记录一次腾讯云对象存储服务(COS)的使用
记录一次腾讯云对象存储服务(COS)的使用
目录
- 记录一次腾讯云对象存储服务(COS)的使用
-
- 1. 导入依赖
- 2. application.yml写入参数
- 3. 注入application.yml参数
- 4. 创建CosUtils工具类
- 5. 在Springboot创建和销毁时执行函数
- 6. 创建PathUtils工具类
- 7. CosUtils工具类完整代码
在完成一个练习项目时,有一个头像上传的功能需要使用 对象存储 服务,这里面的知识点还是比较多的,所以在这里记录一下。
这里我选择的是 腾讯云对象存储服务(COS),所以在这里介绍一下 腾讯云对象存储服务(COS) 的使用。
官方文档:腾讯云对象存储服务java SDK官方文档
1. 导入依赖
将下列依赖导入项目的 pom.xml 文件中:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.qcloudgroupId>
<artifactId>cos_apiartifactId>
<version>5.6.89version>
dependency>
2. application.yml写入参数
使用 cos 时,像 secretId、secretKey 这种参数,一般不会直接写在类中而写在 application.yml 配置文件中,然后通过 @Value 或 @ConfigurationProperties 注解注入到 Spring 类中。
application.yml 配置文件:
cos:
secretId: xxx # 密钥id
secretKey: xxx # 密钥key
bucketName: blog-APPID # 需要使用的存储桶名称
region: ap-nanjing # 存储桶地域
secretId、secretKey 是 腾讯云的 API密钥,
bucketName 是需要使用的存储桶名称,存储桶可以提前创建,也可以在项目中使用代码创建,
region 是 存储桶的地域。
腾讯云密钥查询入口:API密钥管理
腾讯云COS地域简称:COS地域简称
3. 注入application.yml参数
这里我定义了一个 工具类,用于注入 application.yml 中的 cos 参数,然后方便在其它类中使用 secretId、secretKey 等参数。
package com.mrqin.utils;
import lombok.Setter;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component // 声明该类被spring管理
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "cos")
@Setter // 注意:必须有setter方法才能赋值成功
@Slf4j
public class CosPropertiesConstantsUtils implements InitializingBean {
private String secretId;
private String secretKey;
private String bucketName;
private String region;
public static String Tencent_secretId;
public static String Tencent_secretKey;
public static String Tencent_bucketName;
public static String Tencent_region;
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
Tencent_secretId = secretId;
Tencent_secretKey = secretKey;
Tencent_bucketName = bucketName;
Tencent_region = region;
log.info("密钥初始化成功");
}
}
在这里有几个知识点:
快速了解 @ConfigurationProperties
@ConfigurationProperties和@Value孰优孰劣?
@Value @ConfigurationProperties 注释静态变量赋值
@ConfigurationProperties注解用于批量导入application.yml文件中的变量,比@Value更加方便。
想要赋值成功,一定要注意:
- 启动类或配置类上应该添加
@EnableConfigurationProperties注解;- 该类必须添加
@Component注解,表示该类被Spring管理;- 该类必须有属性的
setter方法,才可以成功进行属性注入,这里使用了 lombok 的@Setter注解,简单实现了 setter 方法。
在SpringBoot官方文档中有几个注意点:
- 属性必须要有getter、setter方法;(由于我的类中是静态变量,所以没有getter)
- 如果属性的类型是集合,要确保集合是不可变的;
- 如果使用Lombok自动生成getter/setter方法,一定不要生成对应的任何构造函数,因为Spring IOC容器会自动使用它来实例化对象。
- 使用JavaBean属性绑定的方式只针对标准 Java Bean 属性,不支持对静态属性的绑定。
- 正如注意事项中的:@Configuration不支持对静态属性的绑定,所以这里使用了 afterPropertiesSet 方法(也可以使用其他方法,如使用set方法为静态变量赋值)。
- afterPropertiesSet 执行时间:实例化->生成对象->属性填充后会进行afterPropertiesSet方法,所以这里的afterPropertiesSet 方法执行后,就完成了静态变量的赋值。注意使用afterPropertiesSet需要实现InitializingBean。
4. 创建CosUtils工具类
由于 CosUtils 工具类中内容较多,所以完整代码放在最后,感兴趣的大家可以看一下,这里拆分一下:
初始化CosClient:
/**
* 初始化CosClient实例,在Springboot初始化执行一次,可以保证COSClient实例只有一个
*/
public static void initCosClient() {
//----------------------初始化客户端---------------------------
// 1 初始化用户身份信息(secretId, secretKey)。
String secretId = CosPropertiesConstantsUtils.Tencent_secretId;
String secretKey = CosPropertiesConstantsUtils.Tencent_secretKey;
COSCredentials cred = new BasicCOSCredentials(secretId, secretKey);
// 2 设置 bucket 的地域
// clientConfig 中包含了设置 region, https(默认 http), 超时, 代理等 set 方法, 使用可参见源码或者常见问题 Java SDK 部分。
Region region = new Region(CosPropertiesConstantsUtils.Tencent_region);
ClientConfig clientConfig = new ClientConfig(region);
// 这里建议设置使用 https 协议
// 从 5.6.54 版本开始,默认使用了 https
clientConfig.setHttpProtocol(HttpProtocol.https);
// 3 生成 cos 客户端。
COSClient cosClient = new COSClient(cred, clientConfig);
// 为COSClient静态变量赋值
sCosClient = cosClient;
}
获取CosClient实例:
/**
* 获取COSClient实例
* @return cosclient实例
*/
public static COSClient getCosClient () {
return sCosClient;
}
创建存储桶:
/**
* 创建存储桶,如果在 COS控制台中提前创建好了存储桶,并且没有额外创建存储桶的需求,该方法是不必执行的。
* 注意:这里自动创建了 公有读私有写 的存储桶,如果想要改变,可以将该属性设置为该方法的一个参数
* @param bucketName 存储桶名称
*/
public static void createBucket(String bucketName) {
//-------------------创建存储桶-------------------------
//存储桶名称,格式:BucketName-APPID
CreateBucketRequest createBucketRequest = new CreateBucketRequest(bucketName);
// 设置 bucket 的权限为 Private(私有读写)、其他可选有 PublicRead(公有读私有写)、PublicReadWrite(公有读写)
createBucketRequest.setCannedAcl(CannedAccessControlList.PublicRead);
try {
Bucket bucketResult = sCosClient.createBucket(createBucketRequest);
} catch (CosServiceException serverException) {
serverException.printStackTrace();
} catch (CosClientException clientException) {
clientException.printStackTrace();
}
}
上传文件:
/**
* 上传文件
* @param file MultipartFile类型的文件
* @param bucketName 存储桶名称
* @param key 文件路径及文件名称的组合
* 指定文件上传到 COS 上的路径,即对象键。例如对象键为folder/picture.jpg,则表示将文件 picture.jpg 上传到 folder 路径下
* @return URL对象,在该对象中有很多方法,其中获取 url 链接的方法是:getContent()
* @throws IOException
*/
public static URL uploadFile
(MultipartFile file, String bucketName, String key) throws IOException {
//----------------------上传对象-------------------------
// 指定要上传的文件,这里使用 流类型,不使用文件类型
int inputStreamLength = file.getBytes().length;
InputStream inputStream = file.getInputStream();
// 数据流类型需要额外定义一个参数
ObjectMetadata objectMetadata = new ObjectMetadata();
// 上传的流如果能够获取准确的流长度,则推荐一定填写 content-length
// 如果确实没办法获取到,则下面这行可以省略,但同时高级接口也没办法使用分块上传了
objectMetadata.setContentLength(inputStreamLength);
// 指定文件上传到 COS 上的路径,即对象键。例如对象键为folder/picture.jpg,则表示将文件 picture.jpg 上传到 folder 路径下
// PutObjectRequest putObjectRequest = new PutObjectRequest(bucketName, key, localFile);
PutObjectRequest putObjectRequest = new PutObjectRequest(bucketName, key, inputStream, objectMetadata);
PutObjectResult putObjectResult = sCosClient.putObject(putObjectRequest);
System.out.println(putObjectResult.getRequestId());
return getURL(bucketName, key);
}
/**
* 重写方法,参入参数中没有bucketName,表示默认使用application.yml配置文件中的 bucketName
* @param file MultipartFile类型的文件
* @param key 文件路径及文件名称的组合
* 指定文件上传到 COS 上的路径,即对象键。例如对象键为folder/picture.jpg,则表示将文件 picture.jpg 上传到 folder 路径下
* @return
* @throws IOException
*/
public static URL uploadFile(MultipartFile file, String key) throws IOException {
return uploadFile(file, CosPropertiesConstantsUtils.Tencent_bucketName, key);
}
获取URL对象:
/**
* 根据 bucketName 和 key 获取 URL 对象
* @param bucketName 存储桶名称
* @param key 文件路径及文件内容的组合
* @return URL 对象
*/
public static URL getURL(String bucketName, String key) {
URL url = sCosClient.getObjectUrl(bucketName, key);
return url;
}
/**
* 重写方法,根据 key 获取 URL 对象
* @param key 文件路径及文件内容的组合
* @return URL 对象
*/
public static URL getURL(String key) {
return getURL(CosPropertiesConstantsUtils.Tencent_bucketName, key);
}
关闭CosClient实例:
/**
* 关闭 COSClient 实例,在 springboot 销毁时调用
*/
public static void shutdownClient() {
// 关闭客户端(关闭后台线程)
sCosClient.shutdown();
}
几乎所有的代码在腾讯云对象存储服务java SDK官方文档都有介绍,这里我说一下自己创建工具类时的思路,也当作一种记录吧。
在腾讯云COS官方文档中有一句话:
COSClient 是线程安全的类,允许多线程访问同一实例。因为实例内部维持了一个连接池,创建多个实例可能导致程序资源耗尽,请确保程序生命周期内实例只有一个,并在不再需要使用时,调用 shutdown 方法将其关闭。如果需要新建实例,请先将之前的实例关闭。
在写工具类时,我想到了几种思路:
- 直接在 Service 层调用 initCosClient() 方法,但是每一次调用 initCosClient() 方法后,最后一定要再调用 shutdown() 方法,因为只调用 initCosClient() 方法而不关闭,就会创建多个 CosClient 实例,这是不符合要求的,这里我没有采用该方法。
- 使用静态代码块,当使用该工具类时,首先进行初始化。由于静态代码块只会执行一次,所以整个过程只会创建一个CosClient实例,而且关闭的时候还要手动调用销毁方法,不太合理。
- 整个springboot周期只创建一个CosClient实例,在springboot销毁前销毁CosClient实例,由于我只需要使用一个存储桶,没有麻烦的业务,所以我使用了这种方法。
CosUtils 工具类的创建有很多方法,如果大家有更好的方法希望可以在评论区交流哦!
5. 在Springboot创建和销毁时执行函数
在Springboot创建时执行函数有两种方法:
- 实现 ApplicationRunner 接口:
@Component
public class MyApplicationRunner1 implements ApplicationRunner{
@Override
public void run(ApplicationArguments args) throws Exception {
}
}
- 实现 CommandLineRunner 接口
@Component
public class MyCommandLineRunner1 implements CommandLineRunner{
@Override
public void run(String... args) throws Exception {
}
}
它们两个非常相似,区别就在于ApplicationRunner的参数是spring的参数,CommandLineRunner的参数是命令行参数。如果没有什么特别的要求,用哪个都行。
在springboot销毁时执行方法:继承DisposableBean接口,并将其注册为bean即可:
import org.springframework.beans.factory.DisposableBean;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* 结束的时候执行
*/
@Component
public class MyDisposableBean implements DisposableBean{
@Override
public void destroy() throws Exception {
}
}
参开博客:springboot启动和关闭时的事件操作
这里我自定义了一个Runner类,用于在Springboot执行和销毁时进行CosClient的初始化和销毁。
package com.mrqin.runner;
import com.mrqin.utils.CosUtils;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.DisposableBean;
import org.springframework.boot.ApplicationArguments;
import org.springframework.boot.ApplicationRunner;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@Slf4j
public class CosClientRunner implements ApplicationRunner, DisposableBean {
@Override
public void run(ApplicationArguments args) throws Exception {
CosUtils.initCosClient();
}
@Override
public void destroy() throws Exception {
CosUtils.shutdownClient();
}
}
6. 创建PathUtils工具类
在 CosUtils 中有一个参数:key,在腾讯云官方文档中是这样说明的:
指定文件上传到 COS 上的路径,即对象键。例如对象键为folder/picture.jpg,则表示将文件 picture.jpg 上传到 folder 路径下
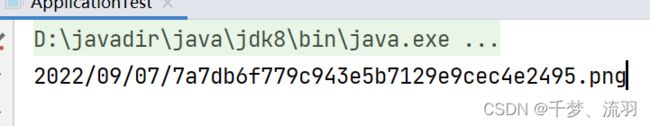
为了保证在COS中的数据名称不重复且比较好分类,这里使用日期作为路径:2022/09/07/,使用 uuid 作为文件名称,使用图片的后缀作为存储文件的后缀:
package com.mrqin.utils;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.UUID;
public class PathUtils {
public static String generateFilePath(String fileName) {
// 根据日期生成路径——2022/09/06/
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy/MM/dd/");
String datePath = sdf.format(new Date());
// uuid作为文件名,并替换掉其中的 “-”
String uuid = UUID.randomUUID().toString().replaceAll("-", "");
// 后缀名和文件后缀一样
int index = fileName.lastIndexOf(".");
// test.jpg -> .jpg
// test.png -> .png
String fileType = fileName.substring(index);
// 拼接cos中的文件路径
String filePath = new StringBuilder().append(datePath).append(uuid).append(fileType).toString();
System.out.println(filePath);
return filePath;
}
}
这样就实现了,测试结果:
7. CosUtils工具类完整代码
package com.mrqin.utils;
import com.qcloud.cos.COSClient;
import com.qcloud.cos.ClientConfig;
import com.qcloud.cos.auth.BasicCOSCredentials;
import com.qcloud.cos.auth.COSCredentials;
import com.qcloud.cos.exception.CosClientException;
import com.qcloud.cos.exception.CosServiceException;
import com.qcloud.cos.http.HttpProtocol;
import com.qcloud.cos.model.*;
import com.qcloud.cos.region.Region;
import org.springframework.web.multipart.MultipartFile;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.net.URL;
public class CosUtils {
/**
* COSClient类型的静态变量
* 注意:请确保程序生命周期内COSClient实例只有一个
*/
private static COSClient sCosClient;
private CosUtils() {
}
/**
* 初始化CosClient实例,在Springboot初始化执行一次,可以保证COSClient实例只有一个
*/
public static void initCosClient() {
//----------------------初始化客户端---------------------------
// 1 初始化用户身份信息(secretId, secretKey)。
String secretId = CosPropertiesConstantsUtils.Tencent_secretId;
String secretKey = CosPropertiesConstantsUtils.Tencent_secretKey;
COSCredentials cred = new BasicCOSCredentials(secretId, secretKey);
// 2 设置 bucket 的地域
// clientConfig 中包含了设置 region, https(默认 http), 超时, 代理等 set 方法, 使用可参见源码或者常见问题 Java SDK 部分。
Region region = new Region(CosPropertiesConstantsUtils.Tencent_region);
ClientConfig clientConfig = new ClientConfig(region);
// 这里建议设置使用 https 协议
// 从 5.6.54 版本开始,默认使用了 https
clientConfig.setHttpProtocol(HttpProtocol.https);
// 3 生成 cos 客户端。
COSClient cosClient = new COSClient(cred, clientConfig);
// 为COSClient静态变量赋值
sCosClient = cosClient;
}
/**
* 获取COSClient实例
* @return cosclient实例
*/
public static COSClient getCosClient () {
return sCosClient;
}
/**
* 创建存储桶,如果在 COS控制台中提前创建好了存储桶,并且没有额外创建存储桶的需求,该方法是不必执行的。
* 注意:这里自动创建了 公有读私有写 的存储桶,如果想要改变,可以将该属性设置为该方法的一个参数
* @param bucketName 存储桶名称
*/
public static void createBucket(String bucketName) {
//-------------------创建存储桶-------------------------
//存储桶名称,格式:BucketName-APPID
CreateBucketRequest createBucketRequest = new CreateBucketRequest(bucketName);
// 设置 bucket 的权限为 Private(私有读写)、其他可选有 PublicRead(公有读私有写)、PublicReadWrite(公有读写)
createBucketRequest.setCannedAcl(CannedAccessControlList.PublicRead);
try {
Bucket bucketResult = sCosClient.createBucket(createBucketRequest);
} catch (CosServiceException serverException) {
serverException.printStackTrace();
} catch (CosClientException clientException) {
clientException.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 上传文件
* @param file MultipartFile类型的文件
* @param bucketName 存储桶名称
* @param key 文件路径及文件名称的组合
* 指定文件上传到 COS 上的路径,即对象键。例如对象键为folder/picture.jpg,则表示将文件 picture.jpg 上传到 folder 路径下
* @return URL对象,在该对象中有很多方法,其中获取 url 链接的方法是:getContent()
* @throws IOException
*/
public static URL uploadFile
(MultipartFile file, String bucketName, String key) throws IOException {
//----------------------上传对象-------------------------
// 指定要上传的文件,这里使用 流类型,不使用文件类型
int inputStreamLength = file.getBytes().length;
InputStream inputStream = file.getInputStream();
// 数据流类型需要额外定义一个参数
ObjectMetadata objectMetadata = new ObjectMetadata();
// 上传的流如果能够获取准确的流长度,则推荐一定填写 content-length
// 如果确实没办法获取到,则下面这行可以省略,但同时高级接口也没办法使用分块上传了
objectMetadata.setContentLength(inputStreamLength);
// 指定文件上传到 COS 上的路径,即对象键。例如对象键为folder/picture.jpg,则表示将文件 picture.jpg 上传到 folder 路径下
// PutObjectRequest putObjectRequest = new PutObjectRequest(bucketName, key, localFile);
PutObjectRequest putObjectRequest = new PutObjectRequest(bucketName, key, inputStream, objectMetadata);
PutObjectResult putObjectResult = sCosClient.putObject(putObjectRequest);
System.out.println(putObjectResult.getRequestId());
return getURL(bucketName, key);
}
/**
* 重写方法,参入参数中没有bucketName,表示默认使用application.yml配置文件中的 bucketName
* @param file MultipartFile类型的文件
* @param key 文件路径及文件名称的组合
* 指定文件上传到 COS 上的路径,即对象键。例如对象键为folder/picture.jpg,则表示将文件 picture.jpg 上传到 folder 路径下
* @return
* @throws IOException
*/
public static URL uploadFile(MultipartFile file, String key) throws IOException {
return uploadFile(file, CosPropertiesConstantsUtils.Tencent_bucketName, key);
}
/**
* 根据 bucketName 和 key 获取 URL 对象
* @param bucketName 存储桶名称
* @param key 文件路径及文件内容的组合
* @return URL 对象
*/
public static URL getURL(String bucketName, String key) {
URL url = sCosClient.getObjectUrl(bucketName, key);
return url;
}
/**
* 重写方法,根据 key 获取 URL 对象
* @param key 文件路径及文件内容的组合
* @return URL 对象
*/
public static URL getURL(String key) {
return getURL(CosPropertiesConstantsUtils.Tencent_bucketName, key);
}
/**
* 关闭 COSClient 实例,在 springboot 销毁时调用
*/
public static void shutdownClient() {
// 关闭客户端(关闭后台线程)
sCosClient.shutdown();
}
}
感谢观看!