微服务学习之路(客户端弹性模式)
微服务学习之路
微服务学习之路,本系列文章是博主学习微服务的路程,特意分享自己的学习笔记,也为了以后能回溯查看。
提示:写完文章后,目录可以自动生成,如何生成可参考右边的帮助文档
客户端弹性模式
- 微服务学习之路
- 前言
- 一、什么是客户端弹性模式
-
- 1.1. 客户端负载均衡模式
- 1.2. 断路器模式
- 1.3. 后备模式
- 1.4. 舱壁模式
- 二、Hystrix
-
- 2.1. 使用Hystrix实现断路器
- 2.2. 后备处理
- 2.3. 实现舱壁模式
- 三、微调Hystrix
- 四、线程上下文和Hystrix
-
- 4.1. HystrixConcurrencyStrategy实战
- 总结
前言
本章将介绍客户端弹性模式。
一、什么是客户端弹性模式
客户端弹性模式的重点是,在远程服务发生错误或表现不佳时保护远程资源(另一个微服务调用或数据库查询)的客户端免于崩溃。这些模式的目标是让客户端“快速失败”,而不消耗诸如数据库连接和线程池之路的宝贵资源。
有4种客户端弹性模式,它们分别是:
- 客户端负载均衡模式。
- 断路器模式。
- 后备模式。
- 舱壁模式。
1.1. 客户端负载均衡模式
客户端负载均衡模式涉及让客户端从服务发现代理查找服务的所有实例,然后缓存服务实例的物理位置。每当服务消费者需要调用该服务实例时,客户端负载均衡将从它维护的服务位置池返回一个位置。
因为客户端负载均衡器位于服务客户端和服务消费者之间,所以负载均衡器可以检测服务实例是否抛出错误或表现不佳。如果客户端负载均衡器检测到问题,它可以从可用服务位置池中移除该服务实例,并防止将来的服务调用访问该服务实例。
1.2. 断路器模式
断路器模式是模仿电路断路器的客户端弹性模式。当远程服务被调用时,断路器将监控这个调用。如果调用时间太长,断路器将会介入并中断调用。此外,断路器将监控所有对远程资源的调用,如果对某一个远程资源的调用失败次数足够多,那么断路器实现就会出现并采取快速失败,阻止将来调用失败的远程资源。
1.3. 后备模式
后备模式,当远程服务调用失败时,服务消费者将执行替代代码路径,并尝试通过其他方式执行操作,而不是生成一个异常。
1.4. 舱壁模式
舱壁模式是建立在造船得概念基础上的。采用舱壁设计,一艘船被划分为完全隔离和防水的隔间,这称为舱壁。即使船的船体被击穿,由于船被划分为水密舱(舱壁),舱壁会将水限制在被击穿的船的区域内,防止整艘船灌满水并沉没。
同样的概念可以应用于必须与多个远程资源交互的服务。通过使用舱壁模式,可以把远程资源的调用分到线程池中,并降低一个缓慢的远程资源调用拖垮整个应用程序的风险。线程池充当服务的“舱壁”。每个远程资源都是隔离的,并分配给线程池。如果一个服务响应缓慢,那么这种服务调用的线程池就会饱和并停止处理请求,而对其他服务的服务调用则不会变得饱和,因为它们被分配给了其他线程池。
二、Hystrix
构建断路器模式、后备模式和舱壁模式的实现需要对线程和线程管理有深入的理解。幸运的是,开发人员可以使用Spring Cloud和Neflix的Hystrix库,这些库久经考验。
开始对Hystrix的探索,需要以下步骤:
// 1、添加Hystrix依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-hystrix</artifactId>
<version>2.1.1.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
@SpringBootApplication
// 2、启用Hystix。告诉Spring Cloud将要为服务使用Hystrix
@EnableHystrix
public class ConfigClient {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ConfigClient.class, args);
}
}
2.1. 使用Hystrix实现断路器
Hystrix和Spring Cloud使用@HystrixCommand注解来将Java类方法标记为由Hystrix断路器进行管理。当Spring框架解析@HystrixCommand时,它将动态生成一个代理,该代理将包装该方法,并通过专门用于处理远程调用的线程池来管理对该方法的所有调用。
@HystrixCommand(
// 设置超时时间
commandProperties = {
@HystrixProperty(name = "execution.isolation.thread.timeoutInMilliseconds", value = "1200")
}
)
public String useNetflixFeign(String userId) {
randomlyRunLong();
return serverAFeignClient.getUserInfo(userId);
}
// 模拟随机超时失败
private void randomlyRunLong() {
Random rand = new Random();
int randomNum = rand.nextInt((3 - 1) + 1) + 1;
if (randomNum==3) sleep();
}
private void sleep() {
try {
Thread.sleep(1100L);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public String helloFallback() {
return "error";
}
2.2. 后备处理
断路器模式有一个好处,由于远程资源的消费者和资源本身之间存在“中间人”,这使得开发人员有机会拦截服务故障,并选择替代方案。
在Hystrix中,这被称为后备策略,具体实现如下:
- 在@HystrixCommand注解中添加一个名为fallbackMethod的属性。该属性将包括一个方法的名称,当Hystrix因为调用耗费时间太长而不得不中断该调用时,该方法将会被调用。
- 定义一个待执行的后备方法。此后备方法必须与由在@HystrixCommand保护的原始方法位于同一个类中,并且必须具有与原始方法完全相同的方法签名,因为传递给由@HystrixCommand保护的原始方法的所有参赛都将传递给后备方法。
@HystrixCommand(fallbackMethod = "helloFallback")
public String useSpringDiscoveryClient(String userId) {
return serverADiscoveryClient.getUserInfo(userId);
}
public String helloFallback() {
return "error";
}
2.3. 实现舱壁模式
在一个应用程序中,通常需要调用到多个微服务来完成特定的任务。在不使用舱壁模式的情况下,这些调用默认是使用同一批线程来执行调用的。这些线程是为了处理整个Java容器的请求而预留的。这样会出现一个服务性能出现问题时,导致整容器都崩溃的情况。舱壁模式将远程资源调用隔离在它们自己的线程池中,以便可以控制单个表现不佳的服务,而不是使该容器崩溃。
Hystrix使用线程池来委派所有对远程服务的请求。在默认的情况下,所有的Hystrix命令都将共享同一个线程池来处理请求。这个线程池将有10个线程来处理远程服务调用,而这些远程服务调用可以是任何东西,包括REST服务调用,数据库调用等。
具体实现步骤如下:
- 为服务调用方法建立一个单独的线程池。
- 设置线程池中的线程数。
- 设置单个线程繁忙时可排队的请求数的队列大小。
示例代码:
@HystrixCommand(
// threadPoolKey属性定义线程池的唯一名称
threadPoolKey = "serverAThreadPool",
// threadPoolProperties属性用于定义和定制threadPool的行为
threadPoolProperties = {
// coreSize属性用于定义线程池中线程的最大数量
@HystrixProperty(name = "coreSize", value = "30"),
// maxQueueSize用于定义一个位于线程池前的队列,它可以对传入的请求进行排队
@HystrixProperty(name = "maxQueueSize", value = "10")
}
)
private String useSpringTemplateWithRibbon(String userId) {
return serverARestTemplateClient.getUserInfo(userId);
}
自定义线程池的适当大小推荐公式:
max_health_count * wait_time + cache_thread_count
max_health_count: 服务在健康状态时每秒支撑的最大请求数。
wait_time: 99%的可延迟时间(以秒为单位)。
cache_thread_count: 用于缓冲的少量额外线程。
三、微调Hystrix
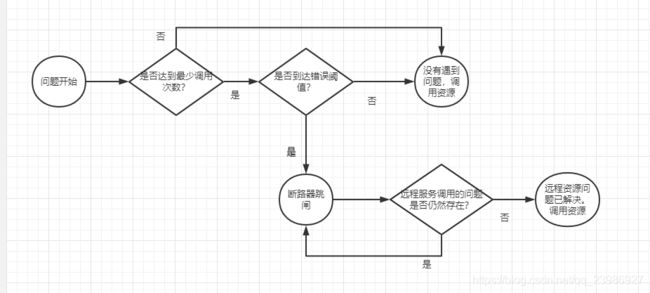
Hystrix不仅能超时长时间运行的调用,它还会监控调用失败的次数,如果调用失败的次数足够多,那么Hystrix会在请求发送到远程资源之前,通过使用调用失败来自动阻止未来的调用到达服务。
- 如果远程资源有性能问题,那么快速失败将防止应用程序等待调用超时。这显著降低了调用应用程序或服务所导致的资源耗尽问题和奔溃的风险。
- 快速失败和阻止来自服务客户端的调用有助于苦苦挣扎的服务保持其负载,而不会彻底崩溃。快速失败给了性能下降的系统一些时间去进行恢复。
下图展示Hystrix在远程资源调用失败时实用的决策过程:
@HystrixCommand注解的配置值
| 属性名称 | 默认值 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| fallbackMethod | None | 标识类中的方法,如果远程调用超时,将调用该方法,回调方法必须与@HystrixComman注解在同一个类中,并且必须具有与调用类相同的方法签名。如果值不存在,Hystrix会抛出异常 |
| threadPoolKey | None | 给予@HysCommand一个唯一的名称,并创建一个独立默认线程池的线程池。如果没有定义任何值,则将使用默认的Hystrix线程池 |
| threadPoolProperties | None | 核心的Hystrix注解属性,用于配置线程池的行为 |
| coresize | 10 | 设置线程池核心线程大小 |
| maxQueueSize | -1 | 设置线程池前面的最大队列大。如果设置为-1,则不使用队列,Hystrix将阻塞请求,查到有一个线程可用来处理 |
| circuitBreaker.requestVolumeThreshold | 20 | 设置Hystrix开始检查断路器是否跳闸之前滚动窗口中必须处理的最小请求数。注意:此值只能使用commanPoolProperties属性设置 |
| circuitBreaker.errorThresholdPercentage | 50 | 在断路器跳闸之前,滚动窗口内必须达到的故障百分比。注意:此值只能使用commanPoolProperties属性设置 |
| circuitBreaker.sleepWindowInMilliseconds | 5000 | 在断路器跳闸之后,Hystrix尝试进行服务调用之前将要等待的时间(毫秒)。注意:此值只能使用commanPoolProperties属性设置 |
| metricRollingStats.timeInMilliseconds | 10000 | Hystrix收集和监控服务调用的统计信息的滚动窗口(毫秒) |
| metricRollingStats.numBuckets | 10 | Hystrix在一个监控窗口中维护的度量桶的数量。监控窗口内的桶数越多,Hystrix在窗口内监控故障的时间越低。 |
四、线程上下文和Hystrix
当一个@HystrixCommand被执行时,它可以使用两种不同的隔离策略:
- THREAD。默认情况下用HREAD隔离策略运行,用于保护调用的每个Hystrix命令都在一个单独的线程池中运行,该线程池不与父线程共享它的上下文。
- SEMAPHORE。Hystrix管理由@HystrixComman注解保护的分布式调用,而不需要启动一个新线程,并且如果调用超时,就会中断父线程。
在默认情况下,Hystrix不会将父线程的上下文传播到由Hystrix命令管理的线程中。这就表明请求的主线程里的ThreadLocal不会被传入到Hystrix的线程中,这就导致获取不到放在请求线程的上下文信息。
针对以上问题,Spring Cloud提供了一种机制,可以将父线程的上下文传播到由Hystrix线程池管理的线程。这种机制被称为HystrixConcurrencyStrategy。
4.1. HystrixConcurrencyStrategy实战
Hystrix允许开发人员定义一种自定义的并发策略,它将包装Hystrix调用,并允许开发人员将附加的父线程上下文注入由Hystrix命令管理的线程中。实现自定义HystrixConcurrencyStrategy需要执行以下步骤:
- 定义自定义的Hystrix并发策略类。
- 定义一个Callable类,将UserContext注入Hystrix命令中。
- 配置Spring Cloud以使用自定义Hystrix并发策略。
// 扩展基本的HystrixConcurrencyStrategy类
public class ThreadLocalAwareStrategy extends HystrixConcurrencyStrategy {
private HystrixConcurrencyStrategy existingConcurrencyStrategy;
// Spring Cloud已经定义了一个并发类。将已经存在的并发策略传入自定义的HystrixConcurrencyStrategy策略类中
public ThreadLocalAwareStrategy(HystrixConcurrencyStrategy existingConcurrencyStrategy) {
this.existingConcurrencyStrategy = existingConcurrencyStrategy;
}
// 有几个方法需要重写,要么用已存在的existingConcurrencyStrategy,要么用父类的方法
@Override
public BlockingQueue<Runnable> getBlockingQueue(int maxQueueSize) {
return existingConcurrencyStrategy != null ? existingConcurrencyStrategy.getBlockingQueue(maxQueueSize)
: super.getBlockingQueue(maxQueueSize);
}
@Override
public <T> HystrixRequestVariable<T> getRequestVariable(HystrixRequestVariableLifecycle<T> rv) {
return existingConcurrencyStrategy != null ? existingConcurrencyStrategy.getRequestVariable(rv)
: super.getRequestVariable(rv);
}
@Override
public ThreadPoolExecutor getThreadPool(HystrixThreadPoolKey threadPoolKey, HystrixThreadPoolProperties threadPoolProperties) {
return existingConcurrencyStrategy != null
? existingConcurrencyStrategy.getThreadPool(threadPoolKey, threadPoolProperties)
: super.getThreadPool(threadPoolKey, threadPoolProperties);
}
@Override
public <T> Callable<T> wrapCallable(Callable<T> callable) {
// 注入Callable实现,它将设置UserContext
return existingConcurrencyStrategy != null
? existingConcurrencyStrategy.wrapCallable(DelegatingUserContextCallable.create(callable,
UserContextHolder.getUserContext()))
: super.wrapCallable(DelegatingUserContextCallable.create(callable, UserContextHolder.getUserContext()));
}
}
public final class DelegatingUserContextCallable<V> implements Callable<V> {
private final Callable<V> delegate;
private UserContext originUserContext;
public DelegatingUserContextCallable(Callable<V> delegate, UserContext originUserContext) {
this.delegate = delegate;
this.originUserContext = originUserContext;
}
@Override
public V call() throws Exception {
// 特别注意:在这里将需要的上下文传递到Hystrix线程中
UserContextHolder.setUserContext(originUserContext);
try {
return delegate.call();
}
finally {
this.originUserContext = null;
}
}
public static <V> Callable<V> create(Callable<V> delegate, UserContext originUserContext) {
return new DelegatingUserContextCallable<>(delegate, originUserContext);
}
}
@Configuration
public class ThreadLocalConfiguration {
@Resource
private HystrixConcurrencyStrategy existingConcurrencyStrategy;
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
// 保留现有的Hystrix插件的引用
HystrixEventNotifier eventNotifier = HystrixPlugins.getInstance().getEventNotifier();
HystrixMetricsPublisher metricsPublisher = HystrixPlugins.getInstance().getMetricsPublisher();
HystrixPropertiesStrategy propertiesStrategy = HystrixPlugins.getInstance().getPropertiesStrategy();
HystrixCommandExecutionHook commandExecutionHook = HystrixPlugins.getInstance().getCommandExecutionHook();
HystrixPlugins.reset();
// 重新注册插件,使用Hystrix插件注册自定义的Hystr并发策略
HystrixPlugins.getInstance().registerConcurrencyStrategy(new ThreadLocalAwareStrategy(existingConcurrencyStrategy));
HystrixPlugins.getInstance().registerEventNotifier(eventNotifier);
HystrixPlugins.getInstance().registerMetricsPublisher(metricsPublisher);
HystrixPlugins.getInstance().registerPropertiesStrategy(propertiesStrategy);
HystrixPlugins.getInstance().registerCommandExecutionHook(commandExecutionHook);
}
}
该处使用的url网络请求的数据。
总结
本章到此已经介绍完了客户端弹性的一些知识点。