重学数据结构与算法
学习数据结构与算法的目的:
优化时间复杂度与空间复杂度 优化时间复杂度与空间复杂度 优化时间复杂度与空间复杂度
教程总纲: 暴力解法(模拟)、算法优化(递归/二分/排序/DP)、时刻转换(数据结构)

-
- 1.时间复杂度的核心方法论
- 2.增删查——选取数据结构的基本方法
- 3.线性表——如何完成基本增删查
- 4.栈——先进后出的增删查
- 5.队列——先进先出的增删查
- 6.数组——基于索引的查找
- 7.字符串——字符串匹配与操作
- 8.树&二叉树——分支与层次关系
- 9.哈希表——高效查找的利器
- 10.递归——解决汉诺塔问题
- 11.分治——利用分治快速完成数据查找
- 12.排序——经典排序算法解析
1.时间复杂度的核心方法论
空间是廉价的,时间是昂贵的
相较于空间复杂度(投入金钱 增加算力),时间复杂度(消耗时间)更为重要!
降低时间与空间复杂度的方法:
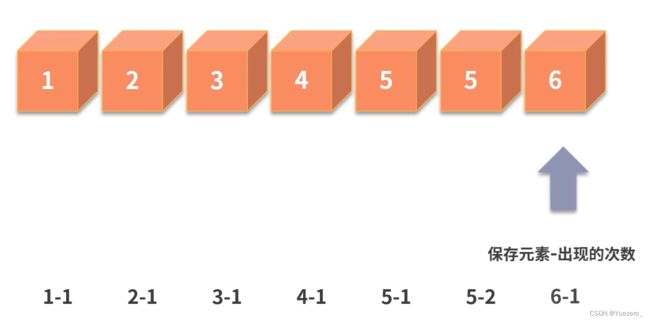
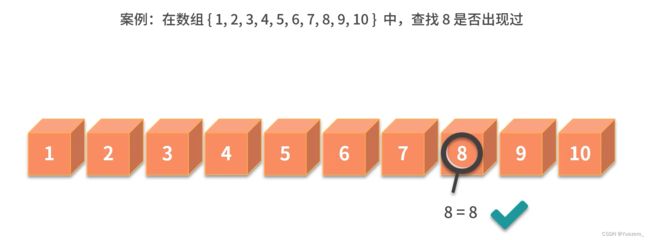
例.输入数组 a = [1,2,3,4,5,5,6] 中查找出现次数最多的数值。
暴力解法是:两层for遍历,维护一个最大次数time_max,对每个元素计算出现次数time_tmp,与time_max进行对比,时间复杂度是 0 ( n 2 ) 0(n^2) 0(n2)
int main(){
vector<int> a={1,2,3,4,5,5,6};
int val_max=-1,time_max=0,time_tmp=0;
for(int i=0;i<a.size();i++){
time_tmp=0;
for(int j=0;j<a.size();j++)
if(a[i]==a[j]) time_tmp++;
if(time_tmp>time_max){
time_max=time_tmp;
val_max=a[i];
}
}
cout<<val_max<<" "<<time_max<<endl;
return 0;
}
优化思想:如何仅用单层for循环完成,用hash思想,引入k-v字典数据结构map,一次for保存每个元素出现的次数,再求每个元素次数的最大值,时间复杂度是 0 ( 2 n ) 0(2n) 0(2n)。
int main(){
vector<int> a={1,2,3,4,5,5,6};
map<int ,int> num_cnt;
int val_max,time_max=0;
for(int i=0;i<a.size();i++){
num_cnt[a[i]]++; //counting the number of times a[i occurs in the vector a.
}
for(auto it:num_cnt){ //iterating over the map and printing the max time a[i] occurs for each element.
if(time_max < it.second){
val_max=it.first; //assigning the maximum value from the map to val_max.
time_max=it.second; //assigning the maximum count from the map to time_max.
}
}
cout<<val_max<<" "<<time_max<<endl;
return 0;
}
2.增删查——选取数据结构的基本方法
当你不知道用什么数据结构的时候:
分析需要对数据进行了哪些操作,根据数据操作,选取合适的数据结构 分析需要对数据进行了哪些操作,根据数据操作,选取合适的数据结构 分析需要对数据进行了哪些操作,根据数据操作,选取合适的数据结构

还用上面的例子介绍:
对于统计次数最多的元素,我们需要对数据结构进行以下操作:

具体的:

所以


3.线性表——如何完成基本增删查
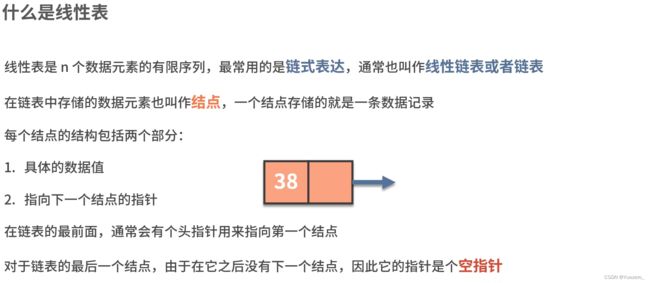
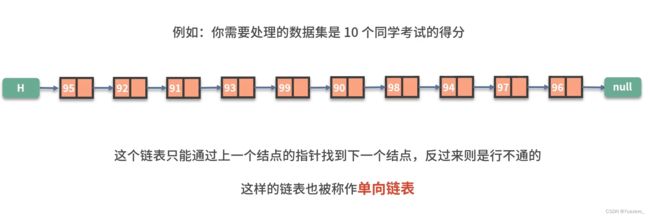
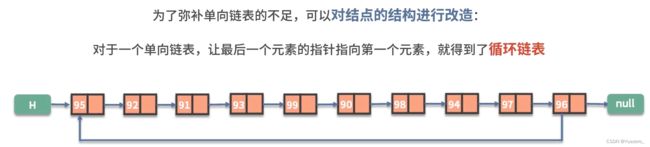
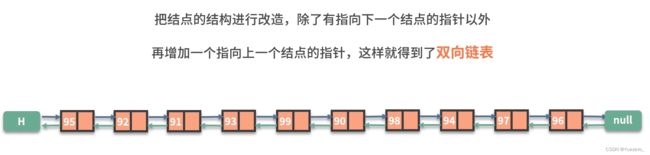
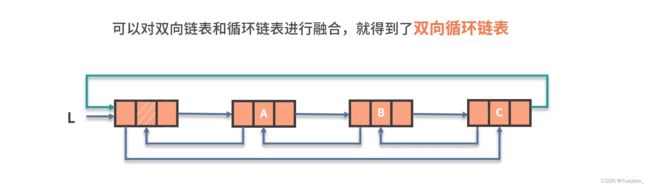
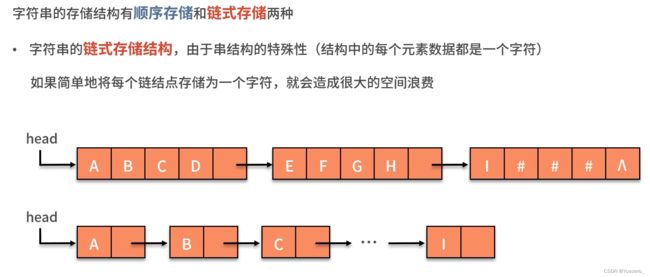
实际上,有线性存储(数组)和链式存储(链表)两种结构,这里仅介绍链式存储。
线性表增删查:其他链表的操作与单向链表雷同,仅介绍单向链表
增加操作: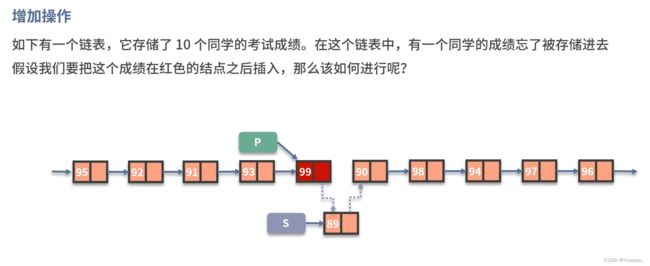
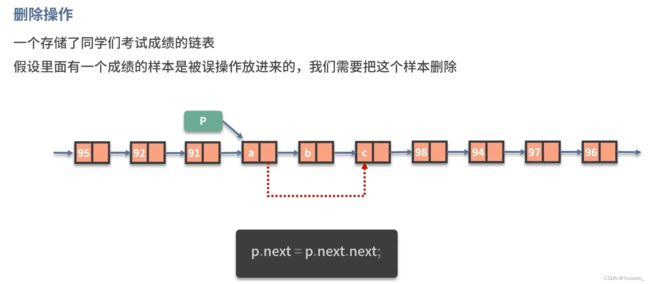
删除操作:
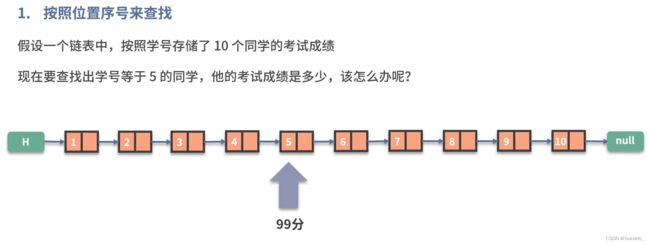
查找操作:
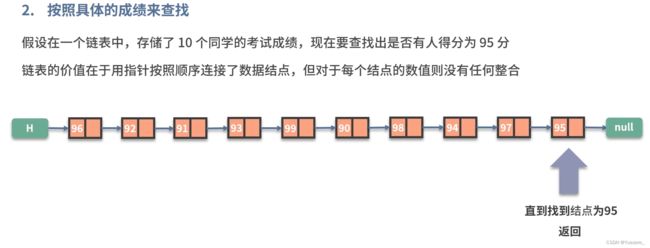
总结:
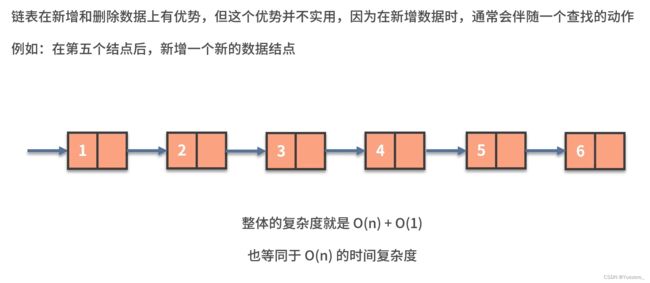
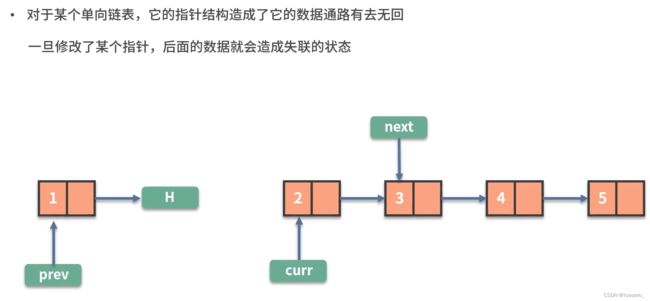
链表的查找速度慢 ( 无法用 i n d e x ) O ( n ) ,但插入和删除 ( 改变指针 ) 方便 O ( 1 ) 链表的查找速度慢(无法用index)O(n),但插入和删除(改变指针)方便O(1) 链表的查找速度慢(无法用index)O(n),但插入和删除(改变指针)方便O(1)
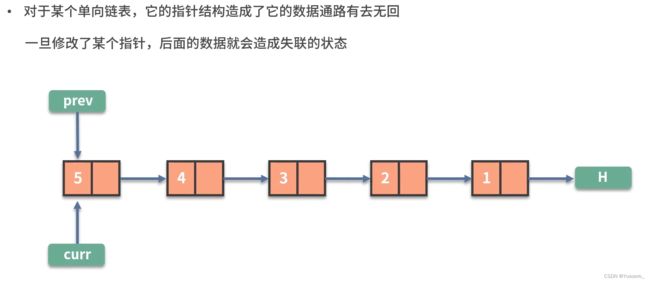
链表的问题常常围绕数据顺序的处理:链表反转,快慢指针
例1.

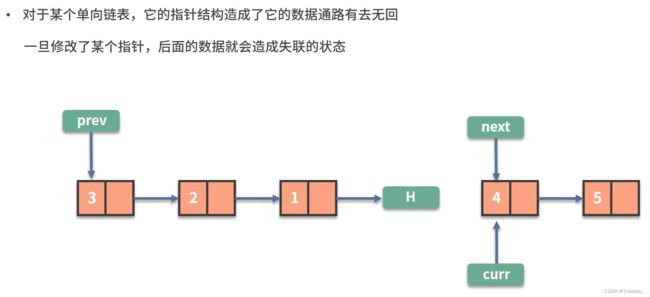
为此,我们使用3个指针prev、curr、next,分别指向 新链表头节点、旧链表转换节点、旧链表转换节点的下一个,完成旧链表向链表逐个节点的转换。
#include例2.
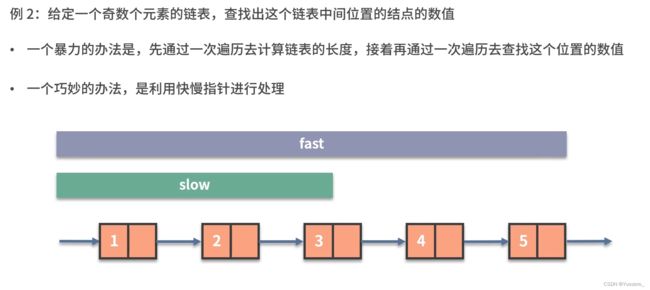

slow走1步,fast走两步。(因为fast一次走两步,所以要防止fast到fast.next.next为空,所以while的判断条件是3个)
fast到达终点时,slow到达中点。
#include例3.
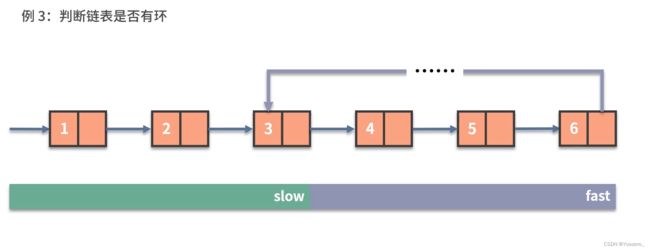
基本思想是利用两个指针,一个快指针和一个慢指针,分别从链表头部开始遍历,快指针每次走两步,慢指针每次走一步,若快指针追上了慢指针,则说明链表存在环路;否则,当快指针到达链表尾部时,结束遍历,slow永远不可能和fast相等,链表不存在环路。
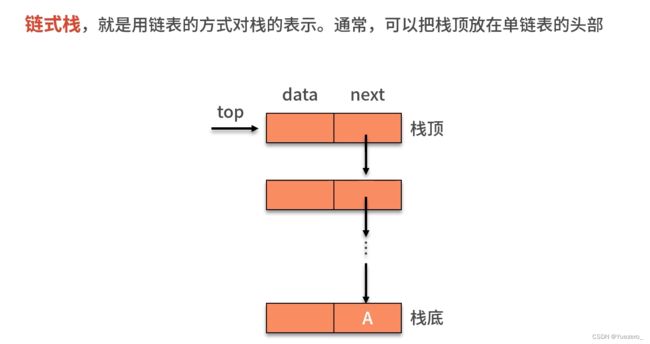
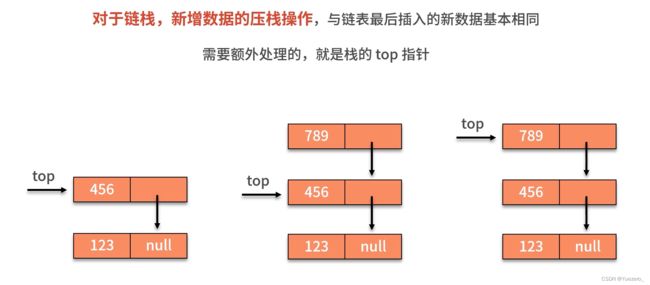
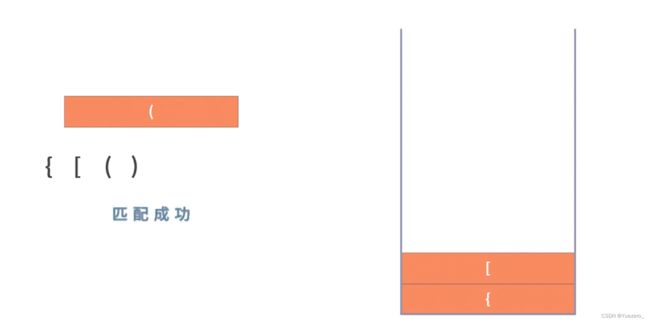
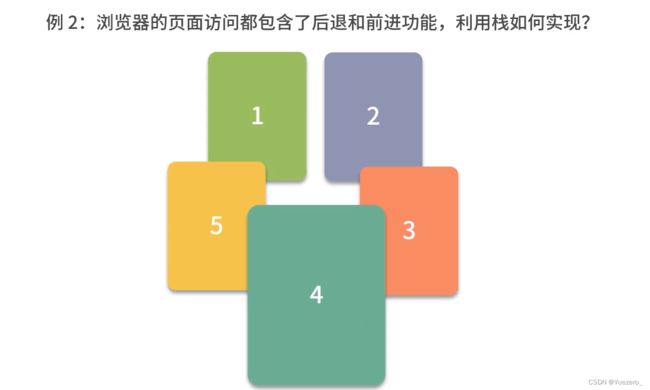
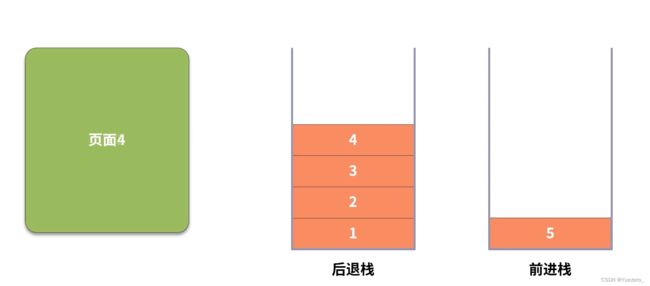
#include4.栈——先进后出的增删查

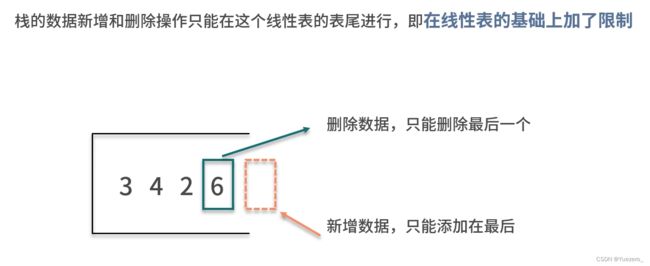

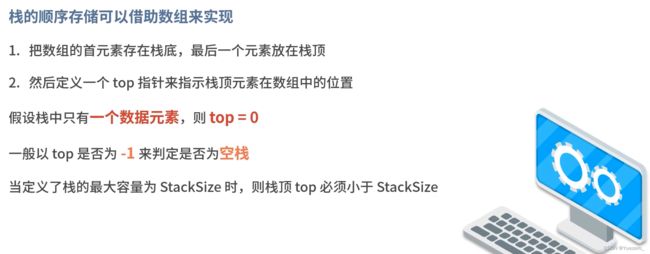
顺序栈:
推荐:用vector模拟栈时,仅允许在线性表尾部(栈顶)插入删除数据,push_back()和pop_back()。
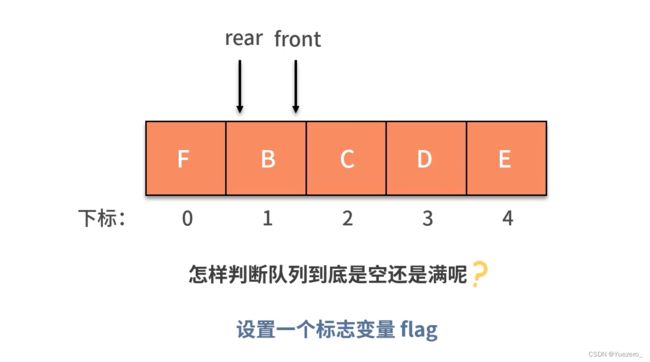
#include#include5.队列——先进先出的增删查
头指针front,尾指针rear
链队: 头节点仅用来表示队列(data=number),不用了存储数据

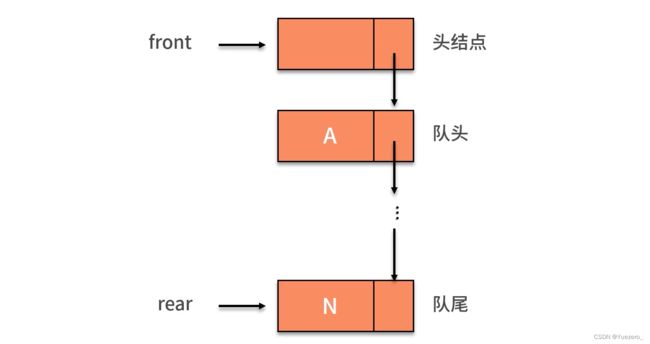
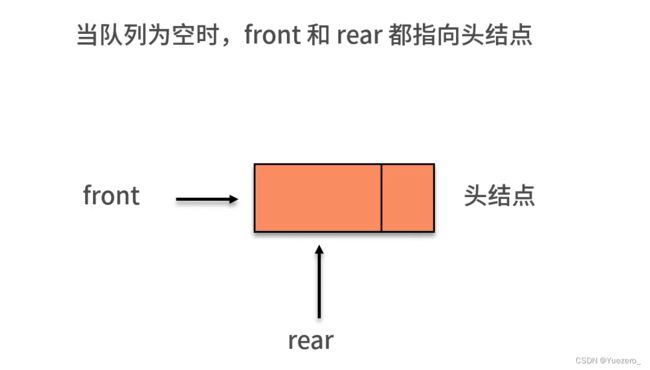


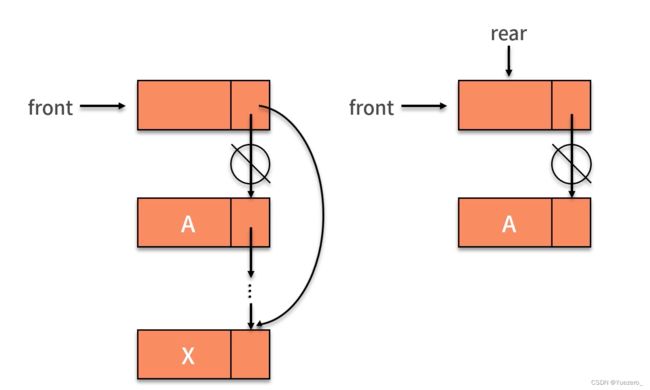
头节点的意义:给空链表的front 和rear指针一个指向,防止变成野指针。
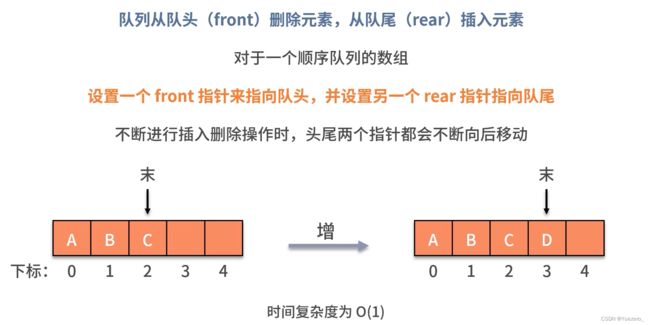
顺序队列: 数组模拟,队尾插入时间复杂度为O(1),队头删除,后面的所有元素前移,时间复杂度为O(n),如果仅通过移动fornt指针的方式,会造成假溢出,空间不足的情况。
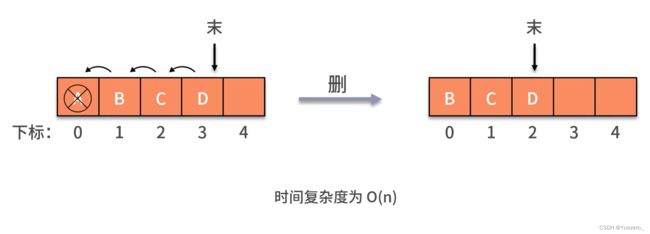
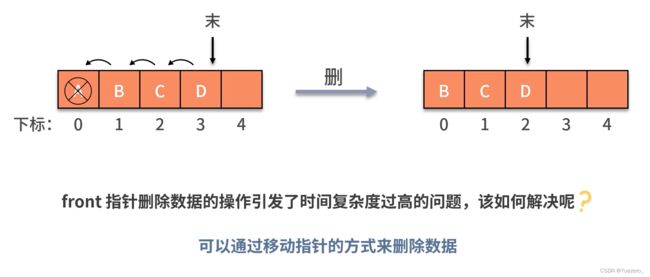
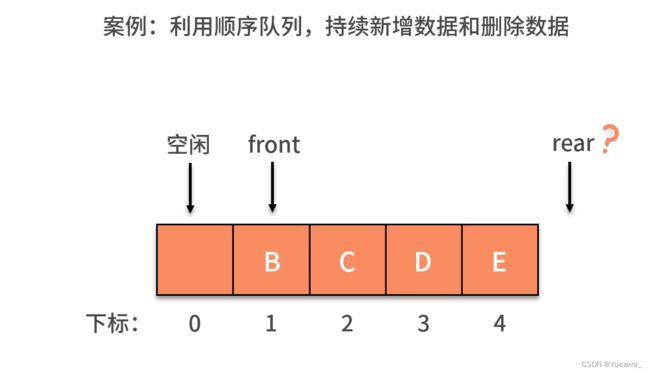

实际上,上述两种解决方法都不好,假溢出最优的解决办法是构造循环队列
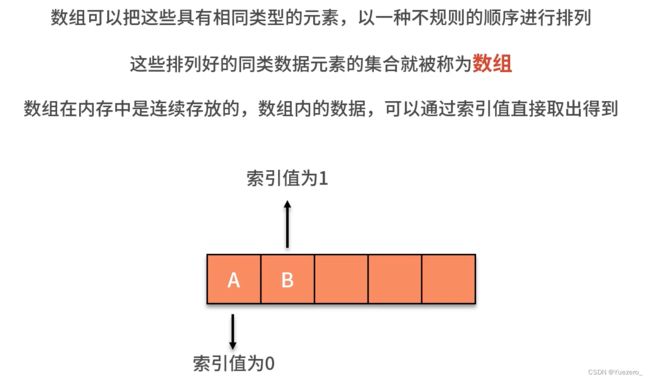
6.数组——基于索引的查找
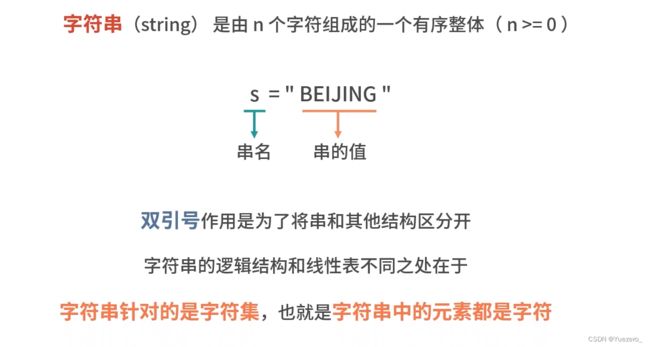
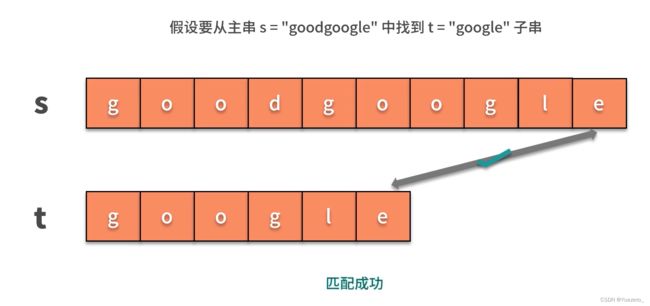
7.字符串——字符串匹配与操作
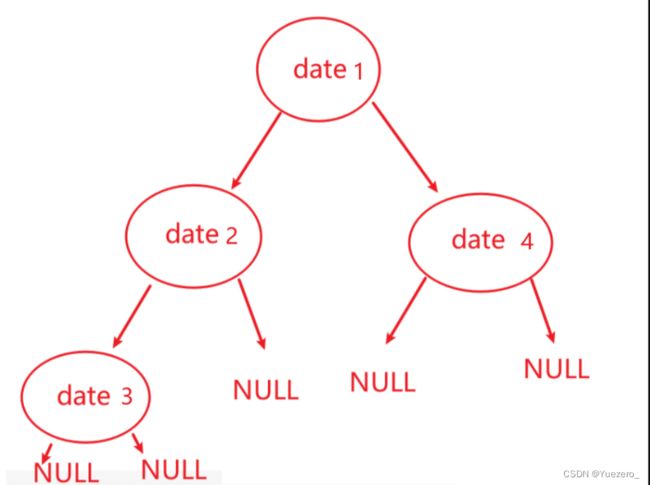
#include#include8.树&二叉树——分支与层次关系
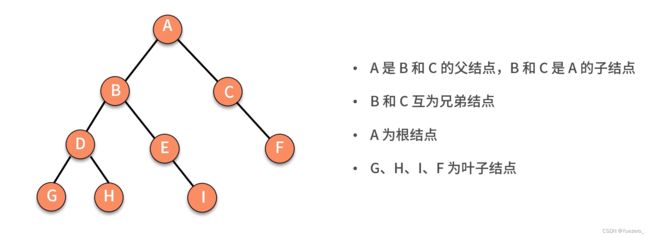

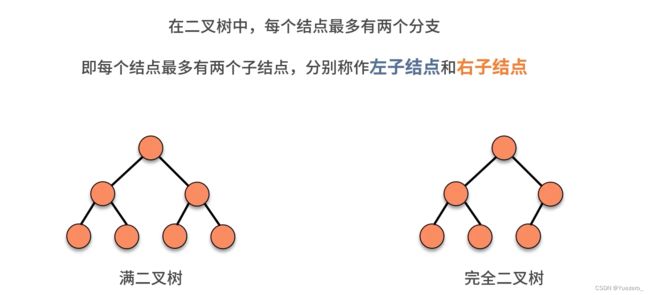
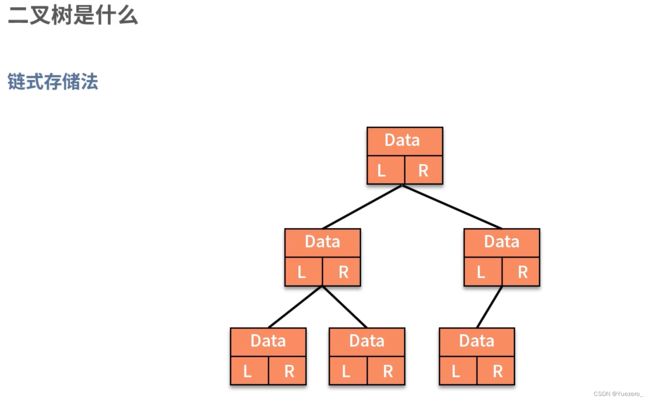
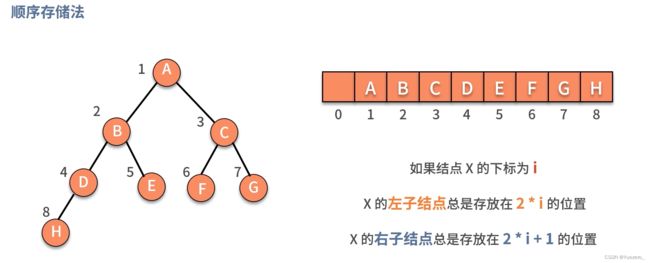
非完全二叉树,使用顺序存储会浪费大量的存储空间!
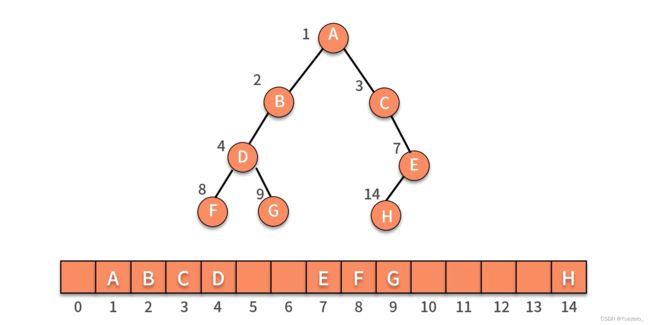


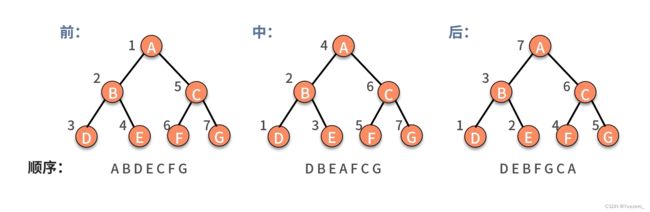
递归实现二叉树的前、中、后序遍历
class node{ public: string val; node* left; node* right;};
void PreOrder(node* NODE){
if(NODE==NULL)return;
cout<<NODE->val<<" ";
PreOrder(NODE->left);
PreOrder(NODE->right);
}
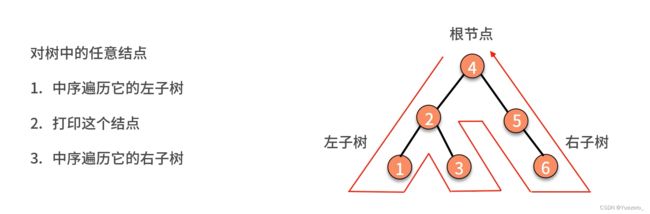
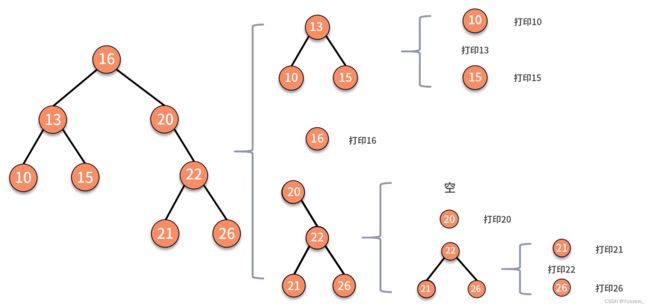
void InOrder(node* NODE){
if(NODE==NULL)return;
InOrder(NODE->left);
cout<<NODE->val<<" ";
InOrder(NODE->right);
}
void PostOrder(node* NODE){
if(NODE==NULL)return;
PostOrder(NODE->left);
PostOrder(NODE->right);
cout<<NODE->val<<" ";
}
二叉查找树(二次排序树): 左小右大,左子树上所有结点的关键字均小于根结点的关键字;右子树上的所有结点的关键字均大于根结点的关键字。中序遍历是有序数列!

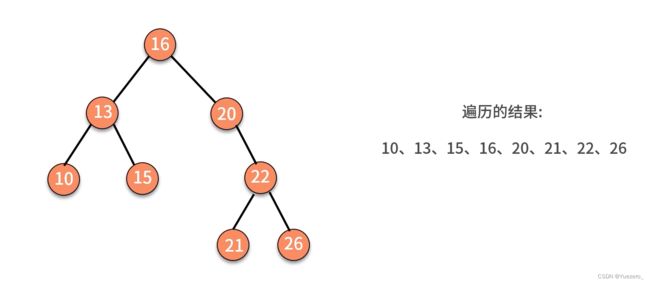
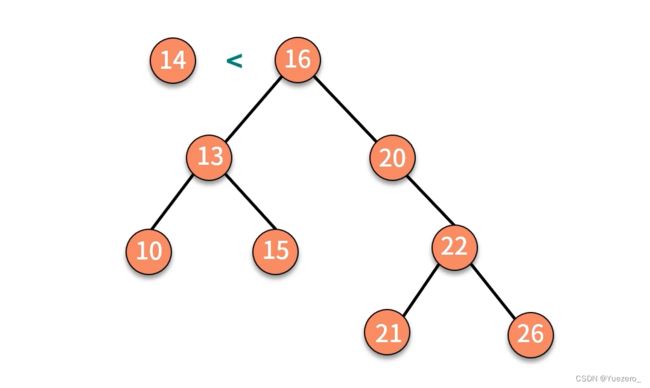
利用二次排序树的性质,可以实现二分查找,加快查找速度!!!

二叉排序树的插入:

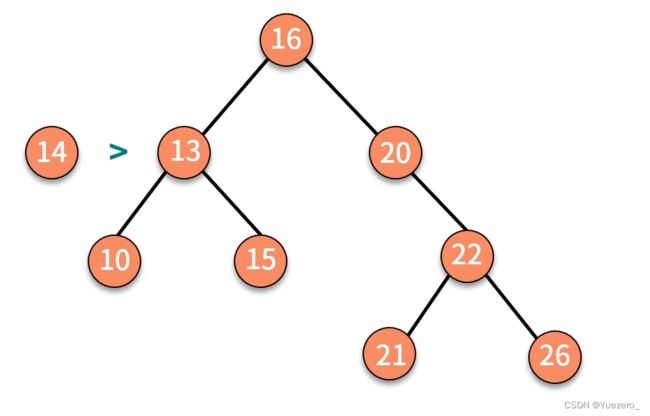
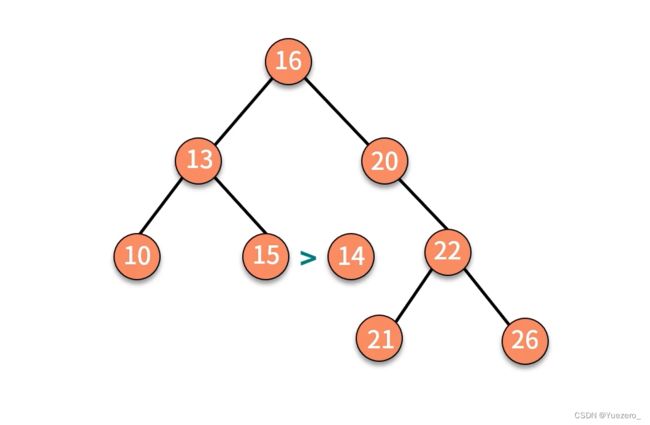
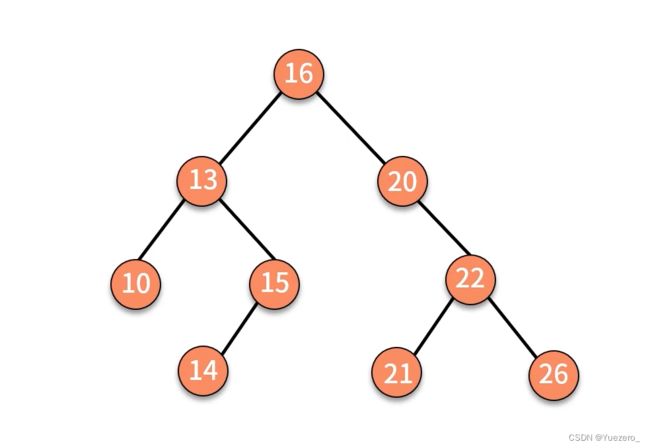

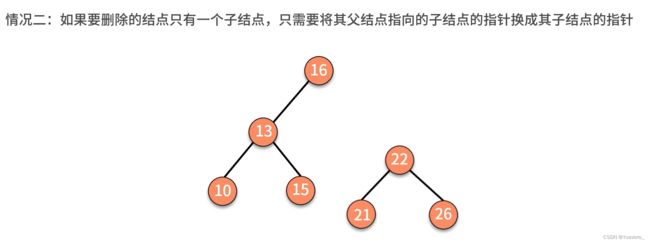
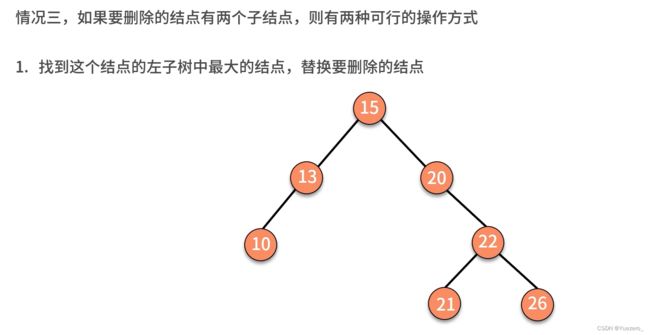
二叉排序树删除:
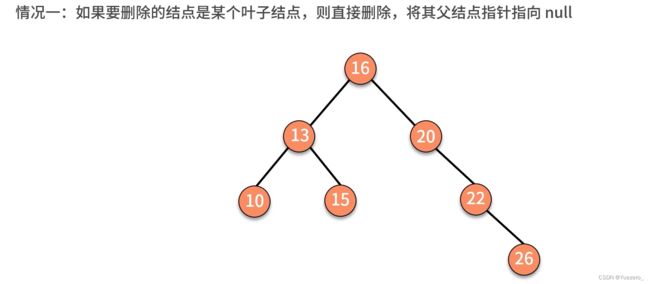

例题.

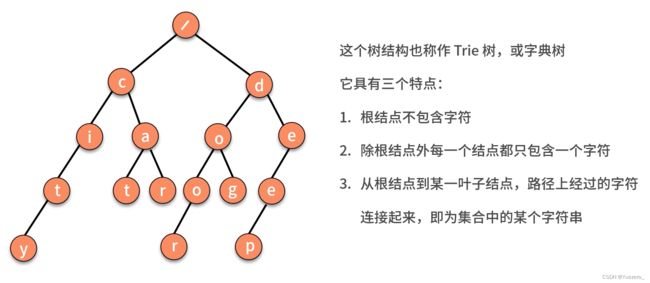
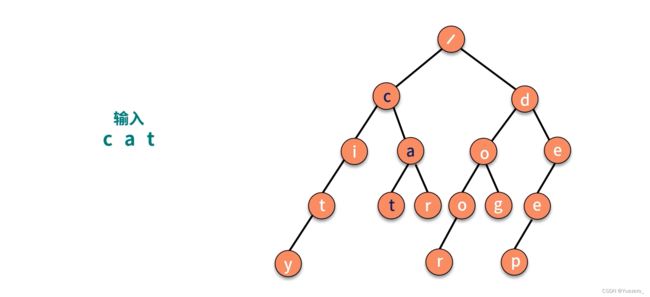
可以暴力搜索,也可以用字典树,层次遍历到叶子节点的路径。


例题.层次遍历,维护OPEN表(队列),不断扩展队首子节点,加入队列。
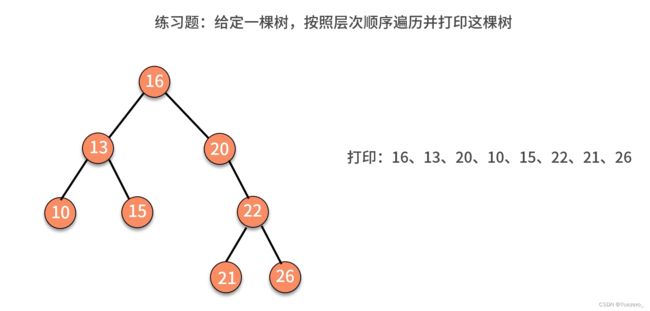
#include9.哈希表——高效查找的利器
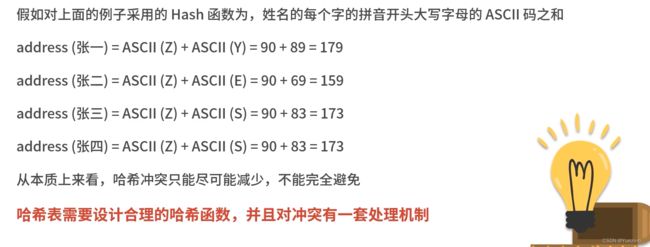
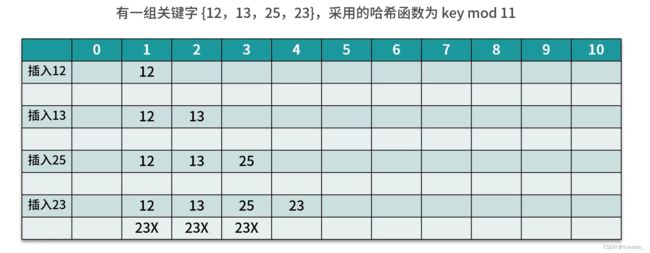
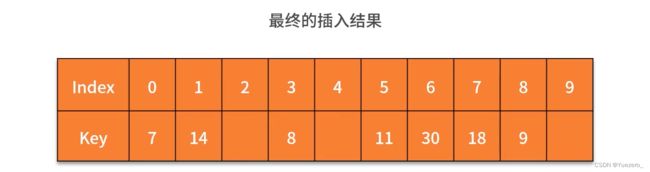
哈希冲突: 不同对象的哈希地址相同(键值对的值相同)
链地址法(将相同哈希地址的记录存放在同一条链表上)

总结:优点(CUDR飞快)、缺点(处理输入顺序敏感的问题时,会破坏序列的构造顺序)

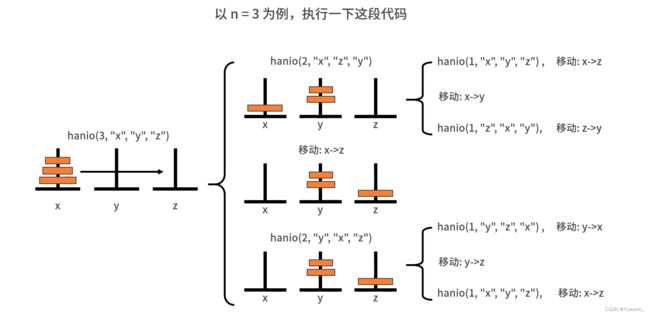
#include10.递归——解决汉诺塔问题
11.分治——利用分治快速完成数据查找
分治需要使用递归
每轮递归的包括:分解问题、解决问题、合并结果
#include12.排序——经典排序算法解析


冒泡排序: 相邻元素两两比较,逆序对交换,每轮将1个大的元素交换到最后,经过多轮迭代完成排序。稳定:元素相等时不做交换
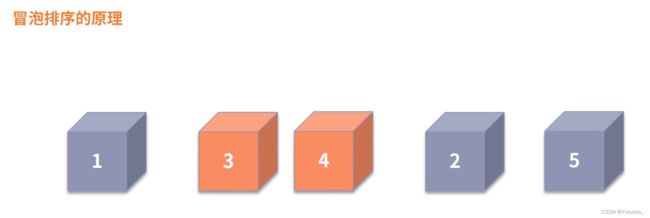

#include插入排序: 维护一个排好序的序列,不断为每个未插入的元素,与序列元素比较,找到合适的插入位置。稳定排序。
#include
归并排序: 将待排序序列从中点位置分成左右两个子序列,分别递归调用归并排序函数,直到子序列长度为1。对两个已经有序的子序列进行合并,得到一个新的有序序列。 稳定排序