【ES】笔记-Promise基本使用
笔记-基本使用
- 一、初始Promise
-
- 1. 抽象表达:
- 2. 具体表达:
- 为什么要用 Promise?
- promise的基本流程
- 二、fs读取文件
- 三、AJAX请求
- 四、Promise封装fs模块
- 五、util.promisify方法
- 六、Promise封装AJAX操作
一、初始Promise
1. 抽象表达:
1. Promise 是一门新的技术(ES6 规范)
2. Promise 是 JS 中进行异步编程的新解决方案
备注:旧方案是单纯使用回调函数
2. 具体表达:
1. 从语法上来说: Promise 是一个构造函数
2. 从功能上来说: promise 对象用来封装一个异步操作并可以获取其成功/
失败的结果值
为什么要用 Promise?
指定回调函数的方式更加灵活
支持链式调用, 可以解决回调地狱问题
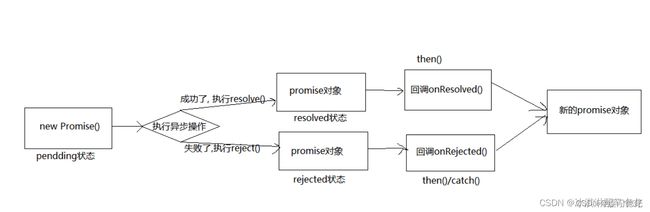
promise的基本流程
- 指定回调函数的方式更加灵活
- 支持链式调用, 可以解决回调地狱问题
实例代码说明:
调用函数resolve()、reject(),还可以传参数,但是函数名不一定为resolve、reject,可以自己设定,但一般默认为这两个。

注意这里需要用then方法进行调用!同理,这里的value、reason形参名不一定为这个,可以自定义,但一般默认这两个。

<body>
<div class="container">
<h2 class="page-header">Promise 初体验h2>
<button class="btn btn-primary" id="btn">点击抽奖button>
div>
<script>
//生成随机数
function rand(m,n){
return Math.ceil(Math.random() * (n-m+1)) + m-1;
}
/**
点击按钮, 1s 后显示是否中奖(30%概率中奖)
若中奖弹出 恭喜恭喜, 奖品为 10万 RMB 劳斯莱斯优惠券
若未中奖弹出 再接再厉
*/
//获取元素对象
const btn = document.querySelector('#btn');
//绑定单击事件
btn.addEventListener('click', function(){
//定时器
// setTimeout(() => {
// //30% 1-100 1 2 30
// //获取从1 - 100的一个随机数
// let n = rand(1, 100);
// //判断
// if(n <= 30){
// alert('恭喜恭喜, 奖品为 10万 RMB 劳斯莱斯优惠券');
// }else{
// alert('再接再厉');
// }
// }, 1000);
//Promise 形式实现
// resolve 解决 函数类型的数据
// reject 拒绝 函数类型的数据
const p = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
//30% 1-100 1 2 30
//获取从1 - 100的一个随机数
let n = rand(1, 100);
//判断
if(n <= 30){
resolve(n); // 将 promise 对象的状态设置为 『成功』
}else{
reject(n); // 将 promise 对象的状态设置为 『失败』
}
}, 1000);
});
console.log(p);
//调用 then 方法
p.then((value) => {
alert('恭喜恭喜, 奖品为 10万 RMB 劳斯莱斯优惠券, 您的中奖数字为 ' + value);
}, (reason) => {
alert('再接再厉, 您的号码为 ' + reason);
});
});
script>
body>
二、fs读取文件
//1. 引入 fs 模块
const fs=require('fs');
//2. 调用方法读取文件
fs.readFile('resources/为学.md',(err,data)=>{
//如果失败,则抛出错误
if(err) throw err;
console.log(data.toString());
});
Promise形式读取文件
const fs = require('fs');
let p = new Promise((resolve , reject) => {
fs.readFile('./resource/content.txt', (err, data) => {
//如果出错
if(err) reject(err);
//如果成功
resolve(data);
});
});
//调用 then
p.then(value=>{
console.log(value.toString());
}, reason=>{
console.log(reason);
});
运行结果:

需要注意的是,这里必须使用toString()方法,不然输出的就是Buffer文件数据

![]()
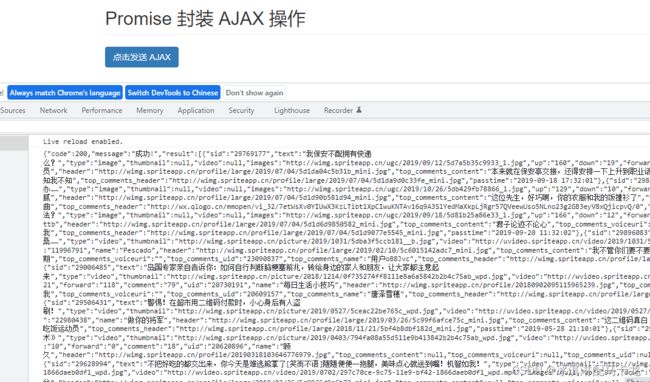
三、AJAX请求
用promise对AJAX方法进行了一个封装
完整代码:
<body>
<div class="container">
<h2 class="page-header">Promise 封装 AJAX 操作</h2>
<button class="btn btn-primary" id="btn">点击发送 AJAX</button>
</div>
<script>
//接口地址 https://api.apiopen.top/getJoke
//获取元素对象
const btn = document.querySelector('#btn');
btn.addEventListener('click', function(){
//创建 Promise
const p = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
//1.创建对象
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
//2. 初始化
xhr.open('GET', 'https://api.apiopen.top/getJoke');
//3. 发送
xhr.send();
//4. 处理响应结果
xhr.onreadystatechange = function(){
if(xhr.readyState === 4){
//判断响应状态码 2xx
if(xhr.status >= 200 && xhr.status < 300){
//控制台输出响应体
resolve(xhr.response);
}else{
//控制台输出响应状态码
reject(xhr.status);
}
}
}
});
//调用then方法
p.then(value=>{
console.log(value);
}, reason=>{
console.warn(reason);
});
});
</script>
</body>
四、Promise封装fs模块
- 封装一个函数mineReadFlie读取文件内容
- 参数:path文件路径
- 返回:promise对象
function mineReadFile(path){
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
//读取文件
require('fs').readFile(path, (err, data) =>{
//判断
if(err) reject(err);
//成功
resolve(data);
});
});
}
mineReadFile('./resource/content.txt')
.then(value=>{
//输出文件内容
console.log(value.toString());
}, reason=>{
console.log(reason);
});
五、util.promisify方法
将回调函数的方法转化为promise函数的方法,使得代码更简洁
//引入 util 模块
const util = require('util');
//引入 fs 模块
const fs = require('fs');
//返回一个新的函数
let mineReadFile = util.promisify(fs.readFile);
mineReadFile('./resource/content.txt').then(value=>{
console.log(value.toString());
});
六、Promise封装AJAX操作
- 封装一个函数sendAJAX 发送GET Ajax请求
- 参数URL
- 返回结果Promise对象
<body>
<script>
/**
* 封装一个函数 sendAJAX 发送 GET AJAX 请求
* 参数 URL
* 返回结果 Promise 对象
*/
function sendAJAX(url){
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
xhr.responseType = 'json';
xhr.open("GET", url);
xhr.send();
//处理结果
xhr.onreadystatechange = function(){
if(xhr.readyState === 4){
//判断成功
if(xhr.status >= 200 && xhr.status < 300){
//成功的结果
resolve(xhr.response);
}else{
reject(xhr.status);
}
}
}
});
}
sendAJAX('https://api.apiopen.top/getJoke')
.then(value => {
console.log(value);
}, reason => {
console.warn(reason);
});
</script>
</body>