【数据压缩(六)】基于C++实现LZW编解码算法
基于C++实现LZW编解码算法
- 一、实验目的
- 二、实验要求
- 三、实验原理
-
- 1、LZW编码
- 2、LZW解码
- 三、实验代码
-
- 1、`bitio.h`头文件
- 2、`main`函数
- 3、`OpenBitFileInput`函数和`OpenBitFileOutput`函数
- 4、LZW编码部分
- 5、LZW解码部分
- 6、`CloseBitFileOutput`函数
- 四、代码测试
-
- 1、LZW编码
- 2、LZW解码
- 五、压缩效率分析
- 六、总结
一、实验目的
- 掌握词典编码的基本原理。
- 在已有LZW编码器的基础上用C++语言编程实现LZW解码器。
- 分析编解码算法。
二、实验要求
- 首先调试LZW的编码程序,以一个文本文件作为输入,得到输出的 LZW 编码文件。
- 以实验步骤一得到的编码文件作为输入编写LZW的解码程序。在写解码程序时需要对关键语句加上注释,并说明进行何操作。 在实验报告中重点说明当前码字在词典中不存在时应如何处理并解释原因。
- 选择至少十种不同格式类型的文件,使用LZW编码器进行压缩得到输出的压缩比特流文件。对各种不同格式的文件进行压缩效率的分析。
- 总结LZW编解码原理及编程实现的算法并写成实验报告。实验报告中应完成实验步骤中的要求 。
三、实验原理
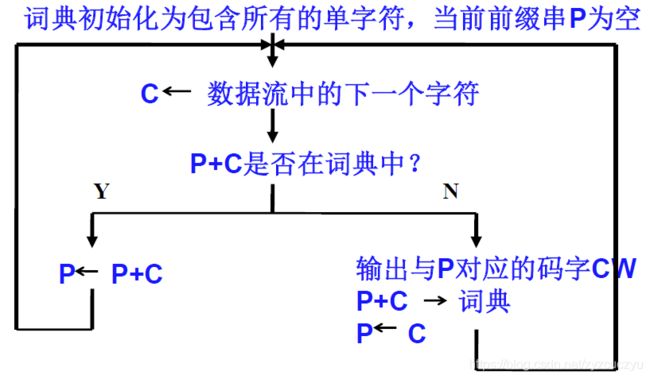
1、LZW编码
- LZW的编码思想是不断地从字符流中提取新的字符串,通俗地理解为新“词条”,然后用“代号”也就是码字表示这个“词条”。这样一来,对字符流的编码就变成了用码字去替换字符流,生成码字流,从而达到压缩数据的目的。
- LZW编码是围绕称为词典的转换表来完成的。LZW编码器通过管理这个词典完成输入与输出之间的转换。
- LZW编码器的输入是字符流,字符流可以是用8位ASCII字符组成的字符串,而输出是用n位(例如12位)表示的码字流。
- 编码步骤如下:
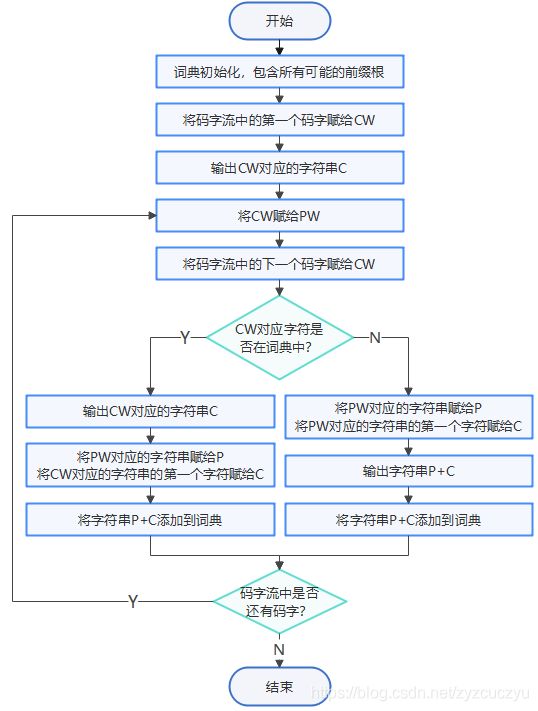
2、LZW解码
- LZW解码算法开始时,译码词典和编码词典相同,包含所有可能的前缀根。
- 解码步骤如下:
- 关于解码时遇到CW对应字符不在词典中的情况举例分析:
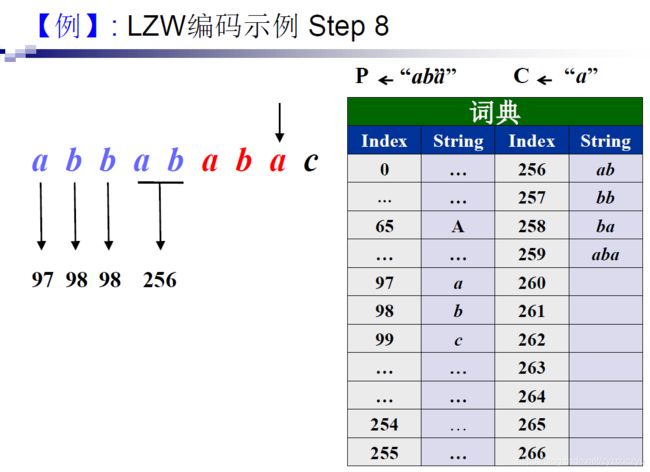
编码示例:
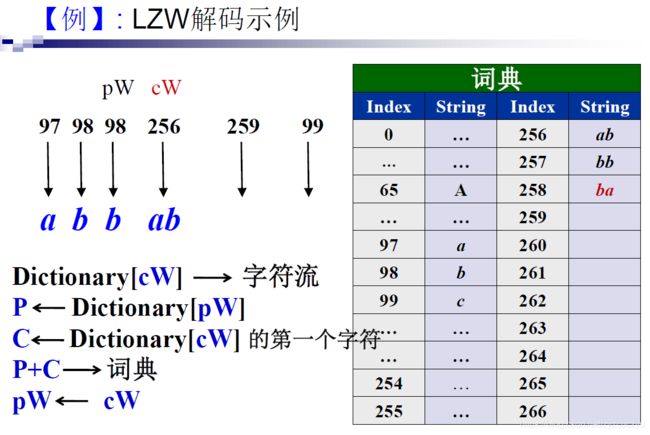
解码示例:
问题:
在编码时,当aba刚加入词典,下一个编码立刻就用到了它,又因为编码比解码快一步,这将导致在解码时,遇到码字259时,词典中并没有对应字符串,无法解码。
解决:
观察可知,只有形如aba这样的头尾字符相同的字符串才会出现这种问题,因此在解码时,遇到无法解出码字的情况时,按照流程图中所说,将PW对应字符串和PW对应字符串的第一个字符拼接即可解出,并将其加入词典。
三、实验代码
1、bitio.h头文件
声明了本次实验中要用到的结构体和方法函数。
/*
* Declaration for bitwise IO
*
* vim: ts=4 sw=4 cindent
*/
#ifndef __BITIO__
#define __BITIO__
#include 2、main函数
主函数即为实际的编解码过程。
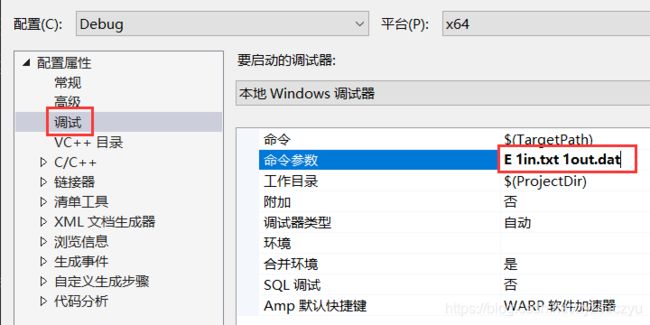
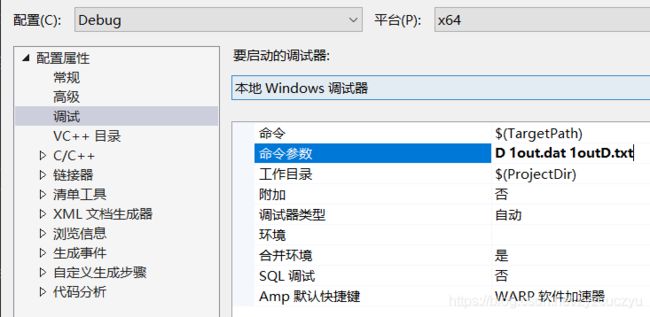
在调试属性内更改命令参数。第一个参数为E时,进行编码操作;第一个参数为D时,进行解码操作。
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
FILE* fp;
BITFILE* bf;
if (4 > argc) {
fprintf(stdout, "usage: \n%s \n" , argv[0]);
fprintf(stdout, "\t: E or D reffers encode or decode\n" );
fprintf(stdout, "\t: input file name\n" );
fprintf(stdout, "\t: output file name\n" );
return -1;
}
if ('E' == argv[1][0]) { // do encoding
fp = fopen(argv[2], "rb");
bf = OpenBitFileOutput(argv[3]);
if (NULL != fp && NULL != bf) {
LZWEncode(fp, bf);
fclose(fp);
CloseBitFileOutput(bf);
fprintf(stdout, "encoding done\n");
}
}
else if ('D' == argv[1][0]) { // do decoding
bf = OpenBitFileInput(argv[2]);
fp = fopen(argv[3], "wb");
if (NULL != fp && NULL != bf) {
LZWDecode(bf, fp);
fclose(fp);
CloseBitFileInput(bf);
fprintf(stdout, "decoding done\n");
}
}
else { // otherwise
fprintf(stderr, "not supported operation\n");
}
return 0;
}
3、OpenBitFileInput函数和OpenBitFileOutput函数
二进制输入文件和输出文件的打开。
BITFILE *OpenBitFileInput( char *filename){
BITFILE *bf;
bf = (BITFILE *)malloc( sizeof(BITFILE));
if( NULL == bf) return NULL;
if( NULL == filename) bf->fp = stdin;
else bf->fp = fopen( filename, "rb");
if( NULL == bf->fp) return NULL;
bf->mask = 0x80;
bf->rack = 0;
return bf;
}
BITFILE *OpenBitFileOutput( char *filename){
BITFILE *bf;
bf = (BITFILE *)malloc( sizeof(BITFILE));
if( NULL == bf) return NULL;
if( NULL == filename) bf->fp = stdout;
else bf->fp = fopen( filename, "wb");
if( NULL == bf->fp) return NULL;
bf->mask = 0x80;
bf->rack = 0;
return bf;
}
4、LZW编码部分
LZWEncode函数
即:LZW编码过程。
void LZWEncode(FILE* fp, BITFILE* bf) {
int character;
int string_code;
int index;
unsigned long file_length;
fseek(fp, 0, SEEK_END);
file_length = ftell(fp);
fseek(fp, 0, SEEK_SET);
BitsOutput(bf, file_length, 4 * 8);
InitDictionary();
string_code = -1;
while (EOF != (character = fgetc(fp))) {
index = InDictionary(character, string_code);
if (0 <= index) { // string+character in dictionary
string_code = index;
}
else { // string+character not in dictionary
output(bf, string_code);
if (MAX_CODE > next_code) { // free space in dictionary
// add string+character to dictionary
AddToDictionary(character, string_code);
}
string_code = character;
}
}
output(bf, string_code);
}
InitDictionary函数
词典初始化。
void InitDictionary(void) {
int i;
for (i = 0; i < 256; i++) {
dictionary[i].suffix = i;
dictionary[i].parent = -1;
dictionary[i].firstchild = -1;
dictionary[i].nextsibling = i + 1;
}
dictionary[255].nextsibling = -1;
next_code = 256;
}
InDictionary函数
判断character是否在词典中。
int InDictionary(int character, int string_code) {
int sibling;
if (0 > string_code) return character;
sibling = dictionary[string_code].firstchild;
while (-1 < sibling) {
if (character == dictionary[sibling].suffix) return sibling;
sibling = dictionary[sibling].nextsibling;
}
return -1;
}
BitOutput函数
向输出文件中写入数据。
#define output(f, x) BitsOutput( f, (unsigned long)(x), 16)
void BitOutput( BITFILE *bf, int bit){
if( 0 != bit) bf->rack |= bf->mask;
bf->mask >>= 1;
if( 0 == bf->mask){ // eight bits in rack
fputc( bf->rack, bf->fp);
bf->rack = 0;
bf->mask = 0x80;
}
}
AddToDictionary函数
将新字符串写入词典。
void AddToDictionary(int character, int string_code) {
int firstsibling, nextsibling;
if (0 > string_code) return;
dictionary[next_code].suffix = character;
dictionary[next_code].parent = string_code;
dictionary[next_code].nextsibling = -1;
dictionary[next_code].firstchild = -1;
firstsibling = dictionary[string_code].firstchild;
if (-1 < firstsibling) { // the parent has child
nextsibling = firstsibling;
while (-1 < dictionary[nextsibling].nextsibling)
nextsibling = dictionary[nextsibling].nextsibling;
dictionary[nextsibling].nextsibling = next_code;
}
else {// no child before, modify it to be the first
dictionary[string_code].firstchild = next_code;
}
next_code++;
}
5、LZW解码部分
LZWDecode函数
即:LZW解码过程。
void LZWDecode(BITFILE* bf, FILE* fp) {
int character;
int new_code, last_code;
int phrase_length;
unsigned long file_length;
file_length = BitsInput(bf, 4 * 8);
if (-1 == file_length) file_length = 0;
/*需填充*/
InitDictionary();//初始化词典
last_code = -1;
while (0 < file_length) {
new_code = input(bf);
if (new_code >= next_code) { // this is the case CSCSC( not in dict)
d_stack[0] = character;
phrase_length = DecodeString(1, last_code);
}
else {
phrase_length = DecodeString(0, new_code);
}
character = d_stack[phrase_length - 1];
while (0 < phrase_length) {
phrase_length--;
fputc(d_stack[phrase_length], fp);
file_length--;
}
if (MAX_CODE > next_code) {// add the new phrase to dictionary
AddToDictionary(character, last_code);
}
last_code = new_code;
}
}
BitsInput函数
输入比特流函数。
unsigned long BitsInput( BITFILE *bf, int count){
unsigned long mask;
unsigned long value;
mask = 1L << (count-1);
value = 0L;
while( 0!=mask){
if( 1 == BitInput( bf))
value |= mask;
mask >>= 1;
}
return value;
}
- 其中调用了
BitInput函数:
int BitInput( BITFILE *bf){
int value;
if( 0x80 == bf->mask){
bf->rack = fgetc( bf->fp);
if( EOF == bf->rack){
fprintf(stderr, "Read after the end of file reached\n");
exit( -1);
}
}
value = bf->mask & bf->rack;
bf->mask >>= 1;
if( 0==bf->mask) bf->mask = 0x80;
return( (0==value)?0:1);
}
Input函数
类型转换为int型后的BitsInput函数
#define input(f) ((int)BitsInput( f, 16))
DecodeString函数
对码字进行解码得到字符。
int DecodeString(int start, int code) {
int count;
count = start;
while (0 <= code) {
d_stack[count] = dictionary[code].suffix;
code = dictionary[code].parent;
count++;
}
return count;
}
6、CloseBitFileOutput函数
二进制文件关闭。
void CloseBitFileOutput( BITFILE *bf){
// Output the remaining bits
if( 0x80 != bf->mask) fputc( bf->rack, bf->fp);
fclose( bf->fp);
free( bf);
}
四、代码测试
1、LZW编码
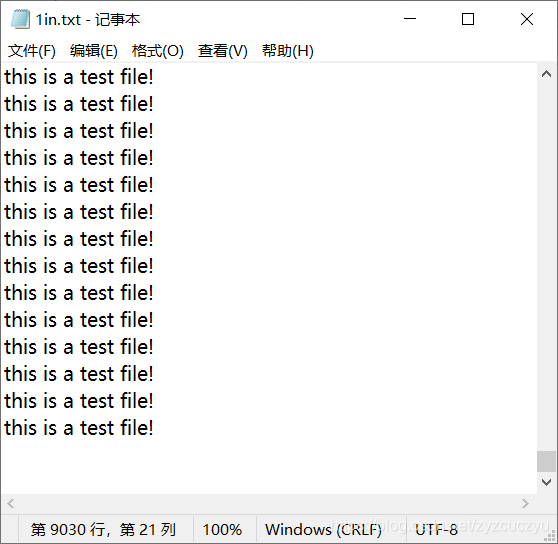
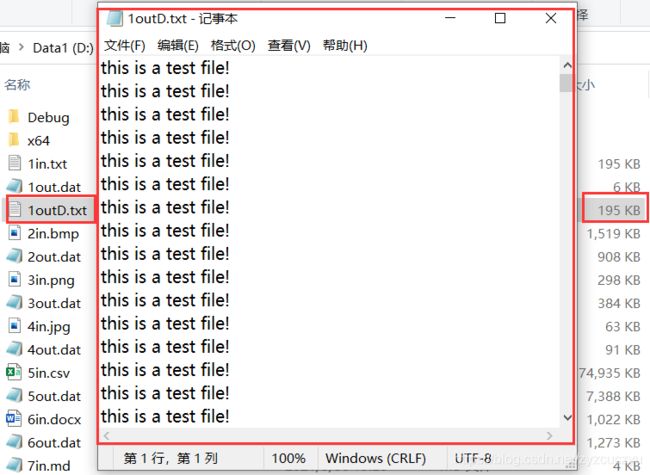
以一个简单的txt文件为例:
可以看到编码效果非常明显,编码成功。
2、LZW解码
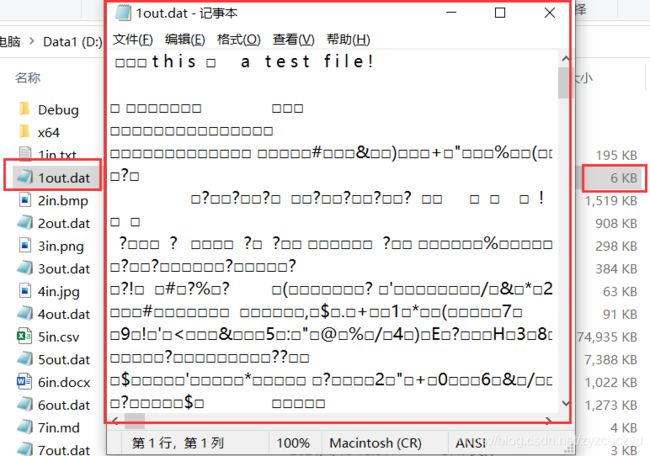
对刚刚编码所得到的二进制文件1out.dat进行解码
可以看到经过解码过后与原来编码前的内容一样,大小一样,解码成功。
五、压缩效率分析
本次实验选择了十种不同格式类型的文件,使用LZW编码器进行压缩得到输出的压缩比特流文件。
压缩前后文件大小如下:
| 文件格式 | 压缩前大小 | 压缩后大小 | 压缩率 |
|---|---|---|---|
| .txt | 195 KB | 6 KB | 3.08% |
| .bmp | 1519 KB | 908 KB | 59.78% |
| .png | 298 KB | 384 KB | 128.86% |
| .jpg | 63 KB | 91 KB | 144.44% |
| .csv | 74935 KB | 7388 KB | 9.86% |
| .docx | 1022 KB | 1273 KB | 124.56% |
| .md | 4 KB | 3 KB | 75.00% |
| .rgb | 192 KB | 179 KB | 93.23% |
| .yuv | 96 KB | 69 KB | 71.88% |
| 3818 KB | 4605 KB | 120.61% |
观察发现,十个文件中,有四个文件在LZW编码后反而变得更大了。
分别查阅了这四种格式文件的资料发现:
- png格式已经是压缩过的文件格式,并且压缩算法更厉害。以下来自百度百科。
png是一种采用无损压缩算法的位图格式,其设计目的是试图替代GIF和TIFF文件格式,同时增加一些GIF文件格式所不具备的特性。PNG使用从LZ77派生的无损数据压缩算法,一般应用于JAVA程序、网页或S60程序中,原因是它压缩比高,生成文件体积小。
- jpg格式同样也是压缩过的文件格式。以下来自百度百科。
JPEG压缩技术十分先进,它可以用有损压缩方式去除冗余的图像数据,换句话说,就是可以用较少的磁盘空间得到较好的图像品质。
六、总结
- 本次实验可以得出一些粗浅的结论,LZW编码在对重复率高的内容压缩效果较好,如
txt csv等文件类型,而对于图片类,已压缩的图片无法起到压缩效果,反而会使文件增大。 - 从理论分析,LZW主要是通过构建词汇表进行编解码,因此也不难得出结论,对于重复率高的内容压缩效果很好。
- 而对于文件大小经过LZW压缩后不减反增的原因,首先可能是文件内容本身重复性就不高,在编码时甚至可能标号所占字节数比原数据都多;其次可能是已经经过压缩的内容,重复性同样已经减少到了一定程度,经过LZW压缩也可能大小不减反增。