算法通关村第一关——链表笔记(青铜挑战)
算法通关村第一关——链表青铜挑战笔记
-
-
- 1 链表的内部结构
-
- 1.1 单链表
- 1.2 双链表
- 2 单向链表
-
- 2.1 设计单向链表
-
- 2.1.1 定义Node类(节点)
- 2.1.2 定义LinkedList类(链表)
- 2.2. 遍历链表
- 2.3 链表插入
- 2.4 链表删除
- 3 双向链表
-
- 3.1 设计双向链表
-
- 3.1.1 定义DoubleNode类(节点)
- 3.1.2 定义DoublyLinkedList类(链表)
- 3.2 遍历链表
- 3.3 链表插入
- 3.4 链表删除
-
1 链表的内部结构
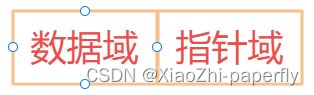
链表的基本单位是结点,也是叫节点,一个意思
在链表中,每个节点都有数据域和指针域,单链表是一个指针域,双链表是两个指针域
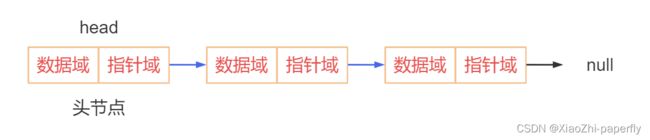
1.1 单链表
从表面上我们就能看出,数据域是存数据,指针域是存下一个节点的位置,如图所示:
1.2 双链表
那么双链表的节点就是,不仅存储下一个节点的位置,还存取上一个节点的位置,如图所示:
双链表节点:
双链表结构:
通过上面的图文,我们对链表有了基本的认识,那么下一步我们就是想如何使用这个数据结构
任何的数据结构基础都是创建+增删改查,所以我们首先设计创建好链表
课外注意事项(刷算法):
如果跟学校学过数据结构的兄弟都知道,书本的头节点是不包含数据的,但是网上刷力扣等算法题的时候,会发现它们自己设置的链表的头节点就是第一个带数据的结点,所以这里要注意,因为我学习这个就是为了刷算法,那么就按照力扣不去定义头节点了,直接让第一个数据就是头节点,不过这样会多很多问题,后面还需要通过定义虚拟节点解决头节点的问题。
2 单向链表
下面我们设计链表的结构会使用力扣等算法题的方式,因为这样定义比较简单,如果按照面向对象规则来定义,会比较麻烦,所以直接用下面的方式
2.1 设计单向链表
由上面的内容可知,一个链表要首先有结点,所以我们先定义一个结点
2.1.1 定义Node类(节点)
定义一个Node类来表示单链表中的节点,包含数据域和指针域。
public class Node {
// 数据域
public int data;
// 指针域
public Node next;
public Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
}
2.1.2 定义LinkedList类(链表)
在LinkedList类中定义一个头结点head,以及链表的大小size。
这里按道理应该用private,然后get,set方法的,偷懒了
public class LinkedList {
Node head;
int size;
public LinkedList(Node head, int size) {
this.head = head;
this.size = size;
}
}
然后我们可以创建一个test类,用来测试一下这个LinkedList,输出一下
public class testLinkedList {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建一个结点,赋值1,命名为头节点head
Node head = new Node(1);
// 创建链表,并且将头节点传进去,进行初始化链表
LinkedList linkedList = new LinkedList(head, 1);
System.out.println(linkedList);
}
}
会发现输出的其实是一个地址值,至于原因,you know
com.XiaoZhi.study.level1.LinkedList@4554617c
所以我们下一步写一个遍历链表的方法
2.2. 遍历链表
链表的遍历,一定是需要通过头指针head,然后通过head.next,就是得到下一个节点的地址,所以遍历就相当于一直拿到节点的next,这样就一直遍历下去就拿到啦~
public String toString(Node head){
if (head == null){
return null;
}
Node curNode = head;
StringBuffer result = new StringBuffer();
while (curNode != null){
result.append(curNode.data).append("\t");
curNode = curNode.next;
}
return result.toString();
}
我们将这个方法写在LinkedList类里,这样链表遍历就设计好了
测试一下:
public class testLinkedList {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node head = new Node(1);
LinkedList linkedList = new LinkedList(head, 1);
System.out.println("遍历链表:"+linkedList.toString(linkedList.head));
}
}
输出:
遍历链表:1
因为我们就只有一个头节点,数据是1,所以答案就是1
竟然如此,我们就写一个在链表插入数据的方法
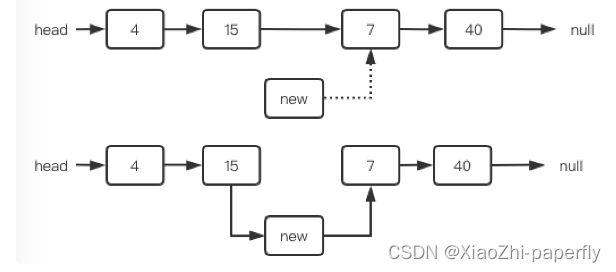
2.3 链表插入
链表插入数据会有三种情况,在头部插入节点,在中间插入一个结点,在尾部插入一个结点
也就是,我们可以写一个链表插入的方法,需要的参数是节点所在的位置,那么
- 头节点的位置就是1
- 中间节点的位置就是int
- 尾节点的位置就是链表长度size的后面加一个节点,也就是size+1
节点插入:找到指定位置的前一个节点,然后将前一天节点指向新节点,新节点指向下一个节点,串联起来,如下图所示:
/**
* 按照指定位置插入新的结点
*
* @param nodeInsert 插入的节点
* @param position 节点要插入的位置
*/
public void insertNode(Node nodeInsert, int position) {
if (nodeInsert == null || head == null) {
System.out.println("插入的节点不允许为空");
return ;
}
if (position < 1 || position > size + 1) {
System.out.println("插入节点的位置不存在");
return ;
}
size ++;
if (position == 1) {
nodeInsert.next = head;
head = nodeInsert;
return ;
}
Node preNode = head;
for (int i=1; i < position -1; i++){
preNode = preNode.next;
}
nodeInsert.next = preNode.next;
preNode.next = nodeInsert;
}
然后测试一下:
public class testLinkedList {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node head = new Node(1);
LinkedList linkedList = new LinkedList(head, 1);
Node insertNode = new Node(2);
linkedList.insertNode(insertNode, 2);
System.out.println("遍历链表:"+linkedList.toString(linkedList.head));
System.out.println("遍历大小:"+linkedList.size);
}
}
输出:
遍历链表:1 2
遍历大小:2
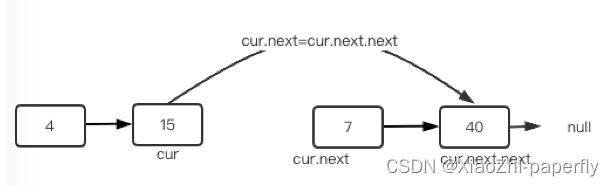
2.4 链表删除
删除节点也是同理,找到需要删除的位置,找到这个节点,并指向,它的next,的next,就OK啦
/**
* 删除指定位置的节点
* @param position
*/
public void deleteNode(int position) {
if (position < 1 || position > size) {
System.out.println("删除的节点不存在");
return;
}
size--;
if (position == 1) {
head = head.next;
return;
}
Node preNode = head;
for (int i = 1; i < position ; i++) {
preNode = preNode.next;
}
preNode.next = preNode.next.next;
}
测试一下:
public class testLinkedList {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 初始化节点和链表
Node head = new Node(1);
LinkedList linkedList = new LinkedList(head, 1);
// 添加节点
Node insertNode = new Node(2);
linkedList.insertNode(insertNode, 2);
// 删除节点
int position = 1;
linkedList.deleteNode(position);
System.out.println("遍历链表:"+linkedList.toString(linkedList.head));
System.out.println("遍历大小:"+linkedList.size);
}
}
输出:
遍历链表:2
遍历大小:1
3 双向链表
3.1 设计双向链表
3.1.1 定义DoubleNode类(节点)
双向链表顾名思义,就有前后两个指针,所以节点就是一个记录前面的节点,一个记录后面的节点
public class DoubleNode {
public int data;
public DoubleNode prev;
public DoubleNode next;
public DoubleNode(){}
public DoubleNode(int data){
this.data = data;
}
}
3.1.2 定义DoublyLinkedList类(链表)
定义双向链表结构的时候,可以设置一个头指针,一个尾指针
我这里设置了两个构造方法,一个无参,一个有参
public class DoublyLinkedList {
int size;
DoubleNode head;
DoubleNode tail;
public DoublyLinkedList() {
this.size = 0;
head = null;
tail = head;
}
public DoublyLinkedList(DoubleNode head, int size ) {
this.size = size;
this.head = head;
tail = head;
}
}
然后简单测试一下能不能用:
public class testDoublyLinkedList {
public static void main(String[] args) {
DoubleNode head = new DoubleNode(1);
DoublyLinkedList doublyLinkedList = new DoublyLinkedList(head,1);
System.out.println(doublyLinkedList);
}
}
3.2 遍历链表
因为双向链表的特殊,那就会出现,可以从头节点遍历,也可以从尾节点遍历
// 从头部开始演绎
public void displayForward(){
System.out.print("List(first--->last): ");
DoubleNode curNode = head;
while (curNode != null){
System.out.print(curNode.data+" ");
curNode = curNode.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
//从尾部开始演绎
public void displayBackward() {
System.out.print("List(last--->first): ");
DoubleNode curNode = tail;
while (curNode != null) {
System.out.print(curNode.data+" ");
curNode = curNode.prev;
}
System.out.println();
}
测试一下:
public class testDoublyLinkedList {
public static void main(String[] args) {
DoubleNode head = new DoubleNode(1);
DoublyLinkedList doublyLinkedList = new DoublyLinkedList(head,1);
// 前遍历
doublyLinkedList.displayForward();
// 后遍历
doublyLinkedList.displayBackward();
System.out.println("链表的长度:"+doublyLinkedList.size);
}
}
输出:
List(first--->last): 1
List(last--->first): 1
链表的长度:1
3.3 链表插入
链表插入,需要判断当前链表是否为空,如果为空,那么插入节点就不一样了
我们分开插入在头节点位置,插入在尾节点的位置和在中间
//检查链表是否为空
public boolean isEmpty() {
return (head == null);
}
//头部插入
public void insertFirst(int data) {
DoubleNode newDoubleNode = new DoubleNode(data);
if (isEmpty()) {
tail = newDoubleNode;
} else {//如果不是第一个结点的情况
head.prev = newDoubleNode; //将还没插入新结点之前链表的第一个结点的previous指向newNode
}
size++; // 插入节点,节点数+1
newDoubleNode.next = head; //将新结点的next指向first
head = newDoubleNode; //将新结点赋给first(链接)成为第一个结点
}
//尾部插入
public void insertLast(int data) {
DoubleNode newDoubleNode = new DoubleNode(data);
if (isEmpty()) {
head = newDoubleNode; //若链表为空,则将first指向新的结点(newNode)
} else {
newDoubleNode.prev = tail; //将新结点的prev指向尾结点(last永远指向的是最后一个结点)
//【此时还没有插入新的结点newNode,所以last指向的是当前链表的最后一个结点】
tail.next = newDoubleNode; //将last.next(当前链表最后一个结点的next域)指向新的结点newNode
}
size++; // 插入节点,节点数+1
tail = newDoubleNode; //由于插入了一个新的结点,又因为是尾部插入,所以将last指向newNode
}
我这里写了两个插入链表的方法:
- 在想要的位置插入节点
- 在带有想要的数据的节点,后面,插入节点
第一种:
/**
* 在某个位置插入节点
* @param index 某个位置
* @param data
*/
public void insertNodeByIndex(int index, int data) {
if (index < 1 || index > size){
System.out.println("该位置不存在");
}
if (index == 1){
insertFirst(data);
return;
}
if (index == size){
insertLast(data);
return;
}
//找到前驱
DoubleNode preNode = head;
for(int i = 1; i < index-1; i++){
preNode = preNode.next;
}
// 新建节点
DoubleNode newNode = new DoubleNode(data);
newNode.next = preNode.next;
preNode.next.prev = newNode;
newNode.prev = preNode;
preNode.next = newNode;
size++;
}
第二种:
/**
* 在某个节点的后面插入节点
* @param key 某个节点的值(也就是要在有这个节点值的后面插入节点)
* @param data
*/
//某个结点的后部插入
public void insertAfter(int key, int data) {
DoubleNode newDoubleNode = new DoubleNode(data);
DoubleNode current = head;
while ((current != null) && (current.data != key)) {
current = current.next;
}
//若当前结点current为空
if (current == null) { //current为null有两种情况 一种是链表为空,一种是找不到key值
if (isEmpty()) { //1、链表为空
head = newDoubleNode; //则插入第一个结点(其实可以调用其它的Insert方法)
tail = newDoubleNode; //first和last均指向该结点(第一个结点)
} else {
tail.next = newDoubleNode; //2、找不到key值
newDoubleNode.prev = tail; //则在链表尾部插入一个新的结点
tail = newDoubleNode;
}
} else {
if (current == tail) { //第三种情况,找到了key值,分两种情况
newDoubleNode.next = null; //1、key值与最后结点的data相等
tail = newDoubleNode; //由于newNode将是最后一个结点,则将last指向newNode
} else {
newDoubleNode.next = current.next; //2、两结点中间插入 四
current.next.prev = newDoubleNode; //将current当前结点的下一个结点赋给newNode.next
} //将current下一个结点即current.next的previous域指向current
current.next = newDoubleNode; //将当前结点的next域指向newNode
newDoubleNode.prev = current; //将新结点的previous域指向current(current在newNode前面一个位置)
}
size++;
}
测试一下:
public class testDoublyLinkedList {
public static void main(String[] args) {
DoubleNode head = new DoubleNode(1);
DoublyLinkedList doublyLinkedList = new DoublyLinkedList(head,1);
doublyLinkedList.insertFirst(2);
doublyLinkedList.insertLast(3);
doublyLinkedList.insertNodeByIndex(2,4);
doublyLinkedList.insertAfter(3,5);
// 前遍历
doublyLinkedList.displayForward();
// 后遍历
doublyLinkedList.displayBackward();
System.out.println("链表的长度:"+doublyLinkedList.size);
}
}
输出:
List(first--->last): 2 4 1 3 5
List(last--->first): 5 3 1 4 2
链表的长度:5
3.4 链表删除
删除节点其实跟插入差别不大,我这里只写了一个按值删除
//从头部删除结点
public DoubleNode deleteFirst() {
DoubleNode temp = head;
if (head.next == null) { //若链表只有一个结点,删除后链表为空,将last指向null
tail = null;
} else {
head.next.prev = null; //若链表有两个(包括两个)以上的结点 ,因为是头部插入,则first.next将变成第一个结点,其previous将变成null
}
head = head.next; //将first.next赋给first
size--;
return temp; //返回删除的结点
}
//从尾部删除结点
public DoubleNode deleteLast() {
DoubleNode temp = tail;
if (head.next == null) { //如果链表只有一个结点,则删除以后为空表,last指向null
head = null;
} else {
tail.prev.next = null; //将上一个结点的next域指向null
}
tail = tail.prev; //上一个结点称为最后一个结点,last指向它
size--;
return temp; //返回删除的结点
}
//按值删除
public DoubleNode deleteKey(int key) {
DoubleNode current = head;
while (current != null && current.data != key) { //遍历链表寻找该值所在的结点
current = current.next;
}
if (current == null) { //若当前结点指向null则返回null,
return null; //两种情况当前结点指向null,一是该链表为空链表,而是找不到该值
} else {
if (current == head) { //如果current是第一个结点
head = current.next; //则将first指向它,将该结点的previous指向null,其余不变
current.next.prev = null;
} else if (current == tail) { //如果current是最后一个结点
tail = current.prev; //将last指向当前结点的上一个结点(我们将当前结点除名了以后它便不再是最后一个了)
current.prev.next = null; //相应的要删除结点的上一个结点的next域应指向null
} else {
current.prev.next = current.next; //当前结点的上一个结点的next域应指向当前的下一个结点
current.next.prev = current.prev; //当前结点的下一个结点的previous域应指向当前结点的上一个结点
}
}
size--;
return current; //返回
}
然后测试一下:
public class testDoublyLinkedList {
public static void main(String[] args) {
DoubleNode head = new DoubleNode(1);
DoublyLinkedList doublyLinkedList = new DoublyLinkedList(head,1);
doublyLinkedList.insertFirst(2);
doublyLinkedList.insertLast(3);
doublyLinkedList.insertNodeByIndex(2,4);
doublyLinkedList.insertAfter(3,5);
/*List(first--->last): 2 4 1 3 5
List(last--->first): 5 3 1 4 2*/
doublyLinkedList.deleteFirst();
doublyLinkedList.deleteLast();
doublyLinkedList.deleteKey(1);
/* List(first--->last): 4 3
List(last--->first): 3 4
链表的长度:2 */
// 前遍历
doublyLinkedList.displayForward();
// 后遍历
doublyLinkedList.displayBackward();
System.out.println("链表的长度:"+doublyLinkedList.size);
}
}
输出:
List(first--->last): 4 3
List(last--->first): 3 4
链表的长度:2
搞定~~~