Java学习笔记20
Java笔记20
集合框架
什么是集合
- 概念:对象的容器,定义了对多个对象进行操作的常用方法。可实现数组的功能。
- 和数组区别:
- 数组长度固定,集合长度不固定
- 数组可以存储基本类型和引用类型,集合只能存储引用类型
- 位置:
java.util.*
Collection集合的体系结构
Collection父接口
-
特点:
Collection表示任意一组对象,这些对象也称为Collection的元素。一些Collection允许有重复的元素(List),而另一些则不允许(Set)。一些Collection是有序的(List),而另一些则是无序的(Set)。所以,从整体上来说,Collection是无序、无下标、元素不能重复的。 -
Collection接口没有自己的实现类,具体的实现类都在他的子接口中,如List和Set。Collection接口中提供了一系列操作集合的方法,比如增加、删除等等 。 -
方法:
boolean add (Object obj) //添加一个对象
boolean addAll(Collection c) //将一个集合中的所有对象添加到此集合中
void clear() //清空此集合中的所有对象
boolean contains(Object o) //检查此集合中是否包含o对象
boolean equals (Object o) //比较此集合是否与指定对象相等
boolean isEmpty() //判断此集合是否为空
boolean remove(Object o) //在此集合中移除o对象
int size() //返回此集合中的元素个数
Object[] toArray() //将此集合转换成数组
- 练习1:使用
Collection保存字符串
package com.clown.collection;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Iterator;
/*
Collection接口的使用: 保存字符串
1. 添加元素
2. 删除元素
3. 遍历元素
4. 判断集合是否包含指定元素、判断集合是否为空
*/
public class Demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建集合
//ArrayList:List接口的可调整大小数组实现 有序 有下标 元素可重复
Collection collection = new ArrayList();
//1. 添加元素
//add(E e); 将指定的元素追加到此集合的末尾
collection.add("苹果");
collection.add("西瓜");
collection.add("榴莲");
//size(); 返回此集合中的元素数
System.out.println("元素个数:"+collection.size());
//打印该集合
System.out.println(collection);
//2. 删除元素
/*
//remove(Object o); 从此集合中删除指定元素的第一个匹配项(如果存在)。如果集合不包含该元素,则它保持不变
collection.remove("榴莲");
System.out.println("删除之后的元素个数:"+collection.size()); //2
*/
/*
//clear(); 从此集合中删除所有元素。此调用返回后,该集合将为空
collection.clear();
System.out.println("清空之后的元素个数:"+collection.size()); //0
*/
//3. 遍历元素 【重点!!!】
//方法一:使用增强for循环遍历元素
System.out.println("========= 1. 使用增强for循环遍历元素 =========");
//增强for循环
for(Object object : collection){
System.out.println((String) object); //转换成字符串形式输出
}
//方法二:使用迭代器遍历元素(迭代器:专门用来遍历集合的一种方式)
System.out.println("=========== 2. 使用迭代器遍历元素 ============");
//iterator(); 返回此集合中元素的迭代器。 Iterator:对集合元素进行迭代(遍历)的迭代器 接口
//Iterator接口类中有三个方法:
//(1) hasNext(); 判断是否有下一个元素
//(2) next(); 获取下一个元素
//(3) remove(); 删除当前元素
Iterator it = collection.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()){ //判断是否有下一个元素
Object object2 = it.next(); //获取下一个元素
System.out.println((String)object2); //转换成字符串形式输出
//collection.remove(); 错误示范!!! 在迭代过程当中,不能使用Collection父接口的remove()方法! 只能使用Iterator接口的remove()方法!
//it.remove(); //删除元素 正确示范!!!
}
//4. 判断集合是否包含指定元素、判断集合是否为空
//contains(Object o); 判断集合是否包含指定元素
System.out.println(collection.contains("西瓜"));
//isEmpty(); 判断集合是否为空
System.out.println(collection.isEmpty());
}
}
运行结果:
- 练习2:使用
Collection保存学生信息
Student.java
package com.clown.collection;
//学生类
public class Student {
//属性
private String name;
private int age;
//无参构造
public Student(){
}
//有参构造
public Student(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
//get() & set()
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
//重写toString() 美化打印
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + ", age=" + age + '}';
}
}
Demo2.java
package com.clown.collection;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Iterator;
//Collection接口的使用: 保存学生信息
public class Demo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建Collection对象
Collection collection = new ArrayList();
//创建学生对象
Student s1 = new Student("张三",20);
Student s2 = new Student("李四",18);
Student s3 = new Student("王五",21);
//1. 添加
collection.add(s1);
collection.add(s2);
collection.add(s3);
System.out.println("元素个数:"+collection.size());
System.out.println(collection.toString());
/*
//2. 删除
collection.remove(s1);
//collection.clear();
System.out.println("删除之后的元素个数:"+collection.size()); //2
*/
//3. 遍历
//(1)使用增强for循环遍历元素
System.out.println("========= 1. 使用增强for循环遍历元素 =========");
for(Object object : collection){
Student s = (Student) object;
System.out.println(s.toString());
}
//(2)使用迭代器遍历
System.out.println("=========== 2. 使用迭代器遍历元素 ============");
Iterator it = collection.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()){
Object object = it.next();
Student s = (Student) object;
System.out.println(s.toString());
}
//4. 判断
System.out.println(collection.contains(s1));
System.out.println(collection.isEmpty());
}
}
运行结果:
List子接口
- 特点:有序、有下标、元素可以重复。
- 方法:
void add(int index,Object o) //在index位置插入对象o
boolean addAll(int index,Collection c) //将一个集合中的元素添加到此集合中的index位置
Object get(int index) //返回集合中指定位置的元素
List subList(int fromIndex,int toIndex) //返回fromIndex和toIndex之间的集合元素
- 练习1:
package com.clown.collection.list;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.ListIterator;
/*
List子接口的使用:
特点:
1. 有序、有下标
2. 元素可以重复
*/
public class Demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建集合对象
List list = new ArrayList();
//1. 添加元素
//add(E e); 将指定的元素追加到此列表的末尾 e:要附加到此列表的元素
list.add("苹果");
list.add("小米");
//add(int index, E element); 将指定的元素插入此List中的指定位置 index:要插入指定元素的下标 element:要插入的元素
list.add(0,"华为");
//打印元素个数
System.out.println("元素个数:"+list.size());
//以字符串形式打印元素
System.out.println(list.toString());
/*
//2. 删除元素
//list.remove("苹果"); //删除元素:"苹果"
//list.clear(); //清空所有元素
//remove(int index); 删除指定下标位置的元素
list.remove(0); //删除下标为0的位置的元素
//打印元素个数
System.out.println("元素个数:"+list.size());
//以字符串形式打印元素
System.out.println(list.toString());
*/
//3. 遍历元素
//(1) 使用for循环遍历元素
System.out.println("=========== 1. 使用for循环遍历元素 ===========");
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
//get(int index); 获取下标位置的元素
Object object = list.get(i);
//转换成字符串形式并输出
System.out.println((String) object);
}
//(2) 使用增强for循环遍历元素
System.out.println("========= 2. 使用增强for循环遍历元素 =========");
for (Object object : list) {
//转换成字符串形式并输出
System.out.println((String) object);
}
//(3) 使用迭代器遍历元素
System.out.println("=========== 3. 使用迭代器遍历元素 ============");
//iterator(); 迭代器
Iterator it = list.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
//获取当前元素
Object object = it.next();
//转换成字符串形式并输出
System.out.println((String) object);
}
//(4) 使用列表迭代器遍历元素
System.out.println("====== 4.1 使用列表迭代器从前往后遍历元素 ======");
//listIterator(); 列表迭代器,允许程序员按任一方向遍历列表、迭代期间修改列表,以及获得迭代器在列表中的当前位置
ListIterator lit = list.listIterator();
//(4.1) 使用列表迭代器从前往后遍历元素
while (lit.hasNext()) { //hasNext(); 判断是否有下一个元素
//nextIndex(); 获取当前元素的位置下标 (从前往后遍历时)
int index = lit.nextIndex();
//next(); 获取当前元素 (从前往后遍历时)
Object object = lit.next();
//打印下标和对应的元素
System.out.println(index+":"+(String) object);
}
//(4.2) 使用列表迭代器从后往前遍历元素
System.out.println("====== 4.2 使用列表迭代器从后往前遍历元素 ======");
while (lit.hasPrevious()) { //hasPrevious(); 判断是否有上一个元素
//previousIndex(); 获取当前元素的位置下标 (从后往前遍历时)
int index = lit.previousIndex();
//previous(); 获取当前元素 (从后往前遍历时)
Object object = lit.previous();
//打印下标和对应的元素
System.out.println(index+":"+(String) object);
}
//4. 判断
System.out.println("=============================================");
//contains(Object o); 判断该集合是否包含指定的元素
System.out.println(list.contains("小米"));
//isEmpty(); 判断该集合是否为空
System.out.println(list.isEmpty());
//5. 获取元素位置下标
System.out.println("=============================================");
//indexOf(Object o); 获取指定元素的位置下标
System.out.println(list.indexOf("华为"));
}
}
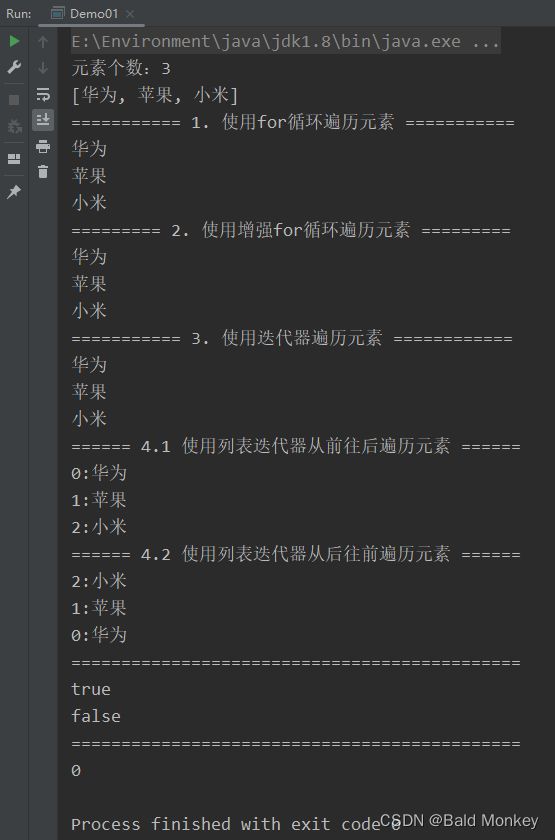
运行结果:
- 练习2:
package com.clown.collection.list;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
//List子接口的使用:
public class Demo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建集合对象
List list = new ArrayList();
//1. 添加数字类型的数据 (自动装箱)
list.add(20);
list.add(30);
list.add(40);
list.add(50);
list.add(60);
//打印元素个数
System.out.println("元素个数:"+list.size());
//以字符串形式打印元素
System.out.println(list.toString());
//2. 删除数字类型的数据
//list.remove(0);
//list.remove(new Integer(20));
list.remove((Object) 20); //注:不能直接用 list.remove(20); 否则报异常:IndexOutOfBoundsException!!!
//打印删除后的元素个数
System.out.println("删除后的元素个数:"+list.size());
//以字符串形式打印元素
System.out.println(list.toString());
//3. 补充方法:subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex)
//subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex); 返回指定下标区间内的子集合 区间:[fromIndex, toIndex)
List sublist = list.subList(1,3); //[1, 3)
//以字符串形式打印元素
System.out.println(sublist.toString());
}
}
运行结果:
List实现类
ArrayList【重点】
-
数组结构实现,查询快、增删慢;
-
JDK1.2版本,运行效率快、线程不安全。
-
源码分析:
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10; //默认容量为10
//注意:如果没有向集合中添加任何元素时,则容量为0;添加任意一元素之后,容量为10;超过最大容量时,每次扩容后的大小为原来的1.5倍
transient Object[] elementData; //存放元素的数组
private int size; //实际的元素个数
构造方法:
public ArrayList() {
this.elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA; //DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA是一个空数组
}
add():
//以创建集合之后,向集合中添加第一个元素的过程为例,分析此过程中add()方法的源码
public boolean add(E e) {
//初始时,集合的元素个数 size: 0;
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
elementData[size++] = e;
return true;
}
//minCapacity: size + 1; size: 0;
private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) {
ensureExplicitCapacity(calculateCapacity(elementData, minCapacity));
}
//minCapacity: size + 1; size: 0;
private static int calculateCapacity(Object[] elementData, int minCapacity) {
//DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA: 空数组
if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) {
//DEFAULT_CAPACITY: 10 --> Math.max(10, 1) --> return 10;
return Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity); //Math.max(int a, int b); 取最大值
}
return minCapacity; //10
}
//minCapacity: 10;
private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) {
modCount++;
// overflow-conscious code
//elementData.length: 0
if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)
grow(minCapacity);
}
//minCapacity: 10;
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
// 0 = 0
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
// 0 = 0 + 0
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);
// 0 - 10
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
// 10 = 10
newCapacity = minCapacity;
// 10 - Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
// minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win:
//copyOf(T[] original, int newLength); 复制指定的数组,并指定其长度 original - 要复制的数组 newLength - 要返回的副本的长度
//newCapacity: 10
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity); //复制一个容量为10的数组
}
- 练习:
Student.java
package com.clown.collection.list;
//学生类
public class Student {
//属性
private String name;
private int age;
//无参构造
public Student(){
}
//有参构造
public Student(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
//get() & set()
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
//重写 toString() 美化打印
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + ", age=" + age + '}';
}
//重写 equals()
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
//1. 判断是否是同一个对象
if (this == obj) {
return true;
}
//2. 判断是否为空
if (obj == null) {
return false;
}
//3. 判断对象 obj是否是 Student类或 Student类的子类所创建的对象
if (obj instanceof Student) {
//将对象 obj强制转换为 Student类型
Student s = (Student) obj;
//4. 依次比较属性是否相等
if (this.name == s.name && this.age == s.age) {
return true;
}
}
//5. 不满足条件时,返回 false
return false;
}
}
ArrayListDemo01.java
package com.clown.collection.list;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.ListIterator;
//ArrayList的使用
//存储方式:数组 查找遍历速度快,增删慢
public class ArrayListDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建集合
ArrayList arrayList = new ArrayList<>();
//创建学生对象 位置: 堆
Student s1 = new Student("张三",20);
Student s2 = new Student("李四",21);
Student s3 = new Student("王五",18);
//1. 添加元素到集合中
arrayList.add(s1);
arrayList.add(s2);
arrayList.add(s3);
//打印此集合中的元素数
System.out.println("元素个数:"+arrayList.size());
//以字符串形式打印该集合
System.out.println(arrayList.toString());
/*
//2. 删除元素
arrayList.remove(new Student("张三",20)); //需要重写 equals(this == obj)方法!!!
//打印删除后此集合中的元素数
System.out.println("删除后的元素个数:"+arrayList.size());
*/
//3. 遍历元素 【重点】
//(1) 使用for循环遍历元素
System.out.println("=========== 1. 使用for循环遍历元素 ===========");
for (int i = 0; i < arrayList.size(); i++) {
Object object = arrayList.get(i);
Student s = (Student) object;
System.out.println(s.toString());
}
//(2) 使用增强for循环遍历元素
System.out.println("========= 2. 使用增强for循环遍历元素 =========");
for (Object object : arrayList) {
Student s = (Student) object;
System.out.println(s.toString());
}
//(3) 使用迭代器遍历元素
System.out.println("=========== 3. 使用迭代器遍历元素 ============");
Iterator it = arrayList.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
Object object = it.next();
Student s = (Student) object;
System.out.println(s.toString());
}
//(4) 使用列表迭代器遍历元素
System.out.println("====== 4.1 使用列表迭代器从前往后遍历元素 ======");
ListIterator lit = arrayList.listIterator();
//(4.1) 使用列表迭代器从前往后遍历元素
while (lit.hasNext()) {
int index = lit.nextIndex();
Object object = lit.next();
Student s = (Student) object;
System.out.println(index+":"+s.toString());
}
//(4.2) 使用列表迭代器从后往前遍历元素
System.out.println("====== 4.2 使用列表迭代器从后往前遍历元素 ======");
while (lit.hasPrevious()) {
int index = lit.previousIndex();
Object object = lit.previous();
Student s = (Student) object;
System.out.println(index+":"+s.toString());
}
//4. 判断
System.out.println("=============================================");
System.out.println(arrayList.contains(new Student("张三",20))); //true 已重写了 equals(this == obj)
System.out.println(arrayList.isEmpty()); //false
//5. 查找元素位置
System.out.println("=============================================");
System.out.println(arrayList.indexOf(new Student("张三",20)));
}
}
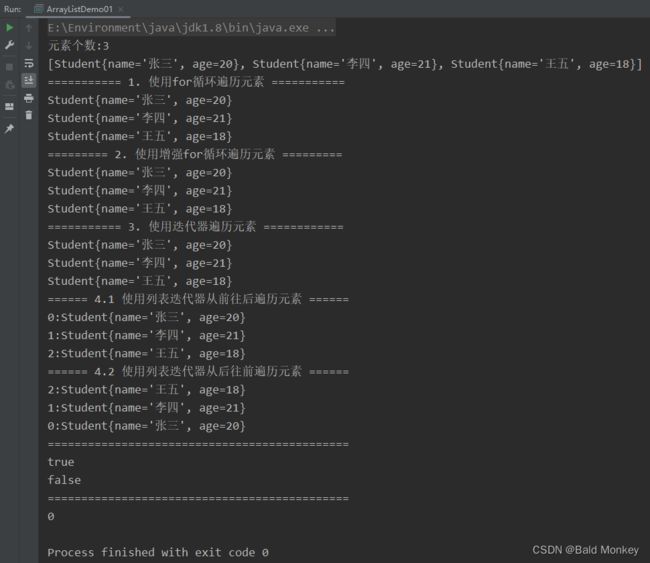
运行结果:
Vector
- 数组结构实现,查询快、增删慢;
- JDK1.0版本,运行效率慢、线程安全。
Vector类可以实现可增长的对象数组。与数组一样,它包含可以使用整数索引进行访问的组件。但是,Vector的大小可以根据需要增大或缩小,以适应创建Vector后进行添加或移除项的操作。- 练习:
package com.clown.collection.list;
import java.util.Enumeration;
import java.util.Vector;
//Vector集合的使用
//存储结构:数组
public class VectorDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建集合
Vector vector = new Vector<>();
//1. 添加元素
vector.add("草莓");
vector.add("芒果");
vector.add("西瓜");
System.out.println("元素个数:"+vector.size());
System.out.println(vector.toString());
System.out.println("=============================");
/*
//2. 删除元素
vector.remove(1);
vector.remove("草莓");
vector.clear();
*/
//3. 遍历元素
//Vector特有:使用枚举器遍历元素
//elements(); 枚举器 返回 Vector中所有元素的枚举
Enumeration en = vector.elements();
while (en.hasMoreElements()) { //hasMoreElements(); 判断是否有下一个元素
//nextElement(); 获取当前元素
Object object = en.nextElement();
String str = (String) object;
System.out.println(str);
}
System.out.println("=============================");
//4. 判断
System.out.println(vector.contains("西瓜"));
System.out.println(vector.isEmpty());
System.out.println("=============================");
//5. 补充:Vector的其他方法
//firstElement(); 获取第一个元素
Object object1 = vector.firstElement();
String str1 = (String) object1;
System.out.println(str1);
//lastElement(); 获取最后一个元素
Object object2 = vector.lastElement();
String str2 = (String) object2;
System.out.println(str2);
//elementAt(int index); 获取指定下标位置的元素
Object object3 = vector.elementAt(0);
String str3 = (String) object3;
System.out.println(str3);
}
}
运行结果:
LinkedList
- 链表结构实现,增删快,查询慢。
- 练习:
Student.java
package com.clown.collection.list;
//学生类
public class Student {
//属性
private String name;
private int age;
//无参构造
public Student(){
}
//有参构造
public Student(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
//get() & set()
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
//重写 toString() 美化打印
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + ", age=" + age + '}';
}
//重写 equals()
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
//1. 判断是否是同一个对象
if (this == obj) {
return true;
}
//2. 判断是否为空
if (obj == null) {
return false;
}
//3. 判断对象 obj是否是 Student类或 Student类的子类所创建的对象
if (obj instanceof Student) {
//将对象 obj强制转换为 Student类型
Student s = (Student) obj;
//4. 依次比较属性是否相等
if (this.name == s.name && this.age == s.age) {
return true;
}
}
//5. 不满足条件时,返回 false
return false;
}
}
LinkedListDemo01.java
package com.clown.collection.list;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.ListIterator;
/*
LinkedList集合的使用:
存储结构:双向链表
*/
public class LinkedListDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建集合
LinkedList linkedList = new LinkedList<>();
//创建学生对象 位置: 堆
Student s1 = new Student("张三",20);
Student s2 = new Student("李四",21);
Student s3 = new Student("王五",18);
//1. 添加元素到集合中
linkedList.add(s1);
linkedList.add(s2);
linkedList.add(s3);
System.out.println("元素个数:"+linkedList.size());
System.out.println(linkedList.toString());
/*
//2. 删除元素
linkedList.remove(s1);
//linkedList,clear();
System.out.println("删除后的元素个数:"+linkedList.size());
*/
//3. 遍历元素 【重点】
//(1) 使用for循环遍历元素
System.out.println("=========== 1. 使用for循环遍历元素 ===========");
for (int i = 0; i < linkedList.size(); i++) {
Object object = linkedList.get(i);
Student s = (Student) object;
System.out.println(s.toString());
}
//(2) 使用增强for循环遍历元素
System.out.println("========= 2. 使用增强for循环遍历元素 =========");
for (Object object : linkedList) {
Student s = (Student) object;
System.out.println(s.toString());
}
//(3) 使用迭代器遍历元素
System.out.println("=========== 3. 使用迭代器遍历元素 ============");
Iterator it = linkedList.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
Object object = it.next();
Student s = (Student) object;
System.out.println(s.toString());
}
//(4) 使用列表迭代器遍历元素
System.out.println("====== 4.1 使用列表迭代器从前往后遍历元素 ======");
ListIterator lit = linkedList.listIterator();
//(4.1) 使用列表迭代器从前往后遍历元素
while (lit.hasNext()) {
int index = lit.nextIndex();
Object object = lit.next();
Student s = (Student) object;
System.out.println(index+":"+s.toString());
}
//(4.2) 使用列表迭代器从后往前遍历元素
System.out.println("====== 4.2 使用列表迭代器从后往前遍历元素 ======");
while (lit.hasPrevious()) {
int index = lit.previousIndex();
Object object = lit.previous();
Student s = (Student) object;
System.out.println(index+":"+s.toString());
}
//4. 判断
System.out.println("=============================================");
System.out.println(linkedList.contains(s1));
System.out.println(linkedList.isEmpty());
//5. 查找元素位置
System.out.println("=============================================");
System.out.println(linkedList.indexOf(s1));
}
}
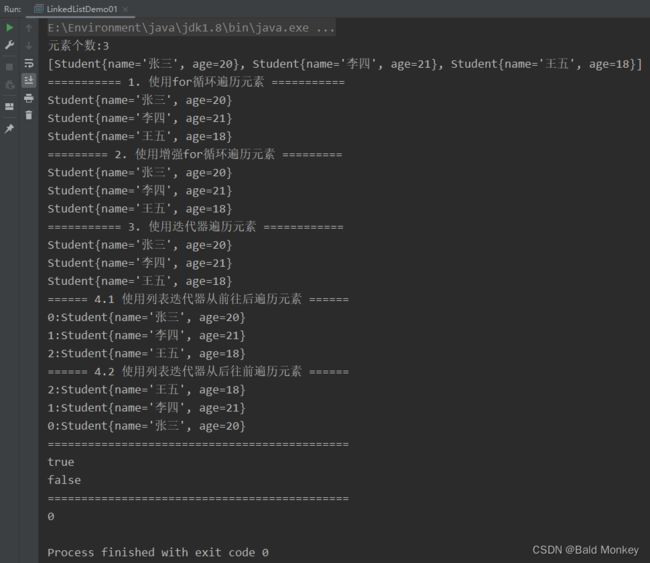
运行结果: