自制编程语言基于c语言实验记录之二:总结三四五六七章之编译类定义
博客前言
由于本书第六七章是编译脚本语言sparrow生成指令、虚拟机运行指令的核心章节,需要连在一起理解,同时三四五章都是六七章的铺垫,所以专门写多篇博客来记录六七章。
同时本书相比《操作系统真相还原》缺少具体例子很难梳理项目整体代码,因此博客主要记录方式是按具体编译sparrow代码的例子,以编译器执行顺序罗列出所有相关代码。
本章博客主要解决sparrow的类的编译,以一个具体例子梳理编译类定义的相关全部代码,列举了编译类定义实例变量、静态变量、实例方法、静态方法、new(实例+静态方法)
1.sparrow语言的简单类
class Foo{
var instantField //实例变量
static var staticField //静态变量
instantField(){} //实例方法
static staticMethod(){} //静态方法
new(){} //构造方法
}
以上述简单类为例,一个类里面只会定义以上五种类型。
2.类定义:compileClassDefinition(CompileUnit* cu)
//编译类定义
static void compileClassDefinition(CompileUnit* cu) {
Variable classVar;
if (cu->scopeDepth != -1) { //目前只支持在模块作用域定义类
COMPILE_ERROR(cu->curParser,
"class definition must be in the module scope!");
}
classVar.scopeType = VAR_SCOPE_MODULE;
consumeCurToken(cu->curParser, TOKEN_ID,
"keyword class should follow by class name!"); //读入类名
classVar.index = declareVariable(cu,
cu->curParser->preToken.start, cu->curParser->preToken.length);
//生成类名,用于创建类
ObjString* className = newObjString(cu->curParser->vm,
cu->curParser->preToken.start, cu->curParser->preToken.length);
//生成加载类名的指令
emitLoadConstant(cu, OBJ_TO_VALUE(className));
if (matchToken(cu->curParser, TOKEN_LESS)) { //类继承
expression(cu, BP_CALL); //把父类名加载到栈顶
} else { //默认加载object类为基类
emitLoadModuleVar(cu, "object");
}
//创建类需要知道域的个数,目前类未定义完,因此域的个数未知,
//因此先临时写为255,待类编译完成后再回填属性数
int fieldNumIndex = writeOpCodeByteOperand(cu, OPCODE_CREATE_CLASS, 255);
//虚拟机执行完OPCODE_CREATE_CLASS后,栈顶留下了创建好的类,
//因此现在可以用该类为之前声明的类名className赋值
if (cu->scopeDepth == -1) {
emitStoreModuleVar(cu, classVar.index);
}
ClassBookKeep classBK;
classBK.name = className;
classBK.inStatic = false; //默认为false
StringBufferInit(&classBK.fields);
IntBufferInit(&classBK.instantMethods);
IntBufferInit(&classBK.staticMethods);
//此时cu是模块的编译单元,跟踪当前编译的类
cu->enclosingClassBK = &classBK;
//读入类名后的'{'
consumeCurToken(cu->curParser, TOKEN_LEFT_BRACE,
"expect '{' after class name in the class declaration!");
//进入类体
enterScope(cu);
//直到类定义结束'}'为止
while (!matchToken(cu->curParser, TOKEN_RIGHT_BRACE)) {
compileClassBody(cu, classVar);
if (PEEK_TOKEN(cu->curParser) == TOKEN_EOF) {
COMPILE_ERROR(cu->curParser, "expect '}' at the end of class declaration!");
}
}
//上面临时写了255个字段,现在类编译完成,回填正确的字段数.
//classBK.fields的是由compileVarDefinition函数统计的
cu->fn->instrStream.datas[fieldNumIndex] = classBK.fields.count;
symbolTableClear(cu->curParser->vm, &classBK.fields);
IntBufferClear(cu->curParser->vm, &classBK.instantMethods);
IntBufferClear(cu->curParser->vm, &classBK.staticMethods);
//enclosingClassBK用来表示是否在编译类,
//编译完类后要置空,编译下一个类时再重新赋值
cu->enclosingClassBK = NULL;
//出作用域,丢弃相关局部变量
leaveScope(cu);
}
本函数在词法分析器读到"class"后开始执行,主要可以总结以下几步:
- 读class后面的类名字符串后,调用declareVariable将类名声明为模块变量,即在ObjModule的objModule->moduleVarName存储名字,objModule->moduleVarValue存储值(目前存储的是NULL作为初始值),索引值存储到classVar.index。
- 调用emitLoadConstant存储类名于常量表cu->fn->constants,再生成加载类名指令于栈顶curThread->esp,若有父类再加载父类名于栈顶,无则加载object于栈顶
- 生成OPCODE_CREATE_CLASS指令创建类,于栈顶留下创建好的类
- 调用emitStoreModuleVar将栈顶的类加载回classVar.index指向的objModule->moduleVarValue中,也就是把刚刚创建好的类(类即是模块变量)覆盖了之前的NULL作为模块变量的值
- while循环调用compileClassBody编译类的大括号里面的代码,生成对应的指令。
2.1 declareVariable(CompileUnit* cu, const char* name, uint32_t length)
2.1.1 defineModuleVar
//在模块objModule中定义名为name,值为value的模块变量
int defineModuleVar(VM* vm, ObjModule* objModule,
const char* name, uint32_t length, Value value) {
if (length > MAX_ID_LEN) {
//也许name指向的变量名并不以'\0'结束,将其从源码串中拷贝出来
char id[MAX_ID_LEN] = {'\0'};
memcpy(id, name, length);
//本函数可能是在编译源码文件之前调用的,
//那时还没有创建parser, 因此报错要分情况:
if (vm->curParser != NULL) { //编译源码文件
COMPILE_ERROR(vm->curParser,
"length of identifier \"%s\" should be no more than %d", id, MAX_ID_LEN);
} else { // 编译源码前调用,比如加载核心模块时会调用本函数
MEM_ERROR("length of identifier \"%s\" should be no more than %d", id, MAX_ID_LEN);
}
}
//从模块变量名中查找变量,若不存在就添加
int symbolIndex = getIndexFromSymbolTable(&objModule->moduleVarName, name, length);
if (symbolIndex == -1) {
//添加变量名
symbolIndex = addSymbol(vm, &objModule->moduleVarName, name, length);
//添加变量值
ValueBufferAdd(vm, &objModule->moduleVarValue, value);
} else if (VALUE_IS_NUM(objModule->moduleVarValue.datas[symbolIndex])) {
//若遇到之前预先声明的模块变量的定义,在此为其赋予正确的值
objModule->moduleVarValue.datas[symbolIndex] = value;
} else {
symbolIndex = -1; //已定义则返回-1,用于判断重定义
}
return symbolIndex;
}
模块变量包括类名,定义模块变量,即ObjModule的objModule->moduleVarName存储名字,objModule->moduleVarValue存储值
2.1.2 declareLocalVar、declareVariable
//添加局部变量到cu
static uint32_t addLocalVar(CompileUnit* cu, const char* name, uint32_t length) {
LocalVar* var = &(cu->localVars[cu->localVarNum]);
var->name = name;
var->length = length;
var->scopeDepth = cu->scopeDepth;
var->isUpvalue = false;
return cu->localVarNum++;
}
//声明局部变量
static int declareLocalVar(CompileUnit* cu, const char* name, uint32_t length) {
if (cu->localVarNum >= MAX_LOCAL_VAR_NUM) {
COMPILE_ERROR(cu->curParser, "the max length of local variable of one scope is %d", MAX_LOCAL_VAR_NUM);
}
//判断当前作用域中该变量是否已存在
int idx = (int)cu->localVarNum - 1;
while (idx >= 0) {
LocalVar* var = &cu->localVars[idx];
//只在当前作用域中查找同名变量,
//如果到了父作用域就退出,减少没必要的遍历
if (var->scopeDepth < cu->scopeDepth) {
break;
}
if (var->length == length && memcmp(var->name, name, length) == 0) {
char id[MAX_ID_LEN] = {'\0'};
memcpy(id, name, length);
COMPILE_ERROR(cu->curParser, "identifier \"%s\" redefinition!", id);
}
idx--;
}
//检查过后声明该局部变量
return addLocalVar(cu, name, length);
}
//根据作用域声明变量
static int declareVariable(CompileUnit* cu, const char* name, uint32_t length) {
//若当前是模块作用域就声明为模块变量
if (cu->scopeDepth == -1) {
int index = defineModuleVar(cu->curParser->vm,
cu->curParser->curModule, name, length, VT_TO_VALUE(VT_NULL));
if (index == -1) { //重复定义则报错
char id[MAX_ID_LEN] = {'\0'};
memcpy(id, name, length);
COMPILE_ERROR(cu->curParser, "identifier \"%s\" redefinition!", id);
}
return index;
}
//否则是局部作用域,声明局部变量
return declareLocalVar(cu, name, length);
}
声明局部变量即把局部变量存储在
CompileUnit cu的cu->localVars[MAX_LOCAL_VAR_NUM]中
cu->localVarNum为最后一个已声明局部变量
2.2 emitLoadConstant
//添加常量并返回其索引
static uint32_t addConstant(CompileUnit* cu, Value constant) {
ValueBufferAdd(cu->curParser->vm, &cu->fn->constants, constant);
return cu->fn->constants.count - 1;
}
//生成加载常量的指令
static void emitLoadConstant(CompileUnit* cu, Value value) {
int index = addConstant(cu, value);
writeOpCodeShortOperand(cu, OPCODE_LOAD_CONSTANT, index);
}
#define PUSH(value) (*curThread->esp++ = value) //压栈
//读取指令流中的2字节
#define READ_SHORT() (ip += 2, (uint16_t)((ip[-2] << 8) | ip[-1]))
CASE(LOAD_CONSTANT):
//指令流: 2字节的常量索引
//加载常量就是把常量表中的数据入栈
PUSH(fn->constants.datas[READ_SHORT()]);
LOOP();
cu->fn->constants中添加Value类型常量,OPCODE_LOAD_CONSTANT用于将cu->fn->constants中的该变量加载到curThread->esp
2.3 emitLoadModuleVar
//生成加载类的指令
static void emitLoadModuleVar(CompileUnit* cu, const char* name) {
int index = getIndexFromSymbolTable(
&cu->curParser->curModule->moduleVarName, name, strlen(name));
ASSERT(index != -1, "symbol should have been defined");
writeOpCodeShortOperand(cu, OPCODE_LOAD_MODULE_VAR, index);
}
CASE(LOAD_MODULE_VAR):
//指令流: 2字节的模块变量索引
PUSH(fn->module->moduleVarValue.datas[READ_SHORT()]);
LOOP();
2.4 CREATE_CLASS
CASE(CREATE_CLASS): {
//指令流: 1字节的field数量
//栈顶: 基类 次栈顶: 子类名
uint32_t fieldNum = READ_BYTE();
Value superClass = curThread->esp[-1]; //基类名
Value className = curThread->esp[-2]; //子类名
//回收基类所占的栈空间,
//次栈顶的空间暂时保留,创建的类会直接用该空间.
DROP();
//校验基类合法性,若不合法则停止运行
validateSuperClass(vm, className, fieldNum, superClass);
Class* class = newClass(vm, VALUE_TO_OBJSTR(className),
fieldNum, VALUE_TO_CLASS(superClass));
//类存储于栈底
stackStart[0] = OBJ_TO_VALUE(class);
LOOP();
}
栈顶是基类(父类)名,次栈顶是子类名。
将newclass出的类转化成Value后存储于运行时栈栈底stackStart[0]
2.5 emitStoreModuleVar
//生成存储模块变量的指令
static void emitStoreModuleVar(CompileUnit* cu, int index) {
//把栈顶数据存储到moduleVarValue[index]
writeOpCodeShortOperand(cu, OPCODE_STORE_MODULE_VAR, index);
writeOpCode(cu, OPCODE_POP); //弹出栈顶数据
}
#define PEEK() (*(curThread->esp - 1)) // 获得栈顶的数据
#define POP() (*(--curThread->esp)) //出栈
CASE(STORE_MODULE_VAR):
//栈顶: 模块变量值
fn->module->moduleVarValue.datas[READ_SHORT()] = PEEK();
LOOP();
CREATE_CLASS将创建的类存储于运行时栈栈底stackStart[0],也就是curThread->esp - 1即栈顶,
栈顶的值即新创建的类存储到fn->module->moduleVarValue.datas[index]中,再弹出无用的栈顶数据
2.6 compileClassBody
//编译类体
static void compileClassBody(CompileUnit* cu, Variable classVar) {
if (matchToken(cu->curParser, TOKEN_STATIC)) {
if (matchToken(cu->curParser, TOKEN_VAR)) { //处理静态域 "static var id"
compileVarDefinition(cu, true);
} else { //处理静态方法,"static methodName"
compileMethod(cu, classVar, true);
}
} else if (matchToken(cu->curParser, TOKEN_VAR)) { //实例域
compileVarDefinition(cu, false);
} else { //类的方法
compileMethod(cu, classVar, false);
}
}
类中编译语句一共四种,实例变量、静态变量,实例方法、静态方法。
new这样的构造方法既属于实例方法又属于静态方法。
词法分析器读到new的时候,由于未读到static,所以走的是实例方法,但是后面方法签名函数idMethodSignature会检测到new这个字符串,所以生成的sign的type为构造函数以此区分。
2.7 compileVarDefinition(CompileUnit* cu, bool isStatic)
//编译变量定义
static void compileVarDefinition(CompileUnit* cu, bool isStatic) {
consumeCurToken(cu->curParser, TOKEN_ID, "missing variable name!");
Token name = cu->curParser->preToken;
//只支持定义单个变量
if (cu->curParser->curToken.type == TOKEN_COMMA) {
COMPILE_ERROR(cu->curParser, "'var' only support declaring a variable.");
}
//一 先判断是否是类中的域定义 确保cu是模块cu
if (cu->enclosingUnit == NULL && cu->enclosingClassBK != NULL) {
if (isStatic) { //静态域
char* staticFieldId = ALLOCATE_ARRAY(cu->curParser->vm, char, MAX_ID_LEN);
memset(staticFieldId, 0, MAX_ID_LEN);
uint32_t staticFieldIdLen;
char* clsName = cu->enclosingClassBK->name->value.start;
uint32_t clsLen = cu->enclosingClassBK->name->value.length;
//用前缀"'Cls '+类名+变量名"做为静态域在模块编译单元中的局部变量
memmove(staticFieldId, "Cls", 3);
memmove(staticFieldId + 3, clsName, clsLen);
memmove(staticFieldId + 3 + clsLen, " ", 1);
const char* tkName = name.start;
uint32_t tkLen = name.length;
memmove(staticFieldId + 4 + clsLen, tkName, tkLen);
staticFieldIdLen = strlen(staticFieldId);
if (findLocal(cu, staticFieldId, staticFieldIdLen) == -1) {
int index = declareLocalVar(cu, staticFieldId, staticFieldIdLen);
writeOpCode(cu, OPCODE_PUSH_NULL);
ASSERT(cu->scopeDepth == 0, "should in class scope!");
defineVariable(cu, index);
//静态域可初始化
Variable var = findVariable(cu, staticFieldId, staticFieldIdLen);
if (matchToken(cu->curParser, TOKEN_ASSIGN)) {
expression(cu, BP_LOWEST);
emitStoreVariable(cu, var);
}
} else {
COMPILE_ERROR(cu->curParser,
"static field '%s' redefinition!", strchr(staticFieldId, ' ') + 1);
}
} else { //定义实例域
ClassBookKeep* classBK = getEnclosingClassBK(cu);
int fieldIndex = getIndexFromSymbolTable(
&classBK->fields, name.start, name.length);
if (fieldIndex == -1) {
fieldIndex = addSymbol(cu->curParser->vm,
&classBK->fields, name.start, name.length);
} else {
if (fieldIndex > MAX_FIELD_NUM) {
COMPILE_ERROR(cu->curParser,
"the max number of instance field is %d!", MAX_FIELD_NUM);
} else {
char id[MAX_ID_LEN] = {'\0'};
memcpy(id, name.start, name.length);
COMPILE_ERROR(cu->curParser,
"instance field '%s' redefinition!", id);
}
if (matchToken(cu->curParser, TOKEN_ASSIGN)) {
COMPILE_ERROR(cu->curParser,
"instance field isn`t allowed initialization!");
}
}
}
return;
}
//二 若不是类中的域定义,就按照一般的变量定义
if (matchToken(cu->curParser, TOKEN_ASSIGN)) {
//若在定义时赋值就解析表达式,结果会留到栈顶
expression(cu, BP_LOWEST);
} else {
//否则就初始化为NULL,即在栈顶压入NULL,
//也是为了与上面显式初始化保持相同栈结构
writeOpCode(cu, OPCODE_PUSH_NULL);
}
uint32_t index = declareVariable(cu, name.start, name.length);
defineVariable(cu, index);
}
词法分析器读到var后会执行此函数,用于编译变量定义语句。另外变量的使用语句的编译属于标识符的编译。此函数共处理定义类的实例变量、静态变量、以及一般的模块变量。
2.7.1 编译定义类静态变量语句:“static var 变量名 = 变量值”
若编译的是静态变量语句"static var 变量名 = 变量值",步骤总结如下:
- 拼静态变量名:静态变量名为cls +类名+变量名
- 在模块cu->LocalVar寻找该静态变量
- 找到报未找到则declareLocalVar把静态变量存入模块cu->LocalVar(仅声明,不包含存储值)、局部变量的值存在运行时栈, OPCODE_PUSH_NULL已经把NULL放在了栈顶作为该局部变量初始值defineVariable啥也不做。
- 若有等于号赋值,则expression解析生成等于号右边的表达式的指令,再emitStoreVariable生成存储指令STORE_LOCAL_VAR再次将expression计算出的已经放入栈顶的值存入运行时栈相应位置,cu->LocalVar的索引和运行时栈索引一致。
cu->enclosingUnit == NULL && cu->enclosingClassBK != NULL表示正在编译类中的"static var 变量名 = 变量值" 语句。
cu->enclosingUnit指向的是父编译单元。如果编译的是方法中的"static var 类名"语句,那么当前cu是方法cu,父cu是模块cu,所以cu->enclosingUnit会指向模块cu而不是NULL。如果是NULL表示当前cu是模块cu。cu->enclosingClassBK指向编译的类,如果不等于NULL说明正在编译类中语句。
静态变量被所有实例共享,因此被当作模块的局部局部变量。由于不同类中可以定义同名静态变量,为了防止同名,静态变量名为cls +类名+变量名。
2.7.1.1 findLocal、defineVariable
//查找局部变量
static int findLocal(CompileUnit* cu, const char* name, uint32_t length) {
//内部作用域变量会覆外层,故从后往前,由最内层逐渐往外层找
int index = cu->localVarNum - 1;
while (index >= 0) {
if (cu->localVars[index].length == length &&
memcmp(cu->localVars[index].name, name, length) == 0) {
return index;
}
index--;
}
return -1;
}
//定义变量为其赋值
static void defineVariable(CompileUnit* cu, uint32_t index) {
//局部变量已存储到栈中,无须处理.
//模块变量并不存储到栈中,因此将其写回相应位置
if (cu->scopeDepth == -1) {
//把栈顶数据存入参数index指定的全局模块变量
writeOpCodeShortOperand(cu, OPCODE_STORE_MODULE_VAR, index);
writeOpCode(cu, OPCODE_POP); //弹出栈顶数据,因为上面OPCODE_STORE_MODULE_VAR已经将其存储了
}
}
CASE(STORE_MODULE_VAR):
//栈顶: 模块变量值
fn->module->moduleVarValue.datas[READ_SHORT()] = PEEK();
LOOP();
注意:编译static var 变量名 = 变量值时,由于是类静态变量,所以cu->scopeDepth等于0,所以defineVariable啥也不执行。类静态变量是模块局部变量,存储在运行时栈中,无需任何处理。也就是类静态变量初始值NULL已经push到了栈中,无需再任何处理。
2.7.1.2 findVariable
//从局部变量,upvalue和模块中查找变量name
static Variable findVariable(CompileUnit* cu, const char* name, uint32_t length) {
//先从局部变量和upvalue中查找
Variable var = getVarFromLocalOrUpvalue(cu, name, length);
if (var.index != -1) return var;
//若未找到再从模块变量中查找
var.index = getIndexFromSymbolTable(
&cu->curParser->curModule->moduleVarName, name, length);
if (var.index != -1) {
var.scopeType = VAR_SCOPE_MODULE;
}
return var;
}
//从局部变量和upvalue中查找符号name
static Variable getVarFromLocalOrUpvalue(CompileUnit* cu, const char* name, uint32_t length) {
Variable var;
//默认为无效作用域类型,查找到后会被更正
var.scopeType = VAR_SCOPE_INVALID;
var.index = findLocal(cu, name, length);
if (var.index != -1) {
var.scopeType = VAR_SCOPE_LOCAL;
return var;
}
var.index = findUpvalue(cu, name, length);
if (var.index != -1) {
var.scopeType = VAR_SCOPE_UPVALUE;
}
return var;
}
//查找局部变量
static int findLocal(CompileUnit* cu, const char* name, uint32_t length) {
//内部作用域变量会覆外层,故从后往前,由最内层逐渐往外层找
int index = cu->localVarNum - 1;
while (index >= 0) {
if (cu->localVars[index].length == length &&
memcmp(cu->localVars[index].name, name, length) == 0) {
return index;
}
index--;
}
return -1;
}
//添加upvalue到cu->upvalues,返回其索引.若已存在则只返回索引
static int addUpvalue(CompileUnit* cu, bool isEnclosingLocalVar, uint32_t index) {
uint32_t idx = 0;
while (idx < cu->fn->upvalueNum) {
//如果该upvalue已经添加过了就返回其索引
if (cu->upvalues[idx].index == index &&
cu->upvalues[idx].isEnclosingLocalVar == isEnclosingLocalVar) {
return idx;
}
idx++;
}
//若没找到则将其添加
cu->upvalues[cu->fn->upvalueNum].isEnclosingLocalVar = isEnclosingLocalVar;
cu->upvalues[cu->fn->upvalueNum].index = index;
return cu->fn->upvalueNum++;
}
//查找name指代的upvalue后添加到cu->upvalues,返回其索引,否则返回-1
static int findUpvalue(CompileUnit* cu, const char* name, uint32_t length) {
if (cu->enclosingUnit == NULL) { //如果已经到了最外层仍未找到,返回-1.
return -1;
}
//进入了方法的cu并且查找的不是静态域,即不是方法的Upvalue,那就没必要再往上找了
if (!strchr(name,' ') && cu->enclosingUnit->enclosingClassBK != NULL) {
return -1;
}
//查看name是否为直接外层的局部变量
int directOuterLocalIndex = findLocal(cu->enclosingUnit, name, length);
//若是,将该外层局部变量置为upvalue,
if (directOuterLocalIndex != -1) {
cu->enclosingUnit->localVars[directOuterLocalIndex].isUpvalue = true;
return addUpvalue(cu, true, (uint32_t)directOuterLocalIndex);
}
//向外层递归查找
int directOuterUpvalueIndex = findUpvalue(cu->enclosingUnit, name, length);
if (directOuterUpvalueIndex != -1) {
return addUpvalue(cu, false, (uint32_t)directOuterUpvalueIndex);
}
//执行到此说明没有该upvalue对应的局部变量,返回-1
return -1;
}
upvalue相关暂时用不上,
2.7.1.3 emitStoreVariable
//为变量var生成存储的指令
static void emitStoreVariable(CompileUnit* cu, Variable var) {
switch (var.scopeType) {
case VAR_SCOPE_LOCAL:
//生成存储局部变量的指令
writeOpCodeByteOperand(cu, OPCODE_STORE_LOCAL_VAR, var.index);
break;
case VAR_SCOPE_UPVALUE:
//生成存储upvalue的指令
writeOpCodeByteOperand(cu, OPCODE_STORE_UPVALUE, var.index);
break;
case VAR_SCOPE_MODULE:
//生成存储模块变量的指令
writeOpCodeShortOperand(cu, OPCODE_STORE_MODULE_VAR, var.index);
break;
default:
NOT_REACHED();
}
}
stackStart = curFrame->stackStart;
CASE(STORE_LOCAL_VAR):
//栈顶: 局部变量值
//指令流: 1字节的局部变量索引
//将PEEK()得到的栈顶数据写入指令参数(即READ_BYTE()得到的值)为索引的栈的slot中
stackStart[READ_BYTE()] = PEEK();
LOOP();
将expression计算出的已经放入栈顶的值放入index指定的运行时栈的slot中。
2.7.2 定义类实例变量
步骤很简单,如下:
- 调用getEnclosingClassBK,查看当前模块cu指向的ClassBookKeep,
- 再调用getIndexFromSymbolTable在classBK的fields查找,存在则报错重定义,不存在则调用addSymbol向classBK->fileds添加
- 实例变量不允许定义的时候赋值,检测到等号则报错。
类实例变量的赋值会在编译标识符语句完成。
2.8 compileMethod
//编译方法定义,isStatic表示是否在编译静态方法
static void compileMethod(CompileUnit* cu, Variable classVar, bool isStatic) {
//inStatic表示是否为静态方法的编译单元
cu->enclosingClassBK->inStatic = isStatic;
methodSignatureFn methodSign =
Rules[cu->curParser->curToken.type].methodSign;
if (methodSign == NULL) {
COMPILE_ERROR(cu->curParser, "method need signature fucntion!");
}
Signature sign;
// curToken是方法名
sign.name = cu->curParser->curToken.start;
sign.length = cu->curParser->curToken.length;
sign.argNum = 0;
cu->enclosingClassBK->signature = &sign;
getNextToken(cu->curParser);
//为了将函数或方法自己的指令流和局部变量单独存储,
//每个函数或方法都有自己的CompileUnit.
CompileUnit methodCU;
//编译一个方法啦,因此形参isMethod为true
initCompileUnit(cu->curParser, &methodCU, cu, true);
//构造签名
methodSign(&methodCU, &sign);
consumeCurToken(cu->curParser, TOKEN_LEFT_BRACE,
"expect '{' at the beginning of method body.");
if (cu->enclosingClassBK->inStatic && sign.type == SIGN_CONSTRUCT) {
COMPILE_ERROR(cu->curParser, "constuctor is not allowed to be static!");
}
char signatureString[MAX_SIGN_LEN] = {'\0'};
uint32_t signLen = sign2String(&sign, signatureString);
//将方法声明
uint32_t methodIndex = declareMethod(cu, signatureString, signLen);
//编译方法体指令流到方法自己的编译单元methodCU
compileBody(&methodCU, sign.type == SIGN_CONSTRUCT);
#if DEBUG
//结束编译并创建方法闭包
endCompileUnit(&methodCU, signatureString, signLen);
#else
//结束编译并创建方法闭包
endCompileUnit(&methodCU);
#endif
//定义方法:将上面创建的方法闭包绑定到类
defineMethod(cu, classVar, cu->enclosingClassBK->inStatic, methodIndex);
if (sign.type == SIGN_CONSTRUCT) {
sign.type = SIGN_METHOD;
char signatureString[MAX_SIGN_LEN] = {'\0'};
uint32_t signLen = sign2String(&sign, signatureString);
uint32_t constructorIndex = ensureSymbolExist(cu->curParser->vm,
&cu->curParser->vm->allMethodNames, signatureString, signLen);
emitCreateInstance(cu, &sign, methodIndex);
//构造函数是静态方法,即类方法
defineMethod(cu, classVar, true, constructorIndex);
}
}
类方法包括一般实例方法,静态方法,getter方法获取对象属性、setter方法设置对象属性,构造方法(既是实例方法也是静态方法)
编译方法步骤如下:
- 调用initCompileUnit初始化一个新的编译单元methodCU用于编译方法。但methodCU->scopeDepth依然为0
- 获取methodSignatureFn methodSign(即id的签名函数idMethodSignature),调用methodSign(&methodCU, &sign)构造签名函数。token为id即标识符的签名函数主要设置了sign的type,然后词法分析器分析了方法的括号后面的形参,对形参依次进行了declareLocalVar(因为是类的方法,已经在类里面了,所以这些形参不会是模块变量而是methodCU->LocalVar里声明好的局部变量。)。
- sign2String、declareMethod生成方法名并声明于vm->allMethodNames,并排查重定义
- 调用compileBody(&methodCU, sign.type == SIGN_CONSTRUCT)开始编译方法体语句生成相应指令。
- 调用endCompileUnit(&methodCU)创建闭包压入栈顶
- defineMethod,把方法闭包赋值到类的methods
- 若编译的方法是构造函数new,则执行emitCreateInstance返回实例对象,再defineMethod将方法复制到元类的method中
2.8.1 initCompileUnit
//初始化CompileUnit
static void initCompileUnit(Parser* parser, CompileUnit* cu,
CompileUnit* enclosingUnit, bool isMethod) {
parser->curCompileUnit = cu;
cu->curParser = parser;
cu->enclosingUnit = enclosingUnit;
cu->curLoop = NULL;
cu->enclosingClassBK = NULL;
//若没有外层,说明当前属于模块作用域
if (enclosingUnit == NULL) {
//编译代码时是从上到下从最外层的模块作用域开始,模块作用域设为-1
cu->scopeDepth = -1;
//模块级作用域中没有局部变量
cu->localVarNum = 0;
} else { //若是内层单元,属局部作用域
if (isMethod) { //若是类中的方法
//如果是类的方法就设定隐式"this"为第0个局部变量,即实例对象,
//它是方法(消息)的接收者.this这种特殊对象被处理为局部变量
cu->localVars[0].name = "this";
cu->localVars[0].length = 4;
} else { //若为普通函数
//空出第0个局部变量,保持统一
cu->localVars[0].name = NULL;
cu->localVars[0].length = 0;
}
//第0个局部变量的特殊性使其作用域为模块级别
cu->localVars[0].scopeDepth = -1;
cu->localVars[0].isUpvalue = false;
cu->localVarNum = 1; //localVars[0]被分配
// 对于函数和方法来说,初始作用域是局部作用域
// 0表示局部作用域的最外层
cu->scopeDepth = 0;
}
//局部变量保存在栈中,初始时栈中已使用的slot数量等于局部变量的数量
cu->stackSlotNum = cu->localVarNum;
cu->fn = newObjFn(cu->curParser->vm, cu->curParser->curModule, cu->localVarNum);
}
2.8.2 idMethodSignature
//标识符的签名函数
static void idMethodSignature(CompileUnit* cu, Signature* sign) {
sign->type = SIGN_GETTER; //刚识别到id,默认为getter
//new方法为构造函数
if (sign->length == 3 && memcmp(sign->name, "new", 3) == 0) {
//构造函数后面不能接'=',即不能成为setter
if (matchToken(cu->curParser, TOKEN_ASSIGN)) {
COMPILE_ERROR(cu->curParser, "constructor shouldn`t be setter!");
}
//构造函数必须是标准的method,即new(_,...),new后面必须接'('
if (!matchToken(cu->curParser, TOKEN_LEFT_PAREN)) {
COMPILE_ERROR(cu->curParser, "constructor must be method!");
}
sign->type = SIGN_CONSTRUCT;
//无参数就直接返回
if (matchToken(cu->curParser, TOKEN_RIGHT_PAREN)) {
return;
}
} else { //若不是构造函数
if (trySetter(cu, sign)) {
//若是setter,此时已经将type改为了setter,直接返回
return;
}
if (!matchToken(cu->curParser, TOKEN_LEFT_PAREN)) {
//若后面没有'('说明是getter,type已在开头置为getter,直接返回
return;
}
//至此type应该为一般形式的SIGN_METHOD,形式为name(paralist)
sign->type = SIGN_METHOD;
//直接匹配到')',说明形参为空
if (matchToken(cu->curParser, TOKEN_RIGHT_PAREN)) {
return;
}
}
//下面处理形参
processParaList(cu, sign);
consumeCurToken(cu->curParser, TOKEN_RIGHT_PAREN, "expect ')' after parameter list!");
}
2.8.2.1 trySetter processParaList
//尝试编译setter
static bool trySetter(CompileUnit* cu, Signature* sign) {
if (!matchToken(cu->curParser, TOKEN_ASSIGN)) {
return false;
}
if (sign->type == SIGN_SUBSCRIPT) {
sign->type = SIGN_SUBSCRIPT_SETTER;
} else {
sign->type = SIGN_SETTER;
}
//读取等号右边的形参左边的'('
consumeCurToken(cu->curParser, TOKEN_LEFT_PAREN, "expect '(' after '='!");
//读取形参
consumeCurToken(cu->curParser, TOKEN_ID, "expect ID!");
//声明形参
declareVariable(cu, cu->curParser->preToken.start, cu->curParser->preToken.length);
//读取等号右边的形参右边的'('
consumeCurToken(cu->curParser, TOKEN_RIGHT_PAREN, "expect ')' after argument list!");
sign->argNum++;
return true;
}
//声明形参列表中的各个形参
static void processParaList(CompileUnit* cu, Signature* sign) {
ASSERT(cu->curParser->curToken.type != TOKEN_RIGHT_PAREN &&
cu->curParser->curToken.type != TOKEN_RIGHT_BRACKET, "empty argument list!");
do {
if (++sign->argNum > MAX_ARG_NUM) {
COMPILE_ERROR(cu->curParser, "the max number of argument is %d!", MAX_ARG_NUM);
}
consumeCurToken(cu->curParser, TOKEN_ID, "expect variable name!");
declareVariable(cu, cu->curParser->preToken.start, cu->curParser->preToken.length);
} while (matchToken(cu->curParser, TOKEN_COMMA));
}
2.8.3 sign2String
//把Signature转换为字符串,返回字符串长度
static uint32_t sign2String(Signature* sign, char* buf) {
uint32_t pos = 0;
//复制方法名xxx
memcpy(buf + pos, sign->name, sign->length);
pos += sign->length;
//下面单独处理方法名之后的部分
switch (sign->type) {
//SIGN_GETTER形式:xxx,无参数,上面memcpy已完成
case SIGN_GETTER:
break;
//SIGN_SETTER形式: xxx=(_),之前已完成xxx
case SIGN_SETTER:
buf[pos++] = '=';
//下面添加=右边的赋值,只支持一个赋值
buf[pos++] = '(';
buf[pos++] = '_';
buf[pos++] = ')';
break;
//SIGN_METHOD和SIGN_CONSTRUCT形式:xxx(_,...)
case SIGN_CONSTRUCT:
case SIGN_METHOD: {
buf[pos++] = '(';
uint32_t idx = 0;
while (idx < sign->argNum) {
buf[pos++] = '_';
buf[pos++] = ',';
idx++;
}
if (idx == 0) { //说明没有参数
buf[pos++] = ')';
} else { //用rightBracket覆盖最后的','
buf[pos - 1] = ')';
}
break;
}
//SIGN_SUBSCRIPT形式:xxx[_,...]
case SIGN_SUBSCRIPT: {
buf[pos++] = '[';
uint32_t idx = 0;
while (idx < sign->argNum) {
buf[pos++] = '_';
buf[pos++] = ',';
idx++;
}
if (idx == 0) { //说明没有参数
buf[pos++] = ']';
} else { //用rightBracket覆盖最后的','
buf[pos - 1] = ']';
}
break;
}
//SIGN_SUBSCRIPT_SETTER形式:xxx[_,...]=(_)
case SIGN_SUBSCRIPT_SETTER: {
buf[pos++] = '[';
uint32_t idx = 0;
//argNum包括了等号右边的1个赋值参数,
//这里是在处理等号左边subscript中的参数列表,因此减1.
//后面专门添加该参数
while (idx < sign->argNum - 1) {
buf[pos++] = '_';
buf[pos++] = ',';
idx++;
}
if (idx == 0) { //说明没有参数
buf[pos++] = ']';
} else { //用rightBracket覆盖最后的','
buf[pos - 1] = ']';
}
//下面为等号右边的参数构造签名部分
buf[pos++] = '=';
buf[pos++] = '(';
buf[pos++] = '_';
buf[pos++] = ')';
}
}
buf[pos] = '\0';
return pos; //返回签名串的长度
}
2.8.4 declareMethod
//声明方法
static int declareMethod(CompileUnit* cu, char* signStr, uint32_t length) {
//确保方法被录入到vm->allMethodNames
int index = ensureSymbolExist(cu->curParser->vm,
&cu->curParser->vm->allMethodNames, signStr, length);
//下面判断方法是否已定义 即排除重定义
IntBuffer* methods = cu->enclosingClassBK->inStatic ?
&cu->enclosingClassBK->staticMethods :
&cu->enclosingClassBK->instantMethods;
uint32_t idx = 0;
while (idx < methods->count) {
if (methods->datas[idx] == index) {
COMPILE_ERROR(cu->curParser, "repeat define method %s in class %s!",
signStr, cu->enclosingClassBK->name->value.start);
}
idx++;
}
//若是新定义就加入,这里并不是注册新方法,
//而是用索引来记录已经定义过的方法,用于以后排重
IntBufferAdd(cu->curParser->vm, methods, index);
return index;
}
2.8.5 compileBody
//编译函数或方法体
static void compileBody(CompileUnit* cu, bool isConstruct) {
//进入本函数前已经读入了'{'
compileBlock(cu);
if (isConstruct) {
//若是构造函数就加载"this对象"做为下面OPCODE_RETURN的返回值
writeOpCodeByteOperand(cu, OPCODE_LOAD_LOCAL_VAR, 0);
} else {
//否则加载null占位
writeOpCode(cu, OPCODE_PUSH_NULL);
}
//返回编译结果,若是构造函数就返回this,否则返回null
writeOpCode(cu, OPCODE_RETURN);
}
//编译代码块
static void compileBlock(CompileUnit* cu) {
//进入本函数前已经读入了'{'
while (!matchToken(cu->curParser, TOKEN_RIGHT_BRACE)) {
if (PEEK_TOKEN(cu->curParser) == TOKEN_EOF) {
COMPILE_ERROR(cu->curParser, "expect '}' at the end of block!");
}
compileProgram(cu);
}
}
//编译程序
static void compileProgram(CompileUnit* cu) {
if (matchToken(cu->curParser, TOKEN_CLASS)) {
compileClassDefinition(cu);
} else if (matchToken(cu->curParser, TOKEN_FUN)) {
compileFunctionDefinition(cu);
} else if (matchToken(cu->curParser, TOKEN_VAR)) {
compileVarDefinition(cu, cu->curParser->preToken.type == TOKEN_STATIC);
} else if (matchToken(cu->curParser, TOKEN_IMPORT)) {
compileImport(cu);
} else {
compileStatment(cu);
}
}
2.8.6 endCompileUnit
//结束cu的编译工作,在其外层编译单元中为其创建闭包
#if DEBUG
static ObjFn* endCompileUnit(CompileUnit* cu,
const char* debugName, uint32_t debugNameLen) {
bindDebugFnName(cu->curParser->vm, cu->fn->debug, debugName, debugNameLen);
#else
static ObjFn* endCompileUnit(CompileUnit* cu) {
#endif
//标识单元编译结束
writeOpCode(cu, OPCODE_END);
if (cu->enclosingUnit != NULL) {
//把当前编译的objFn做为常量添加到父编译单元的常量表
uint32_t index = addConstant(cu->enclosingUnit, OBJ_TO_VALUE(cu->fn));
//内层函数以闭包形式在外层函数中存在,
//在外层函数的指令流中添加"为当前内层函数创建闭包的指令"
writeOpCodeShortOperand(cu->enclosingUnit, OPCODE_CREATE_CLOSURE, index);
//为vm在创建闭包时判断引用的是局部变量还是upvalue,
//下面为每个upvalue生成参数.
index = 0;
while (index < cu->fn->upvalueNum) {
writeByte(cu->enclosingUnit,
cu->upvalues[index].isEnclosingLocalVar ? 1 : 0);
writeByte(cu->enclosingUnit,
cu->upvalues[index].index);
index++;
}
}
///下掉本编译单元,使当前编译单元指向外层编译单元
cu->curParser->curCompileUnit = cu->enclosingUnit;
return cu->fn;
}
CASE(CREATE_CLOSURE): {
//指令流: 2字节待创建闭包的函数在常量表中的索引+函数所用的upvalue数 * 2
//endCompileUnit已经将闭包函数添加进了常量表
ObjFn* objFn = VALUE_TO_OBJFN(fn->constants.datas[READ_SHORT()]);
ObjClosure* objClosure = newObjClosure(vm, objFn);
//将创建好的闭包的value结构压到栈顶,
//后续会有函数如defineMethod从栈底取出
//先将其压到栈中,后面再创建upvalue,这样可避免在创建upvalue过程中被GC
PUSH(OBJ_TO_VALUE(objClosure));
uint32_t idx = 0;
while (idx < objFn->upvalueNum) {
//读入endCompilerUnit函数最后为每个upvale写入的数据对儿
uint8_t isEnclosingLocalVar = READ_BYTE();
uint8_t index = READ_BYTE();
if (isEnclosingLocalVar) { //是直接外层的局部变量
//创建upvalue
objClosure->upvalues[idx] =
createOpenUpvalue(vm, curThread, curFrame->stackStart + index);
} else {
//直接从父编译单元中继承
objClosure->upvalues[idx] = curFrame->closure->upvalues[index];
}
idx++;
}
LOOP();
}
- 将需要结束编译的cu->fn添加进父编译单元的常量表,并返回索引
- 在父编译单元的指令流fn里生成OPCODE_CREATE_CLOSURE指令,此指令会创建新的ObjClosure收集upvalue并压入栈顶。
- 再写入多个upvalue对操作数{是否为直接外层的局部变量,在直接外层的索引}
- 词法分析器的当前编译单元赋值为父编译单元,返回需要结束编译单元cu的fn
2.8.7 defineMethod、emitLoadVariable
//将方法methodIndex指代的方法塞入classVar指代的class.methods中
static void defineMethod(CompileUnit* cu,
Variable classVar, bool isStatic, int methodIndex) {
//1 待绑定的方法在调用本函数之前已经放到栈顶了
//2 将方法所属的类加载到栈顶
emitLoadVariable(cu, classVar);
//3 生成OPCODE_STATIC_METHOD或OPCODE_INSTANCE_METHOD
//在运行时绑定
OpCode opCode = isStatic ?
OPCODE_STATIC_METHOD : OPCODE_INSTANCE_METHOD;
writeOpCodeShortOperand(cu, opCode, methodIndex);
}
//生成把变量var加载到栈的指令
static void emitLoadVariable(CompileUnit* cu, Variable var) {
switch (var.scopeType) {
case VAR_SCOPE_LOCAL:
//生成加载局部变量入栈的指令
writeOpCodeByteOperand(cu, OPCODE_LOAD_LOCAL_VAR, var.index);
break;
case VAR_SCOPE_UPVALUE:
//生成加载upvalue到栈的指令
writeOpCodeByteOperand(cu, OPCODE_LOAD_UPVALUE, var.index);
break;
case VAR_SCOPE_MODULE:
//生成加载模块变量到栈的指令
writeOpCodeShortOperand(cu, OPCODE_LOAD_MODULE_VAR, var.index);
break;
default:
NOT_REACHED();
}
}
CASE(INSTANCE_METHOD):
CASE(STATIC_METHOD): {
//指令流: 待绑定的方法"名字"在vm->allMethodNames中的2字节的索引
//栈顶: 待绑定的类 次栈顶: 待绑定的方法
//获得方法名的索引
uint32_t methodNameIndex = READ_SHORT();
//从栈顶中获得待绑定的类
Class* class = VALUE_TO_CLASS(PEEK());
//从次栈顶中获得待绑定的方法,
//这是由OPCODE_CREATE_CLOSURE操作码生成后压到栈中的
Value method = PEEK2();
bindMethodAndPatch(vm, opCode, methodNameIndex, class, method);
DROP();
DROP();
LOOP();
}
//绑定方法和修正操作数
static void bindMethodAndPatch(VM* vm, OpCode opCode,
uint32_t methodIndex, Class* class, Value methodValue) {
//如果是静态方法,就将类指向meta类(使接收者为meta类)
if (opCode == OPCODE_STATIC_METHOD) {
class = class->objHeader.class;
}
Method method;
method.type = MT_SCRIPT;
method.obj = VALUE_TO_OBJCLOSURE(methodValue);
//修正操作数
patchOperand(class, method.obj->fn);
//修正过后,绑定method到class
bindMethod(vm, class, methodIndex, method);
}
执行上述两个函数后,栈顶是类即模块变量,次栈顶是编译的方法闭包,然后调用OPCODE_STATIC_METHOD或OPCODE_INSTANCE_METHOD将方法绑定到类,也就是把方法赋值到类的methods。

2.9 若编译的是构造方法 emitCreateInstance
//分两步创建实例,constructorIndex是构造函数的索引
static void emitCreateInstance(CompileUnit* cu,
Signature* sign, uint32_t constructorIndex) {
CompileUnit methodCU;
initCompileUnit(cu->curParser, &methodCU, cu, true);
//1 生成OPCODE_CONSTRUCT指令,该指令生成新实例存储到stack[0].
writeOpCode(&methodCU, OPCODE_CONSTRUCT);
//2 生成OPCODE_CALLx指令,该指令调用新实例的构造函数.
writeOpCodeShortOperand(&methodCU,
(OpCode)(OPCODE_CALL0 + sign->argNum), constructorIndex);
//生成return指令,将栈顶中的实例返回
writeOpCode(&methodCU, OPCODE_RETURN);
#if DEBUG
endCompileUnit(&methodCU, "", 0);
#else
endCompileUnit(&methodCU);
#endif
}
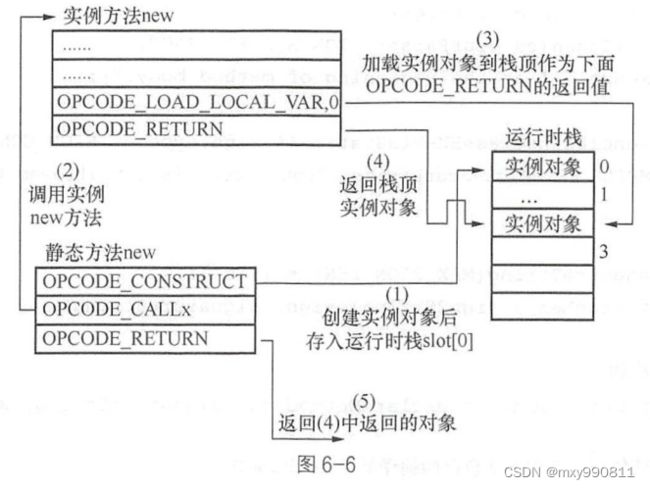
需要注意的是,emitCreateInstance里创建了一个新编译单元,专门写入这三条指令,然后封装成闭包,最后下面的defineMethod将闭包写入元类的method。
整个指令流步骤如下:
- OPCODE_CONSTRUCT创建新实例对象
- OPCODE_CALLX执行实例对象的实例方法指令流(调用emitCreateInstance前已经将实例方法闭包defineMethod到类的method中)
- OPCODE_RETURN返回实例对象。
2.9.1 OPCODE_CONSTRUCT
CASE(CONSTRUCT): {
//栈底: startStart[0]是class
ASSERT(VALUE_IS_CLASS(stackStart[0]),
"stackStart[0] should be a class for OPCODE_CONSTRUCT!");
//将创建的类实例存储到stackStart[0],即this
ObjInstance* objInstance = newObjInstance(vm, VALUE_TO_CLASS(stackStart[0]));
//此时stackStart[0]是类,其类名便是方法所定义的类
//把对象写入stackStart[0]
stackStart[0] = OBJ_TO_VALUE(objInstance);
LOOP();
}
stackStart[0]是类,根据类调用newObjInstance创建了实例对象,放入stackStart[0]
2.9.2 CALLx
CASE(CALL0):
CASE(CALL1):
CASE(CALL2):
CASE(CALL3):
CASE(CALL4):
CASE(CALL5):
CASE(CALL6):
CASE(CALL7):
CASE(CALL8):
CASE(CALL9):
CASE(CALL10):
CASE(CALL11):
CASE(CALL12):
CASE(CALL13):
CASE(CALL14):
CASE(CALL15):
CASE(CALL16):
//指令流1: 2字节的method索引
//因为还有个隐式的receiver(就是下面的args[0]), 所以参数个数+1.
argNum = opCode - OPCODE_CALL0 + 1;
//读取2字节的数据(CALL指令的操作数),index是方法名的索引
index = READ_SHORT();
//为参数指针数组args赋值
args = curThread->esp - argNum;
//获得方法所在的类
class = getClassOfObj(vm, args[0]);
goto invokeMethod;
如果当前 CALLx 调用的是类方法即static方法,那么args[0]是类,因此变量 class 便指向静态方法所属类的 Meta 类。
如果当前调用的是实例方法,那么 args[0]是实例对象 this 变量, class 便是对象实例所属的类。
所以这里会是第二种情况,由OPCODE_CONSTRUCT将对象放入args[0],invokeMethod调用的是该类的methds的方法,也就是对象的实例方法。
invokeMethod:
if ((uint32_t)index > class->methods.count ||
(method = &class->methods.datas[index])->type == MT_NONE) {
RUN_ERROR("method \"%s\" not found!", vm->allMethodNames.datas[index].str);
}
switch (method->type) {
case MT_PRIMITIVE:
//如果返回值为true,则vm进行空间回收的工作
if (method->primFn(vm, args)) {
//args[0]是返回值, argNum-1是保留args[0],
//args[0]的空间最终由返回值的接收者即函数的主调方回收
curThread->esp -= argNum - 1;
} else {
//如果返回false则说明有两种情况:
// 1 出错(比如原生函数primThreadAbort使线程报错或无错退出),
// 2 或者切换了线程,此时vm->curThread已经被切换为新的线程
//保存线程的上下文环境,运行新线程之后还能回到当前老线程指令流的正确位置
STORE_CUR_FRAME();
if (!VALUE_IS_NULL(curThread->errorObj)) {
if (VALUE_IS_OBJSTR(curThread->errorObj)) {
ObjString* err = VALUE_TO_OBJSTR(curThread->errorObj);
printf("%s", err->value.start);
}
//出错后将返回值置为null,避免主调方获取到错误的结果
PEEK() = VT_TO_VALUE(VT_NULL);
}
//如果没有待执行的线程,说明执行完毕
if (vm->curThread == NULL) {
return VM_RESULT_SUCCESS;
}
//vm->curThread已经由返回false的函数置为下一个线程
//切换到下一个线程的上下文
curThread = vm->curThread;
LOAD_CUR_FRAME();
}
break;
case MT_SCRIPT:
STORE_CUR_FRAME();
createFrame(vm, curThread, (ObjClosure*)method->obj, argNum);
LOAD_CUR_FRAME(); //加载最新的frame
break;
case MT_FN_CALL:
ASSERT(VALUE_IS_OBJCLOSURE(args[0]), "instance must be a closure!");
ObjFn* objFn = VALUE_TO_OBJCLOSURE(args[0])->fn;
//-1是去掉实例this
if (argNum - 1 < objFn->argNum) {
RUN_ERROR("arguments less");
}
STORE_CUR_FRAME();
createFrame(vm, curThread, VALUE_TO_OBJCLOSURE(args[0]), argNum);
LOAD_CUR_FRAME(); //加载最新的frame
break;
default:
NOT_REACHED();
}
LOOP();
2.9.3 OPCODE_RETURN
CASE(RETURN): {
//栈顶: 返回值
//获取返回值
Value retVal = POP();
//return是从函数返回 故该堆栈框架使用完毕,增加可用堆栈框架数量
curThread->usedFrameNum--;
//关闭堆栈框架即此作用域内所有upvalue
closeUpvalue(curThread, stackStart);
//如果一个堆栈框架都没用,
//说明它没有调用函数或者所有的函数调用都返回了,可以结束它
if (curThread->usedFrameNum == 0) {
//如果并不是被另一线程调用的,就直接结束
if (curThread->caller == NULL) {
curThread->stack[0] = retVal;
//保留stack[0]中的结果,其它都丢弃
curThread->esp = curThread->stack + 1;
return VM_RESULT_SUCCESS;
}
//恢复主调方线程的调度
ObjThread* callerThread = curThread->caller;
curThread->caller = NULL;
curThread = callerThread;
vm->curThread = callerThread;
//在主调线程的栈顶存储被调线程的执行结果
curThread->esp[-1] = retVal;
} else {
//将返回值置于运行时栈栈顶
stackStart[0] = retVal;
//回收堆栈:保留除结果所在的slot即stackStart[0] 其它全丢弃
curThread->esp = stackStart + 1;
}
LOAD_CUR_FRAME();
LOOP();
}
3. 核心总结
静态变量:被当作模块局部变量,声明于模块cu->LocalVar,定义即赋值于运行时栈(因为是局部变量)
实例变量:声明于模块cu指向的ClassBookKeep的fields里,声明实例对象时不能赋值。实例对象的值只属于实例对象,静态变量的值被所有对象共享。
静态方法:sign2String后声明于vm->allMethodNames,endCompileUnit(&methodCU)创建闭包后赋值于类的元类的methods。
实例方法:sign2String后声明于vm->allMethodNames,endCompileUnit(&methodCU)创建闭包后赋值于类的methods。
new方法:sign2String后声明于vm->allMethodNames,endCompileUnit(&methodCU)创建闭包后赋值于类的methods。emitCreateInstance的三条指令单独创建编译单元并生成闭包赋值于元类的methods