基于ROS的OMPL库RRT*算法代码学习
基于ROS的OMPL库RRT*算法代码学习
-
- 过程演示
- ROS包
- 主要程序文件demo_node.cpp
- 参考引用
本文是在学习路径规划算法中的一篇学习记录,由于对c++掌握粗浅,将整个代码进行了详细的梳理,由于代码中有很多是之前梳理过的《基于ROS的A*算法代码学习》中的,对本文graph_searcher.h注释可参考上一篇的Astar_searcher.h; node.h注释可参考上一篇的node.h; graph_searcher.cpp注释可参考Astar_searcher.cpp; waypoint_generator.cpp可参考上一篇的waypoint_generator.cpp.本文在参考其他博主总结的基础上,整理出了多种代码实现的方法.
(代码注释中英夹杂,英文注释是原来作者的注释,中文注释是本人后来添加的)
过程演示
1.编译功能包.

2.Ctrl+Shift+t新建窗口打开roscore.
3.Ctrl+Shift+t新建窗口打开rviz.
记得要source devel/setup.sh,告诉这个窗口你功能包的位置,否则3d Nav Goal插件会找不到.

4.在rviz中打开demo.rviz(路径src/grid_path_searcher/launch/rviz_config).

5.Ctrl+Shift+t新建窗口加载地图.
记得source.


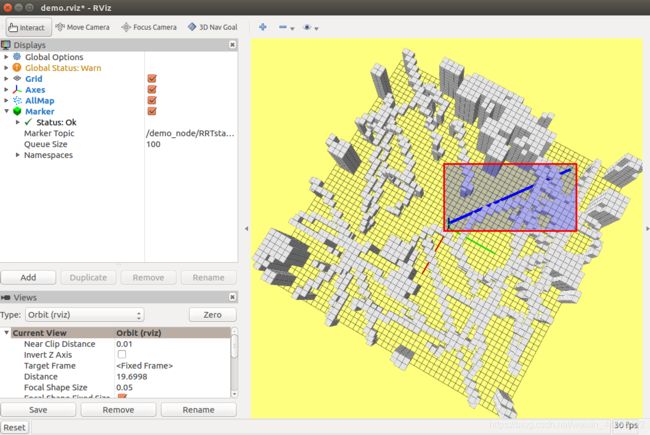
6.RRT*路径搜索.
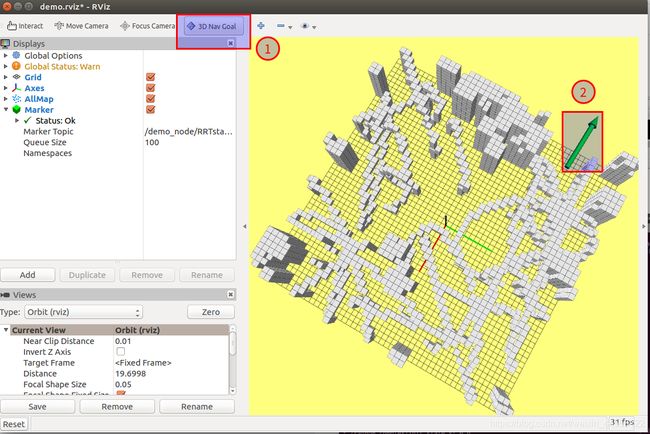
下面是结果
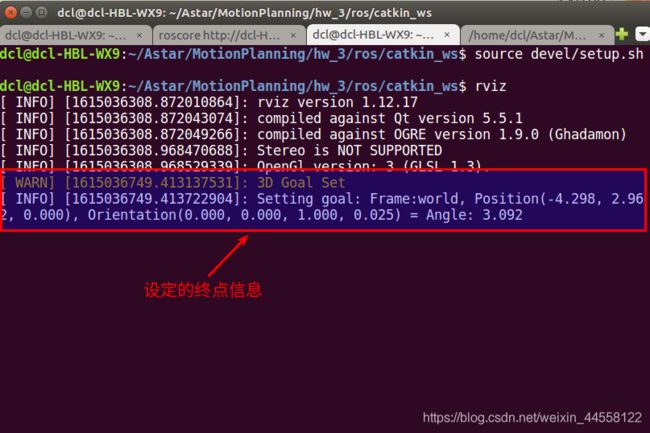
这是终端里的信息

ROS包
主要程序文件demo_node.cpp
#include ()->values[0] = start_pt(0);
// start->as()->values[1] = start_pt(1);
// start->as()->values[2] = start_pt(2);
// 方法4:
start->as<ob::RealVectorStateSpace::StateType>()->operator[](0) = start_pt(0);
start->as<ob::RealVectorStateSpace::StateType>()->operator[](1) = start_pt(1);
start->as<ob::RealVectorStateSpace::StateType>()->operator[](2) = start_pt(2);
// Set our robot's goal state
// 设定终点
ob::ScopedState<> goal(space);
/**
*
*
STEP 3: Finish the initialization of goal state
*
*
*/
// 方法1:
// goal[0] = (&target_pt)->operator[](0) ;
// goal[1] = (&target_pt)->operator[](1) ;
// goal[2] = (&target_pt)->operator[](2) ;
// 方法2:
// goal[0] = target_pt(0);
// goal[1] = target_pt(1);
// goal[2] = target_pt(2);
// 方法3:
// goal->as()->values[0] = target_pt(0);
// goal->as()->values[1] = target_pt(1);
// goal->as()->values[2] = target_pt(2);
// 方法4:
goal->as<ob::RealVectorStateSpace::StateType>()->operator[](0) = target_pt(0);
goal->as<ob::RealVectorStateSpace::StateType>()->operator[](1) = target_pt(1);
goal->as<ob::RealVectorStateSpace::StateType>()->operator[](2) = target_pt(2);
// Create a problem instance
/**
*
*
STEP 4: Create a problem instance,
please define variable as pdef
*
*
*/
// 构造问题实例,传入之前构造的状态空间信息SpaceInformation
auto pdef(std::make_shared<ob::ProblemDefinition>(si));
// Set the start and goal states
// 为问题实例设置起点和终点
pdef->setStartAndGoalStates(start, goal);
// Set the optimization objective
/**
*
*
STEP 5: Set the optimization objective, the options you can choose are defined earlier:
getPathLengthObjective() and getThresholdPathLengthObj()
*
*
*/
// 该语句为本问题设置了一个长度优化器,来自于ompl库自带的路径长度优化类
// 方法1:
// pdef->setOptimizationObjective(getPathLengthObjective(si));
// 方法2:
pdef->setOptimizationObjective(std::make_shared<ob::PathLengthOptimizationObjective>(si));
// Construct our optimizing planner using the RRTstar algorithm.
/**
*
*
STEP 6: Construct our optimizing planner using the RRTstar algorithm,
please define varible as optimizingPlanner
*
*
*/
// 构造一个使用RRTstar算法对状态空间进行规划的规划器
ob::PlannerPtr optimizingPlanner(new og::RRTstar(si));
// Set the problem instance for our planner to solve
// 传入问题实例给规划器
optimizingPlanner->setProblemDefinition(pdef);
// 调用setup()将设置载入。
optimizingPlanner->setup();
// attempt to solve the planning problem within one second of
// planning time
ob::PlannerStatus solved = optimizingPlanner->solve(1.0);
// 如果有解,就将得到的路径压入堆栈,将路径在rviz中显示出来
if (solved)
{
// get the goal representation from the problem definition (not the same as the goal state)
// and inquire about the found path
og::PathGeometric* path = pdef->getSolutionPath()->as<og::PathGeometric>();
vector<Vector3d> path_points;
for (size_t path_idx = 0; path_idx < path->getStateCount (); path_idx++)
{
const ob::RealVectorStateSpace::StateType *state = path->getState(path_idx)->as<ob::RealVectorStateSpace::StateType>();
/**
*
*
STEP 7: Trandform the found path from path to path_points for rviz display
*
*
*/
// 方法1:
// auto x = state->operator[](0);
// auto y = state->operator[](1);
// auto z = state->operator[](2);
// 方法2:
// auto x = (*state)[0];
// auto y = (*state)[1];
// auto z = (*state)[2];
// 方法3:
auto x = state->values[0];
auto y = state->values[1];
auto z = state->values[2];
Vector3d temp_mat(x,y,z);
path_points.push_back(temp_mat);
}
visRRTstarPath(path_points);
}
}
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
ros::init(argc, argv, "demo_node");
ros::NodeHandle nh("~");
_map_sub = nh.subscribe( "map", 1, rcvPointCloudCallBack );
_pts_sub = nh.subscribe( "waypoints", 1, rcvWaypointsCallback );
_grid_map_vis_pub = nh.advertise<sensor_msgs::PointCloud2>("grid_map_vis", 1);
_RRTstar_path_vis_pub = nh.advertise<visualization_msgs::Marker>("RRTstar_path_vis",1);
nh.param("map/cloud_margin", _cloud_margin, 0.0);
nh.param("map/resolution", _resolution, 0.2);
nh.param("map/x_size", _x_size, 50.0);
nh.param("map/y_size", _y_size, 50.0);
nh.param("map/z_size", _z_size, 5.0 );
nh.param("planning/start_x", _start_pt(0), 0.0);
nh.param("planning/start_y", _start_pt(1), 0.0);
nh.param("planning/start_z", _start_pt(2), 0.0);
_map_lower << - _x_size/2.0, - _y_size/2.0, 0.0;
_map_upper << + _x_size/2.0, + _y_size/2.0, _z_size;
_inv_resolution = 1.0 / _resolution;
_max_x_id = (int)(_x_size * _inv_resolution);
_max_y_id = (int)(_y_size * _inv_resolution);
_max_z_id = (int)(_z_size * _inv_resolution);
_RRTstar_preparatory = new RRTstarPreparatory();
_RRTstar_preparatory -> initGridMap(_resolution, _map_lower, _map_upper, _max_x_id, _max_y_id, _max_z_id);
ros::Rate rate(100);
bool status = ros::ok();
while(status)
{
ros::spinOnce();
status = ros::ok();
rate.sleep();
}
delete _RRTstar_preparatory;
return 0;
}
void visRRTstarPath(vector<Vector3d> nodes )
{
visualization_msgs::Marker Points, Line;
Points.header.frame_id = Line.header.frame_id = "world";
Points.header.stamp = Line.header.stamp = ros::Time::now();
Points.ns = Line.ns = "demo_node/RRTstarPath";
Points.action = Line.action = visualization_msgs::Marker::ADD;
Points.pose.orientation.w = Line.pose.orientation.w = 1.0;
Points.id = 0;
Line.id = 1;
Points.type = visualization_msgs::Marker::POINTS;
Line.type = visualization_msgs::Marker::LINE_STRIP;
Points.scale.x = _resolution/2;
Points.scale.y = _resolution/2;
Line.scale.x = _resolution/2;
//points are green and Line Strip is blue
Points.color.g = 1.0f;
Points.color.a = 1.0;
Line.color.b = 1.0;
Line.color.a = 1.0;
geometry_msgs::Point pt;
for(int i = 0; i < int(nodes.size()); i++)
{
Vector3d coord = nodes[i];
pt.x = coord(0);
pt.y = coord(1);
pt.z = coord(2);
Points.points.push_back(pt);
Line.points.push_back(pt);
}
_RRTstar_path_vis_pub.publish(Points);
_RRTstar_path_vis_pub.publish(Line);
}
参考引用
demo_node.cpp注释参考了https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_43795921/article/details/102674696.
代码来源:https://github.com/KailinTong/Motion-Planning-for-Mobile-Robots/tree/master/hw_3.
相关知识来源:深蓝学院<<移动机器人运动规划>>
