路径规划 | 图解Theta*算法(附ROS C++/Python/Matlab仿真)
目录
- 0 专栏介绍
- 1 A*算法的局限性
- 2 Theta*算法原理图解
- 3 Bresenham视线法
- 4 算法仿真测试
-
- 4.1 算法流程图
- 4.2 ROS C++ 实现
- 4.3 Python实现
- 4.4 Matlab实现
0 专栏介绍
附C++/Python/Matlab全套代码课程设计、毕业设计、创新竞赛必备!详细介绍全局规划(图搜索、采样法、智能算法等);局部规划(DWA、APF等);曲线优化(贝塞尔曲线、B样条曲线等)。
详情:图解自动驾驶中的运动规划(Motion Planning),附几十种规划算法
1 A*算法的局限性
A*算法的局限性在于其搜索路径的可行角度被网格形状固定。因此,A* 算法搜索的路径往往不是实际地形下真正的最短路径(由8邻域二维栅格边缘形成的最短路径可能比连续环境中真实的最短路径长多达8%),如图所示。
Theta*算法的核心原理是去除依赖于网格形状的角度约束,不限制路径仅由栅格边缘组成,以提升路径平滑性和最优性
2 Theta*算法原理图解
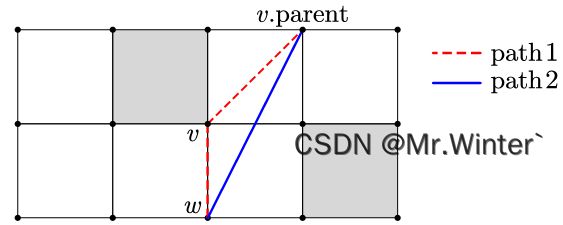
Theta*算法主体流程与A*相同,区别在于扩展节点数据的更新方式。
- A*算法利用邻接节点更新信息(path1),即若 g ( w ) > g ( v ) + d ( v , w ) g\left( w \right) >g\left( v \right) +\mathrm{d}\left( v,w \right) g(w)>g(v)+d(v,w),则令 g ( w ) = g ( v ) + d ( v , w ) g\left( w \right) =g\left( v \right) +\mathrm{d}\left( v,w \right) g(w)=g(v)+d(v,w)
- Theta*额外考虑当前节点的父节点信息(path2),即若 g ( w ) > g ( v . p a r e n t ) + d ( v . p a r e n t , w ) g\left( w \right) >g\left( v.\mathrm{parent} \right) +\mathrm{d}\left( v.\mathrm{parent},w \right) g(w)>g(v.parent)+d(v.parent,w),则令 g ( w ) = g ( v . p a r e n t ) + d ( v . p a r e n t , w ) g\left( w \right) =g\left( v.\mathrm{parent} \right) +\mathrm{d}\left( v.\mathrm{parent},w \right) g(w)=g(v.parent)+d(v.parent,w)。
根据三角形两边之和大于第三边有
d ( v . p a r e n t , w ) < d ( v . p a r e n t , v ) + d ( v , w ) \mathrm{d}\left( v.\mathrm{parent},w \right) <\mathrm{d}\left( v.\mathrm{parent},v \right) +\mathrm{d}\left( v,w \right) d(v.parent,w)<d(v.parent,v)+d(v,w)
因此当 v . p a r e n t v.\mathrm{parent} v.parent与 w w w间不存在障碍物时,算法必然采用path2,实现锯齿路径的平滑
3 Bresenham视线法
在Theta*中,对障碍物的碰撞检测采用Bresenham算法。Bresenham碰撞测试在三种类型的移动中访问单元格:
- x x x方向移动
- y y y方向移动
- 对角线移动
在栅格地图中,碰撞检测点连线经过若干离散栅格,因此每次移动都将产生非连续误差,Bresenham算法要求下一个移动偏差最小。通过迭代即可访问检测线经过的所有栅格,判断这些栅格的代价是否超过阈值即可完成碰撞检测。
算法流程如下所示
4 算法仿真测试
4.1 算法流程图
算法流程与核心函数如下所示
4.2 ROS C++ 实现
核心代码如下
bool ThetaStar::plan(const unsigned char* global_costmap, const Node& start, const Node& goal, std::vector<Node>& path,
std::vector<Node>& expand)
{
// initialize
costs_ = global_costmap;
path.clear();
expand.clear();
// open list and closed list
std::priority_queue<Node, std::vector<Node>, compare_cost> open_list;
std::unordered_set<Node, NodeIdAsHash, compare_coordinates> closed_list;
open_list.push(start);
// get all possible motions
const std::vector<Node> motion = getMotion();
// main process
while (!open_list.empty())
{
// pop current node from open list
Node current = open_list.top();
open_list.pop();
// current node does not exist in closed list
if (closed_list.find(current) != closed_list.end())
continue;
closed_list.insert(current);
expand.push_back(current);
// goal found
if (current == goal)
{
path = _convertClosedListToPath(closed_list, start, goal);
return true;
}
// explore neighbor of current node
for (const auto& m : motion)
{
Node node_new = current + m; // add the x_, y_, g_
// current node do not exist in closed list
if (closed_list.find(node_new) != closed_list.end())
continue;
// explore a new node
// path 1
node_new.h_ = dist(node_new, goal);
node_new.id_ = grid2Index(node_new.x_, node_new.y_);
node_new.pid_ = current.id_;
// next node hit the boundary or obstacle
if ((node_new.id_ < 0) || (node_new.id_ >= ns_) || (costs_[node_new.id_] >= lethal_cost_ * factor_))
continue;
// get the coordinate of parent node
Node parent;
parent.id_ = current.pid_;
index2Grid(parent.id_, parent.x_, parent.y_);
// update g value
auto find_parent = closed_list.find(parent);
if (find_parent != closed_list.end())
{
parent = *find_parent;
_updateVertex(parent, node_new);
}
open_list.push(node_new);
}
}
return false;
}
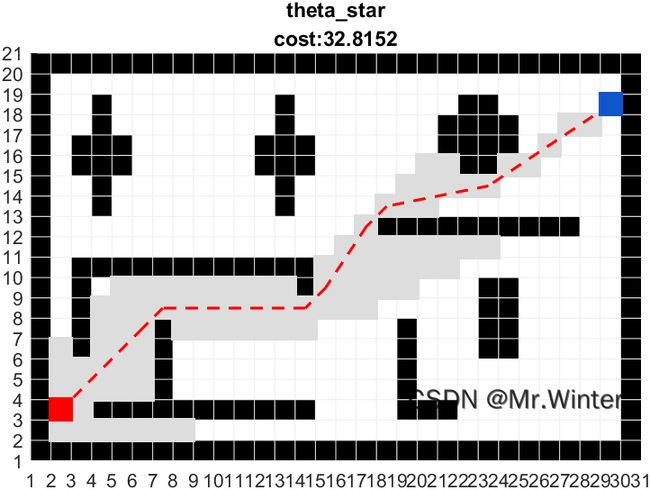
效果如下
4.3 Python实现
核心代码如下
def plan(self):
# OPEN set with priority and CLOSED set
OPEN = []
heapq.heappush(OPEN, self.start)
CLOSED = []
while OPEN:
node = heapq.heappop(OPEN)
# exists in CLOSED set
if node in CLOSED:
continue
# goal found
if node == self.goal:
CLOSED.append(node)
return self.extractPath(CLOSED), CLOSED
for node_n in self.getNeighbor(node):
# exists in CLOSED set
if node_n in CLOSED:
continue
# path1
node_n.parent = node.current
node_n.h = self.h(node_n, self.goal)
try:
p_index = CLOSED.index(Node(node.parent))
node_p = CLOSED[p_index]
except:
node_p = None
if node_p:
self.updateVertex(node_p, node_n)
# goal found
if node_n == self.goal:
heapq.heappush(OPEN, node_n)
break
# update OPEN set
heapq.heappush(OPEN, node_n)
CLOSED.append(node)
return ([], []), []
效果如下
4.4 Matlab实现
核心代码如下
while ~isempty(OPEN)
% pop
f = OPEN(:, 3) + OPEN(:, 4);
[~, index] = min(f);
cur_node = OPEN(index, :);
OPEN(index, :) = [];
% exists in CLOSED set
if loc_list(cur_node, CLOSED, [1, 2])
continue
end
% update expand zone
if ~loc_list(cur_node, EXPAND, [1, 2])
EXPAND = [EXPAND; cur_node(1:2)];
end
% goal found
if cur_node(1) == goal(1) && cur_node(2) == goal(2)
CLOSED = [cur_node; CLOSED];
goal_reached = true;
cost = cur_node(3);
break
end
if (cur_node(1) ==17) &&(cur_node(2) == 26)
cur_node(1);
end
% explore neighbors
for i = 1:motion_num
% path 1
node_n = [
cur_node(1) + motion(i, 1), ...
cur_node(2) + motion(i, 2), ...
cur_node(3) + motion(i, 3), ...
0, ...
cur_node(1), cur_node(2)];
node_n(4) = h(node_n(1:2), goal);
% exists in CLOSED set
if loc_list(node_n, CLOSED, [1, 2])
continue
end
% obstacle
if map(node_n(1), node_n(2)) == 2
continue
end
p_index = loc_list(cur_node(5: 6), CLOSED, [1, 2]);
if p_index
node_p = CLOSED(p_index, :);
else
node_p = 0;
end
if node_p ~= 0
node_n = update_vertex(map, node_p, node_n);
end
% update OPEN set
OPEN = [OPEN; node_n];
end
CLOSED = [cur_node; CLOSED];
完整工程代码请联系下方博主名片获取
更多精彩专栏:
- 《ROS从入门到精通》
- 《Pytorch深度学习实战》
- 《机器学习强基计划》
- 《运动规划实战精讲》
- …