将COLMAP中生成的images.txt结果可视化
instant-ngp中执行scripts/colmap2nerf.py时,在colmap_text目录下会生成images.txt文件,此文件中每两行定义一幅图像的信息:
IMAGE_ID, QW, QX, QY, QZ, TX, TY, TZ, CAMERA_ID, NAME
POINTS2D[] as (X, Y, POINT3D_ID)第二行为关键点(特征点)的位置即执行"colmap bundle_adjuster"后的结果,以像素坐标指定:若3D点标识符(3D point identifier)为-1,则表明此关键点在重建中没有观察(observe)到3D点。
这里已lego为例,即对lego执行完colmap2nerf.py后,将images.txt中关键点信息在图像中画出来已观察准确性,测试代码如下:
import cv2
import sys
import os
from inspect import currentframe, getframeinfo
def parse_txt(txt_name):
coordinates = []
images_name = []
with open(os.path.join(txt_name), "r") as f:
i = 0
for line in f:
line = line.strip()
if line[0] == "#":
continue
i = i + 1
if i % 2 == 1: # get image name
elems = line.split(" ") # 1-4 is quat, 5-7 is trans, 9ff is filename (9, if filename contains no spaces)
images_name.append(str(f"{'_'.join(elems[9:])}"))
if i % 2 == 0: # get coordinates
elems = line.split(" ")
if len(elems) % 3 != 0:
print(f"Error: image name: {images_name[i//2 - 1]}, 2d point(X, Y, POINT3D_ID): {len(elems)}, LINE: {getframeinfo(currentframe()).lineno}")
sys.exit(1)
coordinates.append(elems)
if len(images_name) != len(coordinates):
print(f"Error: length unmatch: {len(images_name) != len(coordinates)}, LINE: {getframeinfo(currentframe()).lineno}")
sys.exit(1)
return images_name, coordinates
def draw_circle(images_name, corrdinates, images_path, result_path):
for index in range(len(images_name)):
img = cv2.imread(images_path+images_name[index])
if img is None:
print(f"Error: fail to imread: {images_path+images_name[index]}, LINE: {getframeinfo(currentframe()).lineno}")
sys.exit(1)
points = [] # (X,Y)
ids = []
for i in range(len(coordinates[index])):
if i % 3 == 2:
ids.append(int(str(corrdinates[index][i])))
else:
points.append(float(str(corrdinates[index][i])))
if len(points) != len(ids) * 2:
print(f"Error: length unmatch: {len(points)}:{len(ids)}, LINE: {getframeinfo(currentframe()).lineno}")
sys.exit(1)
count = 0
for i in range(len(ids)):
if ids[i] != -1:
count = count + 1
img = cv2.circle(img, (int(points[2*i]), int(points[2*i+1])), 2, (0,0,255), -1)
os.makedirs(result_path, exist_ok=True)
cv2.imwrite(result_path+images_name[index], img)
#cv2.imshow("image", img)
#cv2.waitKey(0)
print(f"image:{images_name[index]}, total points: {len(ids)}, valid points: {count}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
txt_name = "test_data/lego/colmap_text/images.txt"
images_name, coordinates = parse_txt(txt_name)
images_path = "test_data/lego/train/"
result_path = "test_data/lego/result/"
draw_circle(images_name, coordinates, images_path, result_path)
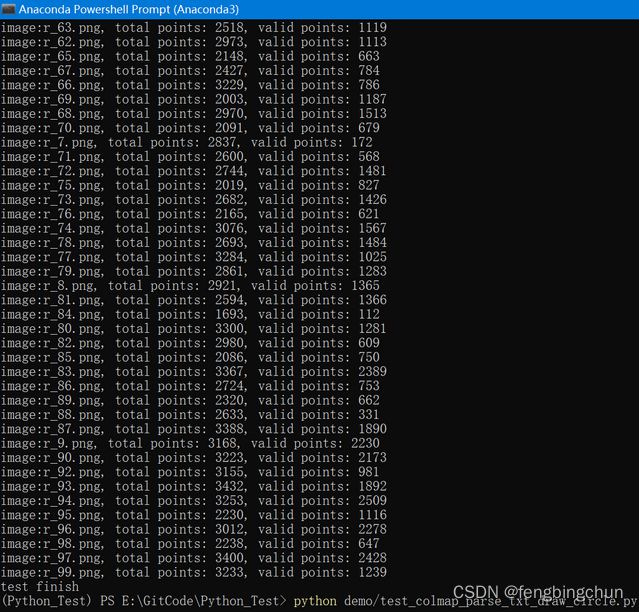
print("test finish")终端输出结果如下:
其中一幅图像的输出结果如下所示:
GitHub:https://github.com/fengbingchun/Python_Test