Android 两个进程之间使用AIDL
我们假定两个应用程序为A和B。
我的意图是在B应用工程中创建Aidl,然后在这里实现 aidl里面的方法,然后在A应用工程中去远程调用:
好了:我先去创建 B应用程序:package com.king.review;
创建一个aidl文件:IService.aidl (com.king.review.aidl.IService)
package com.king.review.aidl; interface IService{ //设置地址 void setAddress(String address); //设置国家 void setCountry(String country); String disPlay(); }
在Aidl程序中不要任何访问修饰符,也不要 static,final 来修饰 ,另外其它的数据类型会有所不同,后期再说:
好了,创建完这个aidl文件,然后就需要我去去实现这个aidl接口的方法(这里我把实现aidl接口的方法与暴露接口的服务写在了一起,方便关联):
RemoteService.java (com.king.review.aidl.RemoteService)
package com.king.review.aidl; import android.app.Service; import android.content.Intent; import android.os.IBinder; import android.os.RemoteException; /** * author: king.liu * data:2013-10-9 上午7:07:32 * do:TODO */ public class RemoteService extends Service { public static final String MY_SERIVCE = "com.king.android.MY_REMOTE_SERIVCE"; @Override public IBinder onBind(Intent arg0) { return stub; }
ps:这里我把实现aidl文件的方法与定义的属性写在了暴露接口的远程服务中,方便关联与使用。 IService.Stub stub = new IService.Stub() { String mCountry; String mAddress; @Override public void setCountry(String country) throws RemoteException { this.mCountry = country; } @Override public void setAddress(String address) throws RemoteException { this.mAddress = address; } @Override public String disPlay() throws RemoteException { return "address:"+mAddress+"--------------mCountry:"+mCountry; } }; }
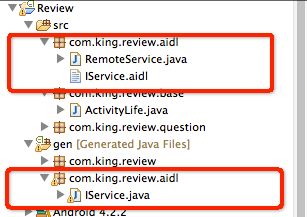
文件结构如上图,其中gen目录下的会自动生成,不用管。
另外需要在Androidmenifest.xml文件中去注册这个服务。以及添加过滤(MY_SERVICE)。。。
这样在B程序程序中的准备工作做完了。。。
A工程中准备工作:
直接把B应用程序中aidl文件所在的包以及,这个Aidl文件copy到 A应用程序中。并保存。。。
好了,这样我们就可以去在A应用程序中调用B应用程序提供的接口方法。。。
package com.king.otherreview; import com.king.review.aidl.IService; import android.app.Activity; import android.app.Service; import android.content.ComponentName; import android.content.Intent; import android.content.ServiceConnection; import android.os.Bundle; import android.os.IBinder; import android.os.RemoteException; import android.view.View; import android.view.View.OnClickListener; import android.widget.Button; import android.widget.Toast; public class MainActivity extends Activity { public static final String MY_SERIVCE = "com.king.android.MY_REMOTE_SERIVCE";//服务指定的动作 private IService iPerson; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); Button btn = new Button(this); setContentView(btn); btn.setWidth(150); btn.setHeight(150); btn.setText("aidl Test"); btn.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE); btn.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View v) { Intent intent = new Intent(); intent.setAction(MY_SERIVCE); bindService(intent, conn, Service.BIND_AUTO_CREATE); } }); } private ServiceConnection conn = new ServiceConnection() { @Override synchronized public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) { iPerson = IService.Stub.asInterface(service); if(null!=iPerson){ //RPC调用方法 try { iPerson.setAddress("shenzhen.guangdong"); iPerson.setCountry("china"); String msg = iPerson.disPlay(); Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, msg, Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show(); } catch (RemoteException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } @Override public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) { } }; }
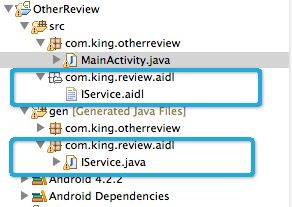
文件结构如图。
在onServiceConnedted中传入需要的参数。
然后去绑定这个服务即可。