leetcode 235. 二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先
给定一个二叉搜索树, 找到该树中两个指定节点的最近公共祖先。
百度百科中最近公共祖先的定义为:“对于有根树 T 的两个结点 p、q,最近公共祖先表示为一个结点 x,满足 x 是 p、q 的祖先且 x 的深度尽可能大(一个节点也可以是它自己的祖先)。”
例如,给定如下二叉搜索树: root = [6,2,8,0,4,7,9,null,null,3,5]
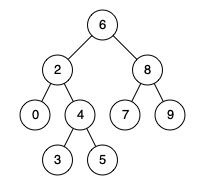
示例 1:
输入: root = [6,2,8,0,4,7,9,null,null,3,5], p = 2, q = 8
输出: 6
解释: 节点 2 和节点 8 的最近公共祖先是 6。
示例 2:
输入: root = [6,2,8,0,4,7,9,null,null,3,5], p = 2, q = 4
输出: 2
解释: 节点 2 和节点 4 的最近公共祖先是 2, 因为根据定义最近公共祖先节点可以为节点本身。
说明:
所有节点的值都是唯一的。
p、q 为不同节点且均存在于给定的二叉搜索树中。
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/lowest-common-ancestor-of-a-binary-search-tree
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
python3的实现方法以及解释:
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution:
def lowestCommonAncestor(self, root: 'TreeNode', p: 'TreeNode', q: 'TreeNode') -> 'TreeNode':
'''获取从root到target的路径'''
def getPath(root: 'TreeNode', target: 'TreeNode') -> List['TreeNode']:
node = root
path = []
'''如果当前的node和target不一致,则继续往树的下面遍历'''
while node != target:
'''将当前的节点加入到path里面'''
path.append(node)
'''如果当前节点的节点值大于target的节点值,则遍历左子树'''
if node.val > target.val:
node = node.left
else:
'''如果当前节点的节点值小于target的节点值,则遍历右子树'''
node = node.right
path.append(node)
return path
ans_p = []
ans_q = []
'''获取从root到p的路径'''
ans_p = getPath(root, p)
'''获取从root到q的路径'''
ans_q = getPath(root, q)
'''分别获取从root到p和q的路径长度'''
len_p = len(ans_p)
len_q = len(ans_q)
i = 0
ancestor = None
'''遍历整个path,找到最后一个祖先节点'''
while i < len_p and i < len_q:
'''如果相等则记录,直到最后一个祖先节点'''
if ans_p[i] == ans_q[i]:
ancestor = ans_p[i]
else:
'''如果不相等,则直接退出,上一个相等的祖先节点即为最终的最近的祖先节点''''
break
i += 1
return ancestor
C语言实现的方法:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* struct TreeNode *left;
* struct TreeNode *right;
* };
*/
struct TreeNode **getPath(struct TreeNode *root, struct TreeNode *target, int *num)
{
struct TreeNode *node = root;
struct TreeNode **path = malloc(sizeof(struct TreeNode) * 2001) ;
while (node != target)
{
path[(*num)++] = node;
if (node->val > target->val)
{
node = node->left;
}
else
{
node = node->right;
}
}
path[(*num)++] = node;
return path;
}
struct TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(struct TreeNode* root, struct TreeNode* p, struct TreeNode* q) {
int num_p = 0, num_q = 0;
struct TreeNode *ancestor;
struct TreeNode** path_p = getPath(root, p, &num_p);
struct TreeNode** path_q = getPath(root, q, &num_q);
for (int i = 0; i < num_p && i < num_q; i++)
{
if (path_p[i] == path_q[i])
{
ancestor = path_p[i];
}
else
{
break;
}
}
return ancestor;
}