VGG网络
目录
一、结构
二、感受野
三、知识点
1. *与**为参数时的意思
2. 关于torch.flatten
3. torch.max与torch.argmax的区别
四、代码
五、结果
一、结构
图片出自于:VERY DEEP CONVOLUTIONAL NETWORKS FOR LARGE-SCALE IMAGE RECOGNITION 这篇文献。
Conv:stride=1 padding=1(对于3×3的卷积核来说,得到的特征图长宽不变)
maxpool:size=2 stride=2
本文使用D配置
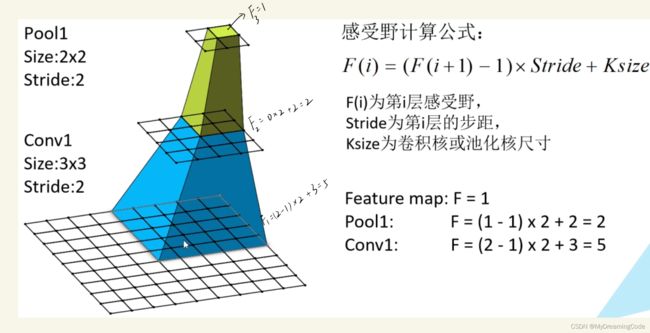
二、感受野
神经元感受野的值越大,意味着能够接触到原始图像的范围也就越大,可能蕴含更为全局,语义层次更高的特征。
感受野:输出feature map上的一个单元对应于输入层上的区域大小。
图片出自:b站up主 霹雳吧啦Wz
https://github.com/WZMIAOMIAO/deep-learning-for-image-processing/tree/master/pytorch_classification
感受野计算公式(反向推):F(i) = (F(i+1) - 1) × Stride + Ksize
F(i):第i层的感受野
Stride:第i层的步距
Ksize:卷积核或池化核尺寸
通过堆叠多个3×3卷积核来代替大尺度卷积核,它们既有相同的感受野,又可以减少所需参数。如:
堆叠两个3×3的卷积核可以替代5×5的卷积核
堆叠三个3×3的卷积核可以替代7×7的卷积核
验证如下:
计算三个3×3的卷积(VGG中,卷积核步距默认为1):
Feature map:F4 = 1(第四个特征图上的一个单元)
Conv3×3(3):F3 = (1-1)×1+3=3,即 3×3
Conv3×3(2):F2 = (3-1)×1+3=5,即 5×5
Conv3×3(1):F1 = (5-1)×1+3=7,即 7×7
参数(设输入输出的通道数为C):
三个3×3的卷积核所需参数:
3×3×C×C+3×3×C×C+3×3×C×C=27C^2
一个7×7的卷积核所需参数:
7×7×C×C=49C^2
很明显使用多个小卷积核堆叠在一起,比使用一个大卷积核所需要的参数少。
三、知识点
1. *与**为参数时的意思
传递参数:
*:对list进行解包,以“位置传参”的形式传递参数
**:对dict进行解包,以”关键字传参“的形式传递参数
接收参数:
*:对list打包,把多个传进来的“位置参数”收集到一个元组中,将元组赋值给args变量
**:对dict打包,把多个传进来的“关键字参数”收集到一个字典中,将字典赋值给kwargs变量
model.py:make_features中的features为列表,但是通过*传递给nn.Sequential,参数以元组的形式被接收。
test.py
def fun(**kwargs):
print(kwargs)
obj = {
'name': 'zs',
'age': 18
}
fun(**obj) # {'name': 'zs', 'age': 18}2. 关于torch.flatten
start_dim为从哪一维度进行展平,默认从第0度开始。
import torch
# [batch,value]
data = [[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9]]
print(torch.flatten(torch.Tensor(data), start_dim=1)) # 从value这一维度展平
# tensor([[1., 2., 3.],
# [4., 5., 6.],
# [7., 8., 9.]])
print(torch.flatten(torch.Tensor(data), start_dim=0)) # 从batch这一维度展平
# tensor([1., 2., 3., 4., 5., 6., 7., 8., 9.])
3. torch.max与torch.argmax的区别
import torch
data = [[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 23, 43, 54, 4], [2, 21, 3, 423, 54, 667, 1, 23, 4]]
data_tensor = torch.Tensor(data)
print(torch.max(data_tensor, dim=1))
# torch.return_types.max(
# values=tensor([ 54., 667.]),
# indices=tensor([7, 5]))
print(torch.argmax(data_tensor, dim=1)) # tensor([7, 5])
print(torch.max(data_tensor, dim=1)[1]) # tensor([7, 5])四、代码
官方的vgg权重下载:
'vgg11': 'https://download.pytorch.org/models/vgg11-bbd30ac9.pth',
'vgg13': 'https://download.pytorch.org/models/vgg13-c768596a.pth',
'vgg16': 'https://download.pytorch.org/models/vgg16-397923af.pth',
'vgg19': 'https://download.pytorch.org/models/vgg19-dcbb9e9d.pth'
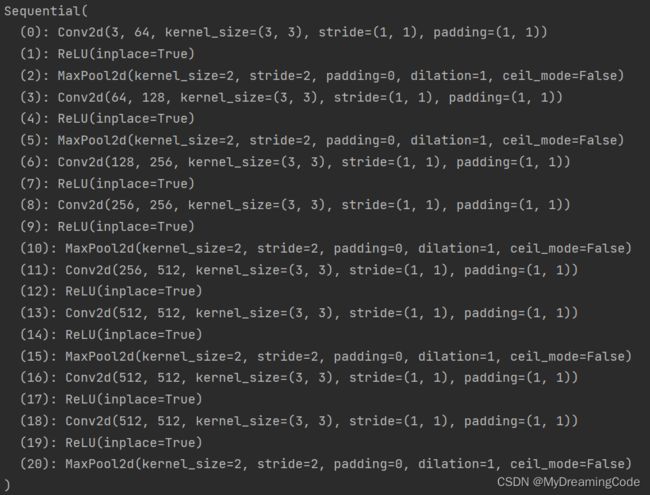
model.py
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
class VGG(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, features, num_classes=1000, init_weights=False):
super(VGG, self).__init__()
# 特征层
self.features = features
# 分类层
self.classifier = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(7 * 7 * 512, 4096),
nn.ReLU(True),
nn.Dropout(p=0.5),
nn.Linear(4096, 4096),
nn.ReLU(True),
nn.Dropout(p=0.5),
nn.Linear(4096, num_classes)
)
if init_weights:
self._initialize_weights()
# 正向传播
def forward(self, x):
# input [N,C,H,W]
x = self.features(x)
# N×512×7×7
x = torch.flatten(x, start_dim=1) # 从channel这一维度开始展平
x = self.classifier(x)
return x
# 初始化权重
def _initialize_weights(self):
for v in self.modules():
if isinstance(v, nn.Conv2d):
nn.init.xavier_uniform_(v.weight)
if v.bias is not None:
nn.init.constant_(v.bias, 0)
if isinstance(v, nn.Linear):
nn.init.xavier_uniform_(v.weight)
if v.bias is not None:
nn.init.constant_(v.bias, 0)
# kernel_num、Maxpool
cfgs = {
'vgg11': [64, 'M', 128, 'M', 256, 256, 'M', 512, 512, 'M', 512, 512, 'M'],
'vgg13': [64, 64, 'M', 128, 128, 'M', 256, 256, 'M', 512, 512, 'M', 512, 512, 'M'],
'vgg16': [64, 64, 'M', 128, 128, 'M', 256, 256, 256, 'M', 512, 512, 512, 'M', 512, 512, 512, 'M'],
'vgg19': [64, 64, 'M', 128, 128, 'M', 256, 256, 256, 256, 'M', 512, 512, 512, 512, 'M', 512, 512, 512, 512, 'M']
}
# get features
def make_features(cfg):
features = []
in_channel = 3
for v in cfg:
if v == 'M':
features += [nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2)]
else:
conv2d = nn.Conv2d(in_channel, v, kernel_size=3, padding=1)
features += [conv2d, nn.ReLU(inplace=True)]
in_channel = v
return nn.Sequential(*features)
# return model
def vgg(model_name='vgg16', **kwargs):
assert model_name in cfgs, "Warning:{} is not in cfgs dict!".format(model_name)
cfg = cfgs[model_name]
model = VGG(make_features(cfg), **kwargs)
return model
train.py
import os
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim as optim
from torchvision import transforms, datasets
import json
from model import vgg
from tqdm import tqdm
def main():
device = torch.device('cuda:0' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
data_transform = {
'train': transforms.Compose([
transforms.RandomResizedCrop(224),
transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize((0.5, 0.5, 0.5), (0.5, 0.5, 0.5))
]),
'val': transforms.Compose([
transforms.Resize((224, 224)),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize((0.5, 0.5, 0.5), (0.5, 0.5, 0.5))
])
}
# get file path
data_root = os.path.abspath(os.getcwd())
image_path = os.path.join(data_root, 'data_set', 'flower_data')
assert os.path.exists(image_path), 'Path:{} is not exist!'.format(image_path)
# get dataset
train_dataset = datasets.ImageFolder(root=os.path.join(image_path, 'train'), transform=data_transform['train'])
train_num = len(train_dataset)
val_dataset = datasets.ImageFolder(root=os.path.join(image_path, 'val'), transform=data_transform['val'])
val_num = len(val_dataset)
# save classes
flower_list = train_dataset.class_to_idx
class_dict = dict((v, k) for k, v in flower_list.items())
json_str = json.dumps(class_dict, indent=4)
with open('class_indices.json', 'w') as file:
file.write(json_str)
# get dataloader
batch_size = 32
train_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(train_dataset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True, num_workers=0)
val_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(val_dataset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=False, num_workers=0)
print('using {} images for training, {} images for validation'.format(train_num, val_num))
# create model
model_name = 'vgg16'
net = vgg(model_name, num_classes=5, init_weights=True)
net.to(device)
loss_function = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = optim.Adam(net.parameters(), lr=0.0001)
epochs = 20
best_acc = 0.0
save_path = './{}Net.pth'.format(model_name)
train_steps = len(train_loader)
for epoch in range(epochs):
# train
net.train()
epoch_loss = 0.0
train_bar = tqdm(train_loader)
for step, data in enumerate(train_bar):
images, labels = data
optimizer.zero_grad()
outputs = net(images.to(device))
loss = loss_function(outputs, labels.to(device))
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
# print statistics
epoch_loss += loss.item()
train_bar.desc = 'train epoch[{}/{}] loss:{:.3f}'.format(epoch + 1, epochs, epoch_loss)
# validate
net.eval()
acc = 0.0
with torch.no_grad():
val_bar = tqdm(val_loader)
for val in val_bar:
val_images, val_labels = valpen
outputs_val = net(val_images.to(device))
predict_y = torch.argmax(outputs_val, dim=1)
acc += torch.eq(predict_y, val_labels.to(device)).sum().item()
val_acc = acc / val_num
print('[epoch %d] train loss:%.3f val_accuracy:%.3f' % (epoch + 1, epoch_loss / train_steps, val_acc))
if val_acc > best_acc:
best_acc = val_acc
torch.save(net.state_dict(), save_path)
print('Train finished!')
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
class_indices.json
{
"0": "daisy",
"1": "dandelion",
"2": "roses",
"3": "sunflowers",
"4": "tulips"
}predict.py
import os
import torch
import torchvision
import torchvision.transforms as transforms
from PIL import Image
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import json
from model import vgg
def main():
device = torch.device('cuda:0' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
data_transform = transforms.Compose([
transforms.Resize((224, 224)),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize((0.5, 0.5, 0.5), (0.5, 0.5, 0.5))
])
# load image
img_path = './1.jpg'
assert os.path.exists(img_path), 'img_path:{} is not exist!'.format(img_path)
img = Image.open(img_path)
plt.imshow(img)
# [N,C,H,W]
img = data_transform(img)
img = torch.unsqueeze(img, dim=0)
# read class_dict
json_path = './class_indices.json'
assert os.path.exists(json_path), 'json path:{} is not exist!'.format(json_path)
with open(json_path, 'r') as file:
class_dict = json.load(file)
# create model
model = vgg(model_name='vgg16', num_classes=5).to(device)
# load weights
weight_path = './vgg16Net.pth'
assert os.path.exists(weight_path), "weight path:{} is not exist!".format(weight_path)
model.load_state_dict(torch.load(weight_path, map_location=device))
# predict
model.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
output = torch.squeeze(model(img.to(device))).cpu()
predict = torch.softmax(output, dim=0)
predict_class = torch.argmax(predict).numpy()
print_res = "class: {} probability: {:.3f}".format(class_dict[str(predict_class)], predict[predict_class].numpy())
plt.title(print_res)
for i in range(len(predict)):
print('class: {:10} probability: {:.3f}'.format(class_dict[str(i)], predict[i].numpy()))
plt.show()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()