限定无环KSP算法
文章目录
-
- 偏离路径算法
-
- 什么是偏离路径
- Yen KSP
- 伪代码
- c代码
目前限定无环KSP算法主要有偏离路径算法和改进Dijkstra算法
偏离路径算法
算法目标:构建包含K个最短路径的K最短路径树T,其根节点为源点s,叶子节点为目标点t的K个备份。树中每个从s到叶子节点的路径都是K个最短路径之一。可以看出此树和平常看到的树不同,它包含了重复节点。
例子:
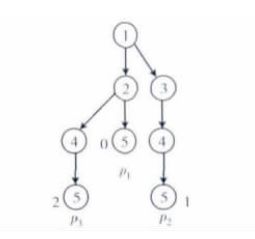
上图源点为1,目标点为5,包含3条最短路径:
p1={1,2,5}
p2={1,3,4,5}
p3={1,2,4,5}
那么这棵树是如何构建的呢?
首先要引入一个重要的概念:偏离路径。
什么是偏离路径
假定存在从s到t的两条路径 p = { v 1 , v 2 , . . . , v t } p=\{v_1,v_2,...,v_t\} p={v1,v2,...,vt}和 p = { u 1 , u 2 , . . . , u w } p=\{u_1,u_2,...,u_w\} p={u1,u2,...,uw},如果存在一个整数 x x x满足以下4个条件:
( 1 ) x < l , 并 且 x < w ; ( 2 ) v i = u i ( 0 ≤ i ≤ x ) ; ( 3 ) v x + 1 ≠ u x + 1 ; ( 4 ) ( u x + 1 , u x + 2 , . . . , u w = t ) 是 从 u x + 1 到 t 的 最 短 路 径 。 \begin{array}{lr} (1)\quad x<l,\quad 并且x<w;\\ (2)\quad v_i=u_i\qquad (0\le i \le x);\\ (3)\quad v_{x+1} \neq u_{x+1}; \\ (4)\quad (u_{x+1},u_{x+2},...,u_w=t)是从u_{x+1}到t的最短路径。\\ \end{array} (1)x<l,并且x<w;(2)vi=ui(0≤i≤x);(3)vx+1̸=ux+1;(4)(ux+1,ux+2,...,uw=t)是从ux+1到t的最短路径。
(注:第3条为不等号,csdn的latex格式有一些问题)
则称 ( u x , u x + 1 ) (u_x,u_{x+1}) (ux,ux+1)为 q q q相对于 p p p的偏离边, u x u_x ux为 q q q相对于 p p p的偏离节点,路径 ( u x + 1 , u x + 2 , . . . , u w = t ) (u_{x+1},u_{x+2},...,u_w=t) (ux+1,ux+2,...,uw=t)为 q q q相对于 p p p的最短偏离路径。
偏离路径算法的核心在于利用已经求得的 p 1 , p 2 , . . . , p k p_1,p_2,...,p_k p1,p2,...,pk的最短偏离路径产生 p k + 1 p_{k+1} pk+1。现在提出的各种偏离路径算法的不同之处在于偏离路径的计算和获取方法。
Yen KSP
最早的偏离路径算法由Yen在1971年提出。s到t的最短路径p1由Dijkstra算法求出,并存入结果列表A中。
求得前k条路径{p1,p2,p3,…,pk}后,第 p k + 1 p_{k+1} pk+1条路径求取过程如下:
(1). 取pk中除终止节点t之外的每个节点vi作为可能的偏离节点,计算vi到节点t的最短路径。在计算vi到t的最短路径时,需要满足一下两个条件:
第一,为了保证无环,该路径不能通过当前那最短路径pk上从s到vi之间的任何节点;
第二,为了避免与以前找到的路径重复,从节点vi分出的边不能与以前找到的最短路径p1,p2,…,pk上从vi分出的边相同。
(2).在找到了vi与t之间满足以上两个条件的最短路径后,将该最短路径与当前路径pk上从s到vi的路径拼接在一起构成 p k + 1 p_{k+1} pk+1的一条最短路径,并将其存储在候选路径列表B中。
(3).从候选路径列表B中选择最短的一条作为 p k + 1 p_{k+1} pk+1,并将其放入结果列表A中。以上过程不断重复,直到得到K条路径为止。
Yen算法的时间花费主要体现在以下四点:
- 最短路径的计算,目前Dijkstra算法求解两点间最短路径的时间花费为 O ( m + n l o g n ) O(m+nlogn) O(m+nlogn);
- 考虑到在结果列表A中最多有K条无环路径需要维护,每次插入新的候选路程需要的时间为 O ( l o g K ) O(logK) O(logK);
- 每条路径 p k + 1 p_{k+1} pk+1最多包含n个节点,因此求每个节点到目的节点的最短路径需要的时间花费为 O ( n ∗ ( m + n l o g n ) ) O(n*(m+nlogn)) O(n∗(m+nlogn));
- p k + 1 p_{k+1} pk+1最多有n个候选路径,从中选择最短的需要时间为 O ( n ) O(n) O(n)。
因此,Yen算法的复杂度是 O ( c ( n ) + K ( n ∗ ( m + n l o g n ) + n + l o g K ) ) O(c(n)+K(n*(m+nlogn)+n+logK)) O(c(n)+K(n∗(m+nlogn)+n+logK)),即 O ( K n ( m + n l o g n ) ) O(Kn(m+nlogn)) O(Kn(m+nlogn))。
Yen算法每次求 p k + 1 p_{k+1} pk+1时,将 p k p_k pk上除了终止节点之外的所有节点都视为潜在的偏离节点进行计算,当该节点不在 p k p_k pk的偏离路径上时就会产生大量重复路径。
伪代码
伪代码引用自wikipadiahttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Yen’s_algorithm
function YenKSP(Graph, source, sink, K):
// Determine the shortest path from the source to the sink.
A[0] = Dijkstra(Graph, source, sink);
// Initialize the set to store the potential kth shortest path.
B = [];
for k from 1 to K:
// The spur node ranges from the first node to the next to last node in the previous k-shortest path.
for i from 0 to size(A[k − 1]) − 2:
// Spur node is retrieved from the previous k-shortest path, k − 1.
spurNode = A[k-1].node(i);
// The sequence of nodes from the source to the spur node of the previous k-shortest path.
rootPath = A[k-1].nodes(0, i);
for each path p in A:
if rootPath == p.nodes(0, i):
// Remove the links that are part of the previous shortest paths which share the same root path.
remove p.edge(i,i + 1) from Graph;
for each node rootPathNode in rootPath except spurNode:
remove rootPathNode from Graph;
// Calculate the spur path from the spur node to the sink.
spurPath = Dijkstra(Graph, spurNode, sink);
// Entire path is made up of the root path and spur path.
totalPath = rootPath + spurPath;
// Add the potential k-shortest path to the heap.
B.append(totalPath);
// Add back the edges and nodes that were removed from the graph.
restore edges to Graph;
restore nodes in rootPath to Graph;
if B is empty:
// This handles the case of there being no spur paths, or no spur paths left.
// This could happen if the spur paths have already been exhausted (added to A),
// or there are no spur paths at all - such as when both the source and sink vertices
// lie along a "dead end".
break;
// Sort the potential k-shortest paths by cost.
B.sort();
// Add the lowest cost path becomes the k-shortest path.
A[k] = B[0];
B.pop();
return A;
c代码
做比赛时撸的,写的稀烂,有空再改
typedef vector<int> ShortPath;
class EdgeIngraph{
public:
int a;
int b;
float weight[CarTypeNum];
ArcNode *arcnode;
EdgeIngraph(GraphNode *g,int a,int b){
this->a = a;
this->b = b;
ArcNode *p = g[a].arc->nextarc;
while(p!=NULL && p->adjvex!=(b+1))
p=p->nextarc;
if(p->adjvex!=(b+1)) {
printf("\nnot found edge!\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
this->arcnode = p;
for(int i=0;i<CarTypeNum;i++)
this->weight[i] = p->info->TimeCost[i];
}
void deletedge(){
for(int i=0;i < CarTypeNum ;i++)
this->arcnode->info->TimeCost[i] = 9999999999999;
}
void restoreedge(){
for(int i=0;i<CarTypeNum;i++)
this->arcnode->info->TimeCost[i] = this->weight[i];
}
};
class NodeIngraph{
public:
int cross;
//float inroad[4][CarTypeNum]; //以cross为如度
//float outroad[4][CarTypeNum];//以cross为出度
Stack<ArcNode*> inroad;
Stack<float> inroadlen; //长度是inroad的CarTypeNum倍
Stack<ArcNode*> outroad;
Stack<float> outroadlen;
NodeIngraph(GraphNode *g,GraphNode *b,int cross){
this->cross = cross;
ArcNode *gp = g[cross].arc->nextarc;
while(gp!=NULL){
for(int i=0;i<CarTypeNum;i++){
this->outroadlen.push( gp->info->TimeCost[i]);
}
this->outroad.push(gp);
gp=gp->nextarc;
}
ArcNode *bq = b[cross].arc->nextarc; //找入度节点
while(bq!=NULL){
int incross = bq->adjvex - 1; //入度节点
//反向找出度
ArcNode* gq = g[incross].arc->nextarc;
while(gq!=NULL && gq->adjvex!=(cross+1)) gq=gq->nextarc;
if(gq->adjvex!=(cross+1)){
printf("\nnot found node\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
//找到出度
for(int i=0;i<CarTypeNum;i++){
this->inroadlen.push( gq->info->TimeCost[i]);
}
this->inroad.push(gq);
bq=bq->nextarc;
}
}
//并没有真正删除,只是设为足够大的数
void deletenode(GraphNode *g,GraphNode *b){
for(auto i = inroad.begin();i!=inroad.end();i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < CarTypeNum; j++) {
(*i)->info->TimeCost[j] = 99999999999999;
}
}
for(auto i = outroad.begin();i!=outroad.end();i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < CarTypeNum; j++) {
(*i)->info->TimeCost[j] = 99999999999999;
}
}
}
void restorenode(GraphNode *g,GraphNode *b) {
while (!inroad.empty() && !inroadlen.empty()) {
for (int i = CarTypeNum - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
inroad.top()->info->TimeCost[i] = inroadlen.top();
inroadlen.pop();
}
inroad.pop();
}
while (!outroad.empty() && !outroadlen.empty()) {
for (int i = CarTypeNum - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
outroad.top()->info->TimeCost[i] = outroadlen.top();
outroadlen.pop();
}
outroad.pop();
}
}
};
class ShortPathAndLen{
public:
ShortPath sp;
TwoNum t;
bool operator < (ShortPathAndLen & b) {
return t.a < b.t.a;
}
bool operator>=(const ShortPathAndLen& r){
return t.a >= r.t.a;
}
};
ShortPath djikstra(GraphNode *g, int src,int dst, int vernum, int cartype){
node d[CrossNum];//源顶点
int parent[CrossNum]; //每个顶点的父亲节点,可以用于还原最短路径树
int path_roadid[CrossNum];//路径记录
ShortPath OnePath;
//void djikstra(GraphNode *g, int s, int vernum, int cartype, node d[], int parent[], int path_roadid[]);
djikstra(g,src, vernum, cartype , d, parent, path_roadid);
//get_path(g, src, dst, vernum, parent, path_roadid, cartype);
OnePath = get_path(g, src, dst, vernum, parent, path_roadid, cartype);
return OnePath;
}
ShortPath get_path(GraphNode *g,int sec,int dst, int vernum, int path[],int path_roadid[],int cartype) {
ShortPath OnePath;// = (ShortPath*)malloc(sizeof(ShortPath));
int j = dst;
stack<combineCrossRoad> q; //由于记录的中途节点是倒序的,所以使用栈(先进后出),获得正序
while (path[j] != -1) { //如果j有中途节点
q.push(combineCrossRoad(j, path_roadid[j])); //将j压入堆
j = path[j]; //将j的前个中途节点赋给j
}
q.push(combineCrossRoad(j, path_roadid[j]));
int flag = 0;
(OnePath).push_back(sec);
int tmp = sec;
while (!q.empty()) { //先进后出,获得正序
if (flag) {
(OnePath).push_back(q.top().crossid);
ArcNode *qp = g[tmp].arc->nextarc;
tmp = q.top().crossid;
while ((qp != NULL) && ((qp->adjvex - 1) != tmp)) { //道路朝向统计
qp = qp->nextarc;
}
}
flag++;
q.pop(); //将堆的头节点弹出
}
return OnePath;
}
void UpdatePathInA(set<int>&PathInA,const ShortPath& Path){
for(int i=0;i<Path.size();i++)
{
PathInA.insert(Path[i]);
}
}
bool ComparePath(const ShortPath& a, const ShortPath& b){
long lena = a.size();
long lenb = b.size();
if(lena != lenb) return 0;
for(int i=0;i<lena;i++){
if(a[i]!=b[i])
return 0;
}
return 1;
}
ShortPath ShortPathCat(ShortPath a,ShortPath b){
ShortPath c;
for(int i=0;i<a.size() - 1;i++){ //多拷贝了一份
c.push_back(a[i]);
}
for(int i=0;i<b.size();i++){
c.push_back(b[i]);
}
return c;
};
int calculateLength(GraphNode *g,const ShortPath a,int cartype){
int len=0;
for(int i=0;i<a.size()-1;i++){
int curcrs = a[i];
ArcNode *p = g[curcrs].arc->nextarc;
while(p!=NULL && (p->adjvex!=(a[i+1]+1)))
p=p->nextarc;
if(p->adjvex!=(a[i+1]+1)){
printf("\nnot found cross\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
len += p->info->TimeCost[cartype];
}
return len;
}
bool compareShortPath(GraphNode *g,ShortPath a,ShortPath b,int cartype){
int lena = calculateLength(g,a,cartype);
int lenb = calculateLength(g,b,cartype);
return lena > lenb;
}
void quickSort(deque<ShortPathAndLen>& s, int l, int r)
{
int n = s.size();
if(l<r)
{
int low=l; //左边第一个,因为第一个已经用pivot保存了
int high=r; //右边
auto pivot = s[l]; //第一个,已被保存
while(low<high) //当左小于右,当相等的时候会跳出循环
{
while(low<high&&s[high]>= pivot) // 从右向左找第一个小于x的数
high--;
if(low<high)
s[low++] = s[high];
while(low<high&&s[low]<pivot) // 从左向右找第一个大于等于x的数
low++;
if(low<high)
s[high--] = s[low];
}
s[low]=pivot;
quickSort(s, l, low - 1); //low左边递归调用
quickSort(s, low + 1, r); //low右边递归调用
}
}
//用到了邻接表和逆邻接表,求src到dst的1条最优最短路径和K条次优最短路径
vector<ShortPath> YenKSP(GraphNode *g,GraphNode *b,int vernum,int src,int dst,int cartype,int K){
// Determine the shortest path from the source to the dst
vector<ShortPath> A;//[Max_K_IN_KSP];// = (ShortPath*)malloc(sizeof(ShortPath));
int cntA = 0;
//A = (ShortPath *) malloc(sizeof(ShortPath) * Max_K_IN_KSP);
std::set<int>PathInA;
//求解src到dst的最短路径
ShortPath tmp = djikstra(g,src, dst,vernum, cartype); //A[0]
A.push_back(tmp);
UpdatePathInA(PathInA,A[0]);
cntA++;
// for(int i=0;i
// printf("\n -> %d",A[0][0][i]);
//Initialize the set to store the potential kth shortest path.
deque<ShortPathAndLen> B;
for(int k=1;k<=K;k++) {
// The spur node ranges from the first node to the next to last node in the previous k-shortest path.
for (int i = 0; i < A[k - 1].size() - 1; i++) {
// Spur node is retrieved from the previous k-shortest path, k − 1.
int spurNode = A[k - 1][i]; //偏离点选择 spurNode = A[k-1].node(i);
// The sequence of nodes from the source to the spur node of the previous k-shortest path.
ShortPath rootPath(A[k - 1].begin(), A[k - 1].begin() + i+1); //rootPath = A[k-1].nodes(0, i);
stack<EdgeIngraph> graphchange;
stack<NodeIngraph> graphchange2;
for (int p = 0; p < cntA; p++) {
ShortPath &Ap = A[p];
ShortPath prootPath(Ap.begin(), Ap.begin() + i+1);
if (ComparePath(rootPath, prootPath)) { //如果相等
// Remove the links that are part of the previous shortest paths which share the same root path.
//remove p.edge(i,i + 1) from Graph;
EdgeIngraph edge(g, A[p][i], A[p][i + 1]);
edge.deletedge();
graphchange.push(edge);
}
}
//for each node rootPathNode in rootPath except spurNode:
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) {
int deletecross = rootPath[j];
NodeIngraph node(g, b, deletecross);
node.deletenode(g, b);
graphchange2.push(node);
}
// Calculate the spur path from the spur node to the sink.
ShortPath spurPath, totalPath;
spurPath = djikstra(g, spurNode, dst, vernum, cartype);//spurPath = Dijkstra(Graph, spurNode, sink);
//dijk失败,复原graph!
if(spurPath.back()!=A[0].back()) {
// Add back the edges and nodes that were removed from the graph.
//restore edges to Graph;
if (!graphchange.empty()) {
graphchange.top().restoreedge();
graphchange.pop();
}
//restore nodes in rootPath to Graph;
if (!graphchange2.empty()) {
graphchange2.top().restorenode(g, b);
graphchange2.pop();
}
continue;
}
// Entire path is made up of the root path and spur path.
totalPath = ShortPathCat(rootPath, spurPath);//totalPath = rootPath + spurPath;
// Add the potential k-shortest path to the heap.
ShortPathAndLen tmp;
TwoNum tmp2;
int len = calculateLength(g, totalPath,cartype);
tmp2.a=len;
tmp2.b = totalPath.size();
tmp.sp = totalPath;
tmp.t = tmp2;
B.push_back(tmp);
// Add back the edges and nodes that were removed from the graph.
//restore edges to Graph;
if (!graphchange.empty()) {
graphchange.top().restoreedge();
graphchange.pop();
}
//restore nodes in rootPath to Graph;
if (!graphchange2.empty()) {
graphchange2.top().restorenode(g, b);
graphchange2.pop();
}
}
if(B.empty()){
// This handles the case of there being no spur paths, or no spur paths left.
// This could happen if the spur paths have already been exhausted (added to A),
// or there are no spur paths at all - such as when both the source and sink vertices
// lie along a "dead end".
break;
}
// Sort the potential k-shortest paths by cost.
//sort(B.begin(),B.end());
quickSort(B,0,B.size()-1);
// Add the lowest cost path becomes the k-shortest path.
A.push_back(B.front().sp);
B.pop_front();
}
return A;
}