原子搜索优化算法ASO
目录
- 主函数
- 结果
- 各种算法的比较
- 结果
- 函数1
- 函数2
- 函数3
- 函数4
- 函数5
- 函数6
- 函数7
- 函数8
- 函数9
- 函数-粒子群优化算法
- 函数10
- 函数11
- 函数12
原子搜索算法(atom search algorithm,ASO)是模仿自然界中原子运动而提出的一种新型优化算法。
原子搜索算法(atom search algorithm,ASO)是根据原子的运动规律,通过种群中各个原子之间的相互作用力来指导群体进行智能优化搜索。算法结构简单,参数较少。
主函数
%% 清空环境变量
clear;clc
SearchAgents_no=50; % 种群数量
Function_name='F8'; % 标准测试函数编号(F1~F23)
Max_iteration=100; % 最大迭代次数
% 获取目标函数对应参数
[lb,ub,dim,fobj]=Get_Functions_details(Function_name);
% ASO寻优
[Best_score,Best_pos,cg_curve]=ASO(SearchAgents_no,Max_iteration,lb,ub,dim,fobj);
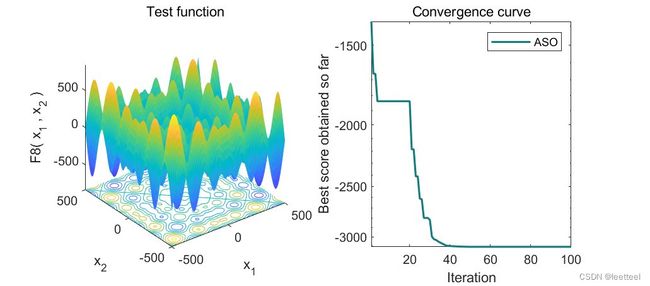
figure('Position',[500 500 660 290])
% 绘制搜索空间
subplot(1,2,1);
func_plot(Function_name);
title('Test function')
xlabel('x_1');
ylabel('x_2');
zlabel([Function_name,'( x_1 , x_2 )'])
grid off
%绘制收敛曲线
subplot(1,2,2);
semilogy(cg_curve,'Color','#167C80','LineWidth',1.5)
title('Convergence curve')
xlabel('Iteration');
ylabel('Best score obtained so far');
axis tight
grid off
box on
legend('ASO')
display(['The best solution obtained by ASO is : ', num2str(Best_pos)]);
display(['The best optimal value of the objective funciton found by ASO is : ', num2str(Best_score)]);
saveas(gcf,'仿真图.jpg')
结果
各种算法的比较
%% 清空环境变量
clear;clc
SearchAgents_no=50; % 种群数量
Function_name='F8'; % 测试函数编号(F1~F23)
Max_iteration=500; % 最大迭代次数
[lb,ub,dim,fobj]=Get_Functions_details(Function_name); % 获取目标函数对应参数
%% 模型训练
[Best_score,Best_pos,cg_curve]=GA(SearchAgents_no,Max_iteration,lb,ub,dim,fobj); % 遗传优化算法
[Best_score1,Best_pos1,cg_curve1]=PSO(SearchAgents_no,Max_iteration,lb,ub,dim,fobj); % 粒子群优化算法
[Best_score2,Best_pos2,cg_curve2]=SA(Max_iteration,lb,ub,dim,fobj); % 模拟退火优化算法
[Best_score3,Best_pos3,cg_curve3]=ASO(SearchAgents_no,Max_iteration,lb,ub,dim,fobj); % 原子搜索优化算法
%% 结果绘图
figure('Position',[500 500 660 290])
% 绘制搜索空间
subplot(1,2,1);
func_plot(Function_name);
title('Test function')
xlabel('x_1');
ylabel('x_2');
zlabel([Function_name,'( x_1 , x_2 )'])
grid off
%绘制收敛曲线
subplot(1,2,2);
semilogy(cg_curve,'Color','#167C80','LineWidth',1.5)
hold on
semilogy(cg_curve1,'Color','#E54B4B','LineWidth',1.5)
hold on
semilogy(cg_curve2,'Color','#ff8946','LineWidth',1.5)
hold on
semilogy(cg_curve3,'Color','#3d7aad','LineWidth',1.5)
legend('GA','PSO','SA','ASO')
grid off
xlabel('迭代次数')
ylabel('目标函数值')
title('不同优化算法的进化曲线对比图')
%% 输出结果
disp('======GA结果==========');
display(['The best solution obtained by GA is : ', num2str(Best_pos)]);
display(['The best optimal value of the objective funciton found by GA is : ', num2str(Best_score)]);
disp('======PSO结果============');
display(['The best solution obtained by PSO is : ', num2str(Best_pos1)]);
display(['The best optimal value of the objective funciton found by PSO is : ', num2str(Best_score1)]);
disp('======SA结果============');
display(['The best solution obtained by SA is : ', num2str(Best_pos2)]);
display(['The best optimal value of the objective funciton found by SA is : ', num2str(Best_score2)]);
disp('======ASO结果============');
display(['The best solution obtained by ASO is : ', num2str(Best_pos3)]);
display(['The best optimal value of the objective funciton found by ASO is : ', num2str(Best_score3)]);
saveas(gcf,'对比图.jpg')
结果
函数1
function Acc=Acceleration(Atom_Pop,Fitness,Iteration,Max_Iteration,Dim,Atom_Num,X_Best,alpha,beta)
%Calculate mass
M=exp(-(Fitness-max(Fitness))./(max(Fitness)-min(Fitness)));
M=M./sum(M);
G=exp(-20*Iteration/Max_Iteration);
Kbest=Atom_Num-(Atom_Num-2)*(Iteration/Max_Iteration)^0.5;
Kbest=floor(Kbest)+1;
[Des_M Index_M]=sort(M,'descend');
for i=1:Atom_Num
E(i,:)=zeros(1,Dim);
MK(1,:)=sum(Atom_Pop(Index_M(1:Kbest),:),1)/Kbest;
Distance=norm(Atom_Pop(i,:)-MK(1,:));
for k=1:Kbest
j=Index_M(k);
%Calculate LJ-potential
Potential=LJPotential(Atom_Pop(i,:),Atom_Pop(j,:),Iteration,Max_Iteration,Distance);
E(i,:)=E(i,:)+rand(1,Dim)*Potential.*((Atom_Pop(j,:)-Atom_Pop(i,:))/(norm(Atom_Pop(i,:)-Atom_Pop(j,:))+eps));
end
E(i,:)=alpha*E(i,:)+beta*(X_Best-Atom_Pop(i,:));
%Calculate acceleration
a(i,:)=E(i,:)./M(i);
end
Acc=a.*G;
函数2
%--------------------------------------------------------------------------
% Developed in MATLAB R2011b
% W. Zhao, L. Wang and Z. Zhang, Atom search optimization and its
% application to solve a hydrogeologic parameter estimation problem,
% Knowledge-Based Systems,2019,163:283-304, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2018.08.030.
%--------------------------------------------------------------------------
% Atom Search Optimization.
function [Fit_XBest,X_Best,Functon_Best]=ASO(Atom_Num,Max_Iteration,Low,Up,Dim,fobj)
alpha=50;
beta=0.2;
Iteration=1;
% [Low,Up,Dim]=Test_Functions_Range(Fun_Index);
% Randomly initialize positions and velocities of atoms.
if size(Up,2)==1
Atom_Pop=rand(Atom_Num,Dim).*(Up-Low)+Low;
Atom_V=rand(Atom_Num,Dim).*(Up-Low)+Low;
end
if size(Up,2)>1
for i=1:Dim
Atom_Pop(:,i)=rand(Atom_Num,1).*(Up(i)-Low(i))+Low(i);
Atom_V(:,i)=rand(Atom_Num,1).*(Up(i)-Low(i))+Low(i);
end
end
% Compute function fitness of atoms.
for i=1:Atom_Num
Fitness(i)=fobj(Atom_Pop(i,:));
end
Functon_Best=zeros(Max_Iteration,1);
[Max_Fitness,Index]=min(Fitness);
Functon_Best(1)=Fitness(Index);
X_Best=Atom_Pop(Index,:);
% Calculate acceleration.
Atom_Acc=Acceleration(Atom_Pop,Fitness,Iteration,Max_Iteration,Dim,Atom_Num,X_Best,alpha,beta);
% Iteration
for Iteration=2:Max_Iteration
Functon_Best(Iteration)=Functon_Best(Iteration-1);
Atom_V=rand(Atom_Num,Dim).*Atom_V+Atom_Acc;
Atom_Pop=Atom_Pop+Atom_V;
for i=1:Atom_Num
% Relocate atom out of range.
TU= Atom_Pop(i,:)>Up;
TL= Atom_Pop(i,:)<Low;
Atom_Pop(i,:)=(Atom_Pop(i,:).*(~(TU+TL)))+((rand(1,Dim).*(Up-Low)+Low).*(TU+TL));
%Evaluate atom.
Fitness(i)=fobj(Atom_Pop(i,:));
end
[Max_Fitness,Index]=min(Fitness);
if Max_Fitness<Functon_Best(Iteration)
Functon_Best(Iteration)=Max_Fitness;
X_Best=Atom_Pop(Index,:);
else
r=fix(rand*Atom_Num)+1;
Atom_Pop(r,:)=X_Best;
end
% Calculate acceleration.
Atom_Acc=Acceleration(Atom_Pop,Fitness,Iteration,Max_Iteration,Dim,Atom_Num,X_Best,alpha,beta);
end
Fit_XBest=Functon_Best(Iteration);
函数3
function ret=Code(lenchrom,bound)
%本函数将变量编码成染色体,用于随机初始化一个种群
% lenchrom input : 染色体长度
% bound input : 变量的取值范围
% ret output: 染色体的编码值
flag=0;
while flag==0
pick=rand(1,lenchrom);
ret=bound(:,1)'+(bound(:,2)-bound(:,1))'.*pick; %线性插值
flag=test(lenchrom,bound,ret); %检验染色体的可行性
end
end
函数4
function ret=Cross(pcross,lenchrom,chrom,sizepop,bound)
%本函数完成交叉操作
% pcorss input : 交叉概率
% lenchrom input : 染色体的长度
% chrom input : 染色体群
% sizepop input : 种群规模
% ret output : 交叉后的染色体
for i=1:sizepop
% 随机选择两个染色体进行交叉
pick=rand(1,2);
while prod(pick)==0
pick=rand(1,2);
end
index=ceil(pick.*sizepop);
% 交叉概率决定是否进行交叉
pick=rand;
while pick==0
pick=rand;
end
if pick>pcross
continue;
end
flag=0;
while flag==0
% 随机选择交叉位置
pick=rand;
while pick==0
pick=rand;
end
pos=ceil(pick.*sum(lenchrom)); %随机选择进行交叉的位置,即选择第几个变量进行交叉,注意:两个染色体交叉的位置相同
pick=rand; %交叉开始
v1=chrom(index(1),pos);
v2=chrom(index(2),pos);
chrom(index(1),pos)=pick*v2+(1-pick)*v1;
chrom(index(2),pos)=pick*v1+(1-pick)*v2; %交叉结束
flag1=test(lenchrom,bound,chrom(index(1),:)); %检验染色体1的可行性
flag2=test(lenchrom,bound,chrom(index(2),:)); %检验染色体2的可行性
if flag1*flag2==0
flag=0;
else flag=1;
end %如果两个染色体不是都可行,则重新交叉
end
end
ret=chrom;
end
函数5
function func_plot(func_name)
[lb,ub,dim,fobj]=Get_Functions_details(func_name);
switch func_name
case 'F1'
x=-100:2:100; y=x; %[-100,100]
case 'F2'
x=-100:2:100; y=x; %[-10,10]
case 'F3'
x=-100:2:100; y=x; %[-100,100]
case 'F4'
x=-100:2:100; y=x; %[-100,100]
case 'F5'
x=-200:2:200; y=x; %[-5,5]
case 'F6'
x=-100:2:100; y=x; %[-100,100]
case 'F7'
x=-1:0.03:1; y=x ; %[-1,1]
case 'F8'
x=-500:10:500;y=x; %[-500,500]
case 'F9'
x=-5:0.1:5; y=x; %[-5,5]
case 'F10'
x=-20:0.5:20; y=x;%[-500,500]
case 'F11'
x=-500:10:500; y=x;%[-0.5,0.5]
case 'F12'
x=-10:0.1:10; y=x;%[-pi,pi]
case 'F13'
x=-5:0.08:5; y=x;%[-3,1]
case 'F14'
x=-100:2:100; y=x;%[-100,100]
case 'F15'
x=-5:0.1:5; y=x;%[-5,5]
case 'F16'
x=-1:0.01:1; y=x;%[-5,5]
case 'F17'
x=-5:0.1:5; y=x;%[-5,5]
case 'F18'
x=-5:0.06:5; y=x;%[-5,5]
case 'F19'
x=-5:0.1:5; y=x;%[-5,5]
case 'F20'
x=-5:0.1:5; y=x;%[-5,5]
case 'F21'
x=-5:0.1:5; y=x;%[-5,5]
case 'F22'
x=-5:0.1:5; y=x;%[-5,5]
case 'F23'
x=-5:0.1:5; y=x;%[-5,5]
end
L=length(x);
f=[];
for i=1:L
for j=1:L
if strcmp(func_name,'F15')==0 && strcmp(func_name,'F19')==0 && strcmp(func_name,'F20')==0 && strcmp(func_name,'F21')==0 && strcmp(func_name,'F22')==0 && strcmp(func_name,'F23')==0
f(i,j)=fobj([x(i),y(j)]);
end
if strcmp(func_name,'F15')==1
f(i,j)=fobj([x(i),y(j),0,0]);
end
if strcmp(func_name,'F19')==1
f(i,j)=fobj([x(i),y(j),0]);
end
if strcmp(func_name,'F20')==1
f(i,j)=fobj([x(i),y(j),0,0,0,0]);
end
if strcmp(func_name,'F21')==1 || strcmp(func_name,'F22')==1 ||strcmp(func_name,'F23')==1
f(i,j)=fobj([x(i),y(j),0,0]);
end
end
end
surfc(x,y,f,'LineStyle','none');
end
函数6
%_________________________________________________________________________%
%遗传算法 %
%_________________________________________________________________________%
function [Best_score,Best_pos,curve]=GA(pop,Max_iter,lb,ub,dim,fobj)
%% 参数初始化
popsize=pop; %种群规模
lenchrom=dim; %变量字串长度
fun = fobj; %适应度函数
pc=0.9; %设置交叉概率
pm=0.2; %设置变异概率
if(max(size(ub)) == 1)
ub = ub.*ones(dim,1);
lb = lb.*ones(dim,1);
end
maxgen=Max_iter; % 进化次数
%种群
bound=[lb,ub]; %变量范围
%% 产生初始粒子和速度
for i=1:popsize
%随机产生一个种群
GApop(i,:)=Code(lenchrom,bound); %随机产生个体
%计算适应度
[fitness(i)]=fun(GApop(i,:)); %染色体的适应度
end
%找最好的染色体
[bestfitness bestindex]=min(fitness);
zbest=GApop(bestindex,:); %全局最佳
gbest=GApop; %个体最佳
fitnessgbest=fitness; %个体最佳适应度值
fitnesszbest=bestfitness; %全局最佳适应度值
%% 迭代寻优
for i=1:maxgen
% disp(['第',num2str(i),'次迭代'])
%种群更新 GA选择更新
GApop=Select2(GApop,fitness,popsize);
% 交叉操作 GA
GApop=Cross(pc,lenchrom,GApop,popsize,bound);
% 变异操作 GA变异
GApop=Mutation(pm,lenchrom,GApop,popsize,[i maxgen],bound);
pop=GApop;
for j=1:popsize
%适应度值
[fitness(j)]=fun(pop(j,:));
%个体最优更新
if fitness(j) < fitnessgbest(j)
gbest(j,:) = pop(j,:);
fitnessgbest(j) = fitness(j);
end
%群体最优更新
if fitness(j) < fitnesszbest
zbest = pop(j,:);
fitnesszbest = fitness(j);
end
end
curve(i)=fitnesszbest;
end
Best_score = fitnesszbest;
Best_pos = zbest;
end
函数7
function [lb,ub,dim,fobj] = Get_Functions_details(F)
switch F
case 'F1'
fobj = @F1;
lb=-100;
ub=100;
dim=10;
case 'F2'
fobj = @F2;
lb=-10;
ub=10;
dim=10;
case 'F3'
fobj = @F3;
lb=-100;
ub=100;
dim=10;
case 'F4'
fobj = @F4;
lb=-100;
ub=100;
dim=10;
case 'F5'
fobj = @F5;
lb=-30;
ub=30;
dim=10;
case 'F6'
fobj = @F6;
lb=-100;
ub=100;
dim=10;
case 'F7'
fobj = @F7;
lb=-1.28;
ub=1.28;
dim=10;
case 'F8'
fobj = @F8;
lb=-500;
ub=500;
dim=10;
case 'F9'
fobj = @F9;
lb=-5.12;
ub=5.12;
dim=10;
case 'F10'
fobj = @F10;
lb=-32;
ub=32;
dim=10;
case 'F11'
fobj = @F11;
lb=-600;
ub=600;
dim=10;
case 'F12'
fobj = @F12;
lb=-50;
ub=50;
dim=10;
case 'F13'
fobj = @F13;
lb=-50;
ub=50;
dim=10;
case 'F14'
fobj = @F14;
lb=-65.536;
ub=65.536;
dim=2;
case 'F15'
fobj = @F15;
lb=-5;
ub=5;
dim=4;
case 'F16'
fobj = @F16;
lb=-5;
ub=5;
dim=2;
case 'F17'
fobj = @F17;
lb=[-5,0];
ub=[10,15];
dim=2;
case 'F18'
fobj = @F18;
lb=-2;
ub=2;
dim=2;
case 'F19'
fobj = @F19;
lb=0;
ub=1;
dim=3;
case 'F20'
fobj = @F20;
lb=0;
ub=1;
dim=6;
case 'F21'
fobj = @F21;
lb=0;
ub=10;
dim=4;
case 'F22'
fobj = @F22;
lb=0;
ub=10;
dim=4;
case 'F23'
fobj = @F23;
lb=0;
ub=10;
dim=4;
end
end
% F1
function o = F1(x)
o=sum(x.^2);
end
% F2
function o = F2(x)
o=sum(abs(x))+prod(abs(x));
end
% F3
function o = F3(x)
dim=size(x,2);
o=0;
for i=1:dim
o=o+sum(x(1:i))^2;
end
end
% F4
function o = F4(x)
o=max(abs(x));
end
% F5
function o = F5(x)
dim=size(x,2);
o=sum(100*(x(2:dim)-(x(1:dim-1).^2)).^2+(x(1:dim-1)-1).^2);
end
% F6
function o = F6(x)
o=sum(abs((x+.5)).^2);
end
% F7
function o = F7(x)
dim=size(x,2);
o=sum([1:dim].*(x.^4))+rand;
end
% F8
function o = F8(x)
o=sum(-x.*sin(sqrt(abs(x))));
end
% F9
function o = F9(x)
dim=size(x,2);
o=sum(x.^2-10*cos(2*pi.*x))+10*dim;
end
% F10
function o = F10(x)
dim=size(x,2);
o=-20*exp(-.2*sqrt(sum(x.^2)/dim))-exp(sum(cos(2*pi.*x))/dim)+20+exp(1);
end
% F11
function o = F11(x)
dim=size(x,2);
o=sum(x.^2)/4000-prod(cos(x./sqrt([1:dim])))+1;
end
% F12
function o = F12(x)
dim=size(x,2);
o=(pi/dim)*(10*((sin(pi*(1+(x(1)+1)/4)))^2)+sum((((x(1:dim-1)+1)./4).^2).*...
(1+10.*((sin(pi.*(1+(x(2:dim)+1)./4)))).^2))+((x(dim)+1)/4)^2)+sum(Ufun(x,10,100,4));
end
% F13
function o = F13(x)
dim=size(x,2);
o=.1*((sin(3*pi*x(1)))^2+sum((x(1:dim-1)-1).^2.*(1+(sin(3.*pi.*x(2:dim))).^2))+...
((x(dim)-1)^2)*(1+(sin(2*pi*x(dim)))^2))+sum(Ufun(x,5,100,4));
end
% F14
function o = F14(x)
aS=[-32 -16 0 16 32 -32 -16 0 16 32 -32 -16 0 16 32 -32 -16 0 16 32 -32 -16 0 16 32;,...
-32 -32 -32 -32 -32 -16 -16 -16 -16 -16 0 0 0 0 0 16 16 16 16 16 32 32 32 32 32];
for j=1:25
bS(j)=sum((x'-aS(:,j)).^6);
end
o=(1/500+sum(1./([1:25]+bS))).^(-1);
end
% F15
function o = F15(x)
aK=[.1957 .1947 .1735 .16 .0844 .0627 .0456 .0342 .0323 .0235 .0246];
bK=[.25 .5 1 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16];bK=1./bK;
o=sum((aK-((x(1).*(bK.^2+x(2).*bK))./(bK.^2+x(3).*bK+x(4)))).^2);
end
% F16
function o = F16(x)
o=4*(x(1)^2)-2.1*(x(1)^4)+(x(1)^6)/3+x(1)*x(2)-4*(x(2)^2)+4*(x(2)^4);
end
% F17
function o = F17(x)
o=(x(2)-(x(1)^2)*5.1/(4*(pi^2))+5/pi*x(1)-6)^2+10*(1-1/(8*pi))*cos(x(1))+10;
end
% F18
function o = F18(x)
o=(1+(x(1)+x(2)+1)^2*(19-14*x(1)+3*(x(1)^2)-14*x(2)+6*x(1)*x(2)+3*x(2)^2))*...
(30+(2*x(1)-3*x(2))^2*(18-32*x(1)+12*(x(1)^2)+48*x(2)-36*x(1)*x(2)+27*(x(2)^2)));
end
% F19
function o = F19(x)
aH=[3 10 30;.1 10 35;3 10 30;.1 10 35];cH=[1 1.2 3 3.2];
pH=[.3689 .117 .2673;.4699 .4387 .747;.1091 .8732 .5547;.03815 .5743 .8828];
o=0;
for i=1:4
o=o-cH(i)*exp(-(sum(aH(i,:).*((x-pH(i,:)).^2))));
end
end
% F20
function o = F20(x)
aH=[10 3 17 3.5 1.7 8;.05 10 17 .1 8 14;3 3.5 1.7 10 17 8;17 8 .05 10 .1 14];
cH=[1 1.2 3 3.2];
pH=[.1312 .1696 .5569 .0124 .8283 .5886;.2329 .4135 .8307 .3736 .1004 .9991;...
.2348 .1415 .3522 .2883 .3047 .6650;.4047 .8828 .8732 .5743 .1091 .0381];
o=0;
for i=1:4
o=o-cH(i)*exp(-(sum(aH(i,:).*((x-pH(i,:)).^2))));
end
end
% F21
function o = F21(x)
aSH=[4 4 4 4;1 1 1 1;8 8 8 8;6 6 6 6;3 7 3 7;2 9 2 9;5 5 3 3;8 1 8 1;6 2 6 2;7 3.6 7 3.6];
cSH=[.1 .2 .2 .4 .4 .6 .3 .7 .5 .5];
o=0;
for i=1:5
o=o-((x-aSH(i,:))*(x-aSH(i,:))'+cSH(i))^(-1);
end
end
% F22
function o = F22(x)
aSH=[4 4 4 4;1 1 1 1;8 8 8 8;6 6 6 6;3 7 3 7;2 9 2 9;5 5 3 3;8 1 8 1;6 2 6 2;7 3.6 7 3.6];
cSH=[.1 .2 .2 .4 .4 .6 .3 .7 .5 .5];
o=0;
for i=1:7
o=o-((x-aSH(i,:))*(x-aSH(i,:))'+cSH(i))^(-1);
end
end
% F23
function o = F23(x)
aSH=[4 4 4 4;1 1 1 1;8 8 8 8;6 6 6 6;3 7 3 7;2 9 2 9;5 5 3 3;8 1 8 1;6 2 6 2;7 3.6 7 3.6];
cSH=[.1 .2 .2 .4 .4 .6 .3 .7 .5 .5];
o=0;
for i=1:10
o=o-((x-aSH(i,:))*(x-aSH(i,:))'+cSH(i))^(-1);
end
end
function o=Ufun(x,a,k,m)
o=k.*((x-a).^m).*(x>a)+k.*((-x-a).^m).*(x<(-a));
end
函数8
function Potential=LJPotential(Atom1,Atom2,Iteration,Max_Iteration,s)
%Calculate LJ-potential
r=norm(Atom1-Atom2);
c=(1-(Iteration-1)/Max_Iteration).^3;
%g0=1.1;
%u=1.24;
rsmin=1.1+0.1*sin(Iteration/Max_Iteration*pi/2);
rsmax=1.24;
if r/s<rsmin
rs=rsmin;
else
if r/s>rsmax
rs=rsmax;
else
rs=r/s;
end
end
Potential=c*(12*(-rs)^(-13)-6*(-rs)^(-7));
函数9
function ret=Mutation(pmutation,lenchrom,chrom,sizepop,pop,bound)
% 本函数完成变异操作
% pcorss input : 变异概率
% lenchrom input : 染色体长度
% chrom input : 染色体群
% sizepop input : 种群规模
% pop input : 当前种群的进化代数和最大的进化代数信息
% ret output : 变异后的染色体
for i=1:sizepop
% 随机选择一个染色体进行变异
pick=rand;
while pick==0
pick=rand;
end
index=ceil(pick*sizepop);
% 变异概率决定该轮循环是否进行变异
pick=rand;
if pick>pmutation
continue;
end
flag=0;
while flag==0
% 变异位置
pick=rand;
while pick==0
pick=rand;
end
pos=ceil(pick*sum(lenchrom)); %随机选择了染色体变异的位置,即选择了第pos个变量进行变异
if pos<=0
pos = 1;
end
if pos>size(bound,1)
pos = size(bound,1);
end
v=chrom(i,pos);
v1=v-bound(pos,1);
v2=bound(pos,2)-v;
pick=rand; %变异开始
if pick>0.5
delta=v2*(1-pick^((1-pop(1)/pop(2))^2));
chrom(i,pos)=v+delta;
else
delta=v1*(1-pick^((1-pop(1)/pop(2))^2));
chrom(i,pos)=v-delta;
end %变异结束
flag=test(lenchrom,bound,chrom(i,:)); %检验染色体的可行性
end
end
ret=chrom;
end
函数-粒子群优化算法
%% 基础粒子群优化算法
function [gBestScore,gBest,cg_curve]=PSO(N,Max_iteration,lb,ub,dim,fobj)
%PSO Infotmation
if(max(size(ub)) == 1)
ub = ub.*ones(1,dim);
lb = lb.*ones(1,dim);
end
Vmax=6;
noP=N;
wMax=0.9;
wMin=0.6;
c1=2;
c2=2;
% Initializations
iter=Max_iteration;
vel=zeros(noP,dim);
pBestScore=zeros(noP);
pBest=zeros(noP,dim);
gBest=zeros(1,dim);
cg_curve=zeros(1,iter);
vel=zeros(N,dim);
pos=zeros(N,dim);
%Initialization
for i=1:size(pos,1)
for j=1:size(pos,2)
pos(i,j)=(ub(j)-lb(j))*rand()+lb(j);
vel(i,j)=0.3*rand();
end
end
for i=1:noP
pBestScore(i)=inf;
end
% Initialize gBestScore for a minimization problem
gBestScore=inf;
for l=1:iter
% Return back the particles that go beyond the boundaries of the search
% space
Flag4ub=pos(i,:)>ub;
Flag4lb=pos(i,:)<lb;
pos(i,:)=(pos(i,:).*(~(Flag4ub+Flag4lb)))+ub.*Flag4ub+lb.*Flag4lb;
for i=1:size(pos,1)
%Calculate objective function for each particle
fitness=fobj(pos(i,:));
if(pBestScore(i)>fitness)
pBestScore(i)=fitness;
pBest(i,:)=pos(i,:);
end
if(gBestScore>fitness)
gBestScore=fitness;
gBest=pos(i,:);
end
end
%Update the W of PSO
w=wMax-l*((wMax-wMin)/iter);
%Update the Velocity and Position of particles
for i=1:size(pos,1)
for j=1:size(pos,2)
vel(i,j)=w*vel(i,j)+c1*rand()*(pBest(i,j)-pos(i,j))+c2*rand()*(gBest(j)-pos(i,j));
if(vel(i,j)>Vmax)
vel(i,j)=Vmax;
end
if(vel(i,j)<-Vmax)
vel(i,j)=-Vmax;
end
pos(i,j)=pos(i,j)+vel(i,j);
end
end
cg_curve(l)=gBestScore;
end
end
函数10
%% 模拟退火算法
function [Best_score,Best_pos,curve]=SA(Mmax,l,u,dim,fobj)
%function [x0,f0]=sim_anl(f,x0,l,u,Mmax,TolFun)
% 输入:
% fobj = 适应度函数
% x0 = 输入种群
% l = 种群下边界
% u = 种群上边界
% Mmax = 最大温度
% TolFun = 优化变化容忍度
%
%
% 输出:
% x0 = 输出优化后的种群
% f0 = 输出优化后的种群的适应度值
TolFun = 10E-10;%模拟退火容忍度
x0 = (u-l)*rand(1,dim)+l;%随机初始化模拟退火;
f = fobj;%适应度函数
x=x0;
fx=feval(f,x);%计算适应度值
f0=fx;
count = 1;%用于记录收敛曲线标记
%模拟退火主要步骤
for m=1:Mmax
T=m/Mmax; %温度
mu=10^(T*1000);
%For each temperature we take 100 test points to simulate reach termal
for k=0:100
dx=mu_inv(2*rand(1,dim)-1,mu).*(u-l);
x1=x+dx;
%边界处理防止越界
x1=(x1 < l).*l+(l <= x1).*(x1 <= u).*x1+(u < x1).*u;
%计算当前位置适应度值和适应度值偏差
fx1=feval(f,x1);df=fx1-fx;
% 如果df<0则接受该解,如果大于0 则利用Metropolis准则进行判断是否接受
if (df < 0 || rand < exp(-T*df/(abs(fx)+eps)/TolFun))==1
x=x1;fx=fx1;
end
%判断当前解是否更优,更优则更新.
if fx1 < f0 ==1
x0=x1;f0=fx1;
end
end
curve(count) = f0;
count = count+1;
end
Best_pos = x0;
Best_score = f0;
end
function x=mu_inv(y,mu)
%模拟退火产生新位置偏差
x=(((1+mu).^abs(y)-1)/mu).*sign(y);
end
函数11
function ret=Select(individuals,fitness,sizepop)
% 本函数对每一代种群中的染色体进行选择,以进行后面的交叉和变异
% individuals input : 种群信息
% fitness input : 适应度
% sizepop input : 种群规模
% opts input : 选择方法的选择
% ret output : 经过选择后的种群
fitness= 1./(fitness);
sumfitness=sum(fitness);
sumf=fitness./sumfitness;
index=[];
for i=1:sizepop %转sizepop次轮盘
pick=rand;
while pick==0
pick=rand;
end
for j=1:sizepop
pick=pick-sumf(j);
if pick<0
index=[index j];
break; %寻找落入的区间,此次转轮盘选中了染色体i,注意:在转sizepop次轮盘的过程中,有可能会重复选择某些染色体
end
end
end
individualsTemp=individuals(index,:);
fitnessTemp=fitness(index);
if(size(individualsTemp,1) == 0)
ret=individuals;
else
ret=individualsTemp;
end
end
函数12
function flag=test(lenchrom,bound,code)
% lenchrom input : 染色体长度
% bound input : 变量的取值范围
% code output: 染色体的编码值
flag=1;
[n,m]=size(code);
for i=1:n
if code(i)<bound(i,1) || code(i)>bound(i,2)
flag=0;
end
end
end