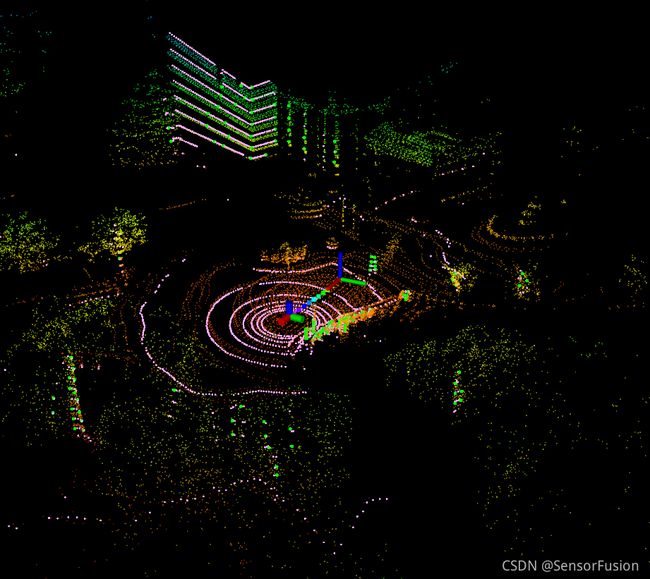
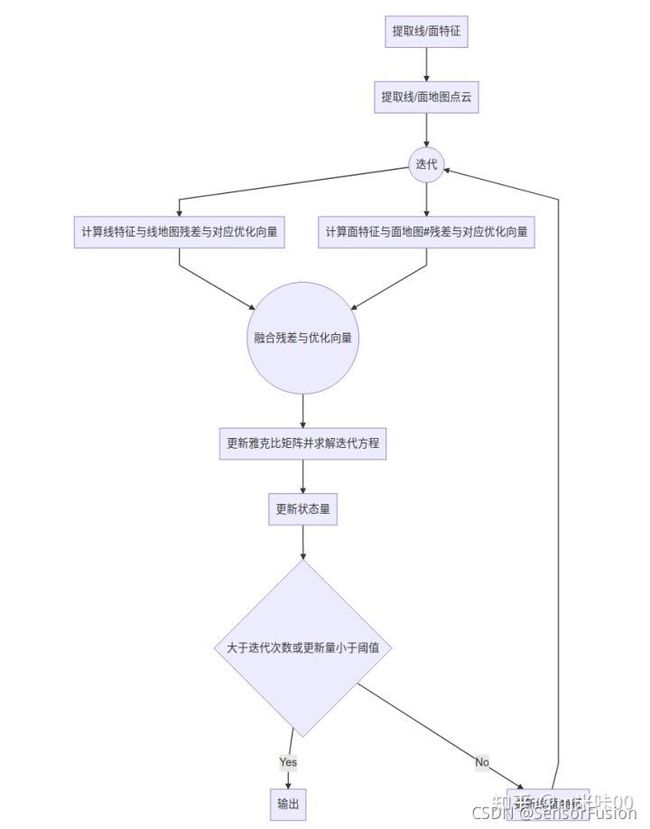
点云slam常见框架、运动补偿、ICP、LM、牛顿法、GTSAM图优化函数库
从落地情况来看,
视觉slam和激光slam,相对来说激光slam更容易落地
视觉相对来说劣势:
视觉,描述子,白天,黑夜,算力相对来说没有激光slam鲁棒
Livox 前言:
1rad=(/180)1°=1/180rad,其中rad是弧度的单位
公式为:
角度=180°×弧度÷π 弧度=角度×π÷180°
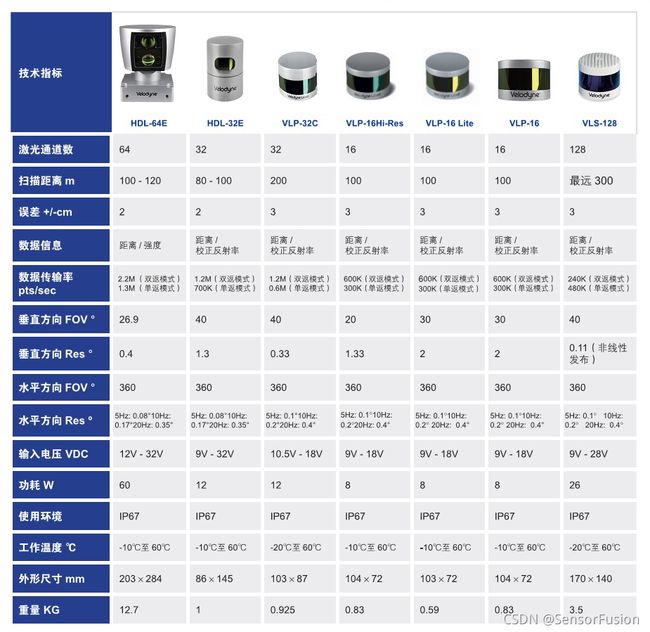
Livox激光雷达
horizon

 livox自定义数据格式转ros点云格式:
livox自定义数据格式转ros点云格式:
#include 看livox_mapping中,对于horizon的处理:
先是经过了livox_repub的处理,将原始消息进行转换:
然后注意:
对于这些scanID,结果全部被串在了laserCloud这个大的队列了。
也没有去计算各个点的horizon角度。
拿到这个串起来的laserCloud数据后,直接对里面的点进行处理:
计算特征,没用用到类似loam那里的处理方式。
#include livox 驱动点云数据格式
代码路径: **livox_ros_driver/livox_ros_driver/lddc.cpp**
包括三种格式的点云数据的呈现
if (kPointCloud2Msg == transfer_format_) {
// ros标注格式
PublishPointcloud2(p_queue, onetime_publish_packets, handle);
} else if (kLivoxCustomMsg == transfer_format_) {
// 自定义格式 需要添加msg
// livox_ros_driver/msg/CustomMsg.msg
// livox_ros_driver/msg/CustomPoint.msg
PublishCustomPointcloud(p_queue, onetime_publish_packets, handle);
} else if (kPclPxyziMsg == transfer_format_) {
// save bag
PublishPointcloudData(p_queue, onetime_publish_packets, handle);
}
首要问题:
0:消除运动畸变
zhihu_show
运动补偿方法:
畸变补偿方法
方法一:
我们再把这个问题分解一下,补偿可分为计算和转换两步,如下
1. 计算相对坐标
在匀速模型假设前提下,坐标 = 运动×时间,所以又可以分解为两步:
1)获取载体运动信息
运动信息在原始数据里已经存在,包括角速度、速度,分别用来计算相对角度和相对位移。而且数据是我们已经做好时间同步的。
2)获取该激光点相对于起始时刻的时间差
由于是顺序扫描,我们可以很容易通过atan2(y, x)来计算出该激光点相对于第一个激光点旋转过的角度 [公式] ,我们知道雷达内部旋转360°用了100ms,那么旋转[公式] 角度用了多长时间,就了然了。
2. 转换激光点
其实就是坐标系×向量,坐标系是转换矩阵,向量是转换之前的激光点坐标,这个转换可以先旋转再平移,也可以用4X4矩阵一次性计算,都行,不是核心问题。
方法二:
由于激光采集的点云并不是在同一时刻采集的,所以就会存在运动畸变(坐标系不同引起的),所以需要根据接收激光点的时间计算位姿把点云投影到同一坐标系。为了补偿每次扫描的时间和位姿不同,我们可以利用:
分段线性:把一个新来的帧分成三个连续的子帧,然后把这三个帧独立的和现阶段构建的地图做匹配。在每个子图做scan-match的过程中利用子图中最后一个点的位姿把所有的点投影到全局地图中,这样每帧采样的时间仅为原来的三分之一。尽管这种方法很简单,但是效果很好(LEGO—LOAM中把一帧分为6份应该也是分段线性的思想),分段线性对于多核的CPU并行运算也有好处。
线性插值:这部分在张籍博士的LAOM中介绍的比较详细,大家在看的时候可以参考。主要思想是在当前帧最后一个激光点得到的雷达位姿[R_k,T_k]和次新帧的[R_k-1,T_k-1]中间的时刻t,利用恒速模型计算中间时刻点的位姿。具体来说:
apollo驱动的方案:
利用imu:
线速度描述质点沿圆周运动快慢;角速度描述质点绕圆心转动快慢
线速度:描述质点沿圆周运动快慢的矢量,方向为圆周上各点的切线方向。为状态量
角速度:描述质点绕圆心转动快慢的矢量,也为状态量
二者关系。线速度等于角速度与转动半径的乘积。为瞬间对应关系
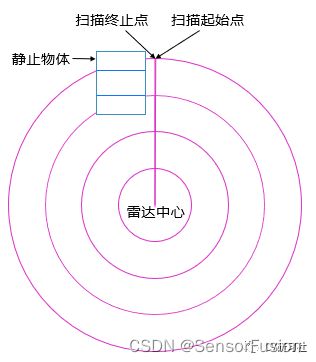
在静止的场景中,即激光雷达载体本身静止且环境中没有运动物体,那么采集到的一帧点云没有畸变,如下图所示,每一条线束打到地面上形成一个闭合的圆形:
在运动的场景中,即激光雷达载体运动或者环境中存在运动物体,采集到的点云数据有畸变现象,如下图所示:激光雷达向前运动,物体相对运动,同一种颜色的线表示一条激光打到地面的线束。采集一帧数据起始点时的雷达原点位置和采集一帧数据终止点时的雷达原点位置出现了位移,三维环境信息出现了拉伸的畸变。(运动物体同理)
由此得出机械式激光点云的畸变产生原因:
激光点的数据不是瞬时获得的
激光测量时伴随载体或目标的运动
激光帧率较低时,载体或目标运动畸变不能忽略
由于雷达计算激光点坐标时,都是以接收到激光束时刻的雷达自身坐标系为基础的,所以载体运动过程中每一列激光点的基准坐标系都是不一样的,但是在同一帧点云里,我们希望能统一在同一个坐标系下,所以需要知道每次采集时的坐标系相对于初始时刻坐标系的转换关系。
https://gitee.com/ApolloAuto/apollo/blob/r6.0.0/modules/drivers/lidar/velodyne/compensator/compensator.cc
/******************************************************************************/
#include "modules/drivers/lidar/velodyne/compensator/compensator.h"
#include 如下激光雷达运动补偿方式:
void compensator(double frame_time,
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZI>::Ptr cloud_raw,
Eigen::Matrix4f &last_mat)
{
double begin_time = frame_time - 0.1;
double end_time = frame_time;
Eigen::Matrix4f begin_pose, end_pose;
bool tf_first = true;
// getTf(end_time, end_pose,tf_first);
// // if(time_syn){
// bool tf_first = true;
// getTf(end_time, end_pose,tf_first);
// tf_first = false;
// begin_time -=first_tf_time;
// getTf(begin_time, begin_pose,tf_first);
// }
// else
// // {
// bool tf_first = false;
getTf(end_time, end_pose,tf_first);
getTf(begin_time, begin_pose,tf_first);
// }
last_mat = end_pose;
using std::abs;
using std::acos;
using std::sin;
Eigen::Vector3f translation =
begin_pose.block(0,3,3,1) - end_pose.block(0,3,3,1); //从0行3列开始,取3行1列数据
Eigen::Matrix3f end_rotation = end_pose.block(0,0,3,3);
Eigen::Matrix3f begin_rotation = begin_pose.block(0,0,3,3);
Eigen::Quaternionf q_max(end_rotation); //转换成四元数
Eigen::Quaternionf q_min(begin_rotation);
Eigen::Quaternionf q1(q_max.conjugate() * q_min);
Eigen::Quaternionf q0(Eigen::Quaternionf::Identity());
q1.normalize();
translation = q_max.conjugate() * translation;
int total = cloud_raw->width * cloud_raw->height;
double d = q0.dot(q1);
double abs_d = abs(d);
if (abs_d < 1.0 - 1.0e-8)
{
double theta = acos(abs_d);
double sin_theta = sin(theta);
double c1_sign = (d > 0) ? 1 : -1;
for (int i = 0; i < total; ++i)
{
pcl::PointXYZI tmp_point = cloud_raw->points[i];
if (std::isnan(tmp_point.x) || std::isnan(tmp_point.y) || std::isnan(tmp_point.z))
continue;
double t = 1. - i*0.0001;
Eigen::Vector3f p(tmp_point.x, tmp_point.y, tmp_point.z);
Eigen::Translation3f ti(t * translation);
double c0 = sin((1 - t) * theta) / sin_theta;
double c1 = sin(t * theta) / sin_theta * c1_sign;
Eigen::Quaternionf qi(c0 * q0.coeffs() + c1 * q1.coeffs());
Eigen::Affine3f trans = ti * qi;
p = trans * p;
cloud_raw->points[i].x = p.x();
cloud_raw->points[i].y = p.y();
cloud_raw->points[i].z = p.z();
}
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < total; ++i)
{
pcl::PointXYZI tmp_point = cloud_raw->points[i];
if (std::isnan(tmp_point.x) || std::isnan(tmp_point.y) || std::isnan(tmp_point.z))
continue;
double t = 1. - i * 0.0001;
Eigen::Vector3f p(tmp_point.x, tmp_point.y, tmp_point.z);
Eigen::Translation3f ti(t * translation);
p = ti * p;
cloud_raw->points[i].x = p.x();
cloud_raw->points[i].y = p.y();
cloud_raw->points[i].z = p.z();
}
}
如利用其他的已知信息,车辆信息,借助匀速运动模型:
如利用车速+ lidar自带的imu角速度
Eigen::Vector3f pi_vector = Eigen::Vector3f(PI, PI, PI);
// 激光位姿转车身位姿
cv::cv2eigen(trans_tele_train.rotate, ER);
tele_euler_angles = pi_vector - ER.eulerAngles(0, 1, 2); // 弧度
train_speed //为车速度;
Eigen::Vector3d vel = Eigen::Vector3d(train_speed * cos(tele_euler_angles[1]), 0, train_speed * sin(tele_euler_angles[1]));
Eigen::Vector3d angular_vel = imu_frames[i].data;
void LidarDetection::UndistortPointPcl(const pcl::PointCloud<PointType>::Ptr &pcl_in_out, const Eigen::Vector3d &vel, const Eigen::Vector3d &angular_vel) {
double dt = 0.1; // 10hz
Eigen::Vector3d trans = dt * vel;
Eigen::Vector3d delta_angle = dt * angular_vel;
Sophus::SO3d rot = Sophus::SO3d::exp(delta_angle);
Eigen::Quaterniond q(1, 0, 0, 0);
Eigen::Vector3d t(0, 0, 0);
// trans_imu_lidar
Sophus::SE3d T_i_l = Sophus::SE3d(q, t);
// trans_last_current
Sophus::SE3d T_l_c(rot, trans);
// trans_lidar_begin_end
Sophus::SE3d T_l_be = T_i_l.inverse() * T_l_c * T_i_l;
const Eigen::Vector3d &tbe = T_l_be.translation();
Eigen::Vector3d rso3_be = T_l_be.so3().log();
for (auto &pt : pcl_in_out->points) {
int ring = int(pt.intensity);
float dt_bi = pt.intensity - ring;
double ratio_bi = dt_bi * 10;
double ratio_ie = 1 - ratio_bi;
Eigen::Vector3d rso3_ie = ratio_ie * rso3_be;
Sophus::SO3d Rie = Sophus::SO3d::exp(rso3_ie);
Eigen::Vector3d tie = ratio_ie * tbe;
Eigen::Vector3d v_pt_i(pt.x, pt.y, pt.z);
Eigen::Vector3d v_pt_comp_e = Rie.inverse() * (v_pt_i - tie);
pt.x = v_pt_comp_e.x();
pt.y = v_pt_comp_e.y();
pt.z = v_pt_comp_e.z();
}
}
IMU数据
// IMU callback
void LidarFusion::GetImu(const sensor_msgs::ImuConstPtr msg) {
// float acc_x = msg->linear_acceleration.x;
// float acc_y = msg->linear_acceleration.y;
// float acc_z = msg->linear_acceleration.z;
Eigen::Quaternionf bt_q(Eigen::Quaternionf::Identity());
if (last_angle_idx_ != -1) {
float diff_time = msg->header.stamp.toSec() - angle_time_[last_angle_idx_];
float roll = msg->angular_velocity.x * diff_time;
float pitch = msg->angular_velocity.y * diff_time;
float yaw = msg->angular_velocity.z * diff_time;
Eigen::AngleAxisf current_rotation_x(roll, Eigen::Vector3f::UnitX());
Eigen::AngleAxisf current_rotation_y(pitch, Eigen::Vector3f::UnitY());
Eigen::AngleAxisf current_rotation_z(yaw, Eigen::Vector3f::UnitZ());
bt_q = current_rotation_z * current_rotation_y * current_rotation_x;
}
angle_mutex.lock();
last_angle_idx_ = (last_angle_idx_ + 1) % 200;
angle_vec_[last_angle_idx_] = bt_q;
angle_time_[last_angle_idx_] = msg->header.stamp.toSec();
angle_mutex.unlock();
vel_mutex.lock();
last_vel_idx_ = (last_vel_idx_ + 1) % 200;
vel_vec_[last_vel_idx_] = 60. / 3.6;
vel_time_[last_vel_idx_] = msg->header.stamp.toSec();
vel_mutex.unlock();
}
Loam 补偿算法思路:
https://blog.csdn.net/liuyanpeng12333/article/details/82737181
//接收imu消息,imu坐标系为x轴向前,y轴向右,z轴向上的右手坐标系
void imuHandler(const sensor_msgs::Imu::ConstPtr& imuIn)
{
double roll, pitch, yaw;
//定义四元数
tf::Quaternion orientation;
//将IMU数据中的四元数转换到定义的四元数中
tf::quaternionMsgToTF(imuIn->orientation, orientation);
//由四元数获得欧拉角
tf::Matrix3x3(orientation).getRPY(roll, pitch, yaw);
//减去重力的影响,求出xyz方向的加速度实际值,并进行坐标轴交换,统一到z轴向前,
//x轴向左的右手坐标系, 交换过后RPY对应fixed axes ZXY(RPY---ZXY)。
//Now R = Ry(yaw)*Rx(pitch)*Rz(roll).
float accX = imuIn->linear_acceleration.y - sin(roll) * cos(pitch) * 9.81;
float accY = imuIn->linear_acceleration.z - cos(roll) * cos(pitch) * 9.81;
float accZ = imuIn->linear_acceleration.x + sin(pitch) * 9.81;
//循环移位效果,形成环形数组
imuPointerLast = (imuPointerLast + 1) % imuQueLength;
imuTime[imuPointerLast] = imuIn->header.stamp.toSec();
imuRoll[imuPointerLast] = roll;
imuPitch[imuPointerLast] = pitch;
imuYaw[imuPointerLast] = yaw;
imuAccX[imuPointerLast] = accX;
imuAccY[imuPointerLast] = accY;
imuAccZ[imuPointerLast] = accZ;
AccumulateIMUShift();
}
void AccumulateIMUShift()
{
//获得由IMUHandler函数得到该帧IMU数据的欧拉角和三轴角加速度
float roll = imuRoll[imuPointerLast];
float pitch = imuPitch[imuPointerLast];
float yaw = imuYaw[imuPointerLast];
float accX = imuAccX[imuPointerLast];
float accY = imuAccY[imuPointerLast];
float accZ = imuAccZ[imuPointerLast];
//将当前时刻的加速度值绕交换过的ZXY固定轴(原XYZ)分别旋转(roll, pitch, yaw)角,转换得到世界
//坐标系下的加速度值(右手法则)
//绕z轴旋转(roll)
float x1 = cos(roll) * accX - sin(roll) * accY;
float y1 = sin(roll) * accX + cos(roll) * accY;
float z1 = accZ;
//绕x轴旋转(pitch)
float x2 = x1;
float y2 = cos(pitch) * y1 - sin(pitch) * z1;
float z2 = sin(pitch) * y1 + cos(pitch) * z1;
//绕y轴旋转(yaw)
accX = cos(yaw) * x2 + sin(yaw) * z2;
accY = y2;
accZ = -sin(yaw) * x2 + cos(yaw) * z2;
//上一个imu点
int imuPointerBack = (imuPointerLast + imuQueLength - 1) % imuQueLength;
//上一个点到当前点所经历的时间,即计算imu测量周期
double timeDiff = imuTime[imuPointerLast] - imuTime[imuPointerBack];
//要求imu的频率至少比lidar高,这样的imu信息才使用,后面校正也才有意义
if (timeDiff < scanPeriod) {//(隐含从静止开始运动)
//求每个imu时间点的位移与速度,两点之间视为匀加速直线运动
imuShiftX[imuPointerLast] = imuShiftX[imuPointerBack] + imuVeloX[imuPointerBack] * timeDiff
+ accX * timeDiff * timeDiff / 2;
imuShiftY[imuPointerLast] = imuShiftY[imuPointerBack] + imuVeloY[imuPointerBack] * timeDiff
+ accY * timeDiff * timeDiff / 2;
imuShiftZ[imuPointerLast] = imuShiftZ[imuPointerBack] + imuVeloZ[imuPointerBack] * timeDiff
+ accZ * timeDiff * timeDiff / 2;
imuVeloX[imuPointerLast] = imuVeloX[imuPointerBack] + accX * timeDiff;
imuVeloY[imuPointerLast] = imuVeloY[imuPointerBack] + accY * timeDiff;
imuVeloZ[imuPointerLast] = imuVeloZ[imuPointerBack] + accZ * timeDiff;
}
}
//计算局部坐标系下点云中的点相对第一个开始点的由于加减速运动产生的位移畸变
void ShiftToStartIMU(float pointTime)
{
//计算相对于第一个点由于加减速产生的畸变位移(全局坐标系下畸变位移量delta_Tg)
//imuShiftFromStartCur = imuShiftCur - (imuShiftStart + imuVeloStart * pointTime)
imuShiftFromStartXCur = imuShiftXCur - imuShiftXStart - imuVeloXStart * pointTime;
imuShiftFromStartYCur = imuShiftYCur - imuShiftYStart - imuVeloYStart * pointTime;
imuShiftFromStartZCur = imuShiftZCur - imuShiftZStart - imuVeloZStart * pointTime;
/********************************************************************************
Rz(pitch).inverse * Rx(pitch).inverse * Ry(yaw).inverse * delta_Tg
transfrom from the global frame to the local frame
*********************************************************************************/
//绕y轴旋转(-imuYawStart),即Ry(yaw).inverse
float x1 = cos(imuYawStart) * imuShiftFromStartXCur - sin(imuYawStart) * imuShiftFromStartZCur;
float y1 = imuShiftFromStartYCur;
float z1 = sin(imuYawStart) * imuShiftFromStartXCur + cos(imuYawStart) * imuShiftFromStartZCur;
//绕x轴旋转(-imuPitchStart),即Rx(pitch).inverse
float x2 = x1;
float y2 = cos(imuPitchStart) * y1 + sin(imuPitchStart) * z1;
float z2 = -sin(imuPitchStart) * y1 + cos(imuPitchStart) * z1;
//绕z轴旋转(-imuRollStart),即Rz(pitch).inverse
imuShiftFromStartXCur = cos(imuRollStart) * x2 + sin(imuRollStart) * y2;
imuShiftFromStartYCur = -sin(imuRollStart) * x2 + cos(imuRollStart) * y2;
imuShiftFromStartZCur = z2;
}
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
再次梳理点云运动补偿:
https://www.guyuehome.com/35597
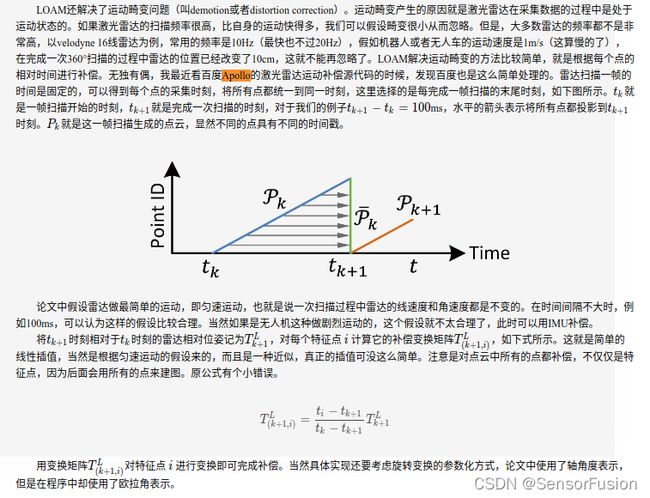
// 这里相当于是一个匀速模型的假设 // 把位姿变换分解成平移和旋转 Eigen::Quaterniond q_point_last = Eigen::Quaterniond::Identity().slerp(s, q_last_curr); Eigen::Vector3d t_point_last = s * t_last_curr;
做一个匀速模型假设,即上一帧的位姿变换,就是这帧的位姿变换,以此来求出输入点坐标系到起始时刻点坐标系的位姿变换,通过上面求的时间占比s。
这里把位姿变换分解成了旋转 + 平移 的方式,由于四元数是一个超复数,不是简单的乘法,求它的占比用的 Eigen的slerp函数(球面线性插值)。


//获取旋转矩阵+平移矩阵
motionCompensation(lidar_data[0].data, sync_frame.lidar_pcd[0], getRotation(imus[0]), Eigen::Vector3d(0.1 * v, 0, 0));
// 获取运动补偿轨迹及位姿变换
motionCompensation(sync_frame, getRotation(imus[0]), Eigen::Vector3d(0.1 * v, 0, 0));
void DataBuffer::motionCompensation(pcl::PointCloud<PointType> &src_pcd,
pcl::PointCloud<PointType> &dst_pcd,
Sophus::SO3d R, Eigen::Vector3d T) {
dst_pcd = src_pcd;
Eigen::Quaterniond q(1, 0, 0, 0);
Eigen::Vector3d t(0, 0, 0);
Sophus::SE3d T_i_l = Sophus::SE3d(q, t);
Sophus::SE3d T_l_c(R, T);
Sophus::SE3d T_l_be = T_i_l.inverse() * T_l_c * T_i_l;
const Eigen::Vector3d &tbe = T_l_be.translation();
const Eigen::Vector3d rso_be = T_l_be.so3().log();
for (auto &pt: dst_pcd.points) {
float ratio_bi_scale = pt.curvature - int(pt.curvature);
double ratio_ie = 1.0 - ratio_bi_scale * 10;
Eigen::Vector3d tie = ratio_ie * tbe;
Eigen::Vector3d rso_ie = ratio_ie * rso_be;
Sophus::SO3d Rie = Sophus::SO3d::exp(rso_ie);
Eigen::Vector3d v_pt_i(pt.x, pt.y, pt.z);
Eigen::Vector3d v_pt_comp_e = Rie.inverse() * (v_pt_i - tie);
pt.x = v_pt_comp_e.x();
pt.y = v_pt_comp_e.y();
pt.z = v_pt_comp_e.z();
}
}
void DataBuffer::motionCompensation(SyncFrame &sync_frame, Sophus::SO3d R, Eigen::Vector3d T) {
sync_frame.q = Eigen::Quaterniond(R.matrix());
sync_frame.t = T;
sync_frame.motion_pcd.clear();
Eigen::Quaterniond q(1, 0, 0, 0);
Eigen::Vector3d t(0, 0, 0);
Sophus::SE3d T_i_l = Sophus::SE3d(q, t);
Sophus::SE3d T_l_c(R, T);
Sophus::SE3d T_l_be = T_i_l.inverse() * T_l_c * T_i_l;
const Eigen::Vector3d &tbe = T_l_be.translation();
const Eigen::Vector3d rso_be = T_l_be.so3().log();
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
PointType pt;
float ratio_bi_scale = i / 100.;
double ratio_ie = 1.0 - ratio_bi_scale * 10;
Eigen::Vector3d tie = ratio_ie * tbe;
Eigen::Vector3d rso_ie = ratio_ie * rso_be;
Sophus::SO3d Rie = Sophus::SO3d::exp(rso_ie);
Eigen::Vector3d v_pt_i(0, 0, 0);
Eigen::Vector3d v_pt_comp_e = Rie.inverse() * (v_pt_i - tie);
pt.x = v_pt_comp_e.x();
pt.y = v_pt_comp_e.y();
pt.z = v_pt_comp_e.z();
sync_frame.motion_pcd.push_back(pt);
}
}
// 没有imu
// 直接 A-loam 方式
// undistort lidar point
void TransformToStart(PointType const *const pi, PointType *const po)
{
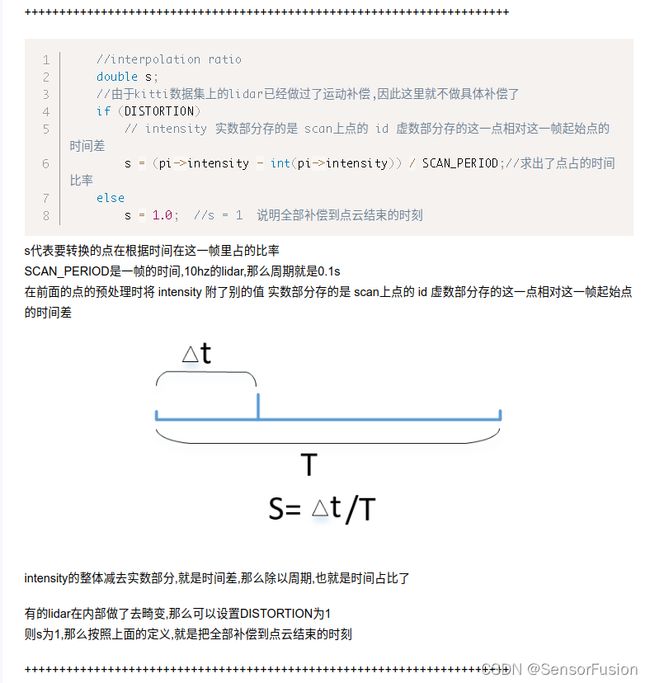
//interpolation ratio
double s;
//由于kitti数据集上的lidar已经做过了运动补偿,因此这里就不做具体补偿了
if (DISTORTION)
// intensity 实数部分存的是 scan上点的 id 虚数部分存的这一点相对这一帧起始点的时间差
s = (pi->intensity - int(pi->intensity)) / SCAN_PERIOD;//求出了点占的时间比率
else
s = 1.0; //s = 1 说明全部补偿到点云结束的时刻
//s = 1;
//所有点的操作方式都是一致的,相当于从结束时刻补偿到起始时刻
// 这里相当于是一个匀速模型的假设
// 把位姿变换分解成平移和旋转
Eigen::Quaterniond q_point_last = Eigen::Quaterniond::Identity().slerp(s, q_last_curr);//求姿态的球面插值
Eigen::Vector3d t_point_last = s * t_last_curr;//求位移的线性插值
Eigen::Vector3d point(pi->x, pi->y, pi->z);//把当前点的坐标取出
Eigen::Vector3d un_point = q_point_last * point + t_point_last;//通过旋转和平移将 当前点转到帧起始时刻坐标系下的坐标
//将求得的转换后的坐标赋值给输出点
po->x = un_point.x();
po->y = un_point.y();
po->z = un_point.z();
po->intensity = pi->intensity;//赋值原的intensity
}
// transform all lidar points to the start of the next frame
void TransformToEnd(PointType const *const pi, PointType *const po)
{
// 首先先做畸变校正,都转到起始时刻
pcl::PointXYZI un_point_tmp;//转到帧起始时刻坐标系下的点
//先统一到起始时刻
TransformToStart(pi, &un_point_tmp);
//再 通过反变换的方式 将起始时刻坐标系下的点 转到 结束时刻坐标系下
Eigen::Vector3d un_point(un_point_tmp.x, un_point_tmp.y, un_point_tmp.z);//取出起始时刻坐标系下的点
//q_last_curr \ t_last_curr 是结束时刻坐标系转到起始时刻坐标系 的 旋转 和 平移
Eigen::Vector3d point_end = q_last_curr.inverse() * (un_point - t_last_curr);//通过反变换,求得转到 结束时刻坐标系下 的点坐标
//将求得的转换后的坐标赋值给输出点
po->x = point_end.x();
po->y = point_end.y();
po->z = point_end.z();
//移除掉 intensity 相对时间的信息
po->intensity = int(pi->intensity);
}
LOAM 方法
/*****************************************************************************
将当前帧点云TransformToStart和将上一帧点云TransformToEnd的作用:
去除畸变,并将两帧点云数据统一到同一个坐标系下计算
*****************************************************************************/
//当前点云中的点相对第一个点去除因匀速运动产生的畸变,效果相当于得到在点云扫描开始位置静止扫描得到的点云
void TransformToStart(PointType const * const pi, PointType * const po)
{
//插值系数计算,云中每个点的相对时间/点云周期10
float s = 10 * (pi->intensity - int(pi->intensity));
//线性插值:根据每个点在点云中的相对位置关系,乘以相应的旋转平移系数
float rx = s * transform[0];
float ry = s * transform[1];
float rz = s * transform[2];
float tx = s * transform[3];
float ty = s * transform[4];
float tz = s * transform[5];
//平移后绕z轴旋转(-rz)
float x1 = cos(rz) * (pi->x - tx) + sin(rz) * (pi->y - ty);
float y1 = -sin(rz) * (pi->x - tx) + cos(rz) * (pi->y - ty);
float z1 = (pi->z - tz);
//绕x轴旋转(-rx)
float x2 = x1;
float y2 = cos(rx) * y1 + sin(rx) * z1;
float z2 = -sin(rx) * y1 + cos(rx) * z1;
//绕y轴旋转(-ry)
po->x = cos(ry) * x2 - sin(ry) * z2;
po->y = y2;
po->z = sin(ry) * x2 + cos(ry) * z2;
po->intensity = pi->intensity;
}
//将上一帧点云中的点相对结束位置去除因匀速运动产生的畸变,效果相当于得到在点云扫描结束位置静止扫描得到的点云
void TransformToEnd(PointType const * const pi, PointType * const po)
{
//插值系数计算
float s = 10 * (pi->intensity - int(pi->intensity));
float rx = s * transform[0];
float ry = s * transform[1];
float rz = s * transform[2];
float tx = s * transform[3];
float ty = s * transform[4];
float tz = s * transform[5];
//平移后绕z轴旋转(-rz)
float x1 = cos(rz) * (pi->x - tx) + sin(rz) * (pi->y - ty);
float y1 = -sin(rz) * (pi->x - tx) + cos(rz) * (pi->y - ty);
float z1 = (pi->z - tz);
//绕x轴旋转(-rx)
float x2 = x1;
float y2 = cos(rx) * y1 + sin(rx) * z1;
float z2 = -sin(rx) * y1 + cos(rx) * z1;
//绕y轴旋转(-ry)
float x3 = cos(ry) * x2 - sin(ry) * z2;
float y3 = y2;
float z3 = sin(ry) * x2 + cos(ry) * z2;//求出了相对于起始点校正的坐标
rx = transform[0];
ry = transform[1];
rz = transform[2];
tx = transform[3];
ty = transform[4];
tz = transform[5];
//绕y轴旋转(ry)
float x4 = cos(ry) * x3 + sin(ry) * z3;
float y4 = y3;
float z4 = -sin(ry) * x3 + cos(ry) * z3;
//绕x轴旋转(rx)
float x5 = x4;
float y5 = cos(rx) * y4 - sin(rx) * z4;
float z5 = sin(rx) * y4 + cos(rx) * z4;
//绕z轴旋转(rz),再平移
float x6 = cos(rz) * x5 - sin(rz) * y5 + tx;
float y6 = sin(rz) * x5 + cos(rz) * y5 + ty;
float z6 = z5 + tz;
//平移后绕z轴旋转(imuRollStart)
float x7 = cos(imuRollStart) * (x6 - imuShiftFromStartX)
- sin(imuRollStart) * (y6 - imuShiftFromStartY);
float y7 = sin(imuRollStart) * (x6 - imuShiftFromStartX)
+ cos(imuRollStart) * (y6 - imuShiftFromStartY);
float z7 = z6 - imuShiftFromStartZ;
//绕x轴旋转(imuPitchStart)
float x8 = x7;
float y8 = cos(imuPitchStart) * y7 - sin(imuPitchStart) * z7;
float z8 = sin(imuPitchStart) * y7 + cos(imuPitchStart) * z7;
//绕y轴旋转(imuYawStart)
float x9 = cos(imuYawStart) * x8 + sin(imuYawStart) * z8;
float y9 = y8;
float z9 = -sin(imuYawStart) * x8 + cos(imuYawStart) * z8;
//
//绕y轴旋转(-imuYawLast)
float x10 = cos(imuYawLast) * x9 - sin(imuYawLast) * z9;
float y10 = y9;
float z10 = sin(imuYawLast) * x9 + cos(imuYawLast) * z9;
//绕x轴旋转(-imuPitchLast)
float x11 = x10;
float y11 = cos(imuPitchLast) * y10 + sin(imuPitchLast) * z10;
float z11 = -sin(imuPitchLast) * y10 + cos(imuPitchLast) * z10;
//绕z轴旋转(-imuRollLast)
po->x = cos(imuRollLast) * x11 + sin(imuRollLast) * y11;
po->y = -sin(imuRollLast) * x11 + cos(imuRollLast) * y11;
po->z = z11;
//只保留线号
po->intensity = int(pi->intensity);
}
Livox解决办法
https://blog.csdn.net/brightming/article/details/117969841
在livox_horizon_loam中,对于利用imu补偿也是这样做的。
这个代码仅仅是对旋转做了补偿,未对位移进行计算,因为位移需要有速度,但是仅仅依靠imu,长时间积分速度会很不准,需要利用反馈信息来纠正,当前没有这样做,所以仅仅是利用了旋转量。
该算法每次都累计若干个imu,对应一帧lidar数据。
为了对这一帧的lidar点进行运动补偿,需要计算出这一帧时间内,旋转了多少。
考虑不到,平移量在各个方向的分量
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
1:Ros的里程计
特征点的关联就是计算历程数据odometry推演,将t时刻的点云和t+1时刻的点云关联起来的一种方法(如果有imu或者里程计可以先进行一个初步的变换,作为初始信息用于匹配)。在t时刻得到的边缘点生成的线和t+1时刻提取的边缘点对应起来,对于t+1时刻的点,在t时刻找到最近的两个点(同时满足两点的线段有意义);同样的考虑平面特征点。t时刻的特征点通过3D的KD-tree建立快速索引。计算这一时刻对应上一时刻最近的两个点,求点到线的距离;同样的考虑点到面的距离。
我举个例子,gmapping导航建图包里建图需要里程计信息,且导航也需要。
hector建图呢有个缺点,如果雷达不够精确,那么建出来的图会导致定位不够精确,这是我们不期望的,所以要实现精确的定位与导航,需要加入里程计信息
ROS gmapping导航包,要求有2 个 输入,一个是激光数据,另一个就是里程计信息。
那么我们该如何获得里程计呢?
里程计又包含2 个方面的信息:
一、是位姿(位置和转角),即(x,y,θ)
二、是速度(前进速度和转向速度)。
2:ceres-solver安装
https://github.com/ceres-solver/ceres-solver
直接下载,unzip解压
安装:
mkdir build
cd build/
cmake ..
make -j3
mkdir build
cd build
cmake -D CMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=/usr/local/ceres .. #前提是在local下自己建立了一个ceres文件
sudo make install
#list( APPEND CMAKE_MODULE_PATH ${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/cmake_modules )#可有可无
set(Ceres_DIR /usr/local/ceres/lib/cmake/Ceres) #important,/usr/local/ceres这种还是报错,要到Ceres才行
find_package(Ceres REQUIRED )
include_directories(${CERES_INCLUDE_DIRS})
link_directories(${CERES_LIBRARY_DIRS})
add_executable( curve_fitting main.cpp )
target_link_libraries( curve_fitting ${CERES_LIBRARIES})
测试:
./bin/simple_bundle_adjuster ../data/problem-16-22106-pre.txt
3:hdl_graph_slam
采集数据方法:
rosparam set use_sim_time true
roslaunch hdl_graph_slam hdl_graph_slam_inin.launch
roscd hdl_graph_slam/rviz
rviz -d hdl_graph_slam.rviz
rosbag play --clock ***.bag
hdl_graph_slam是一套激光slam系统,可融合gps、imu、lidar三种传感器,同时具有闭环检测功能。开源代码地址为:
hdl_graph_slam激光雷达建图系统
github.com
一、优缺点分析
通过实测和阅读代码,它有如下优缺点:
- 优点
1)简洁的流程和代码结构。
激光slam虽然相对简单,但是目前开源的算法里,能够同时融合gps、imu、lidar三种传感器的还比较少。cartographer算是一种,但是相对于它来讲,hdl_graph_slam在资源消耗、代码复杂度、建图流程等方面还是有很大优势。
2)增加地面检测。
当所处的环境中地面为平面时,它就可以作为一个很有效的信息去约束高程的误差,而做过激光slam的都知道,在没有gps的情况下,高程误差是主要的误差项。当然在地面为非平面的时候是不能够使用的,但这不能作为它的缺点,而应该在使用时根据环境决定是否开启这项功能。
3)具有闭环检测功能
闭环检测是slam中的重要功能,不只在没有gps参考的情况下能减小累计误差,即便在有gps约束的情况下也能起到有效的作用,而这一点却是很容易被忽略的地方。很多人认为有了gps就可以不使用闭环修正了,而大量的实验结果表明,这是非常错误的想法。
- 缺点
1)点云匹配精度不高。
这包括前端帧间匹配和闭环检测时的匹配,具体原因我们会在后面介绍到相应的代码时再讲。
二、功能分解
对整套系统的功能进行分解是为了能够更清晰的分析代码。这套系统的内部共包含四个主要功能项,所有的代码也是围绕着这四项功能展开的,它们分别是:
- 地面平面检测
根据点云检测平面,并拟合平面得到平面的数学描述参数,供构建概率图使用。
2. 点云滤波
处理原始点云,得到稀疏点云
3. 前端里程计
帧间匹配,得到每一帧位姿
4. 后端概率图构建
这一项功能承担了整个系统中的大部分内容,它的主要功能又包括:
1)提取关键帧。
前端里程计得到的是每一帧位姿,而构建概率图只需要每隔一段距离取一帧就行,即关键帧。
2)读取gps、imu信息并加入概率图。
即使用gps、imu信息构建对应的边。
3)读取地面检测参数并加入概率图。
同样是构建边,只不过信息变了。
4)检测闭环,若成功,则加入概率图。
同样是构建边。
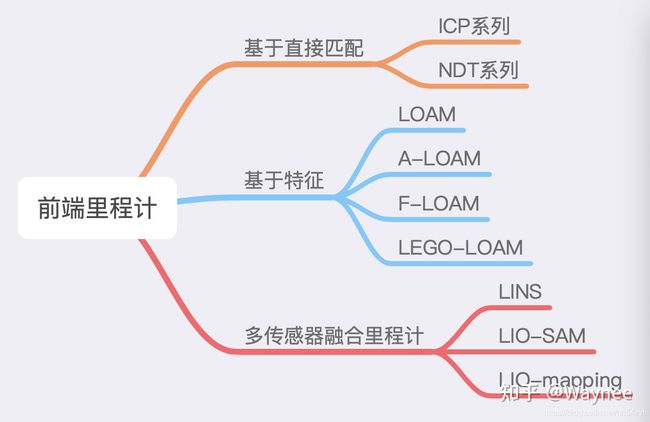
4:loam
A-loam简化loam,去掉imu https://www.guyuehome.com/35597
LOAM解读:
https://blog.csdn.net/u012700322/article/details/103615287
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_41469272/article/details/106432491
适配rslidar和livox
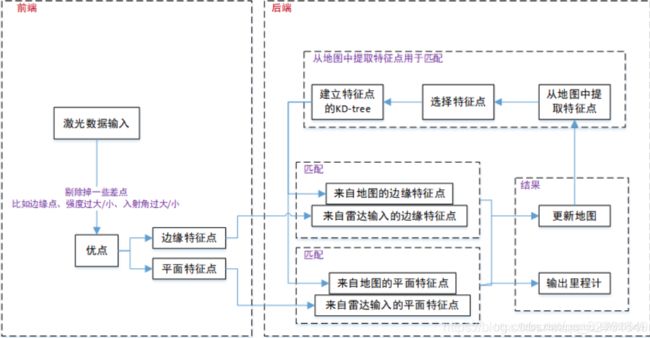
什么是里程计?为什么需要里程计?
里程计是衡量我们从初始位姿到终点位姿的一个标准,通俗的说,我们要实现机器人的定位与导航,就需要知道机器人行进了多少距离,是往哪个方向行进的
loam核心思想是将定位和建图的分割,通过两个算法:一个是执行高频率的里程计但是低精度的运动估计(定位),另一个算法在比定位低一个数量级的频率执行匹配和注册点云信息(建图和校正里程计)。将这两个算法结合就获得了高精度、实时性的激光里程计。
loam通过点云特征提取和点云匹配来解决低漂移和低计算的问题。为什么这么说呢。
我们知道匹配的问题分为scan-to-scan、scan-to-map、map-to-map。而三者各有特点。
首先说scan-to-scan匹配:优点是计算量小速度快,缺点是误差累计大,长距离误差累计后地图就无法看了。map-to-map的匹配:优点是精度高,误差累计小;缺点就是计算量大,实时性压力大。scan-to-map的匹配居中。LOAM的优点就是很好地利用力匹配的优缺点,首先,虽然scan-to-scan匹配精度差,但是我们可以只是使用它做一个获取粗的里程计,用获取的结果用于去除匀速运动造成的运动畸变,由于scan-to-scan的计算量较小因此我们可以高频执行。其次,有了里程计校正后的点云数据,接下来我们就可以做一个map-to-map的匹配了。但是map-to-map存在计算量大的问题,因此 我们可以让其执行的频率降低。这样的高低频率结合就保证了计算量的同时又兼具了精度。
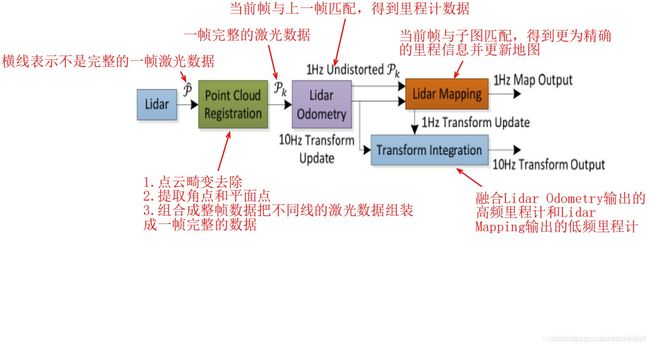
loam算法由四个节点构成。分别完成特征提取,高频低精度odom,低频高精度odom,双频odom融合的功能,每个节点以rosnode形式存在,也就是独立的进程。
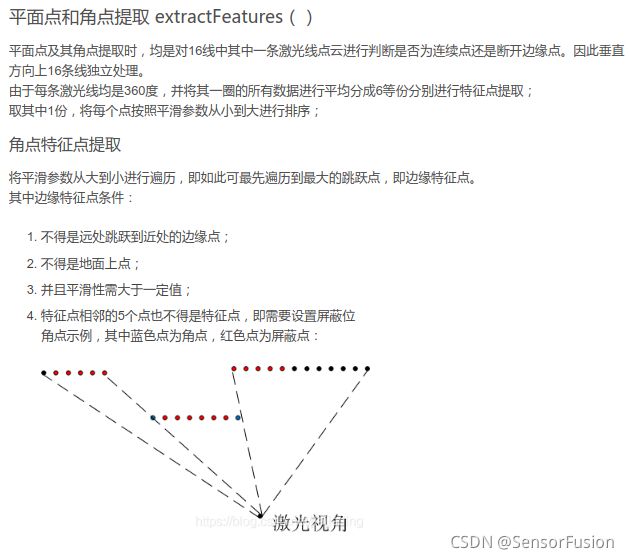
针对Livox需要提取"good points":
所谓提取good points,其实就是滤除bad points,那什么样的是bad points呢?主要包括以下几种
1)接近视角边缘的点
接近视角边缘的点会有一部分变形,会影响特征提取精度
2)反射强度过大或过小的点
作者给出的解释是反射强度过大,会对雷达硬件的信号接收电路产生冲击,从而影响这个点的精度,而反射强度过小的点,信噪比会低
3)和平面夹角过小的点
雷达光束和面特征会有一个夹角,而当夹角过小,即光束和平面接近平行时,这样的特征就不利于匹配,如下图所示,点f就属于这种情况。(这个技巧在原版loam里其实就有)
TransformToStart TransformToEnd
TransformToStart() 当前点云中的点相对第一个点去除因匀速运动产生的畸变,效果相当于得到在点云扫描开始位置静止扫描得到的点云
TransformToEnd() 当前点云中的点相对第一个点去除因匀速运动产生的畸变,效果相当于得到在点云扫描结束位置静止扫描得到的点云
void TransformToStart(PointType const * const pi, PointType * const po)
{
//插值系数计算,云中每个点的相对时间/点云周期10
float s = 10 * (pi->intensity - int(pi->intensity));
//线性插值:根据每个点在点云中的相对位置关系,乘以相应的旋转平移系数
float rx = s * transform[0];
float ry = s * transform[1];
float rz = s * transform[2];
float tx = s * transform[3];
float ty = s * transform[4];
float tz = s * transform[5];
//平移后绕z轴旋转(-rz)
float x1 = cos(rz) * (pi->x - tx) + sin(rz) * (pi->y - ty);
float y1 = -sin(rz) * (pi->x - tx) + cos(rz) * (pi->y - ty);
float z1 = (pi->z - tz);
//绕x轴旋转(-rx)
float x2 = x1;
float y2 = cos(rx) * y1 + sin(rx) * z1;
float z2 = -sin(rx) * y1 + cos(rx) * z1;
//绕y轴旋转(-ry)
po->x = cos(ry) * x2 - sin(ry) * z2;
po->y = y2;
po->z = sin(ry) * x2 + cos(ry) * z2;
po->intensity = pi->intensity;
}
TransformToEnd() 当前点云中的点相对第一个点去除因匀速运动产生的畸变,效果相当于得到在点云扫描结束位置静止扫描得到的点云
void TransformToEnd(PointType const * const pi, PointType * const po)
{
//插值系数计算
float s = 10 * (pi->intensity - int(pi->intensity));
float rx = s * transform[0];
float ry = s * transform[1];
float rz = s * transform[2];
float tx = s * transform[3];
float ty = s * transform[4];
float tz = s * transform[5];
//平移后绕z轴旋转(-rz)
float x1 = cos(rz) * (pi->x - tx) + sin(rz) * (pi->y - ty);
float y1 = -sin(rz) * (pi->x - tx) + cos(rz) * (pi->y - ty);
float z1 = (pi->z - tz);
//绕x轴旋转(-rx)
float x2 = x1;
float y2 = cos(rx) * y1 + sin(rx) * z1;
float z2 = -sin(rx) * y1 + cos(rx) * z1;
//绕y轴旋转(-ry)
float x3 = cos(ry) * x2 - sin(ry) * z2;
float y3 = y2;
float z3 = sin(ry) * x2 + cos(ry) * z2;//求出了相对于起始点校正的坐标
rx = transform[0];
ry = transform[1];
rz = transform[2];
tx = transform[3];
ty = transform[4];
tz = transform[5];
//绕y轴旋转(ry)
float x4 = cos(ry) * x3 + sin(ry) * z3;
float y4 = y3;
float z4 = -sin(ry) * x3 + cos(ry) * z3;
//绕x轴旋转(rx)
float x5 = x4;
float y5 = cos(rx) * y4 - sin(rx) * z4;
float z5 = sin(rx) * y4 + cos(rx) * z4;
//绕z轴旋转(rz),再平移
float x6 = cos(rz) * x5 - sin(rz) * y5 + tx;
float y6 = sin(rz) * x5 + cos(rz) * y5 + ty;
float z6 = z5 + tz;
//平移后绕z轴旋转(imuRollStart)
float x7 = cos(imuRollStart) * (x6 - imuShiftFromStartX)
- sin(imuRollStart) * (y6 - imuShiftFromStartY);
float y7 = sin(imuRollStart) * (x6 - imuShiftFromStartX)
+ cos(imuRollStart) * (y6 - imuShiftFromStartY);
float z7 = z6 - imuShiftFromStartZ;
//绕x轴旋转(imuPitchStart)
float x8 = x7;
float y8 = cos(imuPitchStart) * y7 - sin(imuPitchStart) * z7;
float z8 = sin(imuPitchStart) * y7 + cos(imuPitchStart) * z7;
//绕y轴旋转(imuYawStart)
float x9 = cos(imuYawStart) * x8 + sin(imuYawStart) * z8;
float y9 = y8;
float z9 = -sin(imuYawStart) * x8 + cos(imuYawStart) * z8;
//绕y轴旋转(-imuYawLast)
float x10 = cos(imuYawLast) * x9 - sin(imuYawLast) * z9;
float y10 = y9;
float z10 = sin(imuYawLast) * x9 + cos(imuYawLast) * z9;
//绕x轴旋转(-imuPitchLast)
float x11 = x10;
float y11 = cos(imuPitchLast) * y10 + sin(imuPitchLast) * z10;
float z11 = -sin(imuPitchLast) * y10 + cos(imuPitchLast) * z10;
//绕z轴旋转(-imuRollLast)
po->x = cos(imuRollLast) * x11 + sin(imuRollLast) * y11;
po->y = -sin(imuRollLast) * x11 + cos(imuRollLast) * y11;
po->z = z11;
//只保留线号
po->intensity = int(pi->intensity);
}
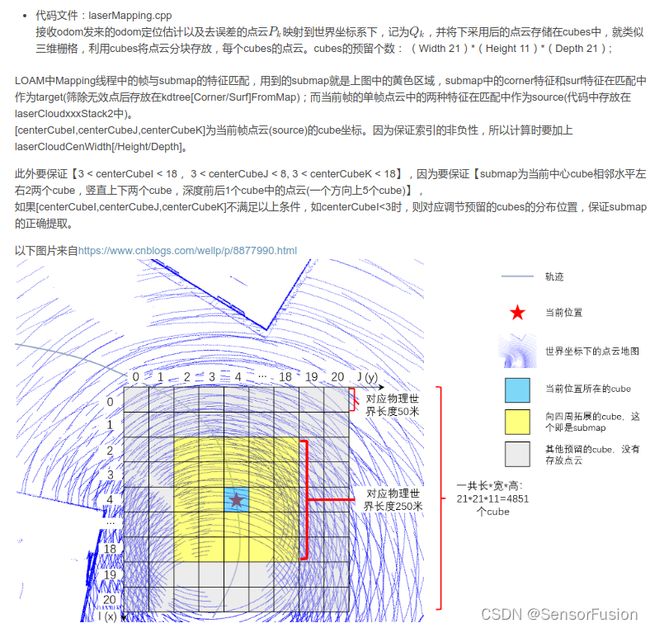
建图方法:
将特征点云封装在不同的cube中,并在地图数组中保存
上一步骤完成了当前帧点云与地图点云的配准,并对Lidar里程计的运动估计结果进行完了优化。在更新了位姿之后,将当前时刻的点云封装到不同cube中,并子啊地图数组中保存。
将特征点按距离(比例尺缩小)归入相应的立方体
特征点下采样
地图帧数+1
// 7.将特征点云封装在不同的cube中,并在地图数组中保存。
//1.将corner points按距离(比例尺缩小)归入相应的立方体
for (int i = 0; i < laserCloudCornerStackNum; i++) {
//转移到世界坐标系
pointAssociateToMap(&laserCloudCornerStack->points[i], &pointSel);
//按50的比例尺缩小,四舍五入,偏移laserCloudCen*的量,计算索引
int cubeI = int((pointSel.x + 25.0) / 50.0) + laserCloudCenWidth;
int cubeJ = int((pointSel.y + 25.0) / 50.0) + laserCloudCenHeight;
int cubeK = int((pointSel.z + 25.0) / 50.0) + laserCloudCenDepth;
if (pointSel.x + 25.0 < 0) cubeI--;
if (pointSel.y + 25.0 < 0) cubeJ--;
if (pointSel.z + 25.0 < 0) cubeK--;
//只挑选-laserCloudCenWidth * 50.0 < point.x < laserCloudCenWidth * 50.0范围内的点,y和z同理
if (cubeI >= 0 && cubeI < laserCloudWidth &&
cubeJ >= 0 && cubeJ < laserCloudHeight &&
cubeK >= 0 && cubeK < laserCloudDepth) {
//按照尺度放进不同的组,每个组的点数量各异
int cubeInd = cubeI + laserCloudWidth * cubeJ + laserCloudWidth * laserCloudHeight * cubeK;
laserCloudCornerArray[cubeInd]->push_back(pointSel);
}
}
//将surf points按距离(比例尺缩小)归入相应的立方体
for (int i = 0; i < laserCloudSurfStackNum; i++) {
pointAssociateToMap(&laserCloudSurfStack->points[i], &pointSel);
int cubeI = int((pointSel.x + 25.0) / 50.0) + laserCloudCenWidth;
int cubeJ = int((pointSel.y + 25.0) / 50.0) + laserCloudCenHeight;
int cubeK = int((pointSel.z + 25.0) / 50.0) + laserCloudCenDepth;
if (pointSel.x + 25.0 < 0) cubeI--;
if (pointSel.y + 25.0 < 0) cubeJ--;
if (pointSel.z + 25.0 < 0) cubeK--;
if (cubeI >= 0 && cubeI < laserCloudWidth &&
cubeJ >= 0 && cubeJ < laserCloudHeight &&
cubeK >= 0 && cubeK < laserCloudDepth) {
int cubeInd = cubeI + laserCloudWidth * cubeJ + laserCloudWidth * laserCloudHeight * cubeK;
laserCloudSurfArray[cubeInd]->push_back(pointSel);
}
}
//2.特征点下采样
for (int i = 0; i < laserCloudValidNum; i++) {
int ind = laserCloudValidInd[i];
laserCloudCornerArray2[ind]->clear();
downSizeFilterCorner.setInputCloud(laserCloudCornerArray[ind]);
downSizeFilterCorner.filter(*laserCloudCornerArray2[ind]);//滤波输出到Array2
laserCloudSurfArray2[ind]->clear();
downSizeFilterSurf.setInputCloud(laserCloudSurfArray[ind]);
downSizeFilterSurf.filter(*laserCloudSurfArray2[ind]);
//Array与Array2交换,即滤波后自我更新
pcl::PointCloud<PointType>::Ptr laserCloudTemp = laserCloudCornerArray[ind];
laserCloudCornerArray[ind] = laserCloudCornerArray2[ind];
laserCloudCornerArray2[ind] = laserCloudTemp;
laserCloudTemp = laserCloudSurfArray[ind];
laserCloudSurfArray[ind] = laserCloudSurfArray2[ind];
laserCloudSurfArray2[ind] = laserCloudTemp;
}
// 3.地图帧数+1
mapFrameCount++;
LOAM ROS节点流程图:
scanRegistration.cpp
外点和运动物体剔除
在实际跑的时候避免不了会有动态的车、人及其他物体。本文的动态物体剔除算法是在每一次迭代优化位姿的过程中重新找到每个特征的最近点把边边残差和面面残差加入到目标函数,第一次只优化两次,然后把残差中最大的20%丢弃来达到剔除外点的目的。
纯粹的
先见图后定位
lidar_localization
laserOdometry.cpp
特征点关联使用scan-to-scan方式t和t+1时刻相邻两帧的点云数据进行配准,分为边缘点匹配和平面点匹配两部分。计算点到直线的距离和点到平面的距离。
姿态解算根据匹配的特征点云使用LM算法估计接收端位姿。
求解的是点云间的相对运动,但他们是在这两帧点云的局部坐标系下的,我们需要把它转换到世界坐标系下,因此需要进行转换。
1: 局部坐标系转移到全局坐标系
2: 根据IMU修正旋转量,插入imu旋转,更新位姿
3: 欧拉角转换成四元数,再发布出去四元数和平移量
4: 对k+1时刻的less特征点(边缘+平面)转移至k+1时刻的sweep的结束位置处的雷达坐标系下
5: 更新,畸变校正之后的点作为last点保存等下个点云进来进行匹配
按照跳帧数publich边沿点,平面点以及全部点给laserMapping(每隔一帧发一次)
LOAM
整体解读:
https://www.cnblogs.com/wellp/p/8877990.html
lidarFactor.hpp 代码解读
// Author: Tong Qin [email protected]
// Shaozu Cao [email protected]
#include q_last_curr{q[3], T(s) * q[0], T(s) * q[1], T(s) * q[2]};
Eigen::Quaternion<T> q_last_curr{q[3], q[0], q[1], q[2]};
Eigen::Quaternion<T> q_identity{T(1), T(0), T(0), T(0)};
q_last_curr = q_identity.slerp(T(s), q_last_curr);
Eigen::Matrix<T, 3, 1> t_last_curr{T(s) * t[0], T(s) * t[1], T(s) * t[2]};
Eigen::Matrix<T, 3, 1> lp;
lp = q_last_curr * cp + t_last_curr;
Eigen::Matrix<T, 3, 1> nu = (lp - lpa).cross(lp - lpb);
Eigen::Matrix<T, 3, 1> de = lpa - lpb;
residual[0] = nu.x() / de.norm();
residual[1] = nu.y() / de.norm();
residual[2] = nu.z() / de.norm();
return true;
}
static ceres::CostFunction *Create(const Eigen::Vector3d curr_point_, const Eigen::Vector3d last_point_a_,
const Eigen::Vector3d last_point_b_, const double s_)
{
return (new ceres::AutoDiffCostFunction<
LidarEdgeFactor, 3, 4, 3>(
new LidarEdgeFactor(curr_point_, last_point_a_, last_point_b_, s_)));
}
Eigen::Vector3d curr_point, last_point_a, last_point_b;
double s;
};
struct LidarPlaneFactor
{
LidarPlaneFactor(Eigen::Vector3d curr_point_, Eigen::Vector3d last_point_j_,
Eigen::Vector3d last_point_l_, Eigen::Vector3d last_point_m_, double s_)
: curr_point(curr_point_), last_point_j(last_point_j_), last_point_l(last_point_l_),
last_point_m(last_point_m_), s(s_)
{
ljm_norm = (last_point_j - last_point_l).cross(last_point_j - last_point_m);
ljm_norm.normalize();
}
template <typename T>
bool operator()(const T *q, const T *t, T *residual) const
{
Eigen::Matrix<T, 3, 1> cp{T(curr_point.x()), T(curr_point.y()), T(curr_point.z())};
Eigen::Matrix<T, 3, 1> lpj{T(last_point_j.x()), T(last_point_j.y()), T(last_point_j.z())};
//Eigen::Matrix lpl{T(last_point_l.x()), T(last_point_l.y()), T(last_point_l.z())};
//Eigen::Matrix lpm{T(last_point_m.x()), T(last_point_m.y()), T(last_point_m.z())};
Eigen::Matrix<T, 3, 1> ljm{T(ljm_norm.x()), T(ljm_norm.y()), T(ljm_norm.z())};
//Eigen::Quaternion q_last_curr{q[3], T(s) * q[0], T(s) * q[1], T(s) * q[2]};
Eigen::Quaternion<T> q_last_curr{q[3], q[0], q[1], q[2]};
Eigen::Quaternion<T> q_identity{T(1), T(0), T(0), T(0)};
q_last_curr = q_identity.slerp(T(s), q_last_curr);
Eigen::Matrix<T, 3, 1> t_last_curr{T(s) * t[0], T(s) * t[1], T(s) * t[2]};
Eigen::Matrix<T, 3, 1> lp;
lp = q_last_curr * cp + t_last_curr;
residual[0] = (lp - lpj).dot(ljm);
return true;
}
static ceres::CostFunction *Create(const Eigen::Vector3d curr_point_, const Eigen::Vector3d last_point_j_,
const Eigen::Vector3d last_point_l_, const Eigen::Vector3d last_point_m_,
const double s_)
{
return (new ceres::AutoDiffCostFunction<
LidarPlaneFactor, 1, 4, 3>(
new LidarPlaneFactor(curr_point_, last_point_j_, last_point_l_, last_point_m_, s_)));
}
Eigen::Vector3d curr_point, last_point_j, last_point_l, last_point_m;
Eigen::Vector3d ljm_norm;
double s;
};
struct LidarPlaneNormFactor
{
LidarPlaneNormFactor(Eigen::Vector3d curr_point_, Eigen::Vector3d plane_unit_norm_,
double negative_OA_dot_norm_) : curr_point(curr_point_), plane_unit_norm(plane_unit_norm_),
negative_OA_dot_norm(negative_OA_dot_norm_) {}
template <typename T>
bool operator()(const T *q, const T *t, T *residual) const
{
Eigen::Quaternion<T> q_w_curr{q[3], q[0], q[1], q[2]};
Eigen::Matrix<T, 3, 1> t_w_curr{t[0], t[1], t[2]};
Eigen::Matrix<T, 3, 1> cp{T(curr_point.x()), T(curr_point.y()), T(curr_point.z())};
Eigen::Matrix<T, 3, 1> point_w;
point_w = q_w_curr * cp + t_w_curr;
Eigen::Matrix<T, 3, 1> norm(T(plane_unit_norm.x()), T(plane_unit_norm.y()), T(plane_unit_norm.z()));
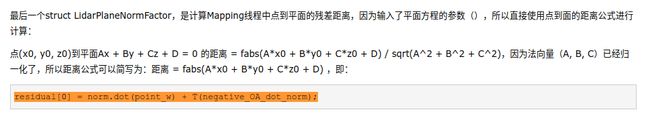
residual[0] = norm.dot(point_w) + T(negative_OA_dot_norm);
return true;
}
static ceres::CostFunction *Create(const Eigen::Vector3d curr_point_, const Eigen::Vector3d plane_unit_norm_,
const double negative_OA_dot_norm_)
{
return (new ceres::AutoDiffCostFunction<
LidarPlaneNormFactor, 1, 4, 3>(
new LidarPlaneNormFactor(curr_point_, plane_unit_norm_, negative_OA_dot_norm_)));
}
Eigen::Vector3d curr_point;
Eigen::Vector3d plane_unit_norm;
double negative_OA_dot_norm;
};
struct LidarDistanceFactor
{
LidarDistanceFactor(Eigen::Vector3d curr_point_, Eigen::Vector3d closed_point_)
: curr_point(curr_point_), closed_point(closed_point_){}
template <typename T>
bool operator()(const T *q, const T *t, T *residual) const
{
Eigen::Quaternion<T> q_w_curr{q[3], q[0], q[1], q[2]};
Eigen::Matrix<T, 3, 1> t_w_curr{t[0], t[1], t[2]};
Eigen::Matrix<T, 3, 1> cp{T(curr_point.x()), T(curr_point.y()), T(curr_point.z())};
Eigen::Matrix<T, 3, 1> point_w;
point_w = q_w_curr * cp + t_w_curr;
residual[0] = point_w.x() - T(closed_point.x());
residual[1] = point_w.y() - T(closed_point.y());
residual[2] = point_w.z() - T(closed_point.z());
return true;
}
static ceres::CostFunction *Create(const Eigen::Vector3d curr_point_, const Eigen::Vector3d closed_point_)
{
return (new ceres::AutoDiffCostFunction<
LidarDistanceFactor, 3, 4, 3>(
new LidarDistanceFactor(curr_point_, closed_point_)));
}
Eigen::Vector3d curr_point;
Eigen::Vector3d closed_point;
};
// 点到线的残差距离计算
struct LidarEdgeFactor
// 计算Odometry线程中点到面的残差距离
struct LidarPlaneFactor
// 计算mapping线程中点到面的残差距离
struct LidarPlaneNormFactor
{
5:Le-GO Loam
https://github.com/wykxwyc/LeGO-LOAM_NOTED
https://blog.csdn.net/wykxwyc/article/details/89605721
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/382460472
特征Image Projection
https://blog.csdn.net/zwhdldz/article/details/109316081
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
imageProjection.cpp
void cloudHandler(const sensor_msgs::PointCloud2ConstPtr& laserCloudMsg){
copyPointCloud(laserCloudMsg);
findStartEndAngle();
projectPointCloud(); // 点云展开
groundRemoval();
cloudSegmentation();
// 思想:
// 在去除地面之后,对接下来的点进行分割。这里通过BFS(深度优先遍历)递归进行查找,从[0,0]点开始,遍历它前、后、左、右的4个点,分别进行对比,如果相对角度大于60°,则认为是同一个点云集群。最后分割出来的点云数量大于30个则认为分割有效(实际上大于5个可能也行)。
publishCloud();
resetParameters();
}
void projectPointCloud(){
float verticalAngle, horizonAngle, range;
size_t rowIdn, columnIdn, index, cloudSize;
PointType thisPoint;
cloudSize = laserCloudIn->points.size();
for (size_t i = 0; i < cloudSize; ++i){
thisPoint.x = laserCloudIn->points[i].x;
thisPoint.y = laserCloudIn->points[i].y;
thisPoint.z = laserCloudIn->points[i].z;
// 计算竖直方向上的角度(雷达的第几线)
verticalAngle = atan2(thisPoint.z, sqrt(thisPoint.x * thisPoint.x + thisPoint.y * thisPoint.y)) * 180 / M_PI;
// rowIdn计算出该点激光雷达是竖直方向上第几线的
// 从下往上计数,-15度记为初始线,第0线,一共16线(N_SCAN=16)
rowIdn = (verticalAngle + ang_bottom) / ang_res_y;
if (rowIdn < 0 || rowIdn >= N_SCAN)
continue;
// atan2(y,x)函数的返回值范围(-PI,PI],表示与复数x+yi的幅角
// 下方角度atan2(..)交换了x和y的位置,计算的是与y轴正方向的夹角大小(关于y=x做对称变换)
// 这里是在雷达坐标系,所以是与正前方的夹角大小
horizonAngle = atan2(thisPoint.x, thisPoint.y) * 180 / M_PI;
// round函数进行四舍五入取整
// 这边确定不是减去180度??? 不是
// 雷达水平方向上某个角度和水平第几线的关联关系???关系如下:
// horizonAngle:(-PI,PI],columnIdn:[H/4,5H/4]-->[0,H] (H:Horizon_SCAN)
// 下面是把坐标系绕z轴旋转,对columnIdn进行线性变换
// x+==>Horizon_SCAN/2,x-==>Horizon_SCAN
// y+==>Horizon_SCAN*3/4,y-==>Horizon_SCAN*5/4,Horizon_SCAN/4
//
// 3/4*H
// | y+
// |
// (x-)H---------->H/2 (x+)
// |
// | y-
// 5/4*H H/4
//
columnIdn = -round((horizonAngle-90.0)/ang_res_x) + Horizon_SCAN/2;
if (columnIdn >= Horizon_SCAN)
columnIdn -= Horizon_SCAN;
// 经过上面columnIdn -= Horizon_SCAN的变换后的columnIdn分布:
// 3/4*H
// | y+
// H |
// (x-)---------->H/2 (x+)
// 0 |
// | y-
// H/4
//
if (columnIdn < 0 || columnIdn >= Horizon_SCAN)
continue;
range = sqrt(thisPoint.x * thisPoint.x + thisPoint.y * thisPoint.y + thisPoint.z * thisPoint.z);
rangeMat.at<float>(rowIdn, columnIdn) = range;
// columnIdn:[0,H] (H:Horizon_SCAN)==>[0,1800]
thisPoint.intensity = (float)rowIdn + (float)columnIdn / 10000.0;
index = columnIdn + rowIdn * Horizon_SCAN;
fullCloud->points[index] = thisPoint;
fullInfoCloud->points[index].intensity = range;
}
}
void cloudSegmentation(){
for (size_t i = 0; i < N_SCAN; ++i)
for (size_t j = 0; j < Horizon_SCAN; ++j)
// 如果labelMat[i][j]=0,表示没有对该点进行过分类
// 需要对该点进行聚类
if (labelMat.at<int>(i,j) == 0)
labelComponents(i, j);
int sizeOfSegCloud = 0;
for (size_t i = 0; i < N_SCAN; ++i) {
// segMsg.startRingIndex[i]
// segMsg.endRingIndex[i]
// 表示第i线的点云起始序列和终止序列
// 以开始线后的第6线为开始,以结束线前的第6线为结束
segMsg.startRingIndex[i] = sizeOfSegCloud-1 + 5;
for (size_t j = 0; j < Horizon_SCAN; ++j) {
// 找到可用的特征点或者地面点(不选择labelMat[i][j]=0的点)
if (labelMat.at<int>(i,j) > 0 || groundMat.at<int8_t>(i,j) == 1){
// labelMat数值为999999表示这个点是因为聚类数量不够30而被舍弃的点
// 需要舍弃的点直接continue跳过本次循环,
// 当列数为5的倍数,并且行数较大,可以认为非地面点的,将它保存进异常点云(界外点云)中
// 然后再跳过本次循环
if (labelMat.at<int>(i,j) == 999999){
if (i > groundScanInd && j % 5 == 0){
outlierCloud->push_back(fullCloud->points[j + i*Horizon_SCAN]);
continue;
}else{
continue;
}
}
// 如果是地面点,对于列数不为5的倍数的,直接跳过不处理
if (groundMat.at<int8_t>(i,j) == 1){
if (j%5!=0 && j>5 && j<Horizon_SCAN-5)
continue;
}
// 上面多个if语句已经去掉了不符合条件的点,这部分直接进行信息的拷贝和保存操作
// 保存完毕后sizeOfSegCloud递增
segMsg.segmentedCloudGroundFlag[sizeOfSegCloud] = (groundMat.at<int8_t>(i,j) == 1);
segMsg.segmentedCloudColInd[sizeOfSegCloud] = j;
segMsg.segmentedCloudRange[sizeOfSegCloud] = rangeMat.at<float>(i,j);
segmentedCloud->push_back(fullCloud->points[j + i*Horizon_SCAN]);
++sizeOfSegCloud;
}
}
// 以结束线前的第5线为结束
segMsg.endRingIndex[i] = sizeOfSegCloud-1 - 5;
}
// 如果有节点订阅SegmentedCloudPure,
// 那么把点云数据保存到segmentedCloudPure中去
if (pubSegmentedCloudPure.getNumSubscribers() != 0){
for (size_t i = 0; i < N_SCAN; ++i){
for (size_t j = 0; j < Horizon_SCAN; ++j){
// 需要选择不是地面点(labelMat[i][j]!=-1)和没被舍弃的点
if (labelMat.at<int>(i,j) > 0 && labelMat.at<int>(i,j) != 999999){
segmentedCloudPure->push_back(fullCloud->points[j + i*Horizon_SCAN]);
segmentedCloudPure->points.back().intensity = labelMat.at<int>(i,j);
}
}
}
}
}
void labelComponents(int row, int col){
float d1, d2, alpha, angle;
int fromIndX, fromIndY, thisIndX, thisIndY;
bool lineCountFlag[N_SCAN] = {false};
queueIndX[0] = row;
queueIndY[0] = col;
int queueSize = 1;
int queueStartInd = 0;
int queueEndInd = 1;
allPushedIndX[0] = row;
allPushedIndY[0] = col;
int allPushedIndSize = 1;
// 标准的BFS
// BFS的作用是以(row,col)为中心向外面扩散,
// 判断(row,col)是否是这个平面中一点
while(queueSize > 0){
fromIndX = queueIndX[queueStartInd];
fromIndY = queueIndY[queueStartInd];
--queueSize;
++queueStartInd;
// labelCount的初始值为1,后面会递增
labelMat.at<int>(fromIndX, fromIndY) = labelCount;
// neighbor=[[-1,0];[0,1];[0,-1];[1,0]]
// 遍历点[fromIndX,fromIndY]边上的四个邻点
for (auto iter = neighborIterator.begin(); iter != neighborIterator.end(); ++iter){
thisIndX = fromIndX + (*iter).first;
thisIndY = fromIndY + (*iter).second;
if (thisIndX < 0 || thisIndX >= N_SCAN)
continue;
// 是个环状的图片,左右连通
if (thisIndY < 0)
thisIndY = Horizon_SCAN - 1;
if (thisIndY >= Horizon_SCAN)
thisIndY = 0;
// 如果点[thisIndX,thisIndY]已经标记过
// labelMat中,-1代表无效点,0代表未进行标记过,其余为其他的标记
// 如果当前的邻点已经标记过,则跳过该点。
// 如果labelMat已经标记为正整数,则已经聚类完成,不需要再次对该点聚类
if (labelMat.at<int>(thisIndX, thisIndY) != 0)
continue;
d1 = std::max(rangeMat.at<float>(fromIndX, fromIndY),
rangeMat.at<float>(thisIndX, thisIndY));
d2 = std::min(rangeMat.at<float>(fromIndX, fromIndY),
rangeMat.at<float>(thisIndX, thisIndY));
// alpha代表角度分辨率,
// X方向上角度分辨率是segmentAlphaX(rad)
// Y方向上角度分辨率是segmentAlphaY(rad)
if ((*iter).first == 0)
alpha = segmentAlphaX;
else
alpha = segmentAlphaY;
// 通过下面的公式计算这两点之间是否有平面特征
// atan2(y,x)的值越大,d1,d2之间的差距越小,越平坦
angle = atan2(d2*sin(alpha), (d1 -d2*cos(alpha)));
if (angle > segmentTheta){
// segmentTheta=1.0472<==>60度
// 如果算出角度大于60度,则假设这是个平面
queueIndX[queueEndInd] = thisIndX;
queueIndY[queueEndInd] = thisIndY;
++queueSize;
++queueEndInd;
labelMat.at<int>(thisIndX, thisIndY) = labelCount;
lineCountFlag[thisIndX] = true;
allPushedIndX[allPushedIndSize] = thisIndX;
allPushedIndY[allPushedIndSize] = thisIndY;
++allPushedIndSize;
}
}
}
bool feasibleSegment = false;
// 如果聚类超过30个点,直接标记为一个可用聚类,labelCount需要递增
if (allPushedIndSize >= 30)
feasibleSegment = true;
else if (allPushedIndSize >= segmentValidPointNum){
// 如果聚类点数小于30大于等于5,统计竖直方向上的聚类点数
int lineCount = 0;
for (size_t i = 0; i < N_SCAN; ++i)
if (lineCountFlag[i] == true)
++lineCount;
// 竖直方向上超过3个也将它标记为有效聚类
if (lineCount >= segmentValidLineNum)
feasibleSegment = true;
}
if (feasibleSegment == true){
++labelCount;
}else{
for (size_t i = 0; i < allPushedIndSize; ++i){
// 标记为999999的是需要舍弃的聚类的点,因为他们的数量小于30个
labelMat.at<int>(allPushedIndX[i], allPushedIndY[i]) = 999999;
}
}
}
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
featureAssociation.cpp
void imuHandler(const sensor_msgs::Imu::ConstPtr &imuIn) {
double roll, pitch, yaw;
tf::Quaternion orientation;
tf::quaternionMsgToTF(imuIn->orientation, orientation);
tf::Matrix3x3(orientation).getRPY(roll, pitch, yaw);
// IMU在三个轴方向上的加速度
float accX = imuIn->linear_acceleration.y - sin(roll) * cos(pitch) * 9.81;
float accY = imuIn->linear_acceleration.z - cos(roll) * cos(pitch) * 9.81;
float accZ = imuIn->linear_acceleration.x + sin(pitch) * 9.81;
imuPointerLast = (imuPointerLast + 1) % imuQueLength;
imuTime[imuPointerLast] = imuIn->header.stamp.toSec();
imuRoll[imuPointerLast] = roll;
imuPitch[imuPointerLast] = pitch;
imuYaw[imuPointerLast] = yaw;
imuAccX[imuPointerLast] = accX;
imuAccY[imuPointerLast] = accY;
imuAccZ[imuPointerLast] = accZ;
// IMU在三个轴方向上的角速度
imuAngularVeloX[imuPointerLast] = imuIn->angular_velocity.x;
imuAngularVeloY[imuPointerLast] = imuIn->angular_velocity.y;
imuAngularVeloZ[imuPointerLast] = imuIn->angular_velocity.z;
AccumulateIMUShiftAndRotation();
// 九轴IMU姿态传感器(角度、加速度,角速度)
// imu数据 : rostopic echo /imu/data
// ---
// header:
// seq: 55530
// stamp:
// secs: 1497705860
// nsecs: 971283089
// frame_id: "imu_link"
// orientation:
// x: 0.0149130431908
// y: 0.00653785190308
// z: 0.516709073569
// w: -0.856006186267
// orientation_covariance: [0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0,
// 0.0]
// angular_velocity:
// x: 0.00527995165792
// y: 0.016317787045
// z: 0.022003317544
// angular_velocity_covariance: [1.218467815533586e-07, 0.0, 0.0,
// 0.0, 1.218467815533586e-07, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.218467815533586e-07]
// linear_acceleration:
// x: 0.213569305256
// y: -0.356384406525
// z: 9.63524944937
// linear_acceleration_covariance: [8.661248102725949e-06, 0.0, 0.0,
// 0.0, 8.661248102725949e-06, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 8.661248102725949e-06]
}
void AccumulateIMUShiftAndRotation() {
float roll = imuRoll[imuPointerLast];
float pitch = imuPitch[imuPointerLast];
float yaw = imuYaw[imuPointerLast];
float accX = imuAccX[imuPointerLast];
float accY = imuAccY[imuPointerLast];
float accZ = imuAccZ[imuPointerLast];
// 先绕Z轴(原x轴)旋转,下方坐标系示意imuHandler()中加速度的坐标轴交换
// z->Y
// ^
// | ^ y->X
// | /
// | /
// | /
// -----> x->Z
//
// |cosrz -sinrz 0|
// Rz=|sinrz cosrz 0|
// |0 0 1|
// [x1,y1,z1]^T=Rz*[accX,accY,accZ]
// 因为在imuHandler中进行过坐标变换,
// 所以下面的roll其实已经对应于新坐标系中(X-Y-Z)的yaw
float x1 = cos(roll) * accX - sin(roll) * accY;
float y1 = sin(roll) * accX + cos(roll) * accY;
float z1 = accZ;
// 绕X轴(原y轴)旋转
// [x2,y2,z2]^T=Rx*[x1,y1,z1]
// |1 0 0|
// Rx=|0 cosrx -sinrx|
// |0 sinrx cosrx|
float x2 = x1;
float y2 = cos(pitch) * y1 - sin(pitch) * z1;
float z2 = sin(pitch) * y1 + cos(pitch) * z1;
// 最后再绕Y轴(原z轴)旋转
// |cosry 0 sinry|
// Ry=|0 1 0|
// |-sinry 0 cosry|
accX = cos(yaw) * x2 + sin(yaw) * z2;
accY = y2;
accZ = -sin(yaw) * x2 + cos(yaw) * z2;
// 进行位移,速度,角度量的累加
int imuPointerBack = (imuPointerLast + imuQueLength - 1) % imuQueLength;
double timeDiff = imuTime[imuPointerLast] - imuTime[imuPointerBack];
if (timeDiff < scanPeriod) {
imuShiftX[imuPointerLast] = imuShiftX[imuPointerBack] +
imuVeloX[imuPointerBack] * timeDiff +
accX * timeDiff * timeDiff / 2;
imuShiftY[imuPointerLast] = imuShiftY[imuPointerBack] +
imuVeloY[imuPointerBack] * timeDiff +
accY * timeDiff * timeDiff / 2;
imuShiftZ[imuPointerLast] = imuShiftZ[imuPointerBack] +
imuVeloZ[imuPointerBack] * timeDiff +
accZ * timeDiff * timeDiff / 2;
imuVeloX[imuPointerLast] = imuVeloX[imuPointerBack] + accX * timeDiff;
imuVeloY[imuPointerLast] = imuVeloY[imuPointerBack] + accY * timeDiff;
imuVeloZ[imuPointerLast] = imuVeloZ[imuPointerBack] + accZ * timeDiff;
imuAngularRotationX[imuPointerLast] =
imuAngularRotationX[imuPointerBack] +
imuAngularVeloX[imuPointerBack] * timeDiff;
imuAngularRotationY[imuPointerLast] =
imuAngularRotationY[imuPointerBack] +
imuAngularVeloY[imuPointerBack] * timeDiff;
imuAngularRotationZ[imuPointerLast] =
imuAngularRotationZ[imuPointerBack] +
imuAngularVeloZ[imuPointerBack] * timeDiff;
}
}
特征提取
点云分割完成之后,接下来对分割后的点云提取特征,提取的特征的目的是进行点云配准,从而得出当前位姿。
LeGO-LOAM的特征提取和点云配准的过程都在"LeGO-LOAM\src\featureAssociation.cpp"中。下面我们开始逐步分析代码。
和点云分割一样,特征提取也是单独的ROS执行程序,函数入口在main函数中。也是在构造函数FeatureAssociation()中申明订阅消息和回调函数,与点云分割不同的是,在主函数中通过循环调用"runFeatureAssociation"来提取特征和特征匹配。
下面我们具体看这4个消息
segmented_cloud 分割好的点云。
segmented_cloud_info 分割好的点云,和segmented_cloud的区别是,cloud_info的强度信息是距离,而segmented_cloud的是range image的行列信息。
outlier_cloud 离群点,也就是分割失败的点。
imuTopic 接收imu的消息。
FeatureAssociation():
nh("~")
{
// 订阅和发布各类话题
subLaserCloud = nh.subscribe<sensor_msgs::PointCloud2>("/segmented_cloud", 1, &FeatureAssociation::laserCloudHandler, this);
subLaserCloudInfo = nh.subscribe<cloud_msgs::cloud_info>("/segmented_cloud_info", 1, &FeatureAssociation::laserCloudInfoHandler, this);
subOutlierCloud = nh.subscribe<sensor_msgs::PointCloud2>("/outlier_cloud", 1, &FeatureAssociation::outlierCloudHandler, this);
// imu 数据进行处理,接着分别对位置、速度和角度做积分,计算出当前的位置、速度和角度。
subImu = nh.subscribe<sensor_msgs::Imu>(imuTopic, 50, &FeatureAssociation::imuHandler, this);
pubCornerPointsSharp = nh.advertise<sensor_msgs::PointCloud2>("/laser_cloud_sharp", 1);
pubCornerPointsLessSharp = nh.advertise<sensor_msgs::PointCloud2>("/laser_cloud_less_sharp", 1);
pubSurfPointsFlat = nh.advertise<sensor_msgs::PointCloud2>("/laser_cloud_flat", 1);
pubSurfPointsLessFlat = nh.advertise<sensor_msgs::PointCloud2>("/laser_cloud_less_flat", 1);
pubLaserCloudCornerLast = nh.advertise<sensor_msgs::PointCloud2>("/laser_cloud_corner_last", 2);
pubLaserCloudSurfLast = nh.advertise<sensor_msgs::PointCloud2>("/laser_cloud_surf_last", 2);
pubOutlierCloudLast = nh.advertise<sensor_msgs::PointCloud2>("/outlier_cloud_last", 2);
pubLaserOdometry = nh.advertise<nav_msgs::Odometry> ("/laser_odom_to_init", 5);
initializationValue();
}
思路:
特征提取,提取线特征和面特征
特征匹配,利用最小二乘法,获取当前最优的位姿
特征提取的过程:
先对点云进行畸变校正(运动补偿),
接着计算点的平滑程度,然后按照平滑度排序,如果是不平滑的点,则选为线特征(柱子或者墙壁的棱角),如果是平滑的点,则选为面特征(地面,墙面等平面)。
同时为了避免选择的特征过于集中在同一个地方,会把360°方向切分为6个区域,每个区域平均选择2个线特征和4个面特征。
void runFeatureAssociation()
{
// 如果有新数据进来则执行,否则不执行任何操作
if (newSegmentedCloud && newSegmentedCloudInfo && newOutlierCloud &&
std::abs(timeNewSegmentedCloudInfo - timeNewSegmentedCloud) < 0.05 &&
std::abs(timeNewOutlierCloud - timeNewSegmentedCloud) < 0.05){
newSegmentedCloud = false;
newSegmentedCloudInfo = false;
newOutlierCloud = false;
}else{
return;
}
// 主要进行的处理是将点云数据进行坐标变换,进行插补等工作
adjustDistortion();
// 不完全按照公式进行光滑性计算,并保存结果
calculateSmoothness();
// 标记阻塞点??? 阻塞点是什么点???
// 参考了csdn若愚maimai大佬的博客,这里的阻塞点指过近的点
// 指在点云中可能出现的互相遮挡的情况
markOccludedPoints();
// 特征抽取,然后分别保存到cornerPointsSharp等等队列中去
// 保存到不同的队列是不同类型的点云,进行了标记的工作,
// 这一步中减少了点云数量,使计算量减少
extractFeatures();
// 发布cornerPointsSharp等4种类型的点云数据
publishCloud();
if (!systemInitedLM) {
checkSystemInitialization();
return;
}
// 预测位姿
// 找到对应的特征平面 // 找到对应的特征边/角点
// 通过角/边特征的匹配,计算变换矩阵
updateInitialGuess();
// 更新变换
updateTransformation();
// 积分总变换
integrateTransformation();
publishOdometry();
publishCloudsLast();
}


去除不理想的点,
包括激光雷达自身测距不准的点,即远近距离过度的点
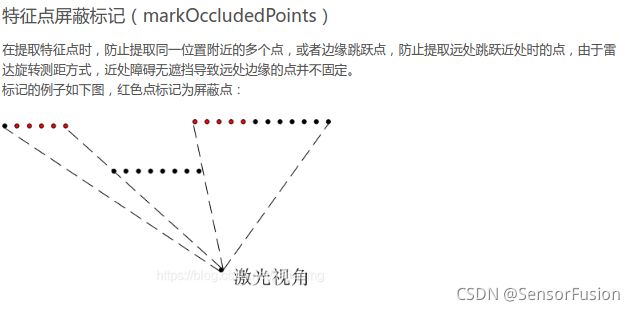
void FeatureAssociation::markOccludedPoints() {
int cloudSize = segmentedCloud->points.size();
for (int i = 5; i < cloudSize - 6; ++i) {
float depth1 = segInfo.segmentedCloudRange[i];
float depth2 = segInfo.segmentedCloudRange[i + 1]; // 遍历提取相邻的两个点的距离
int columnDiff = std::abs(int(segInfo.segmentedCloudColInd[i + 1] - // 获取相邻两个点的在水平方向上的索引号差
segInfo.segmentedCloudColInd[i]));
if (columnDiff < 10) { // 如果水平索引在10个点内,将远处的边缘的5个点标记为1,
if (depth1 - depth2 > 0.3) {
cloudNeighborPicked[i - 5] = 1; // 近处的边缘点则为0
cloudNeighborPicked[i - 4] = 1;
cloudNeighborPicked[i - 3] = 1;
cloudNeighborPicked[i - 2] = 1;
cloudNeighborPicked[i - 1] = 1;
cloudNeighborPicked[i] = 1;
} else if (depth2 - depth1 > 0.3) {
cloudNeighborPicked[i + 1] = 1;
cloudNeighborPicked[i + 2] = 1;
cloudNeighborPicked[i + 3] = 1;
cloudNeighborPicked[i + 4] = 1;
cloudNeighborPicked[i + 5] = 1;
cloudNeighborPicked[i + 6] = 1;
}
}
float diff1 = std::abs(segInfo.segmentedCloudRange[i - 1] -
segInfo.segmentedCloudRange[i]);
float diff2 = std::abs(segInfo.segmentedCloudRange[i + 1] -
segInfo.segmentedCloudRange[i]);
if (diff1 > 0.02 * segInfo.segmentedCloudRange[i] && // 如果两个相邻点的距离超过本点的距离0.02倍时,也标记为1,即孤立的点标记为1
diff2 > 0.02 * segInfo.segmentedCloudRange[i])
cloudNeighborPicked[i] = 1;
}
}
最后总结一下,特征点的选择满足以下3个条件。
选择的边缘点或平面点的数量不能超过每个方向上的最大值,一共有6个方向,每个方向上最多2个线特征,4个面特征。
线特征和面特征周围相邻的点不能被选中。
不能是平行于激光雷达光束的点或者被遮挡的点。
然后接着总结下代码中的输出
cornerPointsSharp 线特征(不为地面),每个方向上最多2个
cornerPointsLessSharp 比cornerPointsSharp平滑的线特征(不为地面),每个方向上20个
surfPointsFlat 面特征(为地面),每个方向上最多4个
surfPointsLessFlat 面特征(地面或者分割点云中不为线特征的点)
void updateTransformation()
中主要是两个部分,一个是找特征平面,通过面之间的对应关系计算出变换矩阵。 另一个部分是通过角、边特征的匹配,计算变换矩阵。 该函数主要由其他四个部分组成:findCorrespondingSurfFeatures,calculateTransformationSurf findCorrespondingCornerFeatures, calculateTransformationCorner 这四个函数分别是对应于寻找对应面、通过面对应计算变换矩阵、寻找对应角/边特征、通过角/边特征计算变换矩阵。
void updateTransformation(){
if (laserCloudCornerLastNum < 10 || laserCloudSurfLastNum < 100)
return;
for (int iterCount1 = 0; iterCount1 < 25; iterCount1++) {
laserCloudOri->clear();
coeffSel->clear();
// 找到对应的特征平面
// 然后计算协方差矩阵,保存在coeffSel队列中
// laserCloudOri中保存的是对应于coeffSel的未转换到开始时刻的原始点云数据
findCorrespondingSurfFeatures(iterCount1);
if (laserCloudOri->points.size() < 10)
continue;
// 通过面特征的匹配,计算变换矩阵
if (calculateTransformationSurf(iterCount1) == false)
break;
}
for (int iterCount2 = 0; iterCount2 < 25; iterCount2++) {
laserCloudOri->clear();
coeffSel->clear();
// 找到对应的特征边/角点
// 寻找边特征的方法和寻找平面特征的很类似,过程可以参照寻找平面特征的注释
findCorrespondingCornerFeatures(iterCount2);
if (laserCloudOri->points.size() < 10)
continue;
// 通过角/边特征的匹配,计算变换矩阵
if (calculateTransformationCorner(iterCount2) == false)
break;
}
}
void run(){
if (newLaserCloudCornerLast && std::abs(timeLaserCloudCornerLast - timeLaserOdometry) < 0.005 &&
newLaserCloudSurfLast && std::abs(timeLaserCloudSurfLast - timeLaserOdometry) < 0.005 &&
newLaserCloudOutlierLast && std::abs(timeLaserCloudOutlierLast - timeLaserOdometry) < 0.005 &&
newLaserOdometry)
{
newLaserCloudCornerLast = false; newLaserCloudSurfLast = false; newLaserCloudOutlierLast = false; newLaserOdometry = false;
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(mtx);
//mappingProcessInterval是0.3秒,以相对较慢的速度进行建图
if (timeLaserOdometry - timeLastProcessing >= mappingProcessInterval) {
timeLastProcessing = timeLaserOdometry;
//把点云坐标均转换到世界坐标系下
transformAssociateToMap();
//由于帧数的频率大于建图的频率,因此需要提取关键帧进行匹配
extractSurroundingKeyFrames();
//降采样匹配以及增加地图点云,回环检测
downsampleCurrentScan();
//
//
// 进行回环检测
//
//
scan2MapOptimization();
saveKeyFramesAndFactor();
//发送TF变换
correctPoses(); // 如果另外一个线程有闭环检测 就矫正
publishTF();
publishKeyPosesAndFrames();
clearCloud();
}
}
}
实现方法:
void cornerOptimization(int iterCount){
updatePointAssociateToMapSinCos();
for (int i = 0; i < laserCloudCornerLastDSNum; i++) {
pointOri = laserCloudCornerLastDS->points[i];
// 进行坐标变换,转换到全局坐标中去(世界坐标系)
// pointSel:表示选中的点,point select
// 输入是pointOri,输出是pointSel
pointAssociateToMap(&pointOri, &pointSel);
// 进行5邻域搜索,
// pointSel为需要搜索的点,
// pointSearchInd搜索完的邻域对应的索引
// pointSearchSqDis 邻域点与查询点之间的距离
kdtreeCornerFromMap->nearestKSearch(pointSel, 5, pointSearchInd, pointSearchSqDis);
// 只有当最远的那个邻域点的距离pointSearchSqDis[4]小于1m时才进行下面的计算
// 以下部分的计算是在计算点集的协方差矩阵,Zhang Ji的论文中有提到这部分
if (pointSearchSqDis[4] < 1.0) {
// 先求5个样本的平均值
float cx = 0, cy = 0, cz = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++) {
cx += laserCloudCornerFromMapDS->points[pointSearchInd[j]].x;
cy += laserCloudCornerFromMapDS->points[pointSearchInd[j]].y;
cz += laserCloudCornerFromMapDS->points[pointSearchInd[j]].z;
}
cx /= 5; cy /= 5; cz /= 5;
// 下面在求矩阵matA1=[ax,ay,az]^t*[ax,ay,az]
// 更准确地说应该是在求协方差matA1
float a11 = 0, a12 = 0, a13 = 0, a22 = 0, a23 = 0, a33 = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++) {
// ax代表的是x-cx,表示均值与每个实际值的差值,求取5个之后再次取平均,得到matA1
float ax = laserCloudCornerFromMapDS->points[pointSearchInd[j]].x - cx;
float ay = laserCloudCornerFromMapDS->points[pointSearchInd[j]].y - cy;
float az = laserCloudCornerFromMapDS->points[pointSearchInd[j]].z - cz;
a11 += ax * ax; a12 += ax * ay; a13 += ax * az;
a22 += ay * ay; a23 += ay * az;
a33 += az * az;
}
a11 /= 5; a12 /= 5; a13 /= 5; a22 /= 5; a23 /= 5; a33 /= 5;
matA1.at<float>(0, 0) = a11; matA1.at<float>(0, 1) = a12; matA1.at<float>(0, 2) = a13;
matA1.at<float>(1, 0) = a12; matA1.at<float>(1, 1) = a22; matA1.at<float>(1, 2) = a23;
matA1.at<float>(2, 0) = a13; matA1.at<float>(2, 1) = a23; matA1.at<float>(2, 2) = a33;
// 求正交阵的特征值和特征向量
// 特征值:matD1,特征向量:matV1中
cv::eigen(matA1, matD1, matV1);
// 边缘:与较大特征值相对应的特征向量代表边缘线的方向(一大两小,大方向)
// 以下这一大块是在计算点到边缘的距离,最后通过系数s来判断是否距离很近
// 如果距离很近就认为这个点在边缘上,需要放到laserCloudOri中
if (matD1.at<float>(0, 0) > 3 * matD1.at<float>(0, 1)) {
float x0 = pointSel.x;
float y0 = pointSel.y;
float z0 = pointSel.z;
float x1 = cx + 0.1 * matV1.at<float>(0, 0);
float y1 = cy + 0.1 * matV1.at<float>(0, 1);
float z1 = cz + 0.1 * matV1.at<float>(0, 2);
float x2 = cx - 0.1 * matV1.at<float>(0, 0);
float y2 = cy - 0.1 * matV1.at<float>(0, 1);
float z2 = cz - 0.1 * matV1.at<float>(0, 2);
// 这边是在求[(x0-x1),(y0-y1),(z0-z1)]与[(x0-x2),(y0-y2),(z0-z2)]叉乘得到的向量的模长
// 这个模长是由0.2*V1[0]和点[x0,y0,z0]构成的平行四边形的面积
// 因为[(x0-x1),(y0-y1),(z0-z1)]x[(x0-x2),(y0-y2),(z0-z2)]=[XXX,YYY,ZZZ],
// [XXX,YYY,ZZZ]=[(y0-y1)(z0-z2)-(y0-y2)(z0-z1),-(x0-x1)(z0-z2)+(x0-x2)(z0-z1),(x0-x1)(y0-y2)-(x0-x2)(y0-y1)]
float a012 = sqrt(((x0 - x1)*(y0 - y2) - (x0 - x2)*(y0 - y1))
* ((x0 - x1)*(y0 - y2) - (x0 - x2)*(y0 - y1))
+ ((x0 - x1)*(z0 - z2) - (x0 - x2)*(z0 - z1))
* ((x0 - x1)*(z0 - z2) - (x0 - x2)*(z0 - z1))
+ ((y0 - y1)*(z0 - z2) - (y0 - y2)*(z0 - z1))
* ((y0 - y1)*(z0 - z2) - (y0 - y2)*(z0 - z1)));
// l12表示的是0.2*(||V1[0]||)
// 也就是平行四边形一条底的长度
float l12 = sqrt((x1 - x2)*(x1 - x2) + (y1 - y2)*(y1 - y2) + (z1 - z2)*(z1 - z2));
// 求叉乘结果[la',lb',lc']=[(x1-x2),(y1-y2),(z1-z2)]x[XXX,YYY,ZZZ]
// [la,lb,lc]=[la',lb',lc']/a012/l12
// LLL=[la,lb,lc]是0.2*V1[0]这条高上的单位法向量。||LLL||=1;
float la = ((y1 - y2)*((x0 - x1)*(y0 - y2) - (x0 - x2)*(y0 - y1))
+ (z1 - z2)*((x0 - x1)*(z0 - z2) - (x0 - x2)*(z0 - z1))) / a012 / l12;
float lb = -((x1 - x2)*((x0 - x1)*(y0 - y2) - (x0 - x2)*(y0 - y1))
- (z1 - z2)*((y0 - y1)*(z0 - z2) - (y0 - y2)*(z0 - z1))) / a012 / l12;
float lc = -((x1 - x2)*((x0 - x1)*(z0 - z2) - (x0 - x2)*(z0 - z1))
+ (y1 - y2)*((y0 - y1)*(z0 - z2) - (y0 - y2)*(z0 - z1))) / a012 / l12;
// 计算点pointSel到直线的距离
// 这里需要特别说明的是ld2代表的是点pointSel到过点[cx,cy,cz]的方向向量直线的距离
float ld2 = a012 / l12;
// 如果在最理想的状态的话,ld2应该为0,表示点在直线上
// 最理想状态s=1;
float s = 1 - 0.9 * fabs(ld2);
// coeff代表系数的意思
// coff用于保存距离的方向向量
coeff.x = s * la;
coeff.y = s * lb;
coeff.z = s * lc;
// intensity本质上构成了一个核函数,ld2越接近于1,增长越慢
// intensity=(1-0.9*ld2)*ld2=ld2-0.9*ld2*ld2
coeff.intensity = s * ld2;
// 所以就应该认为这个点是边缘点
// s>0.1 也就是要求点到直线的距离ld2要小于1m
// s越大说明ld2越小(离边缘线越近),这样就说明点pointOri在直线上
if (s > 0.1) {
laserCloudOri->push_back(pointOri);
coeffSel->push_back(coeff);
}
}
}
}
}
void surfOptimization(int iterCount){
updatePointAssociateToMapSinCos();
for (int i = 0; i < laserCloudSurfTotalLastDSNum; i++) {
pointOri = laserCloudSurfTotalLastDS->points[i];
pointAssociateToMap(&pointOri, &pointSel);
kdtreeSurfFromMap->nearestKSearch(pointSel, 5, pointSearchInd, pointSearchSqDis);
if (pointSearchSqDis[4] < 1.0) {
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++) {
matA0.at<float>(j, 0) = laserCloudSurfFromMapDS->points[pointSearchInd[j]].x;
matA0.at<float>(j, 1) = laserCloudSurfFromMapDS->points[pointSearchInd[j]].y;
matA0.at<float>(j, 2) = laserCloudSurfFromMapDS->points[pointSearchInd[j]].z;
}
// matB0是一个5x1的矩阵
// matB0 = cv::Mat (5, 1, CV_32F, cv::Scalar::all(-1));
// matX0是3x1的矩阵
// 求解方程matA0*matX0=matB0
// 公式其实是在求由matA0中的点构成的平面的法向量matX0
cv::solve(matA0, matB0, matX0, cv::DECOMP_QR);
// [pa,pb,pc,pd]=[matX0,pd]
// 正常情况下(见后面planeValid判断条件),应该是
// pa * laserCloudSurfFromMapDS->points[pointSearchInd[j]].x +
// pb * laserCloudSurfFromMapDS->points[pointSearchInd[j]].y +
// pc * laserCloudSurfFromMapDS->points[pointSearchInd[j]].z = -1
// 所以pd设置为1
float pa = matX0.at<float>(0, 0);
float pb = matX0.at<float>(1, 0);
float pc = matX0.at<float>(2, 0);
float pd = 1;
// 对[pa,pb,pc,pd]进行单位化
float ps = sqrt(pa * pa + pb * pb + pc * pc);
pa /= ps; pb /= ps; pc /= ps; pd /= ps;
// 求解后再次检查平面是否是有效平面
bool planeValid = true;
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++) {
if (fabs(pa * laserCloudSurfFromMapDS->points[pointSearchInd[j]].x +
pb * laserCloudSurfFromMapDS->points[pointSearchInd[j]].y +
pc * laserCloudSurfFromMapDS->points[pointSearchInd[j]].z + pd) > 0.2) {
planeValid = false;
break;
}
}
if (planeValid) {
float pd2 = pa * pointSel.x + pb * pointSel.y + pc * pointSel.z + pd;
// 后面部分相除求的是[pa,pb,pc,pd]与pointSel的夹角余弦值(两个sqrt,其实并不是余弦值)
// 这个夹角余弦值越小越好,越小证明所求的[pa,pb,pc,pd]与平面越垂直
float s = 1 - 0.9 * fabs(pd2) / sqrt(sqrt(pointSel.x * pointSel.x
+ pointSel.y * pointSel.y + pointSel.z * pointSel.z));
coeff.x = s * pa;
coeff.y = s * pb;
coeff.z = s * pc;
coeff.intensity = s * pd2;
// 判断是否是合格平面,是就加入laserCloudOri
if (s > 0.1) {
laserCloudOri->push_back(pointOri);
coeffSel->push_back(coeff);
}
}
}
}
}
// 这部分的代码是基于高斯牛顿法的优化,不是zhang ji论文中提到的基于L-M的优化方法
// 这部分的代码使用旋转矩阵对欧拉角求导,优化欧拉角,不是zhang ji论文中提到的使用angle-axis的优化
bool LMOptimization(int iterCount){
float srx = sin(transformTobeMapped[0]);
float crx = cos(transformTobeMapped[0]);
float sry = sin(transformTobeMapped[1]);
float cry = cos(transformTobeMapped[1]);
float srz = sin(transformTobeMapped[2]);
float crz = cos(transformTobeMapped[2]);
int laserCloudSelNum = laserCloudOri->points.size();
// laser cloud original 点云太少,就跳过这次循环
if (laserCloudSelNum < 50) {
return false;
}
cv::Mat matA(laserCloudSelNum, 6, CV_32F, cv::Scalar::all(0));
cv::Mat matAt(6, laserCloudSelNum, CV_32F, cv::Scalar::all(0));
cv::Mat matAtA(6, 6, CV_32F, cv::Scalar::all(0));
cv::Mat matB(laserCloudSelNum, 1, CV_32F, cv::Scalar::all(0));
cv::Mat matAtB(6, 1, CV_32F, cv::Scalar::all(0));
cv::Mat matX(6, 1, CV_32F, cv::Scalar::all(0));
for (int i = 0; i < laserCloudSelNum; i++) {
pointOri = laserCloudOri->points[i];
coeff = coeffSel->points[i];
// 求雅克比矩阵中的元素,距离d对roll角度的偏导量即d(d)/d(roll)
// 更详细的数学推导参看wykxwyc.github.io
float arx = (crx*sry*srz*pointOri.x + crx*crz*sry*pointOri.y - srx*sry*pointOri.z) * coeff.x
+ (-srx*srz*pointOri.x - crz*srx*pointOri.y - crx*pointOri.z) * coeff.y
+ (crx*cry*srz*pointOri.x + crx*cry*crz*pointOri.y - cry*srx*pointOri.z) * coeff.z;
// 同上,求解的是对pitch的偏导量
float ary = ((cry*srx*srz - crz*sry)*pointOri.x
+ (sry*srz + cry*crz*srx)*pointOri.y + crx*cry*pointOri.z) * coeff.x
+ ((-cry*crz - srx*sry*srz)*pointOri.x
+ (cry*srz - crz*srx*sry)*pointOri.y - crx*sry*pointOri.z) * coeff.z;
float arz = ((crz*srx*sry - cry*srz)*pointOri.x + (-cry*crz-srx*sry*srz)*pointOri.y)*coeff.x
+ (crx*crz*pointOri.x - crx*srz*pointOri.y) * coeff.y
+ ((sry*srz + cry*crz*srx)*pointOri.x + (crz*sry-cry*srx*srz)*pointOri.y)*coeff.z;
/*
在求点到直线的距离时,coeff表示的是如下内容
[la,lb,lc]表示的是点到直线的垂直连线方向,s是长度
coeff.x = s * la;
coeff.y = s * lb;
coeff.z = s * lc;
coeff.intensity = s * ld2;
在求点到平面的距离时,coeff表示的是
[pa,pb,pc]表示过外点的平面的法向量,s是线的长度
coeff.x = s * pa;
coeff.y = s * pb;
coeff.z = s * pc;
coeff.intensity = s * pd2;
*/
matA.at<float>(i, 0) = arx;
matA.at<float>(i, 1) = ary;
matA.at<float>(i, 2) = arz;
// 这部分是雅克比矩阵中距离对平移的偏导
matA.at<float>(i, 3) = coeff.x;
matA.at<float>(i, 4) = coeff.y;
matA.at<float>(i, 5) = coeff.z;
// 残差项
matB.at<float>(i, 0) = -coeff.intensity;
}
// 将矩阵由matA转置生成matAt
// 先进行计算,以便于后边调用 cv::solve求解
cv::transpose(matA, matAt);
matAtA = matAt * matA;
matAtB = matAt * matB;
// 利用高斯牛顿法进行求解,
// 高斯牛顿法的原型是J^(T)*J * delta(x) = -J*f(x)
// J是雅克比矩阵,这里是A,f(x)是优化目标,这里是-B(符号在给B赋值时候就放进去了)
// 通过QR分解的方式,求解matAtA*matX=matAtB,得到解matX
cv::solve(matAtA, matAtB, matX, cv::DECOMP_QR);
// iterCount==0 说明是第一次迭代,需要初始化
if (iterCount == 0) {
cv::Mat matE(1, 6, CV_32F, cv::Scalar::all(0));
cv::Mat matV(6, 6, CV_32F, cv::Scalar::all(0));
cv::Mat matV2(6, 6, CV_32F, cv::Scalar::all(0));
// 对近似的Hessian矩阵求特征值和特征向量,
cv::eigen(matAtA, matE, matV);
matV.copyTo(matV2);
isDegenerate = false;
float eignThre[6] = {100, 100, 100, 100, 100, 100};
for (int i = 5; i >= 0; i--) {
if (matE.at<float>(0, i) < eignThre[i]) {
for (int j = 0; j < 6; j++) {
matV2.at<float>(i, j) = 0;
}
isDegenerate = true;
} else {
break;
}
}
matP = matV.inv() * matV2;
}
if (isDegenerate) {
cv::Mat matX2(6, 1, CV_32F, cv::Scalar::all(0));
matX.copyTo(matX2);
matX = matP * matX2;
}
transformTobeMapped[0] += matX.at<float>(0, 0);
transformTobeMapped[1] += matX.at<float>(1, 0);
transformTobeMapped[2] += matX.at<float>(2, 0);
transformTobeMapped[3] += matX.at<float>(3, 0);
transformTobeMapped[4] += matX.at<float>(4, 0);
transformTobeMapped[5] += matX.at<float>(5, 0);
float deltaR = sqrt(
pow(pcl::rad2deg(matX.at<float>(0, 0)), 2) +
pow(pcl::rad2deg(matX.at<float>(1, 0)), 2) +
pow(pcl::rad2deg(matX.at<float>(2, 0)), 2));
float deltaT = sqrt(
pow(matX.at<float>(3, 0) * 100, 2) +
pow(matX.at<float>(4, 0) * 100, 2) +
pow(matX.at<float>(5, 0) * 100, 2));
// 旋转或者平移量足够小就停止这次迭代过程
if (deltaR < 0.05 && deltaT < 0.05) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
如LOAM的LM
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_44041199/article/details/111033766
代码基于YZX方式
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/400375888

//求roll、pitch、yaw对应的sin和cos,用以求上面提到R对它们的求导
float srx = _transformTobeMapped.rot_x.sin();
float crx = _transformTobeMapped.rot_x.cos();
float sry = _transformTobeMapped.rot_y.sin();
float cry = _transformTobeMapped.rot_y.cos();
float srz = _transformTobeMapped.rot_z.sin();
float crz = _transformTobeMapped.rot_z.cos();
size_t laserCloudSelNum = _laserCloudOri.size();
if (laserCloudSelNum < 50)
continue;
Eigen::Matrix<float, Eigen::Dynamic, 6> matA(laserCloudSelNum, 6);
Eigen::Matrix<float, 6, Eigen::Dynamic> matAt(6, laserCloudSelNum);
Eigen::Matrix<float, 6, 6> matAtA;
Eigen::VectorXf matB(laserCloudSelNum);
Eigen::VectorXf matAtB;
Eigen::VectorXf matX;
//对每个点依次求解
for (int i = 0; i < laserCloudSelNum; i++)
{
//文中提到p^l
pointOri = _laserCloudOri.points[i];
//源点到目标点的方向单位向量,即V
coeff = _coeffSel.points[i];
//雅克比中对roll求导部分
float arx = (crx*sry*srz*pointOri.x + crx * crz*sry*pointOri.y - srx * sry*pointOri.z) * coeff.x
+ (-srx * srz*pointOri.x - crz * srx*pointOri.y - crx * pointOri.z) * coeff.y
+ (crx*cry*srz*pointOri.x + crx * cry*crz*pointOri.y - cry * srx*pointOri.z) * coeff.z;
//雅克比中对pitch求导部分
float ary = ((cry*srx*srz - crz * sry)*pointOri.x
+ (sry*srz + cry * crz*srx)*pointOri.y + crx * cry*pointOri.z) * coeff.x
+ ((-cry * crz - srx * sry*srz)*pointOri.x
+ (cry*srz - crz * srx*sry)*pointOri.y - crx * sry*pointOri.z) * coeff.z;
//雅克比中对yaw求导部分
float arz = ((crz*srx*sry - cry * srz)*pointOri.x + (-cry * crz - srx * sry*srz)*pointOri.y)*coeff.x
+ (crx*crz*pointOri.x - crx * srz*pointOri.y) * coeff.y
+ ((sry*srz + cry * crz*srx)*pointOri.x + (crz*sry - cry * srx*srz)*pointOri.y)*coeff.z;
matA(i, 0) = arx;
matA(i, 1) = ary;
matA(i, 2) = arz;
雅克比中对x,y,z求导部分直,V*E等于V
matA(i, 3) = coeff.x;
matA(i, 4) = coeff.y;
matA(i, 5) = coeff.z;
//残差
matB(i, 0) = -coeff.intensity;
}
matAt = matA.transpose();
matAtA = matAt * matA;
matAtB = matAt * matB;
//求解LM的更新公式JT*J*x=-JT*f
matX = matAtA.colPivHouseholderQr().solve(matAtB);
//作者实际实现的是高斯-牛顿法,可能出现matATA奇异的问题,这里做了一些防止退化的操作,有专门论文讲解,原理是根据特征值和特征向量判断出更新量的向量空间,认为特征值很小的基上的更新量是不可靠的,因此会干掉该分量,有空再写文章记录。
if (iterCount == 0)
{
Eigen::Matrix<float, 1, 6> matE;
Eigen::Matrix<float, 6, 6> matV;
Eigen::Matrix<float, 6, 6> matV2;
Eigen::SelfAdjointEigenSolver< Eigen::Matrix<float, 6, 6> > esolver(matAtA);
matE = esolver.eigenvalues().real();
matV = esolver.eigenvectors().real();
//这儿有个bug,eigen特征向量是列向量,处理是按照行向量处理的
matV2 = matV;
isDegenerate = false;
float eignThre[6] = { 100, 100, 100, 100, 100, 100 };
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++)
{
if (matE(0, i) < eignThre[i])
{
for (int j = 0; j < 6; j++)
{
matV2(i, j) = 0;
}
isDegenerate = true;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
matP = matV.inverse() * matV2;
}
if (isDegenerate)
{
Eigen::Matrix<float, 6, 1> matX2(matX);
matX = matP * matX2;
}
//更新状态量
_transformTobeMapped.rot_x += matX(0, 0);
_transformTobeMapped.rot_y += matX(1, 0);
_transformTobeMapped.rot_z += matX(2, 0);
_transformTobeMapped.pos.x() += matX(3, 0);
_transformTobeMapped.pos.y() += matX(4, 0);
_transformTobeMapped.pos.z() += matX(5, 0);
//单词更新小于阈值,则判断收敛
float deltaR = sqrt(pow(rad2deg(matX(0, 0)), 2) +
pow(rad2deg(matX(1, 0)), 2) +
pow(rad2deg(matX(2, 0)), 2));
float deltaT = sqrt(pow(matX(3, 0) * 100, 2) +
pow(matX(4, 0) * 100, 2) +
pow(matX(5, 0) * 100, 2));
if (deltaR < _deltaRAbort && deltaT < _deltaTAbort)
break;
}
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
mapOptmization.cpp
![]()
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
ros::init(argc, argv, "lego_loam");
ROS_INFO("\033[1;32m---->\033[0m Map Optimization Started.");
mapOptimization MO;
// std::thread 构造函数,将MO作为参数传入构造的线程中使用
// 进行闭环检测与闭环的功能
std::thread loopthread(&mapOptimization::loopClosureThread, &MO);
// 该线程中进行的工作是publishGlobalMap(),将数据发布到ros中,可视化
std::thread visualizeMapThread(&mapOptimization::visualizeGlobalMapThread, &MO);
ros::Rate rate(200);
while (ros::ok())
{
ros::spinOnce();
MO.run();
rate.sleep();
}
loopthread.join();
visualizeMapThread.join();
return 0;
}
回环检测:
频率1HZ
detect函数的流程:
1.使用KDtree寻找当前位姿的历史最近位姿:radiusSearch。当找到的位姿满足时间上与当前帧间隔大于30的条件就认为是合格的最近位置,并保留下来。
2.储存最新的这一帧点云,以作为闭环检测匹配计算中的目标值,并转换到世界坐标系下。
3.储存被找到的那一帧历史点云及其附近的几帧点云,并把他们转换到世界坐标系中。
4.如果订阅者数量不是0,则把数据发布出去。
思路: detectLoopClosure 函数 通过3D位姿旋转距离最近的50帧数据
即 closestHistoryFrameID
//
//
用detect函数,检测出历史位置上的回环,并储存好源和目标点云及位置数据。
void loopClosureThread()
{
if (loopClosureEnableFlag == false)
return;
ros::Rate rate(1);
while (ros::ok()){
rate.sleep();
performLoopClosure();
}
}
bool detectLoopClosure() {
std::cout<<"detection LoopClosure."<<std::endl;
latestSurfKeyFrameCloud->clear();
nearHistorySurfKeyFrameCloud->clear();
nearHistorySurfKeyFrameCloudDS->clear();
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(mtx);
// find the closest history key frame
std::vector<int> pointSearchIndLoop;
std::vector<float> pointSearchSqDisLoop;
kdtreeHistoryKeyPoses->setInputCloud(cloudKeyPoses3D);
kdtreeHistoryKeyPoses->radiusSearch(
currentRobotPosPoint, historyKeyframeSearchRadius, pointSearchIndLoop,
pointSearchSqDisLoop, 0);
closestHistoryFrameID = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < pointSearchIndLoop.size(); ++i) {
int id = pointSearchIndLoop[i];
if (abs(cloudKeyPoses6D->points[id].time - timeLaserOdometry) > 30.0) {
closestHistoryFrameID = id;
break;
}
}
if (closestHistoryFrameID == -1) {
return false;
}
// save latest key frames
latestFrameIDLoopCloure = cloudKeyPoses3D->points.size() - 1;
*latestSurfKeyFrameCloud +=
*transformPointCloud(cornerCloudKeyFrames[latestFrameIDLoopCloure],
&cloudKeyPoses6D->points[latestFrameIDLoopCloure]);
*latestSurfKeyFrameCloud +=
*transformPointCloud(surfCloudKeyFrames[latestFrameIDLoopCloure],
&cloudKeyPoses6D->points[latestFrameIDLoopCloure]);
pcl::PointCloud<PointType>::Ptr hahaCloud(new pcl::PointCloud<PointType>());
int cloudSize = latestSurfKeyFrameCloud->points.size();
for (int i = 0; i < cloudSize; ++i) {
if ((int)latestSurfKeyFrameCloud->points[i].intensity >= 0) {
hahaCloud->push_back(latestSurfKeyFrameCloud->points[i]);
}
}
latestSurfKeyFrameCloud->clear();
*latestSurfKeyFrameCloud = *hahaCloud;
// save history near key frames
for (int j = -historyKeyframeSearchNum; j <= historyKeyframeSearchNum;
++j) {
if (closestHistoryFrameID + j < 0 ||
closestHistoryFrameID + j > latestFrameIDLoopCloure)
continue;
*nearHistorySurfKeyFrameCloud += *transformPointCloud(
cornerCloudKeyFrames[closestHistoryFrameID + j],
&cloudKeyPoses6D->points[closestHistoryFrameID + j]);
*nearHistorySurfKeyFrameCloud += *transformPointCloud(
surfCloudKeyFrames[closestHistoryFrameID + j],
&cloudKeyPoses6D->points[closestHistoryFrameID + j]);
}
downSizeFilterHistoryKeyFrames.setInputCloud(nearHistorySurfKeyFrameCloud);
downSizeFilterHistoryKeyFrames.filter(*nearHistorySurfKeyFrameCloudDS);
std::cout << "detectLoopClosure nearHistorySurfKeyFrameCloudDS size:"
<< nearHistorySurfKeyFrameCloudDS->points.size() << std::endl;
// publish history near key frames
if (pubHistoryKeyFrames.getNumSubscribers() != 0) {
sensor_msgs::PointCloud2 cloudMsgTemp;
pcl::toROSMsg(*nearHistorySurfKeyFrameCloudDS, cloudMsgTemp);
cloudMsgTemp.header.stamp = ros::Time().fromSec(timeLaserOdometry);
cloudMsgTemp.header.frame_id = "/camera_init";
pubHistoryKeyFrames.publish(cloudMsgTemp);
}
return true;
}
回环检测如果成功,会设置aLoopIsClosed为True,将isam优化后的位姿替换之前的位姿。
其中
GTSAM是用于计算机视觉和多传感器融合方面用于平滑和建图的C++库,GTSAM采用因子图和贝叶斯网络的方式最大化后验概率 。
void performLoopClosure() {
if (cloudKeyPoses3D->points.empty() == true)
return;
// try to find close key frame if there are any
if (potentialLoopFlag == false) {
if (detectLoopClosure() == true) {
potentialLoopFlag = true; // find some key frames that is old enough or
// close enough for loop closure
timeSaveFirstCurrentScanForLoopClosure = timeLaserOdometry;
}
if (potentialLoopFlag == false)
return;
}
// reset the flag first no matter icp successes or not
potentialLoopFlag = false;
// ICP Settings
pcl::IterativeClosestPoint<PointType, PointType> icp;
icp.setMaxCorrespondenceDistance(100);
icp.setMaximumIterations(100);
icp.setTransformationEpsilon(1e-6);
icp.setEuclideanFitnessEpsilon(1e-6);
icp.setRANSACIterations(0);
// Align clouds
std::cout << "performLoopClosure latestSurfKeyFrameCloud->points.size:"
<< latestSurfKeyFrameCloud->points.size() << std::endl;
std::cout << "performLoopClosure nearHistorySurfKeyFrameCloudDS->points.size:"
<< nearHistorySurfKeyFrameCloudDS->points.size() << std::endl;
icp.setInputSource(latestSurfKeyFrameCloud);
icp.setInputTarget(nearHistorySurfKeyFrameCloudDS);
pcl::PointCloud<PointType>::Ptr unused_result(
new pcl::PointCloud<PointType>());
icp.align(*unused_result);
if (icp.hasConverged() == false ||
icp.getFitnessScore() > historyKeyframeFitnessScore)
return;
// publish corrected cloud
if (pubIcpKeyFrames.getNumSubscribers() != 0) {
pcl::PointCloud<PointType>::Ptr closed_cloud(
new pcl::PointCloud<PointType>());
pcl::transformPointCloud(*latestSurfKeyFrameCloud, *closed_cloud,
icp.getFinalTransformation());
sensor_msgs::PointCloud2 cloudMsgTemp;
pcl::toROSMsg(*closed_cloud, cloudMsgTemp);
cloudMsgTemp.header.stamp = ros::Time().fromSec(timeLaserOdometry);
cloudMsgTemp.header.frame_id = "/camera_init";
pubIcpKeyFrames.publish(cloudMsgTemp);
}
/*
get pose constraint
*/
float x, y, z, roll, pitch, yaw;
Eigen::Affine3f correctionCameraFrame;
correctionCameraFrame =
icp.getFinalTransformation(); // get transformation in camera frame
// (because points are in camera frame)
pcl::getTranslationAndEulerAngles(correctionCameraFrame, x, y, z, roll,
pitch, yaw);
Eigen::Affine3f correctionLidarFrame =
pcl::getTransformation(z, x, y, yaw, roll, pitch);
// transform from world origin to wrong pose
Eigen::Affine3f tWrong = pclPointToAffine3fCameraToLidar(
cloudKeyPoses6D->points[latestFrameIDLoopCloure]);
// transform from world origin to corrected pose
Eigen::Affine3f tCorrect =
correctionLidarFrame *
tWrong; // pre-multiplying -> successive rotation about a fixed frame
pcl::getTranslationAndEulerAngles(tCorrect, x, y, z, roll, pitch, yaw);
gtsam::Pose3 poseFrom =
Pose3(Rot3::RzRyRx(roll, pitch, yaw), Point3(x, y, z));
gtsam::Pose3 poseTo =
pclPointTogtsamPose3(cloudKeyPoses6D->points[closestHistoryFrameID]);
gtsam::Vector Vector6(6);
float noiseScore = icp.getFitnessScore();
Vector6 << noiseScore, noiseScore, noiseScore, noiseScore, noiseScore,
noiseScore;
constraintNoise = noiseModel::Diagonal::Variances(Vector6);
/*
add constraints
*/
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(mtx);
gtSAMgraph.add(
BetweenFactor<Pose3>(latestFrameIDLoopCloure, closestHistoryFrameID,
poseFrom.between(poseTo), constraintNoise));
isam->update(gtSAMgraph);
isam->update();
gtSAMgraph.resize(0);
std::cout << "回环检测 ok." << std::endl;
aLoopIsClosed = true;
}
函数是根据现有地图与最新点云数据进行配准从而更新机器人精确位姿与融合建图,它分为角点优化、平面点优化、配准与更新等部分。
void scan2MapOptimization(){
// laserCloudCornerFromMapDSNum是extractSurroundingKeyFrames()函数最后降采样得到的coner点云数
// laserCloudSurfFromMapDSNum是extractSurroundingKeyFrames()函数降采样得到的surface点云数
if (laserCloudCornerFromMapDSNum > 10 && laserCloudSurfFromMapDSNum > 100) {
// laserCloudCornerFromMapDS和laserCloudSurfFromMapDS的来源有2个:
// 当有闭环时,来源是:recentCornerCloudKeyFrames,没有闭环时,来源surroundingCornerCloudKeyFrames
kdtreeCornerFromMap->setInputCloud(laserCloudCornerFromMapDS);
kdtreeSurfFromMap->setInputCloud(laserCloudSurfFromMapDS);
for (int iterCount = 0; iterCount < 10; iterCount++) {
// 用for循环控制迭代次数,最多迭代10次
laserCloudOri->clear();
coeffSel->clear();
cornerOptimization(iterCount);
surfOptimization(iterCount);
if (LMOptimization(iterCount) == true)
break;
}
// 迭代结束更新相关的转移矩阵
transformUpdate();
}
}
保存地图:
在运行过程中执行
rosbag record -o out /laser_cloud_surround
来录制Loam后生成的地图
1.保存为pcd格式文件
rosrun pcl_ros bag_to_pcd input.bag /laser_cloud_surround pcd
最后一个pcd文件为我们要保存的pcd文件
使用pcl_viewer来查看我们保存的pcd文件
pcl_viewer xxxxxx.pcd #xxxxx.pcd为文件名
LEGO-SLAM-GTsam
利用gtsam库完成因子图优化简单测试与LeGo-LOAM中的因子图优化
https://blog.csdn.net/lzy6041/article/details/107658568
6:简单几何关系
7:hdl_localization hdl_graph_slam
建图及重定位:
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_34622953/article/details/108597567
 launch出差:
launch出差:
https://github.com/koide3/hdl_graph_slam/issues/4
Hi,we had tested with serverl optimization params and use your g2o branch ,it cound not help . But we found out the problem was caused by g2o or it’s dependences . An good news is that the g2o Debian packages from ros can works well. We had tried on 3 computers with the same problem (start optimizing… then crashed ),it fixed the problem.
Here is the setup:
- sudo apt-get install ros-kinetic-libg2o
- sudo cp -r /opt/ros/kinetic/lib/libg2o_* /usr/local/lib
- sudo cp -r /opt/ros/kinetic/include/g2o /usr/local/include
- rebuild project( must remove the folder ‘hdl_graph_slam’ under catkin_ws/build beford catkin_make ).
- Hope it can help you!
https://github.com/koide3/hdl_localization
基于建图,重定位算法:
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_34622953/article/details/108597567
hdl_graph_slam是由日本风桥科技大学的Kenji Koide开源的六自由度三维激光SLAM算法。
其中主要由激光里程计、回环检测以及后端图优化构成,同时融合了IMU、GPS以及地面检测的信息作为图的额外约束
算法首先读入激光雷达的点云数据,然后将原始的点云数据进行预滤波,经过滤波后的数据分别给到点云匹配里程计以及地面检测节点,两个节点分别计算连续两帧的相对运动和检测到的地面的参数,并将这两种消息送到hdl_graph_slam节点进行位姿图(pose graph)的更新以及回环检测,并发布地图的点云数据
hdl_graph_slam是一套激光slam系统,
可融合gps、imu、lidar三种传感器,同时具有闭环检测功能。
如下,基本解析:
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/89014435
编译出现:
error:
hdl_localization_nodelet.cpp:214:102: error: no matching function for call to ‘transformPointCloud(const char*, pcl::PointCloudpcl::PointXYZI&, pcl::PointCloudpcl::PointXYZI&, tf2_ros::Buffer&)’
if(!pcl_ros::transformPointCloud(odom_child_frame_id.c_str(), pcl_cloud, cloud, this->tf_buffer))
原因:
The reason is that in ros-kinetic, the pcl_ros library transforms.h
has no matching function template with relative input. You can either
upgrade the pcl version or adding functions by yourself, I added it
myself and fixed it.
适配速腾lidar
https://blog.csdn.net/a850565178/article/details/105434696
8:livox loam
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/93579424
做激光slam的应该都知道loam,原版loam是基于机械雷达的,当我们使用Livox固态雷达的时候,loam则不兼容了。这篇论文就是为了解决这个问题,固态雷达的主要问题是视角比较小,原版loam提取特征则不容易得到高精度里程计,需要提高鲁棒性,为了解决这些问题,作者从以下几个大的方面入手:
-
首先设计了基于固态雷达的特征提取和里程解算流程
-
为了增加鲁棒性,设计了一些策略,移除了不好的特征点,并且增加反射强度作为判断条件
-
补畸变
-
对于一些outliers的特征做了剔除
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_40331125/article/details/105057663
图像帧运动补偿
由于激光采集的点云并不是在同一时刻采集的,所以就会存在运动畸变(坐标系不同引起的),所以需要根据接收激光点的时间计算位姿把点云投影到同一坐标系。为了补偿每次扫描的时间和位姿不同,我们可以利用:
分段线性:把一个新来的帧分成三个连续的子帧,然后把这三个帧独立的和现阶段构建的地图做匹配。在每个子图做scan-match的过程中利用子图中最后一个点的位姿把所有的点投影到全局地图中,这样每帧采样的时间仅为原来的三分之一。尽管这种方法很简单,但是效果很好(LEGO—LOAM中把一帧分为6份应该也是分段线性的思想),分段线性对于多核的CPU并行运算也有好处。
线性插值:这部分在张籍博士的LAOM中介绍的比较详细,大家在看的时候可以参考。主要思想是在当前帧最后一个激光点得到的雷达位姿[R_k,T_k]和次新帧的[R_k-1,T_k-1]中间的时刻t,利用恒速模型计算中间时刻点的位姿。
对比差异:
LOAM的特征提取基于曲率,只提取两种特征点,corner和surface,分别对应场景的平面区域和曲折区域。LOAM没有使用特征描述子(连曲率都没有参与后续的匹配)。从代码中的corner与surface的曲率判断阈值可以看出,LOAM提取的corner和surface特征点的曲率, 并没有特别大的差别,这使得LOAM有较强的场景适应性,在场景中比较曲折的区域,corner点会占据主导,而在较为平缓的区域,surface点占据主导. 在激光扫描到的一块区域,总会提取出几个特征点。
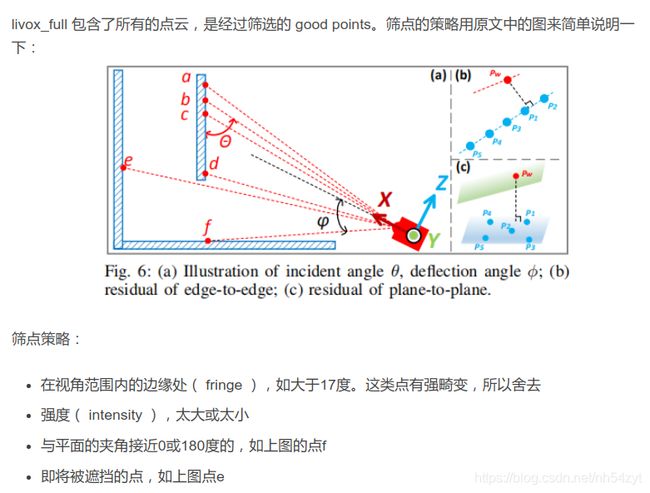
loam-livox 论文解读:
如下blog:
https://www.cnblogs.com/yongqivisionimax/p/14054826.html
位姿优化匹配:
(1)计算线和线的误差
(2)计算面和面的误差
(3)利用两个特征迭代的优化位姿
(4)删除残差中最大的20%
(5)在迭代中如果位姿收敛就break
此外:
外点和运动物体剔除
在实际跑的时候避免不了会有动态的车、人及其他物体。本文的动态物体剔除算法是在每一次迭代优化位姿的过程中重新找到每个特征的最近点把边边残差和面面残差加入到目标函数,第一次只优化两次,然后把残差中最大的20%丢弃来达到剔除外点的目的。
9:kd-tree lm icp匹配策略
距离度量:
https://www.cnblogs.com/mantch/archive/2019/08/02/11287075.html


10:PCA求解平面
https://blog.csdn.net/hanghang_/article/details/107323561
11:梯度下降、牛顿法、Levenberg-Marquardt(LM)
应用解决slam中位姿估计问题,及roll pitch yaw x y z
最后都可以转换为最小二乘法问题。
如果 不是简单的线性函数,那么此最小二乘问题就变为了非线性最小二乘问题,对于不方便求解的非线性最小二乘问题我们一般采用迭代的方式进行计算,
思路是:从一个初始值出发,不断优化当前的优化变量,使得目标函数下降。显然初始值给的越好,优化效果会越好。
LM算法是介于牛顿法和梯度下降法之间的一种非线性优化方法,对于过于参数化问题不敏感,能有效地处理冗余参数问题,使目标函数陷入局部最小值的机会大大减小



四种方法的优劣对比
下面总结以上四种方法的优劣对比:
1.最速下降法:直观上将本算法十分简单,直接按照梯度的反方向下降即可;缺点是过于贪心,容易呈锯齿状下降,从而增加迭代次数。
2.牛顿法:相对而言也非常直观,同时由于引入了二阶导数,可以处理一阶导为0的情况;但缺点是二阶导数具有非常大的计算量。
3.高斯牛顿法:在牛顿法的基础上进行了一定程度的简化, 代替海塞矩阵,避免了二阶导数的计算;缺点在于 很容易病态,导致无法得到正确的结果。
4.LM法:通过引入阻尼项使得 不那么容易病态,并且可以通过调整阻尼完成在梯度法和牛顿法之间切换;缺点不太清楚。
loam lm
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_44041199/article/details/111033766
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_44041199/article/details/110946921#33_Jacobi_587
//*****************构建Jacobi矩阵估计位姿*****************//
cv::Mat matA(pointSelNum, 6, CV_32F, cv::Scalar::all(0));
cv::Mat matAt(6, pointSelNum, CV_32F, cv::Scalar::all(0));
cv::Mat matAtA(6, 6, CV_32F, cv::Scalar::all(0));
cv::Mat matB(pointSelNum, 1, CV_32F, cv::Scalar::all(0));
cv::Mat matAtB(6, 1, CV_32F, cv::Scalar::all(0));
cv::Mat matX(6, 1, CV_32F, cv::Scalar::all(0));
//1.计算matA,matB矩阵
for (int i = 0; i < pointSelNum; i++) {
pointOri = laserCloudOri->points[i];
coeff = coeffSel->points[i];
float s = 1;
float srx = sin(s * transform[0]);
float crx = cos(s * transform[0]);
float sry = sin(s * transform[1]);
float cry = cos(s * transform[1]);
float srz = sin(s * transform[2]);
float crz = cos(s * transform[2]);
float tx = s * transform[3];
float ty = s * transform[4];
float tz = s * transform[5];
float arx = (-s*crx*sry*srz*pointOri.x + s*crx*crz*sry*pointOri.y + s*srx*sry*pointOri.z
+ s*tx*crx*sry*srz - s*ty*crx*crz*sry - s*tz*srx*sry) * coeff.x
+ (s*srx*srz*pointOri.x - s*crz*srx*pointOri.y + s*crx*pointOri.z
+ s*ty*crz*srx - s*tz*crx - s*tx*srx*srz) * coeff.y
+ (s*crx*cry*srz*pointOri.x - s*crx*cry*crz*pointOri.y - s*cry*srx*pointOri.z
+ s*tz*cry*srx + s*ty*crx*cry*crz - s*tx*crx*cry*srz) * coeff.z;
float ary = ((-s*crz*sry - s*cry*srx*srz)*pointOri.x
+ (s*cry*crz*srx - s*sry*srz)*pointOri.y - s*crx*cry*pointOri.z
+ tx*(s*crz*sry + s*cry*srx*srz) + ty*(s*sry*srz - s*cry*crz*srx)
+ s*tz*crx*cry) * coeff.x
+ ((s*cry*crz - s*srx*sry*srz)*pointOri.x
+ (s*cry*srz + s*crz*srx*sry)*pointOri.y - s*crx*sry*pointOri.z
+ s*tz*crx*sry - ty*(s*cry*srz + s*crz*srx*sry)
- tx*(s*cry*crz - s*srx*sry*srz)) * coeff.z;
float arz = ((-s*cry*srz - s*crz*srx*sry)*pointOri.x + (s*cry*crz - s*srx*sry*srz)*pointOri.y
+ tx*(s*cry*srz + s*crz*srx*sry) - ty*(s*cry*crz - s*srx*sry*srz)) * coeff.x
+ (-s*crx*crz*pointOri.x - s*crx*srz*pointOri.y
+ s*ty*crx*srz + s*tx*crx*crz) * coeff.y
+ ((s*cry*crz*srx - s*sry*srz)*pointOri.x + (s*crz*sry + s*cry*srx*srz)*pointOri.y
+ tx*(s*sry*srz - s*cry*crz*srx) - ty*(s*crz*sry + s*cry*srx*srz)) * coeff.z;
float atx = -s*(cry*crz - srx*sry*srz) * coeff.x + s*crx*srz * coeff.y
- s*(crz*sry + cry*srx*srz) * coeff.z;
float aty = -s*(cry*srz + crz*srx*sry) * coeff.x - s*crx*crz * coeff.y
- s*(sry*srz - cry*crz*srx) * coeff.z;
float atz = s*crx*sry * coeff.x - s*srx * coeff.y - s*crx*cry * coeff.z;
float d2 = coeff.intensity;
matA.at<float>(i, 0) = arx;
matA.at<float>(i, 1) = ary;
matA.at<float>(i, 2) = arz;
matA.at<float>(i, 3) = atx;
matA.at<float>(i, 4) = aty;
matA.at<float>(i, 5) = atz;
matB.at<float>(i, 0) = -0.05 * d2;
}
//2.最小二乘法计算(QR分解)
cv::transpose(matA, matAt);
matAtA = matAt * matA;
matAtB = matAt * matB;
//求解matAtA * matX = matAtB
cv::solve(matAtA, matAtB, matX, cv::DECOMP_QR);
//3.出现退化用预测矩阵P
if (iterCount == 0) {
//特征值1*6矩阵
cv::Mat matE(1, 6, CV_32F, cv::Scalar::all(0));
//特征向量6*6矩阵
cv::Mat matV(6, 6, CV_32F, cv::Scalar::all(0));
cv::Mat matV2(6, 6, CV_32F, cv::Scalar::all(0));
//求解特征值/特征向量
cv::eigen(matAtA, matE, matV);
matV.copyTo(matV2);
isDegenerate = false;
//特征值取值门槛
float eignThre[6] = {10, 10, 10, 10, 10, 10};
for (int i = 5; i >= 0; i--) {//从小到大查找
if (matE.at<float>(0, i) < eignThre[i]) {//特征值太小,则认为处在兼并环境中,发生了退化
for (int j = 0; j < 6; j++) {//对应的特征向量置为0
matV2.at<float>(i, j) = 0;
}
isDegenerate = true;
} else {
break;
}
}
//计算P矩阵
matP = matV.inv() * matV2;
}
if (isDegenerate) {//如果发生退化,只使用预测矩阵P计算
cv::Mat matX2(6, 1, CV_32F, cv::Scalar::all(0));
matX.copyTo(matX2);
matX = matP * matX2;
}
//累加每次迭代的旋转平移量
transform[0] += matX.at<float>(0, 0);
transform[1] += matX.at<float>(1, 0);
transform[2] += matX.at<float>(2, 0);
transform[3] += matX.at<float>(3, 0);
transform[4] += matX.at<float>(4, 0);
transform[5] += matX.at<float>(5, 0);
for(int i=0; i<6; i++){
if(isnan(transform[i]))//判断是否非数字
transform[i]=0;
}
//计算旋转平移量,如果很小就停止迭代
float deltaR = sqrt(
pow(rad2deg(matX.at<float>(0, 0)), 2) +
pow(rad2deg(matX.at<float>(1, 0)), 2) +
pow(rad2deg(matX.at<float>(2, 0)), 2));
float deltaT = sqrt(
pow(matX.at<float>(3, 0) * 100, 2) +
pow(matX.at<float>(4, 0) * 100, 2) +
pow(matX.at<float>(5, 0) * 100, 2));
if (deltaR < 0.1 && deltaT < 0.1) {//迭代终止条件
break;
}
}
}
12:A LOAM
我们通过scan-to-scan获得一个粗位姿之后开始建图,在另一个线程中我们通过scan-to-map的方式获得更加准确的位姿,SLAM最终的精度也就是取决于scan-to-map的精度,而scan-to-scan则可以有IMU或者视觉里程计代替(VLOAM就是这个基本原理),在scan-to-map中匹配方式主要有以下几点不同
数量不同,在scan-to-map的过程中参与计算的特征点是scan-to-scan的十倍以上;
线特征和面特征获得相邻点的方式不同,在scan-to-scan中是通过直接搜索最近的激光点获得的直线上的两个点或者平面上的三个点,但是在scan-to-map中是搜索最近的5个点,然后通过主成分分析或者最小二乘的方式获得直线和平面的表达式,最后通过采样来获得最后的匹配点,这样做显然会更加鲁棒。
#include