:06
* @versoin 1.0.0
**/
public class UnsafeTest {
private static final Unsafe unsafe = getUnsafe();
private static long staticNameOffset = 0;
private static long memberVariableOffset = 0;
private static String staticName = "lifly_001";
private String memberVariable = "lifly_001";
static {
try {
staticNameOffset = unsafe.staticFieldOffset(UnsafeTest.class.getDeclaredField("staticName"));
memberVariableOffset = unsafe.objectFieldOffset(UnsafeTest.class.getDeclaredField("memberVariable"));
}catch (NoSuchFieldException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
UnsafeTest unsafeTest = new UnsafeTest();
System.out.println("修改前的值如下:");
System.out.println("staticName"+staticName+",memberVariableOffset"+unsafeTest.memberVariable);
unsafe.putObject(UnsafeTest.class,staticNameOffset,"lifly_static");
unsafe.compareAndSwapObject(unsafeTest,memberVariableOffset,"lifly_001","lifly_variable");
System.out.println("修改后的值如下:");
System.out.println("staticName"+staticName+",memberVariableOffset"+unsafeTest.memberVariable);
}
private static Unsafe getUnsafe(){
Unsafe unsafe = null;
try {
Field singleOneInstanceField = Unsafe.class.getDeclaredField("theUnsafe");
singleOneInstanceField.setAccessible(true);
unsafe = (Unsafe) singleOneInstanceField.get(null);
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
return unsafe;
}
}
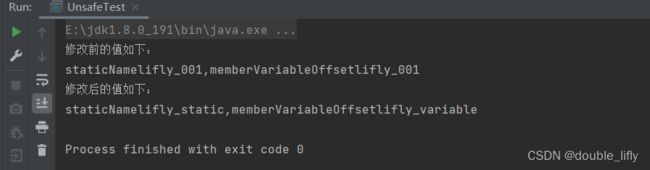
在上述代码中,首先通过getUnsafe()方法获取Unsafe实例对象,然后定义了两个long类型的静态变量staticNameOffset和memberVariableOffset,分别表示静态变量staticName和成员变量memberVariable的偏移量。
接下来,定义了一个String类型的静态变量staticName,初始值为lifly_001,定义一个String类型的成员变量memberVariable,初始值为lifly_001。
然后在静态代码块中调用Unsafe类中的putObject()方法修改静态变量staticName的值,调用Unsafe类的compareAndSwapObject()方法修改成员变量memberVariable的值。预期的结果是将静态变量staticName的值修改为lifly_static,将成员变量memberVariable的值修改为lifly_variable,如图所示,结果也符合预期。
使用CAS实现count++
设置20个线程并行运行,每个线程通过都通过CAS自旋的方式对一个共享变量的数据进行自增操作,每个线程运行的次数为500次,最终得出的结果为10000
程序实现
package com.lifly;
import sun.misc.Unsafe;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;
import java.util.stream.IntStream;
/**
* @author lifly
* @description
* @date 2023-04-08 13:59
* @versoin 1.0.0
**/
public class CasCountIncrement {
/**
* 获取unsafe对象
*/
private static final Unsafe unsafe = getUnsafe();
/**
* 现成的数量
*/
private static final int THREAD_COUNT = 20;
/**
* 每个线程运行的次数
*/
private static final int EXECUTE_COUNT_EVERY_THREDA = 500;
/**
* 自增的count值
*/
private volatile int count = 0;
/**
* count的偏移量
*/
private static long countOffset;
/**
* 在静态代码块中通过Unsafe类的objectFieldOffset()方法获取count变量的偏移量。将其赋值给countOffset静态变量
*/
static {
try {
countOffset = unsafe.objectFieldOffset(CasCountIncrement.class.getDeclaredField("count"));
}catch (NoSuchFieldException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 以CAS的方式对count值进行自增操作
*/
public void incrementCountByCas(){
//将count的值赋值给oldCount
int oldCount = 0;
do {
oldCount = count;
}while (!unsafe.compareAndSwapInt(this,countOffset,oldCount,oldCount+1));
}
/**
* 获取Unsafe实例对象
* @return unsafe
*/
private static Unsafe getUnsafe() {
Unsafe unsafe = null;
try {
Field singleoneInstanceField = Unsafe.class.getDeclaredField("theUnsafe");
singleoneInstanceField.setAccessible(true);
unsafe = (Unsafe) singleoneInstanceField.get(null);
} catch (NoSuchFieldException | IllegalAccessException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
return unsafe;
}
/**
* 创建main方法,循环20次,在每次循环中创建一个线程,每个线程中调用incrementCountByCas方法,同时在每个线程执行完毕,
* 都调用CountDownLatch的countDown方法使计数器减1.
* 然后再main方法中调用countDownLatch类的await方法阻塞main线程,直到CountDownLatch中的计数器减为0,才继续执行
* 最后,打印count的最终结果数据
* @param args
* @throws InterruptedException
*/
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
CasCountIncrement casCountIncrement = new CasCountIncrement();
CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(THREAD_COUNT);
IntStream.range(0,THREAD_COUNT).forEach((i)->{
new Thread(()->{
IntStream.range(0,EXECUTE_COUNT_EVERY_THREDA).forEach((j)->{
casCountIncrement.incrementCountByCas();
});
countDownLatch.countDown();
}).start();
});
countDownLatch.await();
System.out.println("count的最终结果为:"+casCountIncrement.count);
}
}

可以看到,count的最终结果为10000,与程序的预期结果符合。
ABA问题
ABA问题概述
ABA问题简单来说就是一个变量的初始值为A,被修改为B,然后再次被修改为A了。在使用CAS算法进行检测时,无法检测出A的值是否经历过被修改为B,又再次被修改为A的过程。

由上图可以看出,当线程A准备调用CAS(1,2)将变量V的值由1修改为2时,CPU发生了线程切换,切换线程B上,线程B在执行业务逻辑的过程中,调用CAS(2,1)将变量V的值由1修改为了2,又调用CAS(2,1)将变量V的值由2修改为了1.然后CPU又发生了线程切换切换到了线程A上,执行CAS(1,2)将变量V的值由1修改为2.虽然线程A的CAS操作能够执行成功,但是期间线程B已经修改了变量V的值了,从而造成了ABA问题。
ABA问题解决方案
ABA问题最典型的解决方案就是使用版本号问题。具体的操作方法就是在每次修改数据时都携带一个版本号,只有当该版本号与数据的版本号一致时,才能执行数据的修改,否则修改失败。因为操作的时候携带了版本号,而版本号在每次修改时都会增加,并且只会增加不会减少,所以可以有效的避免ABA问题。
Java如何解决ABA问题
在java.util.concurrent.atomic包下提供了AtomicStampedReference类和AtomicMarkableReference类以解决ABA问题。
AtomicStampedReference类在CAS的基础上增加了一个类似于版本号的时间戳,可以将这个时间戳作为版本号来防止ABA问题,例如AtomicStampedReference类中的warkCompareAndSet()方法和compareAndSet(),AtomicStampedReference类中的warkCompareAndSet()方法和compareAndSet()反复噶的源码如下:
public boolean weakCompareAndSet(V expectedReference,
V newReference,
int expectedStamp,
int newStamp) {
return compareAndSet(expectedReference, newReference,
expectedStamp, newStamp);
}
public boolean compareAndSet(V expectedReference,
V newReference,
int expectedStamp,
int newStamp) {
Pair<V> current = pair;
return
expectedReference == current.reference &&
expectedStamp == current.stamp &&
((newReference == current.reference &&
newStamp == current.stamp) ||
casPair(current, Pair.of(newReference, newStamp)));
}
从源码中可以看出,AtomicStampedReference类中的weakCompareAndSet()方法内部调用的是compareAndSet()方法实现的。compareAndSet()方法的4个参数如下:
- expectedReference:期望的引用值
- newReference:更新的引用值
- expectedStamp:预期的时间戳
- newStamp:更新后的时间戳
AtomicStampedReference类中CAS的实现方式为如果当前的引用值等于预期的引用值,并且当前的时间戳等于预期的时间戳,就会以原子的方式将引用值和时间戳修改为给定的引用值和时间戳。
AtomicMarkableReference类的实现中不关心修改过的次数,只关心是否修改过。
AtomicMarkableRederence类的weakCompareAndSet()方法和compareAndSet()方法的源码如下:
public boolean weakCompareAndSet(V expectedReference,
V newReference,
boolean expectedMark,
boolean newMark) {
return compareAndSet(expectedReference, newReference,
expectedMark, newMark);
}
public boolean compareAndSet(V expectedReference,
V newReference,
boolean expectedMark,
boolean newMark) {
Pair<V> current = pair;
return
expectedReference == current.reference &&
expectedMark == current.mark &&
((newReference == current.reference &&
newMark == current.mark) ||
casPair(current, Pair.of(newReference, newMark)));
}
从源码中可以看出,在AtomicMarkableReference类的weakCompareAndSet()方法compareAndSet()方法的实现中,增加了boolean类型的参数,只判断对象是否被修改过。