Kotlin数据结构
数据结构基础
什么是数据结构
在计算机科学中,数据结构(Data Structure)是计算机中存储、组织数据的方式。数据结构是各种编程语言的基础。
一些使用场景
- 不同的数据结构适用于不同的应用场景。比如HashMap与ConcurrentHashMap,ArrayList与LinkedList。
- 使用正确的数据结构可以提高算法的效率(时间和空间)。比如使用Map(常数时间复杂度)将双重循环优化为一重循环。
数据之间的逻辑结构
数据在计算机中的存储方式(存储结构)
- 顺序存储结构:把逻辑上相邻的元素存储在物理位置相邻的存储单元中
- 链式存储结构:对逻辑上相邻的元素不要求其物理位置相邻,元素间的逻辑关系通过指针来表示
- 索引存储结构:在存储节点的同时,还需要建立附加的索引表
- 散列存储结构:以数据元素的关键字的值为自变量,通过散列函数计算出该元素的存储位置
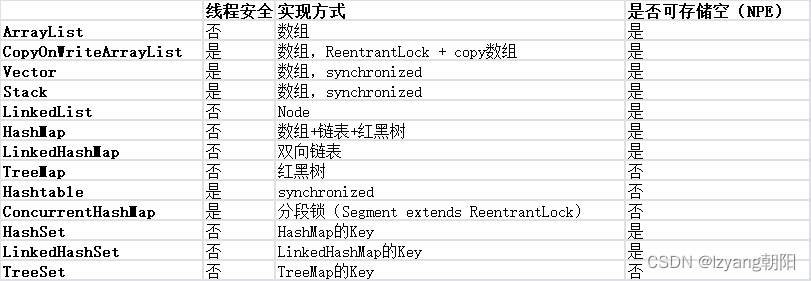
集合框架
现代编程语言及其API中都包含了多种默认的数据结构,Java集合框架、Kotlin集合框架就是其中的代表。
因为数据结构的知识体系比较广,除了各种线性、非线性结构,还有广义表、排序、查找,而排序中又有快速排序、堆排序等。对于大部分Android开发来说,更多的是直接使用编程语言的集合框架。所以接下来通过介绍Java和Kotlin集合框架来展开。
Java的集合框架
这里先通过介绍Java的集合框架来更好的引入Kotlin。
题外:针对Java的集合框架推荐梳理类图配合阅读源码及其注释的的方式来加深理解,同理对于Java的IO框架、Android的View框架、Android的Context框架也适用。
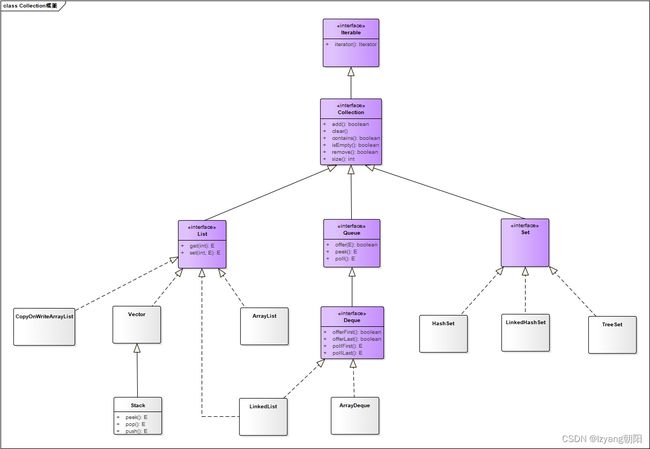
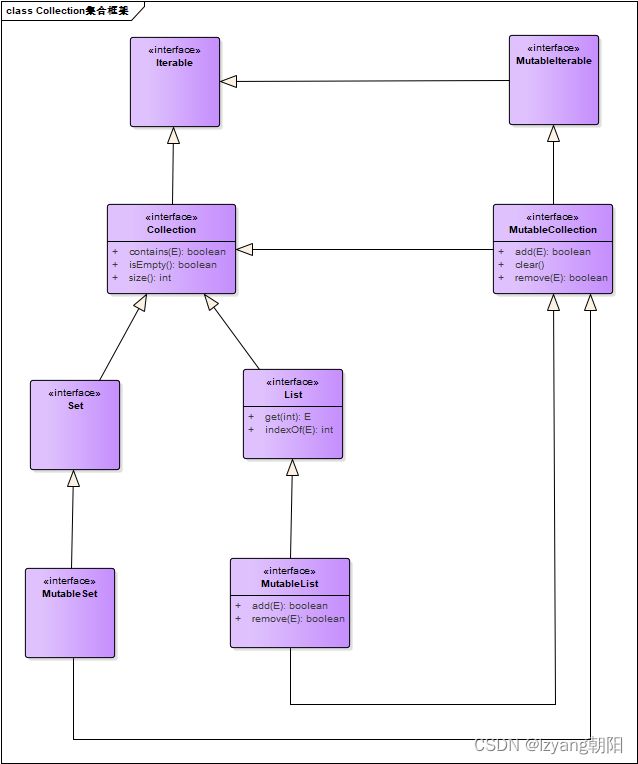
Collection类图
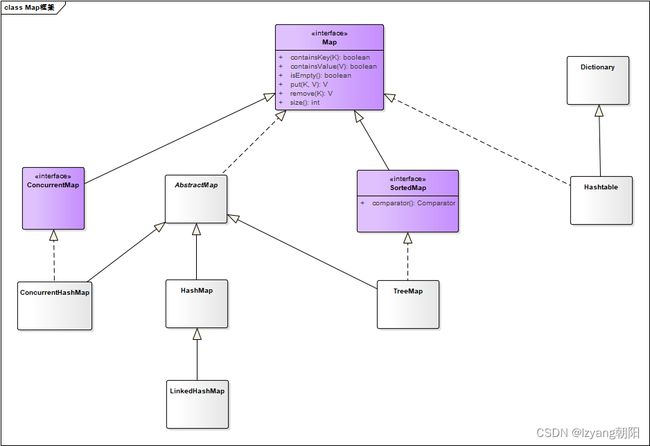
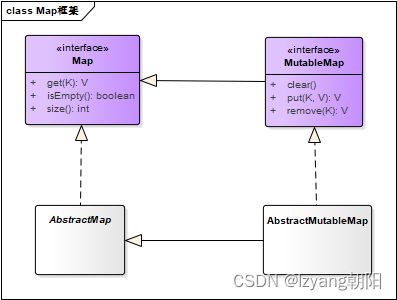
Map类图
纵向对比
Kotlin的集合框架
Collection类图
Map类图
Kotlin的集合创建
除了直接实例化Java的集合类之外,还可以使用标准库(stdlib)中的以下函数来创建
val listOf = listOf(1, 2, 3) //ArrayList
val arrayListOf = arrayListOf(1, 2, 3) // ArrayList
val mutableListOf = mutableListOf(1, 2, 3) // ArrayList
val setOf = setOf(1, 2, 3) // LinkedHashSet
val hashSetOf = hashSetOf(1, 2, 3) // HashSet
val mutableSetOf = mutableSetOf(1, 2, 3) // LinkedHashSet
val mapOf = mapOf("a" to 1, "b" to 2) // LinkedHashMap
val hashMapOf = hashMapOf("a" to 1, "b" to 2) // HashMap
val mutableMapOf = mutableMapOf("a" to 1, "b" to 2) // LinkedHashMap
Kotlin集合的操作
Kotlin 标准库提供了用于对集合执行操作的多种函数。这包括简单的操作,例如获取或添加元素,以及更复杂的操作,包括搜索、排序、过滤、转换等。
转换
- map:映射,返回将给定变换函数应用于原始集合中每个元素的结果的列表。
val numbers = setOf(1, 2, 3)
println(numbers.map { it * 3 })
val mapIndexed = numbers.mapIndexed { idx, value -> "$value + $idx" }
val s = mapIndexed[0]
println(s::class.java) // class java.lang.String
- zip:压合,调用应用于每对元素的提供的变换函数,返回从此集合和具有相同索引的另一个集合的元素构建的列表。
val colors = listOf("red", "brown", "grey")
val animals = listOf("fox", "bear", "wolf", "dog")
println(colors.zip(animals) { color, animal -> "$color $animal"}) // [red fox, brown bear, grey wolf]
- flatten:压平,返回给定集合中所有集合中所有元素的单个列表。
val numberSets = listOf(setOf(1, 2, 3), setOf(4, 5, 6), setOf(1, 2))
println(numberSets.flatten()) // [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 1, 2]
过滤
- filter:过滤,返回仅包含满足条件的元素的列表。
val numberStr = listOf("one", "two", "three", "four")
val longerThan3 = numberStr.filter { it.length > 3 }
println(longerThan3) // [three, four]
- partition:划分,将集合拆分为一对列表,其中第一个列表包含满足条件的元素,而第二个列表包含余下的元素。
val numberStr = listOf("one", "two", "three", "four")
val pair = numberStr.partition { it.length > 3 }
println(pair.first) // [three, four]
println(pair.second) // [one, two]
分组
- groupBy:对集合的元素进行分组,并返回一个map。
val numberStr = listOf("one", "two", "three", "four")
val map = numberStr.groupBy { it.first() }
println(map) // {o=[one], t=[two, three], f=[four]}
排序
- sorted:自然排序,排序算法是稳定的
val numberStr = listOf("one", "two", "three", "four")
println(numberStr.sorted()) // [four, one, three, two]
- sortedWith:自定义排序
val numberStr = listOf("one", "two", "three", "four")
val lengthComparator = Comparator { str1: String, str2: String -> str1.length - str2.length }
println(numberStr.sortedWith(lengthComparator)) // [one, two, four, three]
- sortedBy:自定义排序,内部调用的是sortedWith
val numberStr = listOf("one", "two", "three", "four")
println(numberStr.sortedBy { it.length }) // [one, two, four, three]