五种混沌映射的种群初始化(可适用多数算法改进)附Matlab代码
沌映射被用于生成混沌序列,这是一种由简单的确定性系统产生的随机性序列。一般混沌序列具有以下主要特征:非线性;对初值的敏感依赖性;遍历性;随机性;奇异吸引子(混沌吸引子);分数维持性;整体稳定局部不稳定;长期不可预测性;轨道不稳定性及分叉;普适性和Feigenbaum常数。由于目前大多数智群能算法在初始化阶段都是随机生成,因此很多研究者将混沌映射应用于种群初始化,以增加算法的随机性和多样性。本文介绍了以下五种混沌映射,包括:Logistic映射、Circle映射、Sine映射、Singer映射和Cubic映射,并将以上映射方式应用于鲸鱼优化算法中,若需要应用在其他算法,只需替换初始化函数即可。
一、运行结果
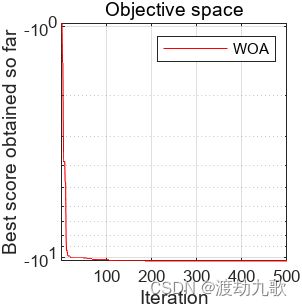
Logistic映射结果
The best solution obtained by WOA is : 3.999 4.0162 4.0002 3.985The best optimal value of the objective funciton found by WOA is : -10.3575
二、部分Matlab代码
clc
clear
close all
SearchAgents_no=30; % Number of search agents
%种群数量
Function_name='F22'; % Name of the test function that can be from F1 to F23 (Table 1,2,3 in the paper)
%使用方程的名字,对应Functions_details 文件
Max_iteration=500; % Maximum numbef of iterations
%最大迭代次数
% Load details of the selected benchmark function
[lb,ub,dim,fobj]=Get_Functions_details(Function_name);%得到具体的方程即目标函数,变量的维度
[Best_score,Best_pos,WOA_cg_curve]=WOA(SearchAgents_no,Max_iteration,lb,ub,dim,fobj);
%最小值,优化每个维度x的值,迭代曲线
figure('Position',[269 240 660 290])
%Draw search space
subplot(1,2,1);
func_plot(Function_name);
title('Parameter space')
xlabel('x_1');
ylabel('x_2');
zlabel([Function_name,'( x_1 , x_2 )'])
%Draw objective space
subplot(1,2,2);
semilogy(WOA_cg_curve,'Color','r')
title('Objective space')
xlabel('Iteration');
ylabel('Best score obtained so far');
axis tight
grid on
box on
legend('WOA')
display(['The best solution obtained by WOA is : ', num2str(Best_pos)]);
display(['The best optimal value of the objective funciton found by WOA is : ', num2str(Best_score)]);
function [Leader_score,Leader_pos,Convergence_curve]=WOA(SearchAgents_no,Max_iter,lb,ub,dim,fobj)
% initialize position vector and score for the leader
Leader_pos=zeros(1,dim);
Leader_score=inf; %change this to -inf for maximization problems
%Initialize the positions of search agents
Positions=initialization(SearchAgents_no,dim,ub,lb);
Convergence_curve=zeros(1,Max_iter);
t=0;% Loop counter
% Main loop
while tub;
Flag4lb=Positions(i,:) for maximization problem
Leader_score=fitness; % Update alpha
Leader_pos=Positions(i,:);
end
end
a=2-t*((2)/Max_iter); % a decreases linearly fron 2 to 0 in Eq. (2.3)
% a2 linearly dicreases from -1 to -2 to calculate t in Eq. (3.12)
a2=-1+t*((-1)/Max_iter);
% Update the Position of search agents
for i=1:size(Positions,1)
r1=rand(); % r1 is a random number in [0,1]
r2=rand(); % r2 is a random number in [0,1]
A=2*a*r1-a; % Eq. (2.3) in the paper
C=2*r2; % Eq. (2.4) in the paper
b=1; % parameters in Eq. (2.5)
l=(a2-1)*rand+1; % parameters in Eq. (2.5)
p = rand(); % p in Eq. (2.6)
for j=1:size(Positions,2)
if p<0.5
if abs(A)>=1
rand_leader_index = floor(SearchAgents_no*rand()+1);
X_rand = Positions(rand_leader_index, :);
D_X_rand=abs(C*X_rand(j)-Positions(i,j)); % Eq. (2.7)
Positions(i,j)=X_rand(j)-A*D_X_rand; % Eq. (2.8)
elseif abs(A)<1
D_Leader=abs(C*Leader_pos(j)-Positions(i,j)); % Eq. (2.1)
Positions(i,j)=Leader_pos(j)-A*D_Leader; % Eq. (2.2)
end
elseif p>=0.5
distance2Leader=abs(Leader_pos(j)-Positions(i,j));
% Eq. (2.5)
Positions(i,j)=distance2Leader*exp(b.*l).*cos(l.*2*pi)+Leader_pos(j);
end
end
end
t=t+1;
Convergence_curve(t)=Leader_score;
end
end
function Positions=initialization(SearchAgents_no,dim,ub,lb)
Boundary_no= size(ub,2); % numnber of boundaries
Positions=zeros(SearchAgents_no,dim);
%% Logistic映射
u=4; % a的范围是[0,4]
for i=1:SearchAgents_no