LeetCode编程笔记--C语言
11月12日
- 绝对值函数 abs -------------- #include
- 快排函数 qsort --------------- #include
void qsort (
void* base, //要排序的目标数组
size_t num, //待排序的元素个数
size_t width, //一个元素的大小,单位是字节
int(*cmp)(const void* e1, const void* e2) // e1 - e2 为升序,反之为降序
);
其中cmp是函数指针,cmp指向的是:排序时,用来比较两个元素的函数。需要自己编写。
参考链接:qsort排序
821.字符串中所有字符到某一个字符的最短距离
https://leetcode.cn/problems/shortest-distance-to-a-character/
- 找到单个字符到某一个字符的最短距离
- 遍历整个字符串
题解:
/**
1. Note: The returned array must be malloced, assume caller calls free().
*/
int* shortestToChar(char * s, char c, int* returnSize){
int size = strlen(s);
*returnSize = size;
int temp = 0;
int *answer = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * size);
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
answer[i] = 1000;
}
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < size; j++) { // 找出一个字符到某一个字符的最短距离
if (s[j] == c) {
int temp = abs(i - j);
if (answer[i] > temp) {
answer[i] = temp;
}
}
}
printf("%d ", answer[i]);
}
return answer;
}
int* shortestToChar(char * s, char c, int* returnSize){
int size = strlen(s);
*returnSize = size;
int temp = 0;
int *answer = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * size);
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
answer[i] = 1000;
}
int left = size;
int right = size;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
for (int j = i; j >= 0; j--) { // 向左找最近的字符c
if (s[j] == c) {
left = abs(i - j);
break;
}
}
for (int j = i; j < size; j++) { // 向右找最近的字符c
if (s[j] == c) {
right = abs(i - j);
break;
}
}
answer[i] = left > right ? right : left;
left = size;
right = size;
printf("%d ", answer[i]);
}
return answer;
}
217.存在重复元素
https://leetcode.cn/problems/contains-duplicate/
- 排序
- 遍历并判断相邻的两个元素是否相等
题解:
#include 11月13日
- sprintf 、itoa----- 可以将整数转换成字符串,
- atoi -------- 可以将字符串转换成整数(0-10),数字字符串转换成整形数字
atoi函数参考链接:https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/2153891?from=15425
1281. 整数的各位积和之差
https://leetcode.cn/problems/subtract-the-product-and-sum-of-digits-of-an-integer/
- 将整数转换字符串
- 求和、求积 作差返回
int subtractProductAndSum(int n){
char buf[10000];
sprintf(buf, "%d", n);
printf("%s\n", buf);
int sum = 0;
int b = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < strlen(buf); i++) {
sum += buf[i] - '0';
b *= buf[i] - '0';
}
return b - sum;
}
面试题 01.06. 字符串压缩
https://leetcode.cn/problems/compress-string-lcci/description/
53. 最大子数组和
https://leetcode.cn/problems/maximum-subarray/?envType=study-plan&id=shu-ju-jie-gou-ru-men&plan=data-structures&plan_progress=197r58g
- 找到包含自己的最大子数组和
- 遍历所有数数组
int maxSubArray(int* nums, int numsSize){
// maxNums[0] = nums[0]
// maxNums[i] = max(nums[i] + maxNUmx[i-1], num[i])
// max = max(max, maxNums[i]);
int* maxSum = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * numsSize);
maxSum[0] = nums[0];
int max = maxSum[0];
for (int i = 1; i < numsSize; i++) {
maxSum[i] = fmax(nums[i] + maxSum[i - 1], nums[i]);
if (maxSum[i] > max) {
max = maxSum[i];
}
}
return max;
}
11月14日
202. 快乐数
https://leetcode.cn/problems/happy-number/description/
使用快慢指针来求解,fast 走两次,low走一次。快慢指针是处理有环退出问题的必杀技。
- 如果为循环则退出 使用 fast != low
- 为啥一定会循环,而且循环不大。
详情:
https://leetcode.cn/problems/happy-number/solutions/224894/kuai-le-shu-by-leetcode-solution/
int myFuction(int n)
{
int ret = 0;
while (n != 0) {
int temp = n % 10;
ret += temp * temp;
n /= 10;
}
return ret;
}
bool isHappy(int n){
int fast = n;
int low = n;
do {
low = myFuction(low);
fast = myFuction(fast);
fast = myFuction(fast);
} while (fast != low);
if (fast == 1) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
643. 大小为k的最大子数组和
https://leetcode.cn/problems/maximum-average-subarray-i/description/
- 使用滑动窗口保存k个数的和
double findMaxAverage(int* nums, int numsSize, int k){
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) { // 前k个数之和
sum += nums[i];
}
int left = 0;
int right = k;
int temp = sum;
while (right < numsSize) {
temp += nums[right++] - nums[left++]; // 保存滑动窗口的和
if (temp > sum) { // 保存最大值到sum
sum = temp;
}
}
return sum / (double)k;
}
11月16日
349. 两个数组的交集
https://leetcode.cn/problems/intersection-of-two-arrays/description/
1、两个数组排序
2、双指针移动
3、相等时并判断此值与将要插入的值的前一个比较(相等不插入)。
4、那个小(升序就小,降序就大)就向下移动
int cmp(const void *a, const void *b)
{
return *(int *)a - *(int *)b;
}
int* intersection(int* nums1, int nums1Size, int* nums2, int nums2Size, int* returnSize){
qsort(nums1, nums1Size, sizeof(nums1[0]), cmp);
qsort(nums2, nums2Size, sizeof(nums2[0]), cmp);
int *ret = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int) * 1000);
(*returnSize) = 0; // 返回数组的大小可以用做index
int index1 = 0;
int index2 = 0;
while (index1 < nums1Size && index2 < nums2Size) {
if (nums1[index1] == nums2[index2]) {
// 保证ret的唯一性,将相同的值与将前一个ret中的值比较区重复
if ((*returnSize == 0) || nums1[index1] != ret[*returnSize - 1]) {
ret[(*returnSize)++] = nums1[index1];
}
index1++;
index2++;
} else if (nums1[index1] > nums2[index2]) {
index2++;
} else {
index1++;
}
}
return ret;
}
哈希数组映射解法
https://leetcode.cn/problems/intersection-of-two-arrays/solutions/1947189/349-liang-ge-shu-zu-de-jiao-ji-ha-xi-bia-w8hl/
350. 两个数组的交集 II
https://leetcode.cn/problems/intersection-of-two-arrays-ii/
使用哈希数组映射解法 — 针对有限的个数
1、初始化哈希数组
2、初始化哈希数组,value为key的个数
3、查找匹配,匹配到一个,value–
int* intersect(int* nums1, int nums1Size, int* nums2, int nums2Size, int* returnSize){
int min = (nums1Size > nums2Size)? nums2Size : nums1Size;
int hash[1001] = {0};
int *ret = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * min);
int index = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < nums1Size; i++) {
hash[nums1[i]]++;
}
for (int i = 0; i < nums2Size; i++) {
if (hash[nums2[i]] > 0) {
ret[index++] = nums2[i];
hash[nums2[i]]--;
}
}
(*returnSize) = index;
return ret;
}
11月17日
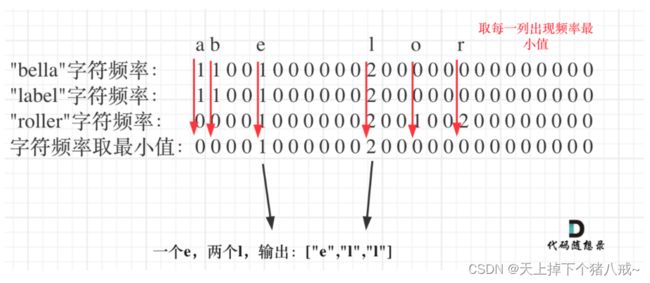
1002. 查找共用字符
使用二维的哈希数组映射解法 — 针对有限的个数
https://leetcode.cn/problems/find-common-characters/description/
- 使用一个二维数组哈希表保存words中字符出现的次数
- 获取每一列的最小值 最小值为几就输出当前字符多少次
char ** commonChars(char ** words, int wordsSize, int* returnSize){
char hash[101][26] = {0};
int j = 0;
int row = 0;
// 使用一个二维数组哈希表保存words中字符出现的次数
for (int i = 0; i < wordsSize; i++) {
j = 0;
while (words[i][j] != '\0') {
hash[row][words[i][j] - 'a']++;
j++;
}
row++;
}
// 二维数组的开辟 == 开辟一个指针数组
char **ret = (char**)malloc(sizeof(char*) * 101);
int ret_row = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 101; i++) {
ret[i] = (char*)malloc(sizeof(char)*2);
memset(ret[i], 0, 2);
}
// 获取每一列的最小值 最小值为几就输出当前字符多少次
for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++) {
for (int k = 1; k < wordsSize; k++) {
if (hash[0][i] > hash[k][i]) { // 把每一列的最小值放到第一行
hash[0][i] = hash[k][i];
}
}
for (int index = 0; index < hash[0][i]; index++) { // 输出到ret中
ret[ret_row++][0] = i + 'a';
}
}
*returnSize = ret_row;
return ret;
}
更多hash类型的题目请参考
https://leetcode.cn/problems/find-common-characters/solutions/445914/1002-cha-zhao-chang-yong-zi-fu-ha-xi-fa-jing-dian-/
代码随想录编程
https://leetcode.cn/problems/remove-duplicates-from-sorted-array/
11月20日
26. 删除有序数组中的重复项
https://leetcode.cn/problems/remove-duplicates-from-sorted-array-ii/description/
- 将要插入的元素 不等于新数组的最后一个元素时。直接插入
int removeDuplicates(int* nums, int numsSize){
int slow = 0;
int fast = 0;
nums[slow] = nums[fast];
for (fast = 1; fast < numsSize; fast++) {
if (nums[slow] != nums[fast]) {
nums[++slow] = nums[fast];
}
}
return ++slow;
}
80. 删除有序数组中的重复项 II
https://leetcode.cn/problems/remove-duplicates-from-sorted-array-ii/submissions/383397313/
- 将要插入的元素 不等于新数组的最后一个元素时。直接插入并标记为count = 1;
- 将要插入的元素 等于新数组的最后一个元素时,判断是否count == 1 ;则添加进去,并将cont =1;
int removeDuplicates(int* nums, int numsSize){
int count = 0;
int slow = 0;
int fast = 0;
count = 1;
for (fast = 1; fast < numsSize; fast++) {
if (nums[slow] != nums[fast]) {
nums[++slow] = nums[fast];
count = 1;
} else if (nums[slow] == nums[fast] && count == 1) {
nums[++slow] = nums[fast];
count = 0;
}
}
return slow + 1;
}
12月06
203. 移除链表元素
https://leetcode.cn/problems/remove-linked-list-elements/description/
struct ListNode* removeElements(struct ListNode* head, int val){
if (head == NULL) {
return head;
}
struct ListNode *myHead = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
myHead->next = head;
struct ListNode *p = myHead;
while (p->next != NULL) {
// printf("%d \n", p->next->val);
struct ListNode *temp = p->next;
if (temp->val == val) {
p->next = p->next->next;
free(temp);
} else {
p = p->next;
}
}
return myHead->next;
}
206. 反转链表
https://leetcode.cn/problems/reverse-linked-list/description/
- 转换为遍历链表将节点插入新的链表中
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head){
struct ListNode *myHead = (struct ListNode *)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode)); // 新链表的空头节点
myHead->next = NULL;
struct ListNode *tempHead = myHead;
struct ListNode *temp;
struct ListNode *p = head;
while (p != NULL) { // 遍历链表
temp = p;
p = p->next;
temp->next = tempHead->next; // 将原来链表中的节点插入新的链表中
tempHead->next = temp;
}
return tempHead->next;
}
24. 两两交换链表中的节点
https://leetcode.cn/problems/swap-nodes-in-pairs/description/
struct ListNode* swapPairs(struct ListNode* head){
struct ListNode* myHead = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
myHead->next = head;
struct ListNode* temp = myHead;
while (temp->next != NULL && temp->next->next != NULL) {
struct ListNode* node_1 = temp->next;
struct ListNode* node_2 = temp->next->next;
temp->next = node_2; // 表示第0个节点的next指向第2个节点,
node_1->next = node_2->next;// 表示将第一个节点的next指向第4个节点,
node_2->next = node_1; // 表示将第二个节点的next 指向第1个节点
temp = node_1;
}
return myHead->next;
}
19. 删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点
https://leetcode.cn/problems/remove-nth-node-from-end-of-list/description/
struct ListNode* removeNthFromEnd(struct ListNode* head, int n){
struct ListNode* myHead = (struct ListNode *)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
myHead->next = head;
struct ListNode* p = myHead;
int count = 0;
while (p->next != NULL) {
count++;
p = p->next;
}
printf("%d\n", count);
p = myHead;
int num = count - n;
while (num--) {
p = p->next;
}
struct ListNode* temp = p->next;
p->next = p->next->next;
free(temp);
return myHead->next;
}
面试题 02.07. 链表相交
https://leetcode.cn/problems/intersection-of-two-linked-lists-lcci/description/
struct ListNode *Fuction(struct ListNode *headA, struct ListNode *headB)
{
while(headA->next != headB->next) {
headA = headA->next;
headB = headB->next;
}
if (headA->next == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
return headA->next;
}
struct ListNode *getIntersectionNode(struct ListNode *headA, struct ListNode *headB) {
if (headA == NULL || headB == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
struct ListNode *pAHead = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
struct ListNode *pBHead = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
pAHead->next = headA;
pBHead->next = headB;
struct ListNode *pA = pAHead;
struct ListNode *pB = pBHead;
int size_a = 0;
int size_b = 0;
while (pA->next != NULL) {
size_a++;
pA = pA->next;
}
// printf("%d\n", size_a);
while (pB->next != NULL) {
size_b++;
pB = pB->next;
}
// printf("%d\n", size_b);
if (size_a > size_b) {
for (int i = 0; i < size_a - size_b; i++) {
pAHead = pAHead->next;
}
} else if (size_a < size_b) {
for (int i = 0; i < size_b - size_a; i++) {
pBHead = pBHead->next;
}
}
return Fuction(pAHead, pBHead);
}
12月07日
142. 环形链表 II
https://leetcode.cn/problems/linked-list-cycle-ii/description/
struct ListNode *detectCycle(struct ListNode *head) {
struct ListNode* myHead = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
myHead->next = head;
struct ListNode *p = myHead;
while (p->next != NULL) {
struct ListNode* temp = myHead;
while(temp->next != p->next) { // 循环判断p->next->next 是否指向前面的节点
if (temp->next == p->next->next) {
return p->next->next;
}
temp = temp->next;
}
if (p->next == p->next->next) { // 判断自己指向自己的情况
return p->next->next;
}
p = p->next;
}
return NULL;
}
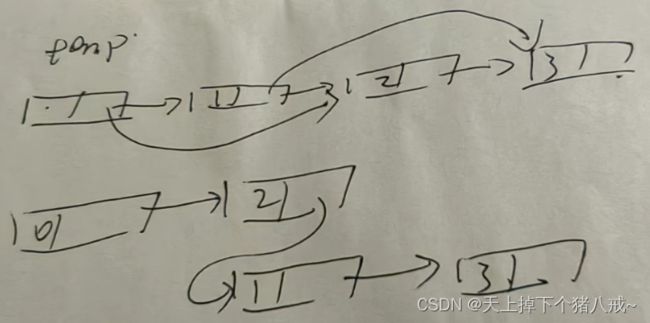
59. 螺旋矩阵 II
https://leetcode.cn/problems/spiral-matrix-ii/description/
int** generateMatrix(int n, int* returnSize, int** returnColumnSizes){
*returnSize = n;
*returnColumnSizes = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*n);
int** ret = (int**)malloc(sizeof(int*) * (*returnSize));
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
ret[i] = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * n);
memset(ret[i], 0, sizeof(int) * n);
(*returnColumnSizes)[i] = n;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
//printf("%d ", ret[i][i]);
}
//printf("\n");
}
int left = 0;
int right = n - 1;
int up = 0;
int down = n -1;
int index = 1;
while (index <= n*n) {
for(int i = left; i <= right; i++){
ret[up][i] = index++;
printf("%d ", ret[up][i]);
}
printf("\n");
up++;
for (int i = up; i <= down; i++) {
ret[i][right] = index++;
printf("%d ", ret[i][right]);
}
printf("\n");
right--;
for (int i = right; i >= left; i--) {
ret[down][i] = index++;
printf("%d ", ret[down][i]);
}
printf("\n");
down--;
for (int i = down; i >= up; i--) {
ret[i][left] = index++;
printf("%d ", ret[i][left]);
}
printf("\n");
left++;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
printf("%d ", ret[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
return ret;
}