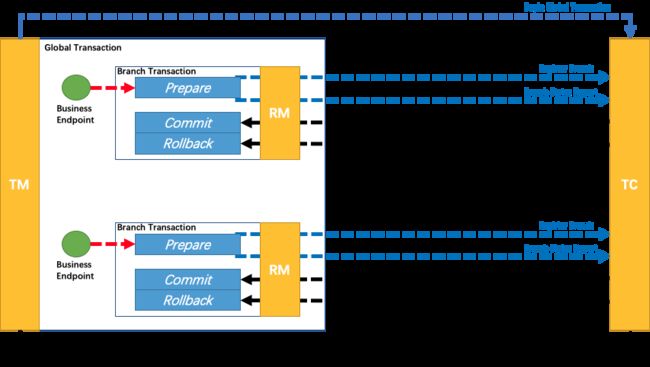
分布式事务框架(seata1.5.0)源码分析-通信模型
目录
Client端
TM / RM初始化
TM / RM注册Channel
NettyClientChannelManager
seata报文传输协议
解码-ProtocolV1Decoder
编码-ProtocolV1Encoder
TM / RM发送请求
TM / RM接收请求/响应
Server端
TC浅析
Client端
TM / RM初始化
我们以RMClient为例,分析客户端的初始化、请求发送,请求/响应接收,从代码的角度来讲,TM和RM只是处理的请求对象不同,还有就是TM注册和RM注册存在细微差异,其他逻辑基本一致。
来到入口类GlobalTransactionScanner的afterPropertiesSet方法,这个方法在spring初始化GlobalTransactionScanner这个bean的时候会被调用。
public class GlobalTransactionScanner extends AbstractAutoProxyCreator
implements ConfigurationChangeListener, InitializingBean, ApplicationContextAware, DisposableBean {
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
if (disableGlobalTransaction) {
if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOGGER.info("Global transaction is disabled.");
}
ConfigurationCache.addConfigListener(ConfigurationKeys.DISABLE_GLOBAL_TRANSACTION,
(ConfigurationChangeListener)this);
return;
}
if (initialized.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
//初始化客户端
initClient();
}
}
private void initClient() {
if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOGGER.info("Initializing Global Transaction Clients ... ");
}
if (DEFAULT_TX_GROUP_OLD.equals(txServiceGroup)) {
LOGGER.warn("the default value of seata.tx-service-group: {} has already changed to {} since Seata 1.5, " +
"please change your default configuration as soon as possible " +
"and we don't recommend you to use default tx-service-group's value provided by seata",
DEFAULT_TX_GROUP_OLD, DEFAULT_TX_GROUP);
}
if (StringUtils.isNullOrEmpty(applicationId) || StringUtils.isNullOrEmpty(txServiceGroup)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(String.format("applicationId: %s, txServiceGroup: %s", applicationId, txServiceGroup));
}
//TM 初始化
TMClient.init(applicationId, txServiceGroup, accessKey, secretKey);
if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOGGER.info("Transaction Manager Client is initialized. applicationId[{}] txServiceGroup[{}]", applicationId, txServiceGroup);
}
//RM 初始化
RMClient.init(applicationId, txServiceGroup);
if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOGGER.info("Resource Manager is initialized. applicationId[{}] txServiceGroup[{}]", applicationId, txServiceGroup);
}
if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOGGER.info("Global Transaction Clients are initialized. ");
}
registerSpringShutdownHook();
}
}
RmNettyRemotingClient(RM)和TmNettyRemotingClient(TM)都继承自AbstractNettyRemotingClient。
public class RMClient {
public static void init(String applicationId, String transactionServiceGroup) {
// 创建RmNettyRemotingClient对象与TC进行通信
RmNettyRemotingClient rmNettyRemotingClient = RmNettyRemotingClient.getInstance(applicationId, transactionServiceGroup);
// 设置RM资源管理器DefaultResourceManager
rmNettyRemotingClient.setResourceManager(DefaultResourceManager.get());
// 设置RM消息处理器,接收TC发起的分支请求
rmNettyRemotingClient.setTransactionMessageHandler(DefaultRMHandler.get());
// 初始化
rmNettyRemotingClient.init();
}
}
public final class RmNettyRemotingClient extends AbstractNettyRemotingClient {
@Override
public void init() {
// 这里很重要,根据请求和响应的类型注册各自的处理器,处理器分2类:
// 第1种:对TC发起的请求作响应的处理。RmBranchCommitProcessor、RmBranchRollbackProcessor、RmUndoLogProcessor
// 第2种:对RM请求TC后,接收TC返回的响应作处理。ClientOnResponseProcessor、ClientHeartbeatProcessor
registerProcessor();
if (initialized.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
// 接着往父类看
super.init();
// Found one or more resources that were registered before initialization
// 如果已经有分支注册到了resourceManager中,向TC发起RM注册,RM 通过channel与TC服务端建立连接,若未连接过,会开启一个channel(开启RM通信端口)
// 由于此时还未完成初始化,所以一般不会走这段逻辑
if (resourceManager != null
&& !resourceManager.getManagedResources().isEmpty()
&& StringUtils.isNotBlank(transactionServiceGroup)) {
getClientChannelManager().reconnect(transactionServiceGroup);
}
}
}
} RmNettyRemotingClient装载了2个对象:
- DefaultResourceManager:管理注册好的所有分支事务
- DefaultRMHandler:处理分支事务注册、提交、回滚请求
再来看下父类的构造方法
public abstract class AbstractNettyRemotingClient extends AbstractNettyRemoting implements RemotingClient {
public AbstractNettyRemotingClient(NettyClientConfig nettyClientConfig, EventExecutorGroup eventExecutorGroup,
ThreadPoolExecutor messageExecutor, NettyPoolKey.TransactionRole transactionRole) {
super(messageExecutor);
// 角色:RM
this.transactionRole = transactionRole;
// netty客户端
clientBootstrap = new NettyClientBootstrap(nettyClientConfig, eventExecutorGroup, transactionRole);
// 这个handler很重要,netty都是将请求委托给handler进行处理。也就是说RM收到的请求,最后会到ClientHandler中处理
clientBootstrap.setChannelHandlers(new ClientHandler());
// NettyClientChannelManager:netty通信管道管理器
// getPoolKeyFunction():根据TC server端地址组装 RM注册请求,server端不同的机器对应不同的NettyPoolKey
clientChannelManager = new NettyClientChannelManager(
new NettyPoolableFactory(this, clientBootstrap), getPoolKeyFunction(), nettyClientConfig);
}
}
public final class RmNettyRemotingClient extends AbstractNettyRemotingClient {
@Override
protected Function getPoolKeyFunction() {
return serverAddress -> {
// 获取所有已注册的resourceId用“,”隔开,拼接成字符串
String resourceIds = getMergedResourceKeys();
if (resourceIds != null && LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOGGER.info("RM will register :{}", resourceIds);
}
// 组装成RM注册请求对象
RegisterRMRequest message = new RegisterRMRequest(applicationId, transactionServiceGroup);
message.setResourceIds(resourceIds);
// 保装成NettyPoolKey
return new NettyPoolKey(NettyPoolKey.TransactionRole.RMROLE, serverAddress, message);
};
}
}
netty都是将请求委托给handler进行处理。其实TC向RM/TM发送的请求最后都会到ClientHandler中进行处理,这个我们后面再看。
TM / RM注册Channel
NettyClientChannelManager
这里还有个特殊的类:NettyClientChannelManager,Client端有2种通信角色,RM和TM。它们两个都要向TC注册,并保持连接。NettyClientChannelManager就是用来管理他们两个产生的Channel通道,当前的角色是RM,那就是管理RM相关信息,TM同理。
class NettyClientChannelManager {
/**
* 支持按serverAddress维度加锁(synchronized)
*/
private final ConcurrentMap channelLocks = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
/**
* 缓存了 serverAddress >> NettyPoolKey的映射关系
*/
private final ConcurrentMap poolKeyMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
/**
* 缓存了 serverAddress >> Channel的映射关系(与每台server建立的连接通道)
*/
private final ConcurrentMap channels = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
/**
* 缓存池包装对象,与NettyPoolableFactory配合创建channel,并缓存NettyPoolKey >> Channel映射关系
*/
private final GenericKeyedObjectPool nettyClientKeyPool;
/**
* 根据 serverAddress 创建RM/TM请求对象
*/
private Function poolKeyFunction;
NettyClientChannelManager(final NettyPoolableFactory keyPoolableFactory, final Function poolKeyFunction,
final NettyClientConfig clientConfig) {
// keyPoolableFactory 很重要,真正建立channel的地方
nettyClientKeyPool = new GenericKeyedObjectPool<>(keyPoolableFactory);
nettyClientKeyPool.setConfig(getNettyPoolConfig(clientConfig));
this.poolKeyFunction = poolKeyFunction;
}
/**
* Acquire netty client channel connected to remote server.
* 获取server端地址对应的channel对象,连接server端
* @param serverAddress server address
* @return netty channel
*/
Channel acquireChannel(String serverAddress) {
Channel channelToServer = channels.get(serverAddress);
if (channelToServer != null) {
channelToServer = getExistAliveChannel(channelToServer, serverAddress);
if (channelToServer != null) {
return channelToServer;
}
}
if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOGGER.info("will connect to {}", serverAddress);
}
Object lockObj = CollectionUtils.computeIfAbsent(channelLocks, serverAddress, key -> new Object());
synchronized (lockObj) {
//建立建立
return doConnect(serverAddress);
}
}
/**
* Reconnect to remote server of current transaction service group.
* 与server端重连
* @param transactionServiceGroup transaction service group
*/
void reconnect(String transactionServiceGroup) {
List availList = null;
try {
// 从注册中心拉取server端地址
availList = getAvailServerList(transactionServiceGroup);
} catch (Exception e) {
LOGGER.error("Failed to get available servers: {}", e.getMessage(), e);
return;
}
// 日志打印
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(availList)) {
RegistryService registryService = RegistryFactory.getInstance();
String clusterName = registryService.getServiceGroup(transactionServiceGroup);
if (StringUtils.isBlank(clusterName)) {
LOGGER.error("can not get cluster name in registry config '{}{}', please make sure registry config correct",
ConfigurationKeys.SERVICE_GROUP_MAPPING_PREFIX,
transactionServiceGroup);
return;
}
if (!(registryService instanceof FileRegistryServiceImpl)) {
LOGGER.error("no available service found in cluster '{}', please make sure registry config correct and keep your seata server running", clusterName);
}
return;
}
Set channelAddress = new HashSet<>(availList.size());
try {
// 与server端的每个实例建立连接
for (String serverAddress : availList) {
try {
acquireChannel(serverAddress);
channelAddress.add(serverAddress);
} catch (Exception e) {
LOGGER.error("{} can not connect to {} cause:{}", FrameworkErrorCode.NetConnect.getErrCode(),
serverAddress, e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
} finally {
if (CollectionUtils.isNotEmpty(channelAddress)) {
List aliveAddress = new ArrayList<>(channelAddress.size());
for (String address : channelAddress) {
String[] array = address.split(":");
aliveAddress.add(new InetSocketAddress(array[0], Integer.parseInt(array[1])));
}
RegistryFactory.getInstance().refreshAliveLookup(transactionServiceGroup, aliveAddress);
} else {
RegistryFactory.getInstance().refreshAliveLookup(transactionServiceGroup, Collections.emptyList());
}
}
}
private Channel doConnect(String serverAddress) {
// 通过serverAddress尝试从缓存中获取channel
Channel channelToServer = channels.get(serverAddress);
// 检活
if (channelToServer != null && channelToServer.isActive()) {
return channelToServer;
}
Channel channelFromPool;
try {
// 创建TM/RM注册请求对象
NettyPoolKey currentPoolKey = poolKeyFunction.apply(serverAddress);
// 如果是TM注册请求
if (currentPoolKey.getMessage() instanceof RegisterTMRequest) {
// 保存TM serverAddress >> NettyPoolKey映射关系
poolKeyMap.put(serverAddress, currentPoolKey);
} else {// RM注册请求
// 保存RM serverAddress >> NettyPoolKey映射关系
NettyPoolKey previousPoolKey = poolKeyMap.putIfAbsent(serverAddress, currentPoolKey);
if (previousPoolKey != null && previousPoolKey.getMessage() instanceof RegisterRMRequest) {
// 更新RegisterRMRequest中的resourceId
RegisterRMRequest registerRMRequest = (RegisterRMRequest) currentPoolKey.getMessage();
((RegisterRMRequest) previousPoolKey.getMessage()).setResourceIds(registerRMRequest.getResourceIds());
}
}
// 还未建立过channel,创建channel通道
channelFromPool = nettyClientKeyPool.borrowObject(poolKeyMap.get(serverAddress));
channels.put(serverAddress, channelFromPool);
} catch (Exception exx) {
LOGGER.error("{} register RM failed.", FrameworkErrorCode.RegisterRM.getErrCode(), exx);
throw new FrameworkException("can not register RM,err:" + exx.getMessage());
}
return channelFromPool;
}
/**
* 从注册中心,拉取服务端可用的TC server端地址
* @param transactionServiceGroup
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
private List getAvailServerList(String transactionServiceGroup) throws Exception {
List availInetSocketAddressList = RegistryFactory.getInstance()
.lookup(transactionServiceGroup);
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(availInetSocketAddressList)) {
return Collections.emptyList();
}
return availInetSocketAddressList.stream()
.map(NetUtil::toStringAddress)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
/**
* 从缓存中获取存活的channel
* @param rmChannel
* @param serverAddress
* @return
*/
private Channel getExistAliveChannel(Channel rmChannel, String serverAddress) {
if (rmChannel.isActive()) {
return rmChannel;
} else {
int i = 0;
for (; i < NettyClientConfig.getMaxCheckAliveRetry(); i++) {
try {
Thread.sleep(NettyClientConfig.getCheckAliveInterval());
} catch (InterruptedException exx) {
LOGGER.error(exx.getMessage());
}
rmChannel = channels.get(serverAddress);
if (rmChannel != null && rmChannel.isActive()) {
return rmChannel;
}
}
if (i == NettyClientConfig.getMaxCheckAliveRetry()) {
LOGGER.warn("channel {} is not active after long wait, close it.", rmChannel);
releaseChannel(rmChannel, serverAddress);
return null;
}
}
return null;
}
}
NettyClientChannelManager为TM、RM提供了请求对象、channel的缓存功能,方便TM、RM向TC发起注册请求。实际真正创建channel的地方却是在NettyPoolableFactory类中。
public class NettyPoolableFactory implements KeyedPoolableObjectFactory {
@Override
public Channel makeObject(NettyPoolKey key) {
// 要连接的server端地址
InetSocketAddress address = NetUtil.toInetSocketAddress(key.getAddress());
if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOGGER.info("NettyPool create channel to " + key);
}
// 创建channel
Channel tmpChannel = clientBootstrap.getNewChannel(address);
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
Object response;
Channel channelToServer = null;
if (key.getMessage() == null) {
throw new FrameworkException("register msg is null, role:" + key.getTransactionRole().name());
}
try {
// 向TC发起TM/RM注册请求
response = rpcRemotingClient.sendSyncRequest(tmpChannel, key.getMessage());
if (!isRegisterSuccess(response, key.getTransactionRole())) {
// 失败回调处理
rpcRemotingClient.onRegisterMsgFail(key.getAddress(), tmpChannel, response, key.getMessage());
} else {
channelToServer = tmpChannel;
// 成功回调处理
rpcRemotingClient.onRegisterMsgSuccess(key.getAddress(), tmpChannel, response, key.getMessage());
}
} catch (Exception exx) {
if (tmpChannel != null) {
tmpChannel.close();
}
throw new FrameworkException(
"register " + key.getTransactionRole().name() + " error, errMsg:" + exx.getMessage());
}
if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOGGER.info("register success, cost " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start) + " ms, version:" + getVersion(
response, key.getTransactionRole()) + ",role:" + key.getTransactionRole().name() + ",channel:"
+ channelToServer);
}
return channelToServer;
}
}
我们接着看父类AbstractNettyRemotingClient的init方法
public abstract class AbstractNettyRemotingClient extends AbstractNettyRemoting implements RemotingClient {
@Override
public void init() {
//启动定时器,发起RM注册请求,与TC服务端保持连接,保活
timerExecutor.scheduleAtFixedRate(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
// 利用前面介绍的NettyClientChannelManager与server端注册连接。
clientChannelManager.reconnect(getTransactionServiceGroup());
}
}, SCHEDULE_DELAY_MILLS, SCHEDULE_INTERVAL_MILLS, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
//是否允许批量发送请求,默认为true
//单线程轮询basketMap中的RpcMessage,合并多条请求信息发送过去
//而发送请求时会将RpcMessage放到basketMap中
if (this.isEnableClientBatchSendRequest()) {
mergeSendExecutorService = new ThreadPoolExecutor(MAX_MERGE_SEND_THREAD,
MAX_MERGE_SEND_THREAD,
KEEP_ALIVE_TIME, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(),
new NamedThreadFactory(getThreadPrefix(), MAX_MERGE_SEND_THREAD));
mergeSendExecutorService.submit(new MergedSendRunnable());
}
//定时清理掉超时的请求任务,避免future阻塞
super.init();
//这里的内容值得关注一下,RM netty客户端配置
clientBootstrap.start();
}
}
这里我们看到init中启动了一个定时任务取执行clientChannelManager.reconnect,前面我们已经介绍过NettyClientChannelManager的作用了,这个定时任务的作用就是发起RM/TM注册请求,与TC服务端保持连接。
除此之外还提交了一个MergedSendRunnable到线程池中。这个任务的作用,我们暂且不说,后面再介绍。继续关注clientBootstrap.start()这里。
@Override
public void start() {
if (this.defaultEventExecutorGroup == null) {
this.defaultEventExecutorGroup = new DefaultEventExecutorGroup(nettyClientConfig.getClientWorkerThreads(),
new NamedThreadFactory(getThreadPrefix(nettyClientConfig.getClientWorkerThreadPrefix()),
nettyClientConfig.getClientWorkerThreads()));
}
this.bootstrap.group(this.eventLoopGroupWorker).channel(
nettyClientConfig.getClientChannelClazz()).option(
ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY, true).option(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true).option(
ChannelOption.CONNECT_TIMEOUT_MILLIS, nettyClientConfig.getConnectTimeoutMillis()).option(
ChannelOption.SO_SNDBUF, nettyClientConfig.getClientSocketSndBufSize()).option(ChannelOption.SO_RCVBUF,
nettyClientConfig.getClientSocketRcvBufSize());
if (nettyClientConfig.enableNative()) {
if (PlatformDependent.isOsx()) {
if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOGGER.info("client run on macOS");
}
} else {
bootstrap.option(EpollChannelOption.EPOLL_MODE, EpollMode.EDGE_TRIGGERED)
.option(EpollChannelOption.TCP_QUICKACK, true);
}
}
// 前面是一堆netty配置,重点看这里
bootstrap.handler(
new ChannelInitializer() {
@Override
public void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) {
ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline();
pipeline.addLast(
new IdleStateHandler(nettyClientConfig.getChannelMaxReadIdleSeconds(),
nettyClientConfig.getChannelMaxWriteIdleSeconds(),
nettyClientConfig.getChannelMaxAllIdleSeconds()))
// 解码器
.addLast(new ProtocolV1Decoder())
// 编码器
.addLast(new ProtocolV1Encoder());
if (channelHandlers != null) {
// 这里就是我们前面说的,接收到的请求经过ProtocolV1Decoder解码器后
// 最终会委托给我们的ClientHandler进行处理
addChannelPipelineLast(ch, channelHandlers);
}
}
});
if (initialized.compareAndSet(false, true) && LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOGGER.info("NettyClientBootstrap has started");
}
} 到这里我们可以明确的看到,client端发送请求是通过ProtocolV1Encoder编码器将请求对象序列化为字节流传输给TC,而client端接收到的请求/响应经过ProtocolV1Decoder解码器解码后,最终会委托给ClientHandler进行处理。
seata报文传输协议
接下来要看看请求编码/解码的过程,在这之前先熟悉一下seata约定的报文传输协议。
| 长度 | 可选值 | 描述 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Head | 2byte | 2个0xdada | 魔数(magic code) |
| 1byte | 1 | 版本号(version) | |
| 4byte | 总长度(fullLength) | ||
| 2byte | 头部长度(headLength) | ||
| 1byte | 0-request 1-response 2-Request which no need response 3-Heartbeat Request 4-Heartbeat Response |
消息类型(messageType) | |
| 1byte | 1-seata 2-protobuf 4-kryo 8-fst 22-hessian(看代码注释是16才对,实际值却是0x16) |
序列化类型(codecType) | |
| 1byte | 0-none 1-gzip 2-zip ...... 7-zstd |
压缩类型(compressorType) | |
| 4byte | 请求ID(requestId) | ||
| headLength-16 | (不一定有) | headMap | |
| Body | fullLength-headLength | 请求体(body) |
解码-ProtocolV1Decoder
public class ProtocolV1Decoder extends LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder {
@Override
protected Object decode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf in) throws Exception {
Object decoded;
try {
decoded = super.decode(ctx, in);
if (decoded instanceof ByteBuf) {
ByteBuf frame = (ByteBuf)decoded;
try {
// 解码
return decodeFrame(frame);
} finally {
frame.release();
}
}
} catch (Exception exx) {
LOGGER.error("Decode frame error, cause: {}", exx.getMessage());
throw new DecodeException(exx);
}
return decoded;
}
public Object decodeFrame(ByteBuf frame) {
// 2byte 魔数
byte b0 = frame.readByte();
byte b1 = frame.readByte();
if (ProtocolConstants.MAGIC_CODE_BYTES[0] != b0
|| ProtocolConstants.MAGIC_CODE_BYTES[1] != b1) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unknown magic code: " + b0 + ", " + b1);
}
// 1byte version版本
byte version = frame.readByte();
// TODO check version compatible here
// 4byte 总长度
int fullLength = frame.readInt();
// 2byte 头部长度
short headLength = frame.readShort();
// 1byte 消息类型
byte messageType = frame.readByte();
// 1byte 序列化类型 seata、hessian、protobuf、kryo等
byte codecType = frame.readByte();
// 1byte 压缩类型 如zip、gzip等
byte compressorType = frame.readByte();
// 4byte 请求id
int requestId = frame.readInt();
RpcMessage rpcMessage = new RpcMessage();
rpcMessage.setCodec(codecType);
rpcMessage.setId(requestId);
rpcMessage.setCompressor(compressorType);
rpcMessage.setMessageType(messageType);
// direct read head with zero-copy
// headMap 长度=headLength-16 (前面的16位头部信息)
int headMapLength = headLength - ProtocolConstants.V1_HEAD_LENGTH;
if (headMapLength > 0) {
// headMap反序列化
Map map = HeadMapSerializer.getInstance().decode(frame, headMapLength);
rpcMessage.getHeadMap().putAll(map);
}
// read body
// 解析请求体
if (messageType == ProtocolConstants.MSGTYPE_HEARTBEAT_REQUEST) {
// 心跳请求
rpcMessage.setBody(HeartbeatMessage.PING);
} else if (messageType == ProtocolConstants.MSGTYPE_HEARTBEAT_RESPONSE) {
// 心跳响应
rpcMessage.setBody(HeartbeatMessage.PONG);
} else {
// 请求体长度
int bodyLength = fullLength - headLength;
if (bodyLength > 0) {
byte[] bs = new byte[bodyLength];
frame.readBytes(bs);
// 根据压缩类型code,获取压缩器,默认不压缩
Compressor compressor = CompressorFactory.getCompressor(compressorType);
// 解压
bs = compressor.decompress(bs);
// 根据序列化类型code,使用spi加载具体的序列化器
Serializer serializer = SerializerServiceLoader.load(SerializerType.getByCode(rpcMessage.getCodec()));
// 反序列化转变成具体的请求对象
rpcMessage.setBody(serializer.deserialize(bs));
}
}
return rpcMessage;
}
}
编码-ProtocolV1Encoder
public class ProtocolV1Encoder extends MessageToByteEncoder {
@Override
public void encode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg, ByteBuf out) {
try {
if (msg instanceof RpcMessage) {
RpcMessage rpcMessage = (RpcMessage) msg;
int fullLength = ProtocolConstants.V1_HEAD_LENGTH;
int headLength = ProtocolConstants.V1_HEAD_LENGTH;
byte messageType = rpcMessage.getMessageType();
// 写入2byte 魔数
out.writeBytes(ProtocolConstants.MAGIC_CODE_BYTES);
// 写入1byte的version
out.writeByte(ProtocolConstants.VERSION);
// full Length(4B) and head length(2B) will fix in the end.
// 给 fullLength(4B) 和 headLength(2B)预留 6byte的长度,因为这2个长度,最后才能算出来
out.writerIndex(out.writerIndex() + 6);
// 写入1byte的消息类型
out.writeByte(messageType);
// 写入1byte的序列化类型
out.writeByte(rpcMessage.getCodec());
// 写入1byte的压缩类型
out.writeByte(rpcMessage.getCompressor());
// 写入4byte的请求ID
out.writeInt(rpcMessage.getId());
// direct write head with zero-copy
// 写入headMap,并累加full Length 和 head length
Map headMap = rpcMessage.getHeadMap();
if (headMap != null && !headMap.isEmpty()) {
int headMapBytesLength = HeadMapSerializer.getInstance().encode(headMap, out);
headLength += headMapBytesLength;
fullLength += headMapBytesLength;
}
// 请求体
byte[] bodyBytes = null;
// 心跳请求/心跳响应是没有body的
if (messageType != ProtocolConstants.MSGTYPE_HEARTBEAT_REQUEST
&& messageType != ProtocolConstants.MSGTYPE_HEARTBEAT_RESPONSE) {
// heartbeat has no body
// 找到序列化类型code,通过spi加载序列化器
Serializer serializer = SerializerServiceLoader.load(SerializerType.getByCode(rpcMessage.getCodec()));
// 消息体序列化成bytes
bodyBytes = serializer.serialize(rpcMessage.getBody());
// 压缩字节
Compressor compressor = CompressorFactory.getCompressor(rpcMessage.getCompressor());
bodyBytes = compressor.compress(bodyBytes);
// 累加fullLength
fullLength += bodyBytes.length;
}
// 写入消息体字节
if (bodyBytes != null) {
out.writeBytes(bodyBytes);
}
// fix fullLength and headLength
int writeIndex = out.writerIndex();
// skip magic code(2B) + version(1B)
// 调整写入下标回到 fullLength的位置
out.writerIndex(writeIndex - fullLength + 3);
// 写入总长度
out.writeInt(fullLength);
// 写入头部长度
out.writeShort(headLength);
// 重新回到写入下标的最新位置
out.writerIndex(writeIndex);
} else {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("Not support this class:" + msg.getClass());
}
} catch (Throwable e) {
LOGGER.error("Encode request error!", e);
}
}
}
通过编码解码的代码,可以看出发送请求时通过ProtocolV1Encoder对消息体进行序列化,接收请求/响应时通过ProtocolV1Decoder进行反序列化。
TM / RM发送请求
我们再来看看发送请求的代码,AbstractNettyRemotingClient中的sendSyncRequest
/**
* Obtain the return result through MessageFuture blocking.
* 保存请求ID >> MessageFuture的映射,用于获取响应结果
* @see AbstractNettyRemoting#sendSync
*/
protected final ConcurrentHashMap futures = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
/**
* When batch sending is enabled, the message will be stored to basketMap
* Send via asynchronous thread {@link MergedSendRunnable}
* {@link this#isEnableClientBatchSendRequest()}
* serverAddress >> 消息请求阻塞队列,每个server端实例对应一个阻塞队列
*/
protected final ConcurrentHashMap> basketMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
@Override
public Object sendSyncRequest(Object msg) throws TimeoutException {
//从注册中心拉去服务端server地址列表,经过负载均衡选取一个地址
String serverAddress = loadBalance(getTransactionServiceGroup(), msg);
long timeoutMillis = this.getRpcRequestTimeout();
//组装请求对象,包括请求ID,序列号方式等
RpcMessage rpcMessage = buildRequestMessage(msg, ProtocolConstants.MSGTYPE_RESQUEST_SYNC);
// send batch message
// put message into basketMap, @see MergedSendRunnable
// 如果允许批量发送请求
if (this.isEnableClientBatchSendRequest()) {
// send batch message is sync request, needs to create messageFuture and put it in futures.
// 生产MessageFuture放到futures中,key为请求ID
MessageFuture messageFuture = new MessageFuture();
messageFuture.setRequestMessage(rpcMessage);
messageFuture.setTimeout(timeoutMillis);
futures.put(rpcMessage.getId(), messageFuture);
// put message into basketMap
// 将请求对象按照server地址放入basketMap中,供MergedSendRunnable任务从basketMap拉取请求,批量发送到server端
BlockingQueue basket = CollectionUtils.computeIfAbsent(basketMap, serverAddress,
key -> new LinkedBlockingQueue<>());
if (!basket.offer(rpcMessage)) {
LOGGER.error("put message into basketMap offer failed, serverAddress:{},rpcMessage:{}",
serverAddress, rpcMessage);
return null;
}
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOGGER.debug("offer message: {}", rpcMessage.getBody());
}
// 生产消费模式,唤醒MergedSendRunnable线程
if (!isSending) {
synchronized (mergeLock) {
mergeLock.notifyAll();
}
}
try {
// TC 服务端返回的响应最终会到ClientOnResponseProcessor进行处理
// 通过ClientOnResponseProcessor关联MessageFuture获取结果
return messageFuture.get(timeoutMillis, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
} catch (Exception exx) {
LOGGER.error("wait response error:{},ip:{},request:{}",
exx.getMessage(), serverAddress, rpcMessage.getBody());
if (exx instanceof TimeoutException) {
throw (TimeoutException) exx;
} else {
throw new RuntimeException(exx);
}
}
} else {
Channel channel = clientChannelManager.acquireChannel(serverAddress);
// 同步发送
return super.sendSync(channel, rpcMessage, timeoutMillis);
}
}
/**
* rpc sync request
* Obtain the return result through MessageFuture blocking.
* 通过 MessageFuture 阻塞等待结果,同步发送
* @param channel netty channel
* @param rpcMessage rpc message
* @param timeoutMillis rpc communication timeout
* @return response message
* @throws TimeoutException
*/
protected Object sendSync(Channel channel, RpcMessage rpcMessage, long timeoutMillis) throws TimeoutException {
if (timeoutMillis <= 0) {
throw new FrameworkException("timeout should more than 0ms");
}
if (channel == null) {
LOGGER.warn("sendSync nothing, caused by null channel.");
return null;
}
MessageFuture messageFuture = new MessageFuture();
messageFuture.setRequestMessage(rpcMessage);
messageFuture.setTimeout(timeoutMillis);
// 放入futures中
futures.put(rpcMessage.getId(), messageFuture);
channelWritableCheck(channel, rpcMessage.getBody());
String remoteAddr = ChannelUtil.getAddressFromChannel(channel);
doBeforeRpcHooks(remoteAddr, rpcMessage);
// 写入数据
channel.writeAndFlush(rpcMessage).addListener((ChannelFutureListener) future -> {
if (!future.isSuccess()) {
MessageFuture messageFuture1 = futures.remove(rpcMessage.getId());
if (messageFuture1 != null) {
messageFuture1.setResultMessage(future.cause());
}
destroyChannel(future.channel());
}
});
try {
// 等待结果,
// TC 服务端返回的响应最终会到ClientOnResponseProcessor进行处理
// 通过ClientOnResponseProcessor关联MessageFuture获取结果
Object result = messageFuture.get(timeoutMillis, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
doAfterRpcHooks(remoteAddr, rpcMessage, result);
return result;
} catch (Exception exx) {
LOGGER.error("wait response error:{},ip:{},request:{}", exx.getMessage(), channel.remoteAddress(),
rpcMessage.getBody());
if (exx instanceof TimeoutException) {
throw (TimeoutException) exx;
} else {
throw new RuntimeException(exx);
}
}
} 这里发送请求的代码很简单,如果是支持批量提交请求,将请求封装成MessageFuture放入basketMap中就行了,由MergedSendRunnable轮询basketMap中的任务,批量发送请求。
如果不支持批量发送,那么通过NettyClientChannelManager获取channel写入数据,但不管是不是支持批量,都是将请求封装成MessageFuture放入futures,以获取响应结果。那响应结果又是如何放入到MessageFuture中的呢?这个后面说,先来看看MergedSendRunnable
前面我们分析在初始化时,如果支持批量发送请求,会启动一个单线程执行MergedSendRunnable任务批量发送请求,现在来看看MergedSendRunnable的具体实现
public abstract class AbstractNettyRemotingClient extends AbstractNettyRemoting implements RemotingClient {
@Override
public void init() {
//启动定时器,发起RM注册请求,与TC服务端保持连接,保活
timerExecutor.scheduleAtFixedRate(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
// 利用前面介绍的NettyClientChannelManager与server端注册连接。
clientChannelManager.reconnect(getTransactionServiceGroup());
}
}, SCHEDULE_DELAY_MILLS, SCHEDULE_INTERVAL_MILLS, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
......
}
private class MergedSendRunnable implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
// 典型的生产-消费模式
while (true) {
synchronized (mergeLock) {
try {
mergeLock.wait(MAX_MERGE_SEND_MILLS);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
}
isSending = true;
// 遍历 serverAddress >> 消息请求阻塞队列 map
basketMap.forEach((address, basket) -> {
if (basket.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
MergedWarpMessage mergeMessage = new MergedWarpMessage();
// 取出阻塞队列中所有请求,组装成MergedWarpMessage
while (!basket.isEmpty()) {
RpcMessage msg = basket.poll();
mergeMessage.msgs.add((AbstractMessage) msg.getBody());
mergeMessage.msgIds.add(msg.getId());
}
if (mergeMessage.msgIds.size() > 1) {
printMergeMessageLog(mergeMessage);
}
Channel sendChannel = null;
try {
// send batch message is sync request, but there is no need to get the return value.
// Since the messageFuture has been created before the message is placed in basketMap,
// the return value will be obtained in ClientOnResponseProcessor.
// 获取 TM/RM通道
sendChannel = clientChannelManager.acquireChannel(address);
// 批量发送请求,没必要获取返回值,请求通过绑定MessageFuture获取响应结果。
// 前面我们介绍过client注册2类processor,第1种:对TC发起的请求作响应的处理,第2种:对RM请求TC后,接收TC返回的响应作处理
// 很明显这里属于第2种,ClientOnResponseProcessor就是用来处理TC的响应结果,通过message ID关联了请求所绑定的MessageFuture
AbstractNettyRemotingClient.this.sendAsyncRequest(sendChannel, mergeMessage);
} catch (FrameworkException e) {
if (e.getErrcode() == FrameworkErrorCode.ChannelIsNotWritable && sendChannel != null) {
destroyChannel(address, sendChannel);
}
// fast fail
for (Integer msgId : mergeMessage.msgIds) {
MessageFuture messageFuture = futures.remove(msgId);
if (messageFuture != null) {
messageFuture.setResultMessage(null);
}
}
LOGGER.error("client merge call failed: {}", e.getMessage(), e);
}
});
isSending = false;
}
}
}
很明显,MergedSendRunnable就是在轮询basketMap中的请求对象,并将多个请求合并成MergedWarpMessage,发送给TC。
下面再来看看Cilent端是如何接收TC返回的响应,并返回结果到MessageFuture中。
TM / RM接收请求/响应
前面我们说过Client端接收到的请求/响应经过ProtocolV1Decoder解码器解码后,最终委托给了ClientHandler,下面就来看看ClientHandler
class ClientHandler extends ChannelDuplexHandler {
@Override
public void channelRead(final ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
if (!(msg instanceof RpcMessage)) {
return;
}
// 请求消息处理
processMessage(ctx, (RpcMessage) msg);
}
}
protected void processMessage(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, RpcMessage rpcMessage) throws Exception {
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOGGER.debug(String.format("%s msgId:%s, body:%s", this, rpcMessage.getId(), rpcMessage.getBody()));
}
//拿到消息体
Object body = rpcMessage.getBody();
if (body instanceof MessageTypeAware) {
MessageTypeAware messageTypeAware = (MessageTypeAware) body;
// MessageTypeAware 有非常多的子类,对应不同的请求类型
// 通过请求类型的code码 从processorTable中 找到 对应的RemotingProcessor
final Pair pair = this.processorTable.get((int) messageTypeAware.getTypeCode());
if (pair != null) {
if (pair.getSecond() != null) {
try {
// 有配置线程池,则异步执行,像分支提交、回滚请求对于client而已就是可以异步执行的
pair.getSecond().execute(() -> {
try {
// 执行procecc处理
pair.getFirst().process(ctx, rpcMessage);
} catch (Throwable th) {
LOGGER.error(FrameworkErrorCode.NetDispatch.getErrCode(), th.getMessage(), th);
} finally {
MDC.clear();
}
});
} catch (RejectedExecutionException e) {
......
}
} else {
try {
// 同步执行procecc处理
pair.getFirst().process(ctx, rpcMessage);
} catch (Throwable th) {
LOGGER.error(FrameworkErrorCode.NetDispatch.getErrCode(), th.getMessage(), th);
}
}
} else {
LOGGER.error("This message type [{}] has no processor.", messageTypeAware.getTypeCode());
}
} else {
LOGGER.error("This rpcMessage body[{}] is not MessageTypeAware type.", body);
}
} ClientHandler的核心逻辑就是根据请求对象的typeCode去map中查找对应的处理器,由对应的处理器执行具体处理逻辑,而Client端在初始化的时候就已经注册好了对应的处理器。
public final class RmNettyRemotingClient extends AbstractNettyRemotingClient {
@Override
public void init() {
// 这里很重要,根据请求和响应的类型注册各自的处理器,处理器分2类:
// 第1种:对TC发起的请求作响应的处理。RmBranchCommitProcessor、RmBranchRollbackProcessor、RmUndoLogProcessor
// 第2种:对RM请求TC后,接收TC返回的响应作处理。ClientOnResponseProcessor、ClientHeartbeatProcessor
registerProcessor();
if (initialized.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
// 接着往父类看
super.init();
// Found one or more resources that were registered before initialization
// 如果已经有分支注册到了resourceManager中,向TC发起RM注册,RM 通过channel与TC服务端建立连接,若未连接过,会开启一个channel(开启RM通信端口)
// 由于此时还未完成初始化,所以一般不会走这段逻辑
if (resourceManager != null
&& !resourceManager.getManagedResources().isEmpty()
&& StringUtils.isNotBlank(transactionServiceGroup)) {
getClientChannelManager().reconnect(transactionServiceGroup);
}
}
}
private void registerProcessor() {
// 1.registry rm client handle branch commit processor
// TC发起的RM分支提交请求处理
RmBranchCommitProcessor rmBranchCommitProcessor = new RmBranchCommitProcessor(getTransactionMessageHandler(), this);
super.registerProcessor(MessageType.TYPE_BRANCH_COMMIT, rmBranchCommitProcessor, messageExecutor);
// 2.registry rm client handle branch rollback processor
// TC发起的RM分支回滚请求处理
RmBranchRollbackProcessor rmBranchRollbackProcessor = new RmBranchRollbackProcessor(getTransactionMessageHandler(), this);
super.registerProcessor(MessageType.TYPE_BRANCH_ROLLBACK, rmBranchRollbackProcessor, messageExecutor);
// 3.registry rm handler undo log processor
// RM分支UndoLog删除请求处理
RmUndoLogProcessor rmUndoLogProcessor = new RmUndoLogProcessor(getTransactionMessageHandler());
super.registerProcessor(MessageType.TYPE_RM_DELETE_UNDOLOG, rmUndoLogProcessor, messageExecutor);
// 4.registry TC response processor
// 接收TC响应相关处理,注意看这里传入了uper.getFutures(),也就是MessageFuture的map
ClientOnResponseProcessor onResponseProcessor =
new ClientOnResponseProcessor(mergeMsgMap, super.getFutures(), getTransactionMessageHandler());
super.registerProcessor(MessageType.TYPE_SEATA_MERGE_RESULT, onResponseProcessor, null);
super.registerProcessor(MessageType.TYPE_BRANCH_REGISTER_RESULT, onResponseProcessor, null);
super.registerProcessor(MessageType.TYPE_BRANCH_STATUS_REPORT_RESULT, onResponseProcessor, null);
super.registerProcessor(MessageType.TYPE_GLOBAL_LOCK_QUERY_RESULT, onResponseProcessor, null);
super.registerProcessor(MessageType.TYPE_REG_RM_RESULT, onResponseProcessor, null);
super.registerProcessor(MessageType.TYPE_BATCH_RESULT_MSG, onResponseProcessor, null);
// 5.registry heartbeat message processor
// 向TC发起心跳请求
ClientHeartbeatProcessor clientHeartbeatProcessor = new ClientHeartbeatProcessor();
super.registerProcessor(MessageType.TYPE_HEARTBEAT_MSG, clientHeartbeatProcessor, null);
}
}
@Override
public void registerProcessor(int requestCode, RemotingProcessor processor, ExecutorService executor) {
Pair pair = new Pair<>(processor, executor);
// 注册到map中
this.processorTable.put(requestCode, pair);
} 分析到这里,逻辑已经很清晰,Client端接收到的请求/响应由对应的RemotingProcessor来处理,主要分2类:
- 处理TC发起的请求:RmBranchCommitProcessor、RmBranchRollbackProcessor、RmUndoLogProcessor (TM同理)
- 处理TC的响应:对RM请求TC后,TC返回的响应结果作处理。ClientOnResponseProcessor、ClientHeartbeatProcessor(TM同理)
也就是说TC返回的响应,由ClientOnResponseProcessor进行处理。
注意:注册ClientOnResponseProcessor时,futures对象跟ClientOnResponseProcessor绑定在一起了。那么一起来看看ClientOnResponseProcessor是如何关联MessageFuture获取响应结果的呢
public class ClientOnResponseProcessor implements RemotingProcessor {
/**
* The Merge msg map from io.seata.core.rpc.netty.AbstractNettyRemotingClient#mergeMsgMap.
*/
private Map mergeMsgMap;
/**
* The Futures from io.seata.core.rpc.netty.AbstractNettyRemoting#futures
*/
private final ConcurrentMap futures;
@Override
public void process(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, RpcMessage rpcMessage) throws Exception {
// 返回批量结果
if (rpcMessage.getBody() instanceof MergeResultMessage) {
MergeResultMessage results = (MergeResultMessage) rpcMessage.getBody();
MergedWarpMessage mergeMessage = (MergedWarpMessage) mergeMsgMap.remove(rpcMessage.getId());
for (int i = 0; i < mergeMessage.msgs.size(); i++) {
// 遍历每一个future,获取id
int msgId = mergeMessage.msgIds.get(i);
MessageFuture future = futures.remove(msgId);
if (future == null) {
if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOGGER.info("msg: {} is not found in futures.", msgId);
}
} else {
// 设置结果
future.setResultMessage(results.getMsgs()[i]);
}
}
} else if (rpcMessage.getBody() instanceof BatchResultMessage) {
// 1.5 可以使用BatchResultMessage替代MergeResultMessage,不再需要缓存mergeMsgMap
try {
BatchResultMessage batchResultMessage = (BatchResultMessage) rpcMessage.getBody();
for (int i = 0; i < batchResultMessage.getMsgIds().size(); i++) {
int msgId = batchResultMessage.getMsgIds().get(i);
// 遍历每一个future,获取id
MessageFuture future = futures.remove(msgId);
if (future == null) {
if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOGGER.info("msg: {} is not found in futures.", msgId);
}
} else {
// 设置结果
future.setResultMessage(batchResultMessage.getResultMessages().get(i));
}
}
} finally {
// In order to be compatible with the old version, in the batch sending of version 1.5.0,
// batch messages will also be placed in the local cache of mergeMsgMap,
// but version 1.5.0 no longer needs to obtain batch messages from mergeMsgMap
mergeMsgMap.clear();
}
} else {
// 同步发送的情况
MessageFuture messageFuture = futures.remove(rpcMessage.getId());
if (messageFuture != null) {
messageFuture.setResultMessage(rpcMessage.getBody());
} else {
if (rpcMessage.getBody() instanceof AbstractResultMessage) {
if (transactionMessageHandler != null) {
transactionMessageHandler.onResponse((AbstractResultMessage) rpcMessage.getBody(), null);
}
}
}
}
}
}
ClientOnResponseProcessor 根据请求ID,从futures中找到对应的MessageFuture,将结果set进去,到这里,client端就分析完了。下面继续看Server端的处理
Server端
TC浅析
直接来到Server端的启动类
public class Server {
public static void start(String[] args) {
// create logger
final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(Server.class);
//initialize the parameter parser
//Note that the parameter parser should always be the first line to execute.
//Because, here we need to parse the parameters needed for startup.
//启动参数
ParameterParser parameterParser = new ParameterParser(args);
//initialize the metrics
//统计指标
MetricsManager.get().init();
System.setProperty(ConfigurationKeys.STORE_MODE, parameterParser.getStoreMode());
// server端工作线程池
ThreadPoolExecutor workingThreads = new ThreadPoolExecutor(NettyServerConfig.getMinServerPoolSize(),
NettyServerConfig.getMaxServerPoolSize(), NettyServerConfig.getKeepAliveTime(), TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(NettyServerConfig.getMaxTaskQueueSize()),
new NamedThreadFactory("ServerHandlerThread", NettyServerConfig.getMaxServerPoolSize()), new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy());
// server端netty启动类
NettyRemotingServer nettyRemotingServer = new NettyRemotingServer(workingThreads);
UUIDGenerator.init(parameterParser.getServerNode());
//log store mode : file, db, redis
//存储模式
SessionHolder.init(parameterParser.getSessionStoreMode());
//锁管理
LockerManagerFactory.init(parameterParser.getLockStoreMode());
//这个是server端的消息处理器
DefaultCoordinator coordinator = DefaultCoordinator.getInstance(nettyRemotingServer);
//全局事务的重试提交/回滚、超时检测等
coordinator.init();
//绑定coordinator
nettyRemotingServer.setHandler(coordinator);
// let ServerRunner do destroy instead ShutdownHook, see https://github.com/seata/seata/issues/4028
// 使用spring的destroy钩子函数
ServerRunner.addDisposable(coordinator);
//127.0.0.1 and 0.0.0.0 are not valid here.
if (NetUtil.isValidIp(parameterParser.getHost(), false)) {
XID.setIpAddress(parameterParser.getHost());
} else {
String preferredNetworks = ConfigurationFactory.getInstance().getConfig(REGISTRY_PREFERED_NETWORKS);
if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(preferredNetworks)) {
XID.setIpAddress(NetUtil.getLocalIp(preferredNetworks.split(REGEX_SPLIT_CHAR)));
} else {
XID.setIpAddress(NetUtil.getLocalIp());
}
}
//重点看这里,server端初始化
nettyRemotingServer.init();
}
}来看看server端初始化都干了什么,首先看下NettyRemotingServer的构造方法
public class NettyRemotingServer extends AbstractNettyRemotingServer {
public NettyRemotingServer(ThreadPoolExecutor messageExecutor) {
super(messageExecutor, new NettyServerConfig());
}
}
public abstract class AbstractNettyRemotingServer extends AbstractNettyRemoting implements RemotingServer {
public AbstractNettyRemotingServer(ThreadPoolExecutor messageExecutor, NettyServerConfig nettyServerConfig) {
super(messageExecutor);
// netty server
serverBootstrap = new NettyServerBootstrap(nettyServerConfig);
// 这里很重要,将接收到的请求/响应委托给ServerHandler进行处理
serverBootstrap.setChannelHandlers(new ServerHandler());
}
} 构造方法中设置了netty的handler为ServerHandler,继续跟踪init方法
public class NettyRemotingServer extends AbstractNettyRemotingServer {
@Override
public void init() {
// registry processor
// 跟client端差不多,注册处理器
registerProcessor();
if (initialized.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
// 继续看父类init
super.init();
}
}
private void registerProcessor() {
// 1. registry on request message processor
// 1. ServerOnRequestProcessor 用于接收client端发送过来的请求
ServerOnRequestProcessor onRequestProcessor =
new ServerOnRequestProcessor(this, getHandler());
ShutdownHook.getInstance().addDisposable(onRequestProcessor);
super.registerProcessor(MessageType.TYPE_BRANCH_REGISTER, onRequestProcessor, messageExecutor);
super.registerProcessor(MessageType.TYPE_BRANCH_STATUS_REPORT, onRequestProcessor, messageExecutor);
super.registerProcessor(MessageType.TYPE_GLOBAL_BEGIN, onRequestProcessor, messageExecutor);
super.registerProcessor(MessageType.TYPE_GLOBAL_COMMIT, onRequestProcessor, messageExecutor);
super.registerProcessor(MessageType.TYPE_GLOBAL_LOCK_QUERY, onRequestProcessor, messageExecutor);
super.registerProcessor(MessageType.TYPE_GLOBAL_REPORT, onRequestProcessor, messageExecutor);
super.registerProcessor(MessageType.TYPE_GLOBAL_ROLLBACK, onRequestProcessor, messageExecutor);
super.registerProcessor(MessageType.TYPE_GLOBAL_STATUS, onRequestProcessor, messageExecutor);
super.registerProcessor(MessageType.TYPE_SEATA_MERGE, onRequestProcessor, messageExecutor);
// 2. registry on response message processor
// 2. ServerOnResponseProcessor 用于处理TC请求client后 client返回的响应
ServerOnResponseProcessor onResponseProcessor =
new ServerOnResponseProcessor(getHandler(), getFutures());
super.registerProcessor(MessageType.TYPE_BRANCH_COMMIT_RESULT, onResponseProcessor, branchResultMessageExecutor);
super.registerProcessor(MessageType.TYPE_BRANCH_ROLLBACK_RESULT, onResponseProcessor, branchResultMessageExecutor);
// 3. registry rm message processor
// 3. RegRmProcessor 用于处理RM注册请求
RegRmProcessor regRmProcessor = new RegRmProcessor(this);
super.registerProcessor(MessageType.TYPE_REG_RM, regRmProcessor, messageExecutor);
// 4. registry tm message processor
// 4. RegTmProcessor 用于处理TM注册请求
RegTmProcessor regTmProcessor = new RegTmProcessor(this);
super.registerProcessor(MessageType.TYPE_REG_CLT, regTmProcessor, null);
// 5. registry heartbeat message processor
// 5. ServerHeartbeatProcessor向client返回心跳响应结果
ServerHeartbeatProcessor heartbeatMessageProcessor = new ServerHeartbeatProcessor(this);
super.registerProcessor(MessageType.TYPE_HEARTBEAT_MSG, heartbeatMessageProcessor, null);
}
}基本模式跟client端是一样的,也是注册了一堆各类请求的处理器,继续跟踪父类init
public abstract class AbstractNettyRemotingServer extends AbstractNettyRemoting implements RemotingServer {
@Override
public void init() {
// 检查超时的messageFuture
super.init();
// 重点在这里,启动netty server
serverBootstrap.start();
}
}
public class NettyServerBootstrap implements RemotingBootstrap {
@Override
public void start() {
// 一堆netty相关配置
this.serverBootstrap.group(this.eventLoopGroupBoss, this.eventLoopGroupWorker)
.channel(NettyServerConfig.SERVER_CHANNEL_CLAZZ)
.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, nettyServerConfig.getSoBackLogSize())
.option(ChannelOption.SO_REUSEADDR, true)
.childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true)
.childOption(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY, true)
.childOption(ChannelOption.SO_SNDBUF, nettyServerConfig.getServerSocketSendBufSize())
.childOption(ChannelOption.SO_RCVBUF, nettyServerConfig.getServerSocketResvBufSize())
.childOption(ChannelOption.WRITE_BUFFER_WATER_MARK,
new WriteBufferWaterMark(nettyServerConfig.getWriteBufferLowWaterMark(),
nettyServerConfig.getWriteBufferHighWaterMark()))
.localAddress(new InetSocketAddress(getListenPort()))
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer() {
@Override
public void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) {
ch.pipeline().addLast(new IdleStateHandler(nettyServerConfig.getChannelMaxReadIdleSeconds(), 0, 0))
// seata协议解码器
.addLast(new ProtocolV1Decoder())
// seata协议编码器
.addLast(new ProtocolV1Encoder());
if (channelHandlers != null) {
// 将收到的请求委托给 ServerHandler处理
addChannelPipelineLast(ch, channelHandlers);
}
}
});
try {
this.serverBootstrap.bind(getListenPort()).sync();
XID.setPort(getListenPort());
LOGGER.info("Server started, service listen port: {}", getListenPort());
// 注册到注册中心
RegistryFactory.getInstance().register(new InetSocketAddress(XID.getIpAddress(), XID.getPort()));
initialized.set(true);
} catch (SocketException se) {
throw new RuntimeException("Server start failed, the listen port: " + getListenPort(), se);
} catch (Exception exx) {
throw new RuntimeException("Server start failed", exx);
}
}
}
从代码中,我们看到server端发送请求一样是经过ProtocolV1Encoder,接收请求也是经过ProtocolV1Decoder最后委托给了ServerHandler进行处理
class ServerHandler extends ChannelDuplexHandler {
/**
* Channel read.
*
* @param ctx the ctx
* @param msg the msg
* @throws Exception the exception
*/
@Override
public void channelRead(final ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
if (!(msg instanceof RpcMessage)) {
return;
}
// 找到各类请求对应的请求处理器,进行处理
processMessage(ctx, (RpcMessage) msg);
}
} 处理机制跟Client端是一样的,都是通过RemotingProcessor来处理。到这里,初始化就告一段落。
接下来看下TC是如何接收RM/TM的注册请求的,我们前面分析了RM/TM通过注册中心查找到TC的服务端口,向TC发起注册,打开channel端口。那TC如果要访问Client端,又是如何找到RM/TM的channel的呢?答案就在RegRmProcessor 和 RegTmProcessor中。
public class RegRmProcessor implements RemotingProcessor {
@Override
public void process(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, RpcMessage rpcMessage) throws Exception {
//处理RM注册消息
onRegRmMessage(ctx, rpcMessage);
}
private void onRegRmMessage(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, RpcMessage rpcMessage) {
RegisterRMRequest message = (RegisterRMRequest) rpcMessage.getBody();
// client端ip 端口
String ipAndPort = NetUtil.toStringAddress(ctx.channel().remoteAddress());
boolean isSuccess = false;
String errorInfo = StringUtils.EMPTY;
try {
if (null == checkAuthHandler || checkAuthHandler.regResourceManagerCheckAuth(message)) {
// 注册RM最重要的一部,就是将对应的channel缓存到ChannelManager中
ChannelManager.registerRMChannel(message, ctx.channel());
Version.putChannelVersion(ctx.channel(), message.getVersion());
isSuccess = true;
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOGGER.debug("RM checkAuth for client:{},vgroup:{},applicationId:{} is OK", ipAndPort, message.getTransactionServiceGroup(), message.getApplicationId());
}
} else {
if (LOGGER.isWarnEnabled()) {
LOGGER.warn("RM checkAuth for client:{},vgroup:{},applicationId:{} is FAIL", ipAndPort, message.getTransactionServiceGroup(), message.getApplicationId());
}
}
} catch (Exception exx) {
isSuccess = false;
errorInfo = exx.getMessage();
LOGGER.error("RM register fail, error message:{}", errorInfo);
}
RegisterRMResponse response = new RegisterRMResponse(isSuccess);
if (StringUtils.isNotEmpty(errorInfo)) {
response.setMsg(errorInfo);
}
remotingServer.sendAsyncResponse(rpcMessage, ctx.channel(), response);
if (isSuccess && LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOGGER.info("RM register success,message:{},channel:{},client version:{}", message, ctx.channel(),
message.getVersion());
}
}
}重点关注ChannelManager
public class ChannelManager {
/**
* channel -> RpcContext
*/
private static final ConcurrentMap IDENTIFIED_CHANNELS = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
/**RM缓存
* resourceId -> applicationId -> ip -> port -> RpcContext
*/
private static final ConcurrentMap>>> RM_CHANNELS = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
/**TM缓存
* ip+appname,port
*/
private static final ConcurrentMap> TM_CHANNELS
= new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
/**
* Register tm channel.
*
* @param request the request
* @param channel the channel
* @throws IncompatibleVersionException the incompatible version exception
*/
public static void registerTMChannel(RegisterTMRequest request, Channel channel)
throws IncompatibleVersionException {
Version.checkVersion(request.getVersion());
// 组装TM的RpcContext,包括版本号、应用id、group、resouceId集合
// 完成 Channel >> RpcContext的映射
RpcContext rpcContext = buildChannelHolder(NettyPoolKey.TransactionRole.TMROLE, request.getVersion(),
request.getApplicationId(),
request.getTransactionServiceGroup(),
null, channel);
rpcContext.holdInIdentifiedChannels(IDENTIFIED_CHANNELS);
// 按照 应用id+ip -> port -> rpcContext 缓存TM注册信息到TM_CHANNELS中
String clientIdentified = rpcContext.getApplicationId() + Constants.CLIENT_ID_SPLIT_CHAR
+ ChannelUtil.getClientIpFromChannel(channel);
ConcurrentMap clientIdentifiedMap = CollectionUtils.computeIfAbsent(TM_CHANNELS,
clientIdentified, key -> new ConcurrentHashMap<>());
rpcContext.holdInClientChannels(clientIdentifiedMap);
}
/**
* Register rm channel.
*
* @param resourceManagerRequest the resource manager request
* @param channel the channel
* @throws IncompatibleVersionException the incompatible version exception
*/
public static void registerRMChannel(RegisterRMRequest resourceManagerRequest, Channel channel)
throws IncompatibleVersionException {
Version.checkVersion(resourceManagerRequest.getVersion());
// rm resourceid集合
Set dbkeySet = dbKeytoSet(resourceManagerRequest.getResourceIds());
RpcContext rpcContext;
// 组装rm的RpcContext,包括版本号、应用id、group、resouceId集合
// 完成 Channel >> RpcContext的映射
if (!IDENTIFIED_CHANNELS.containsKey(channel)) {
rpcContext = buildChannelHolder(NettyPoolKey.TransactionRole.RMROLE, resourceManagerRequest.getVersion(),
resourceManagerRequest.getApplicationId(), resourceManagerRequest.getTransactionServiceGroup(),
resourceManagerRequest.getResourceIds(), channel);
rpcContext.holdInIdentifiedChannels(IDENTIFIED_CHANNELS);
} else {
rpcContext = IDENTIFIED_CHANNELS.get(channel);
rpcContext.addResources(dbkeySet);
}
if (dbkeySet == null || dbkeySet.isEmpty()) { return; }
for (String resourceId : dbkeySet) {
String clientIp;
// 按照 resourceId -> applicationId -> ip -> port -> RpcContext 缓存RM注册信息到RM_CHANNELS中
ConcurrentMap portMap = CollectionUtils.computeIfAbsent(RM_CHANNELS, resourceId, key -> new ConcurrentHashMap<>())
.computeIfAbsent(resourceManagerRequest.getApplicationId(), key -> new ConcurrentHashMap<>())
.computeIfAbsent(clientIp = ChannelUtil.getClientIpFromChannel(channel), key -> new ConcurrentHashMap<>());
rpcContext.holdInResourceManagerChannels(resourceId, portMap);
updateChannelsResource(resourceId, clientIp, resourceManagerRequest.getApplicationId());
}
}
/**
* Gets get same income client channel.
* 获取同一个客户端,主要是检活。
* 用于响应Client端的请求
* @param channel the channel
* @return the get same income client channel
*/
public static Channel getSameClientChannel(Channel channel) {
if (channel.isActive()) {
return channel;
}
// 直接尝试根据channel获取rpcContext,理论上将是一定有值的
// 因为这个方法使用场景是在client端发送请求,TC响应回去使用的
RpcContext rpcContext = getContextFromIdentified(channel);
if (rpcContext == null) {
LOGGER.error("rpcContext is null,channel:{},active:{}", channel, channel.isActive());
return null;
}
// 检活
if (rpcContext.getChannel().isActive()) {
// recheck 还活着直接返回
return rpcContext.getChannel();
}
// 走到这里就说明IDENTIFIED_CHANNELS缓存中的这个已经断开了,得看看是不是有其他的channel可以用
// 获取client的端口号
Integer clientPort = ChannelUtil.getClientPortFromChannel(channel);
NettyPoolKey.TransactionRole clientRole = rpcContext.getClientRole();
// 如果是TM的请求,直接通过 应用id、ip、port从TM_CHANNELS缓存中查找相同IP,但不同port的channel
if (clientRole == NettyPoolKey.TransactionRole.TMROLE) {
String clientIdentified = rpcContext.getApplicationId() + Constants.CLIENT_ID_SPLIT_CHAR
+ ChannelUtil.getClientIpFromChannel(channel);
if (!TM_CHANNELS.containsKey(clientIdentified)) {
return null;
}
ConcurrentMap clientRpcMap = TM_CHANNELS.get(clientIdentified);
return getChannelFromSameClientMap(clientRpcMap, clientPort);
} else if (clientRole == NettyPoolKey.TransactionRole.RMROLE) {
// 如果是RM的请求,从rpcContext的缓存中查找相同IP,但不同port的channel
for (Map clientRmMap : rpcContext.getClientRMHolderMap().values()) {
Channel sameClientChannel = getChannelFromSameClientMap(clientRmMap, clientPort);
if (sameClientChannel != null) {
return sameClientChannel;
}
}
}
return null;
}
/**
* Gets get channel.
* 根据resourceId,clientId 获取Channel。
* 用于TC向client端发起分支事务的提交/回滚请求
* @param resourceId Resource ID
* @param clientId Client ID - ApplicationId:IP:Port
* @return Corresponding channel, NULL if not found.
*/
public static Channel getChannel(String resourceId, String clientId) {
Channel resultChannel = null;
String[] clientIdInfo = readClientId(clientId);
if (clientIdInfo == null || clientIdInfo.length != 3) {
throw new FrameworkException("Invalid Client ID: " + clientId);
}
// 应用id
String targetApplicationId = clientIdInfo[0];
// IP
String targetIP = clientIdInfo[1];
// 端口
int targetPort = Integer.parseInt(clientIdInfo[2]);
// 先用resourceid找第一层map
ConcurrentMap>> applicationIdMap = RM_CHANNELS.get(resourceId);
if (targetApplicationId == null || applicationIdMap == null || applicationIdMap.isEmpty()) {
if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOGGER.info("No channel is available for resource[{}]", resourceId);
}
return null;
}
// 接着用 应用id找第2层map
ConcurrentMap> ipMap = applicationIdMap.get(targetApplicationId);
if (ipMap != null && !ipMap.isEmpty()) {
// Firstly, try to find the original channel through which the branch was registered.
// 优先找 注册分支的那个channel通道(ip+port)
ConcurrentMap portMapOnTargetIP = ipMap.get(targetIP);
if (portMapOnTargetIP != null && !portMapOnTargetIP.isEmpty()) {
RpcContext exactRpcContext = portMapOnTargetIP.get(targetPort);
if (exactRpcContext != null) {
Channel channel = exactRpcContext.getChannel();
if (channel.isActive()) {
resultChannel = channel;
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOGGER.debug("Just got exactly the one {} for {}", channel, clientId);
}
} else {
// 不可用,移除
if (portMapOnTargetIP.remove(targetPort, exactRpcContext)) {
if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOGGER.info("Removed inactive {}", channel);
}
}
}
}
// The original channel was broken, try another one.
// 注册分支的那个channel不可用,继续循环遍历同一台机器的其他channel(port)
if (resultChannel == null) {
for (ConcurrentMap.Entry portMapOnTargetIPEntry : portMapOnTargetIP
.entrySet()) {
Channel channel = portMapOnTargetIPEntry.getValue().getChannel();
if (channel.isActive()) {
resultChannel = channel;
if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOGGER.info(
"Choose {} on the same IP[{}] as alternative of {}", channel, targetIP, clientId);
}
break;
} else {
// 不可用的都移除
if (portMapOnTargetIP.remove(portMapOnTargetIPEntry.getKey(),
portMapOnTargetIPEntry.getValue())) {
if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOGGER.info("Removed inactive {}", channel);
}
}
}
}
}
}
// No channel on the this app node, try another one.
// 尝试寻找这个resource的其他机器
if (resultChannel == null) {
for (ConcurrentMap.Entry> ipMapEntry : ipMap
.entrySet()) {
if (ipMapEntry.getKey().equals(targetIP)) { continue; }
ConcurrentMap portMapOnOtherIP = ipMapEntry.getValue();
if (portMapOnOtherIP == null || portMapOnOtherIP.isEmpty()) {
continue;
}
for (ConcurrentMap.Entry portMapOnOtherIPEntry : portMapOnOtherIP.entrySet()) {
Channel channel = portMapOnOtherIPEntry.getValue().getChannel();
if (channel.isActive()) {
resultChannel = channel;
if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOGGER.info("Choose {} on the same application[{}] as alternative of {}", channel, targetApplicationId, clientId);
}
break;
} else {
if (portMapOnOtherIP.remove(portMapOnOtherIPEntry.getKey(),
portMapOnOtherIPEntry.getValue())) {
if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOGGER.info("Removed inactive {}", channel);
}
}
}
}
if (resultChannel != null) { break; }
}
}
}
if (resultChannel == null) {
resultChannel = tryOtherApp(applicationIdMap, targetApplicationId);
if (resultChannel == null) {
if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOGGER.info("No channel is available for resource[{}] as alternative of {}", resourceId, clientId);
}
} else {
if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOGGER.info("Choose {} on the same resource[{}] as alternative of {}", resultChannel, resourceId, clientId);
}
}
}
return resultChannel;
}
} 通过ChannelManager的缓存就可以快速的查找到Client端对应的Channel了。
总的来说,TC端请求发送/接收套路跟Client端是一样的,只有一些细节上的差异,比如说TC是不需要批量提交请求的,Client端通过注册中心拉取Server端IP端口,建立连接。而TC端只需要从缓存中获取到已经建立好的Channel就可以进行通信了。