STL——array和vector容器
作者介绍:22级树莓人(计算机专业),热爱编程<目前在c++阶段>——目标Windows,MySQL,Qt,数据结构与算法,Linux,多线程,会持续分享学习成果和小项目的
作者主页:热爱编程的小K
专栏链接:c++欢迎各位→点赞 + 收藏 + 留言
总结:希望你看完之后,能对你有所帮助,不足请指正!共同学习交流
目录文章
-
-
-
- 一、array
-
- 1、array概念
- 2、操作基本数据类型
- 3、操作自定义类型
- 4、函数介绍
- 二、vector
-
- 1、Vector概念
- 2、操作基本类型
- 3、操作自定义类型
- 三、vector和array的嵌套
-
- 1、array嵌套
- 2、vector嵌套
-
-
一、array
1、array概念
array是一个容器,封装了固定大小的数组。
该容器是聚合类型,其语义与C风格数组的结构相同, T [ N ]作为其唯一的非静态数据成员。与c风格数组不同的是,它不会自动衰减为T*。(数组名不会自动转为数组首地址)
该容器将C风格数组的
性能和可访问性与标准容器的优点相结合,比如知道自己的大小、支持赋值、随机访问迭代器等。
2、操作基本数据类型
初始化不赋初值,里面的值不会自动初始化,因为rray没有构造函数,也没有私有或保护成员,所以不初始化读出来的是野值
void testOne()
{
array pos;
for (int i = 0; i < pos.size(); i++)
{
cin >> pos[i];
}
for (int i = 0; i < pos.size(); i++)
{
/* code */
cout << pos[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
array nums = { 1.11,2.22,3.33 };
//迭代器方式访问
for (array::iterator iter = nums.begin(); iter != nums.end(); iter++)
{
cout << *iter << " ";
}
cout << endl;
//新版for循环方式访问
for (auto v : nums)
{
cout << v << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
3、操作自定义类型
操作自定义类型时要记得重载运算符
class MM
{
public:
MM(int age = 0, string name = "") :age(age), name(name) {}
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const MM& object)
{
out << object.name << " " << object.age << endl;
return out;
}
string getName() const { return name; }
int getAge() const { return age; }
protected:
int age;
string name;
};
bool seacherName(const MM& object) {
return object.getName() == "貂蝉";
}
void testtwo() {
array info;
info[0] = { 18,"貂蝉" };
info[1] = { 19,"杨玉环" };
info[2] = { 16,"坤坤" };
for (auto v : info)
{
cout << v << endl;
}
array::iterator iter = find_if(info.begin(), info.end(), seacherName);
if (iter != info.end())
{
cout << (*iter).getName() << " " << iter->getAge() << endl;
}
}
4、函数介绍
| 函数名 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| size() | 读取数组大小 |
| empty() | 判断数组是否为空 |
| front() | 读取数组首元素 |
| back() | 读取数组末尾元素 |
| fill() | 用某元素填充数组 |
void test3() {
array king = { 1,2,3,4,5 };
cout << "size:" << king.size() << endl;
cout << "empty:" << king.empty() << endl;
cout << "front" << king.front() << endl;
cout << "back:" << king.back() << endl;
cout << "填充:";
king.fill(5);
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
cout << king[i] << " ";
}
二、vector
1、Vector概念
vector 容器是 STL 中最常用的容器之一,它和 array 容器非常类似,都可以看做是对 C++普通数组的“升级版”。不同之处在于,array 实现的是静态数组(容量固定的数组),而 vector 实现的是一个动态数组,即可以进行元素的插入和删除,在此过程中,vector 会动态调整所占用的内存空间,整个过程无需人工干预。
vector尾部添加或移除元素非常快速。但是在中部或头部插入元素或移除元素比较费时
2、操作基本类型
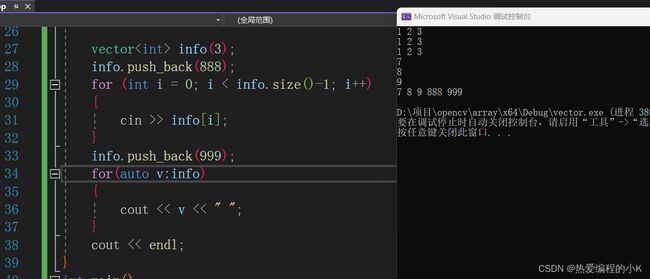
注意:成员函数
push_back()是在容器的最后面插入,如图,原先建立的时候是3个空间,用成员函数插入一个,空间变成4个,以及最后又在后面插入了一个999
//操作基本数据类型
bool cmpData(int data) { return data == 888; }
void testOne()
{
//不带长度的构建方式,不能采用下标法插入,只能采用成员函数插入
vector king;
//king[0] = 1;
king.push_back(1);
king.push_back(2);
king.push_back(3);
for (int i = 0; i < king.size(); i++)
{
cout << king[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
for (auto v : king) {
cout << v << " ";
}
cout << endl;
for (vector::iterator iter = king.begin(); iter != king.end(); iter++) {
cout << *iter << " ";
}
cout << endl;
vector info(3);
info.push_back(888);
for (int i = 0; i < info.size()-1; i++)
{
cin >> info[i];
}
info.push_back(999);
for(auto v:info)
{
cout << v << " ";
}
cout << endl;
vector::iterator iter = find_if(info.begin(), info.end(), cmpData);
if (iter != info.end()) cout << *iter << endl;
}
3、操作自定义类型
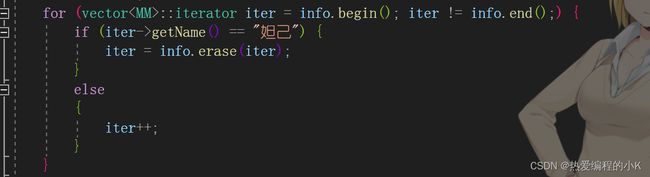
这里用迭代器进行删除的时候,成员函数erase()会把删除的下一个位置返回回来
//操作自定义数据类型
class MM
{
public:
MM(int age=0,string name=" "):age(age),name(name){}
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const MM& object) {
out << object.name << " " << object.age << endl; \
return out;
}
string getName() { return name; }
int getAge() { return age; }
protected:
int age;
string name;
};
void testTwo() {
vector info;
info.push_back(MM(19, "西施"));
info.push_back(MM(18, "貂蝉"));
info.push_back(MM(20, "妲己"));
for (auto v : info) {
cout << v;
}
cout << endl;
for (vector::iterator iter = info.begin(); iter != info.end();) {
if (iter->getName() == "妲己") {
iter = info.erase(iter);
}
else
{
iter++;
}
}
for (auto v : info) {
cout << v;
}
}
三、vector和array的嵌套
1、array嵌套
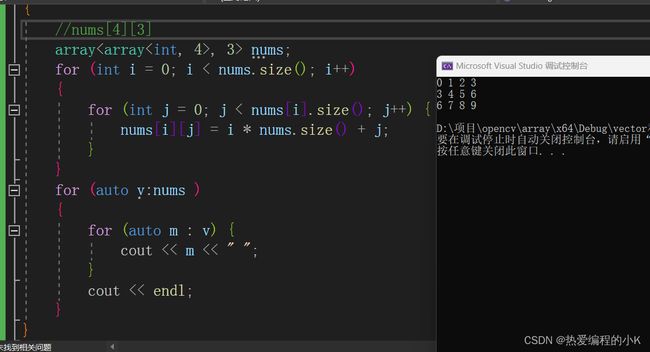
void testOne()
{
//nums[4][3]
array, 3> nums;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < nums[i].size(); j++) {
nums[i][j] = i * nums.size() + j;
}
}
for (auto v:nums )
{
for (auto m : v) {
cout << m << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
}
2、vector嵌套
void testTwo() {
vector> info;
for (int i = 0; i <=3; i++)
{
vector temp;
for (int j = 0; j <= i; j++)
{
temp.push_back(j);
}
info.push_back(temp);
}
for (auto v : info) {
for (auto m : v) {
cout << m << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
}