【算法】换根DP
文章目录
- 什么是换根DP
- 例题分析——P3478 [POI2008] STA-Station
- 题目列表1
-
- 834. 树中距离之和⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐(两次 dfs)
-
- 思路——冷静分析,列出式子
- 算法分析⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
- 310. 最小高度树⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
- 2581. 统计可能的树根数目⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
- C. Bear and Tree Jumps
- 287. 积蓄程度
- 题目列表2
-
- Atcoder Educational DP Contest, Problem V, Subtree
- Educational Codeforces Round 67, Problem E, Tree Painting
- POJ 3585 Accumulation Degree
- [USACO10MAR]Great Cow Gathering G
- CodeForce 708C Centroids
- 相关链接
什么是换根DP
https://oi-wiki.org/dp/tree/#%E6%8D%A2%E6%A0%B9-dp
树形 DP 中的换根 DP 问题又被称为二次扫描,通常不会指定根结点,并且根结点的变化会对一些值,例如子结点深度和、点权和等产生影响。
通常需要两次 DFS,第一次 DFS 预处理诸如深度,点权和之类的信息,在第二次 DFS 开始运行换根动态规划。
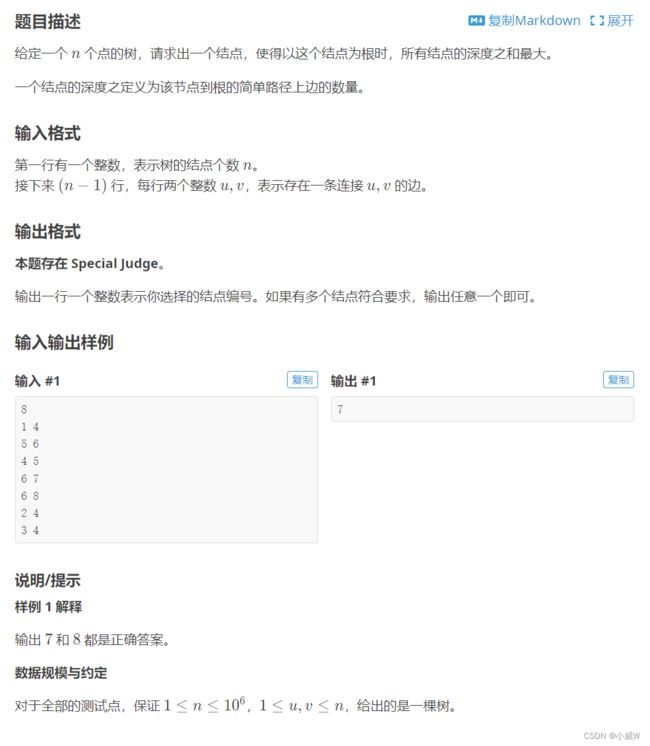
例题分析——P3478 [POI2008] STA-Station
https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P3478
题目列表1
834. 树中距离之和⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐(两次 dfs)
834. 树中距离之和
思路——冷静分析,列出式子
https://leetcode.cn/problems/sum-of-distances-in-tree/solutions/103325/c-liang-ci-dfsde-dao-da-an-by-congwang357-2/
将问题拆分:对于两个相邻节点A和B,将树拆分为两个子树,根节点分别为A和B,A节点到其他所有节点的距离和 ans(A) = A子树中所有节点到A节点的距离和sum(A) + B子树中所有节点到B节点的距离和sum(B) + B子树的大小cnt(B);
同理,ans(B) = sum(B) + sum(A) + cnt(A);
由此我们得到: ans(A) = sum(A) + sum(B) + cnt(B); ans(B) = sum(B) + sum(A) + cnt(A);
则,两个相邻接点的解之间的关系为:ans(A) = ans(B) - cnt(A) + cnt(B) = ans(B) - cnt(A) + (N - cnt(A));
因此,对于根节点root的任意子节点child,ans(child) = ans(root) - cnt(child) + N - cnt(child);
class Solution {
List<Integer>[] g;
int[] ans, size; // size是各个节点作为根节点的子树大小
int n;
public int[] sumOfDistancesInTree(int n, int[][] edges) {
g = new ArrayList[n];
Arrays.setAll(g, e -> new ArrayList<Integer>());
for (int[] edge: edges) {
int x = edge[0], y = edge[1];
g[x].add(y);
g[y].add(x);
}
this.n = n;
ans = new int[n];
size = new int[n];
Arrays.fill(size, 1);
dfs(0, -1, 0);
reroot(0, -1);
return ans;
}
// 求ans[0]和各个size[i]
void dfs(int x, int fa, int depth) {
ans[0] += depth; // depth 是 0 到 x 的距离
for (int y: g[x]) {
if (y != fa) {
dfs(y, x, depth + 1);
size[x] += size[y]; // 累加 x 的儿子 y 的子树大小
}
}
}
// 求答案
void reroot(int x, int fa) {
for (int y: g[x]) {
if (y != fa) {
ans[y] = ans[x] + n - 2 * size[y];
reroot(y, x);
}
}
}
}
算法分析⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
https://leetcode.cn/problems/sum-of-distances-in-tree/solutions/2345592/tu-jie-yi-zhang-tu-miao-dong-huan-gen-dp-6bgb/

我们得到了重要公式:
a n s [ y ] = a n s [ x ] + n − 2 ∗ s i z e [ y ] ans[y] = ans[x] + n - 2 * size[y] ans[y]=ans[x]+n−2∗size[y]
如何理解?
y 和以 y为根的子树的距离相比 x 与 以 y为根的子树的距离 少了 cnt[y]
除了 以 y为根的子树,剩下的节点数量是 n - cnt[y],这些和 y 的距离相比 和 x 的距离多了 n - cnt[y]
因此:ans[y] = ans[x] + n - 2 * size[y]
310. 最小高度树⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
https://leetcode.cn/problems/minimum-height-trees/description/
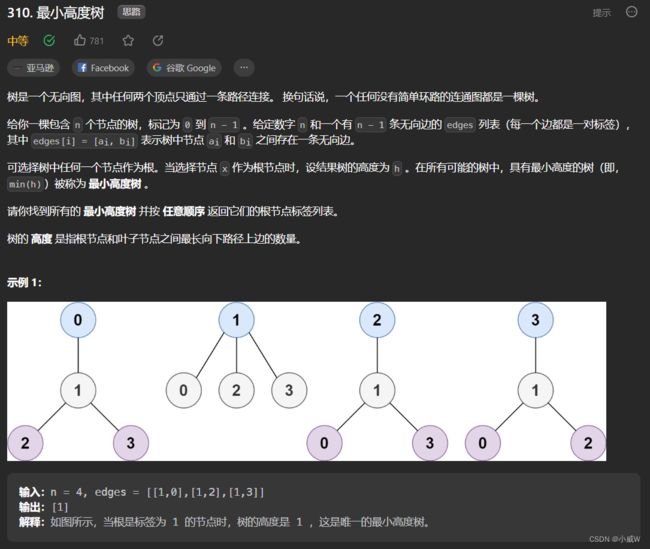
提示:
1 <= n <= 2 * 10^4
edges.length == n - 1
0 <= ai, bi < n
ai != bi
所有 (ai, bi) 互不相同
给定的输入 保证 是一棵树,并且 不会有重复的边
主要参考 :https://leetcode.cn/problems/minimum-height-trees/solutions/1397830/c-huan-gen-by-vclip-sa84/ 编写的代码。
class Solution {
List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<Integer>();
List<Integer>[] g;
int n;
int[] ds, ds2;
public List<Integer> findMinHeightTrees(int n, int[][] edges) {
this.n = n;
ds = new int[n];
ds2 = new int[n];
// 建树
g = new ArrayList[n];
Arrays.setAll(g, e -> new ArrayList());
for (int[] edge: edges) {
int x = edge[0], y = edge[1];
g[x].add(y);
g[y].add(x);
}
dfs(0, -1); // 求各个节点为根的子树高度(以0节点为最根节点)
dfs2(0, -1); // 换根dp
// 求答案
int h = n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if (ds2[i] < h) {
h = ds2[i];
ans.clear();
}
if (ds2[i] == h) ans.add(i);
}
return ans;
}
// 计算以0号节点为根的树中,以各个节点为根的子树高
public int dfs(int x, int fa) {
for (int y: g[x]) {
if (y != fa) {
ds[x] = Math.max(ds[x], dfs(y, x) + 1);
}
}
return ds[x];
}
// 进行换根动态规划,计算出所有的树高
public void dfs2(int x, int fa) {
// 计算 x 的子树高的最大值和次大值
int first = -1, second = -1; // 默认是没有子树
for (int y: g[x]) {
if (ds[y] > first) {
second = first;
first = ds[y];
} else if (ds[y] > second) second = ds[y];
}
ds2[x] = first + 1; // 计算出 x 为根的树高
// 进行换根,计算x作为以y为根节点的树的子树时的高度
for (int y: g[x]) {
if (y != fa) {
ds[x] = (ds[y] != first? first: second) + 1;
dfs2(y, x);
}
}
}
}
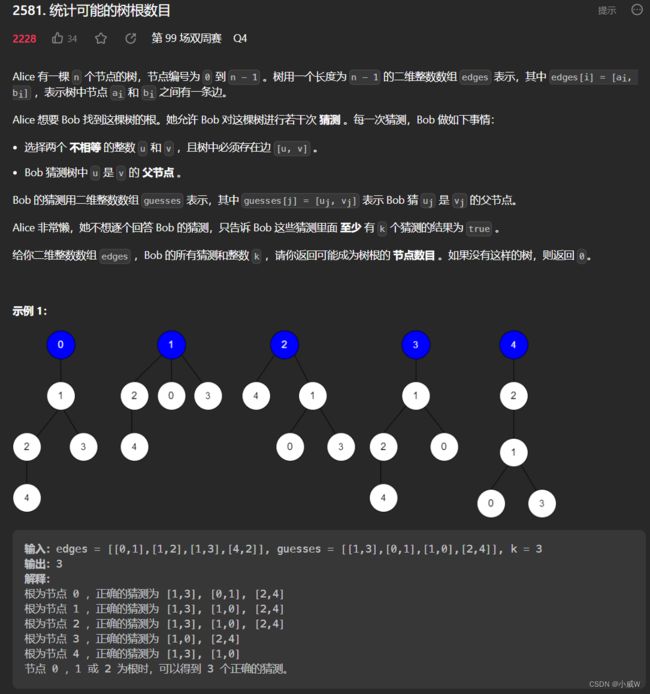
2581. 统计可能的树根数目⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
https://leetcode.cn/problems/count-number-of-possible-root-nodes/
edges.length == n - 1
2 <= n <= 10^5
1 <= guesses.length <= 10^5
0 <= ai, bi, uj, vj <= n - 1
ai != bi
uj != vj
edges 表示一棵有效的树。
guesses[j] 是树中的一条边。
guesses 是唯一的。
0 <= k <= guesses.length
在这里插入代码片
C. Bear and Tree Jumps
https://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/771/C
在这里插入代码片
287. 积蓄程度
https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/289/

题目列表2
Atcoder Educational DP Contest, Problem V, Subtree
https://atcoder.jp/contests/dp/tasks/dp_v
Educational Codeforces Round 67, Problem E, Tree Painting
https://codeforces.com/contest/1187/problem/E
POJ 3585 Accumulation Degree
http://poj.org/problem?id=3585
[USACO10MAR]Great Cow Gathering G
https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P2986
CodeForce 708C Centroids
https://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/708/C
相关链接
关于基础树形DP可见:
【算法】树形DP ①(树的直径)
【算法】树形DP ② 打家劫舍Ⅲ(树上最大独立集)