在C++中如何对自定义类型做hash操作
概述
哈希函数(hash function)的目的是根据给定对象算出一个哈希码(hash code),使得对象经过hash code映射之后能够乱且随机地被放置在哈希表(hashtable)中,从而尽量避免发生哈希碰撞。
C++标准库中提供地hash函数版本如下(使用偏特化,对于数值型地数据hash函数得到地hash code就是原值,对于字符串则提供了专门地hash表达式):
template<class key> struct hash{};//泛化
//偏特化
template<> struct hash<char>{size_t operator()(char x)const{return x;}};
template<> struct hash<short>{size_t operator()(shortx)const{return x;}};
template<> struct hash<int>{size_t operator()(int x)const{return x;}};
......
template<> struct hash<long>{size_t operator()(longx)const{return x;}};
......
template<> struct hash<char*>{size_t operator()(char* s)const{return _stl_hash_string(s);}};
size_t _stl_hash_string(const char* s)
{
unsigned long h=0;
for(;*s;++s)h=5*h+*s;
return size_t(s);
}
众所周知,在C++的STL中,unordered_set、unordered_multiset、unordered_map、unordered_multimap的底层数据结构就是hash表,至于hash表的底层原理请看我的上一篇博客。对于我们常见的数据类型如int、double、char、char*、string等,STL专家已经帮忙写好了hash函数,因此可以直接使用。以unordered_set为例,作为模板类具体形式如下:
unordered_set<typename _Kty,typename _Hasher=hash<_Kty>,typename _Keyeq=equal_to<_Kty>,typename _Allocator<_Kty>>
从上面可以看到unordered_set有四个模板参数,第一个模板参数为向unordered_set安插的对象类型,第二个模板参数为hash函数,第三个参数对象为两个对象相等的判别条件(这里需要说明的是对于set、map容器,需要有一个机制来专门判断安插的两个对象是否相等,然后决定是否插入以及插入位置),第四个模板参数为分配器。显然后三个模板参数已经有了默认值(都是重载了()的类,可以方便的创建出函数对象方便调用)。
对于C++标准库中已有的数据类型,unordered_set的使用十分方便:
unordered_set<int> uset1;
unordered_set<string> uset2;//C++11后string才提供了默认hash函数
而对于自定义数据类型使用unordered_set,则需要自定义hash操作。具体有以下四种方式:
使用标准库提供的hash函数
方式一:使用仿函数
#include uset;
unordered_set<Person,Hasher> uset;
uset.insert(Person("a", "a", 10));
uset.insert(Person("b", "b", 11));
uset.insert(Person("c", "c", 12));
uset.insert(Person("d", "d", 13));
uset.insert(Person("e", "e", 14));
for (Person p : uset) {
cout << p;
}
}

实例中有两个需要关注的点:
①创建一个仿函数,将自定义数据转为哈希码
②需要为自定义类型提供判断两对象是否相等的功能,有两种方式:第一种是在类中重载==运算符,第二种是创建一个实现对象比较功能的仿函数并作为模板参数传递给unordered_set。
方式二:使用全局函数
该方式与方式一大同小异,唯一的区别是将仿函数换成了全局函数,将全局函数的地址作为模板参数传递给unordered_set。
#include方式三:使用偏特化实现hash函数
因为C++标准库已经提供了hash的类模板,并且也提供了int、string、char等偏特化版本,所以这里可以直接对自定义类型做一个偏特化版本。
可能会觉得和方式一形式很像,但原理是不一样的,而且使用时不需要以模板参数的形式传递给容器。
#include,hash())
public:
size_t operator()(const Person& p)const {
return hash<string>()(p.firstname)+ hash<string>()(p.lastname)+ hash<int>()(p.age);
}
};
void main()
{
unordered_set<Person> uset;
uset.insert(Person("a", "a", 10));
uset.insert(Person("a", "a", 10));
uset.insert(Person("c", "c", 12));
uset.insert(Person("d", "d", 13));
uset.insert(Person("e", "e", 14));
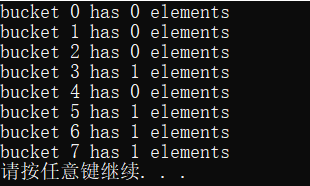
for (int i = 0; i < uset.bucket_count(); i++) {
cout << "bucket " << i << " has " << uset.bucket_size(i) << " elements" << endl;
}
}
使用自定义hash函数
方式四:使用自定义hash函数
这里用到了泛型中的可变模板(variadic templates)的知识,在对对象做hash操作时,通过步骤①②③依次获取对象中参与hash的数据成员,构思非常巧妙,需要细细体会。
这里的在求得对象哈希码时虽然也用到了标准库提供的hash函数,但和方式一与方式二不同的是,我们终于获得了自己定义hash表达式的机会,我们甚至在这里可以直接去掉标准库提供的hash函数,完全自己定义hash表达式,前提是你要有足够的自信来打乱hash码。
#include()(arg)操作也可以有我们自己来做)
//不同用户在这里可以有不同的数,只要能够将原始数据尽可能打乱即可
//0x9e3779b9涉及到数学中的黄金比例,实际上并不需要一定是这个数
seed ^= hash<T>()(arg) + 0x9e3779b9 + (seed << 6) + (seed >> 2);
}
template<typename T>
void hashValue(size_t& seed, const T& arg)//③递归出口
{
hashCombine(seed, arg);
}
template<typename T1, typename... T2>
void hashValue(size_t& seed,const T1& arg,const T2&... args)//②在这里通过递归逐步拿到所有参数,当args...的大小为1时跳出该递归,接着进入③
{
hashCombine(seed, arg);
hashValue(seed, args...);//递归
}
template<typename... T>//T为模板参数包,可以代表任意多个类型;args为函数参数包,可以代表任意多个函数参数
size_t hashValue(const T&... args)//①在这里完成参数的第一次拆分,接着进入②
{
size_t seed = 0;//种子,以引用方式传递
hashValue(seed, args...);//args...中为T类型对象中的所有用于hash的数据成员
return seed;
}
class Hasher {//hash函数
public:
size_t operator()(const Person& p)const {
return hashValue(p.firstname,p.lastname,p.age);
}
};
void main()
{
unordered_set<Person, Hasher> uset;
uset.insert(Person("a", "a", 10));
uset.insert(Person("a", "a", 10));
uset.insert(Person("c", "c", 12));
uset.insert(Person("d", "d", 13));
uset.insert(Person("e", "e", 14));
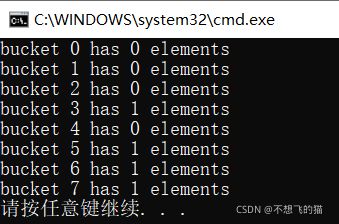
for (int i = 0; i < uset.bucket_count(); i++) {
cout << "bucket " << i << " has " << uset.bucket_size(i) << " elements" << endl;
}
}
总结
方式一、二、三形式上相对比较简单,基本完全依赖C++标准库提供地hash函数,对于简单地程序可以直接用。而对于企业级地程序,基本上都会基于测试构建自己地hash表达式,一般会使用方式四。
以上是我对C++ hash操作的基本理解,出处是侯捷老师的《STL标准库和泛型编程》,感觉讲得很精彩,所以整理了以下,如果有错误或见解,希望不吝赐教。