圆的反演 hdu 4773
欢迎关注更多精彩
关注我,学习常用算法与数据结构,一题多解,降维打击。
题目大意
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=4773
给定2个不相交的圆以及圆外1点P。求过P并且与另两个圆相切(外切)的圆,这种圆有可能有多个。
基本思路
圆的反演有如下性质:
- 圆C的圆心为O,则如果有一个圆过点O,则该圆对C的反演是一条直线。反之直线可以反演成圆。
- 如果两个圆相切,则反演后的几何形状还是相切。
题目要求的是过点P的圆,可以把圆先以P为圆心(半径取1即可)进行反演,然后求公切线,再将切线反演成圆,判断是否外切。
内公切线反演后必有1个圆是内切

反演可以理解为一种凸镜反射,反射的特点就是位置会相反,远近会颠倒。
从上图可以看出,当圆处于公切线与P的另一边时,最终结果是内切。
两个圆的内部公切线必有1个圆是处于这种情况。所以只要求外公切线即可。
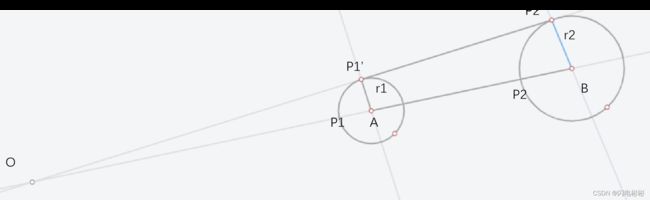
求解外公切线
根据圆的公切线性质可知,
∠ P 1 A P 1 ′ = ∠ P 2 B P 2 ′ ,设置值为 α \angle P1AP1'=\angle P2BP2',设置值为\alpha ∠P1AP1′=∠P2BP2′,设置值为α
∴ △ O A P 1 ′ ∼ △ O B P 2 ′ , 相似比是 r 1 r 2 \therefore \triangle OAP1' \sim \triangle OBP2', 相似比是\frac {r_1}{r_2} ∴△OAP1′∼△OBP2′,相似比是r2r1
P1’, P2’ 可以用P1, P2经过一个旋转得到。
P 1 ′ = [ c o s α − s i n α s i n α c o s α ] ⋅ ( P 1 − A ) + A P1' = \begin {bmatrix} cos\alpha&-sin\alpha\\sin\alpha&cos\alpha \end {bmatrix}\cdot (P1-A)+A P1′=[cosαsinα−sinαcosα]⋅(P1−A)+A
P 2 ′ = [ c o s α − s i n α s i n α c o s α ] ⋅ ( P 2 − B ) + B P2' = \begin {bmatrix} cos\alpha&-sin\alpha\\sin\alpha&cos\alpha \end {bmatrix}\cdot (P2-B)+B P2′=[cosαsinα−sinαcosα]⋅(P2−B)+B
另一边的公切线,相当于是逆时针旋转
P 1 ′ = [ c o s α s i n α − s i n α c o s α ] ⋅ ( P 1 − A ) + A P1' = \begin {bmatrix} cos\alpha&sin\alpha\\-sin\alpha&cos\alpha \end {bmatrix}\cdot (P1-A)+A P1′=[cosα−sinαsinαcosα]⋅(P1−A)+A
P 2 ′ = [ c o s α s i n α − s i n α c o s α ] ⋅ ( P 2 − B ) + B P2' = \begin {bmatrix} cos\alpha&sin\alpha\\-sin\alpha&cos\alpha \end {bmatrix}\cdot (P2-B)+B P2′=[cosα−sinαsinαcosα]⋅(P2−B)+B
通过相似三角形可以解出OA
c o s α = r 1 O A , s i n α = 1 − s i n 2 α cos\alpha =\frac {r_1}{OA}, sin\alpha = \sqrt{1-sin^2\alpha} cosα=OAr1,sinα=1−sin2α
代码实现
#include本人码农,希望通过自己的分享,让大家更容易学懂计算机知识。
![]()