数仓_Hive全部基础知识点
文章目录
- 1 Hive入门
-
- 1.1 什么是Hive
- 1.2 Hive的优缺点
-
- 1.2.1 优点
- 1.2.2 缺点
- 1.3 Hive架构原理
- 1.4 Hive和数据库的比较
-
- 1.4.1 查询语言
- 1.4.2 数据存储位置
- 1.4.3 数据更新
- 1.4.4 索引
- 1.4.5 执行
- 1.4.6 执行延迟
- 1.4.7 可扩展性
- 1.4.8 数据规模
- 2 Hive安装
-
- 2.1 Hive安装地址
- 2.2 Hive安装部署
- 3 Hive数据类型
-
- 3.1 基本数据类型
- 3.2 集合数据类型
- 3.3 类型转换
- 4 DDL数据定义
-
- 4.1 创建数据库
- 4.2 查询数据库
-
- 4.2.1 显示数据库
- 4.2.2 查看数据库详情
- 4.3 修改数据库
- 4.4 删除数据库
- 4.5 创建表
-
- 4.5.1 管理表
- 4.5.2 外部表
- 4.5.3 管理表与外部表的相互转换
- 4.6 分区表
-
- 4.6.1 分区表基本操作
- 4.6.2 分区表注意事项
- 4.7 修改表
-
- 4.7.1 重命名表
- 4.7.3 增加/修改/替换列信息
- 5 DML数据操作
-
- 5.1 数据导入
-
- 5.1.1 load to table
- 5.1.2 通过查询语句向表中插入数据(insert)
- 5.1.3 查询语句中创建表并加载数据(AS select)
- 5.1.4 创建表时通过Location指定加载数据路径
- 5.1.5 Import 数据到指定Hive表中
- 5.2 数据导出
-
- 5.2.1 Insert导出
- 5.2.2 Hadoop命令导出到本地
- 5.2.3 Hive Shell 命令导出
- 5.2.4 Export导出到HDFS上
- 5.2.5 Sqoop导出
- 6 查询
-
-
- 6.3.1 Group By 语句
- 6.3.2 Having语句
- 6.4 Join语句
-
- 6.4.2 表的别名
- 6.4.3 内连接
- 6.4.4 左外连接
- 6.4.5 右外连接
- 6.4.6 满外连接
- 6.4.7 多表连接
- 6.4.8 笛卡尔积
- 6.4.9 连接谓词中不支持or
- 6.5 排序
-
- 6.5.1 全局排序(Order By)
- 6.5.2 按照别名排序
- 6.5.3 多个列排序
- 6.5.4 每个MapReduce内部排序(Sort By)
- 6.5.5 分区排序(Distribute By)
- 6.5.6 Cluster By
- 6.6 分桶及抽样查询
-
- 6.6.1 分桶表数据存储
- 6.6.2 分桶的抽样查询
- 6.7 其他常用查询函数
-
- 6.7.1 空字段赋值
- 6.7.2 CASE WHEN
- 6.7.3 行转列
- 6.7.4 列转行
- 6.7.5 窗口函数
- 6.7.6 OLAP函数
-
- GROUPING SETS
- CUBE
- ROLLUP
-
1 Hive入门
1.1 什么是Hive
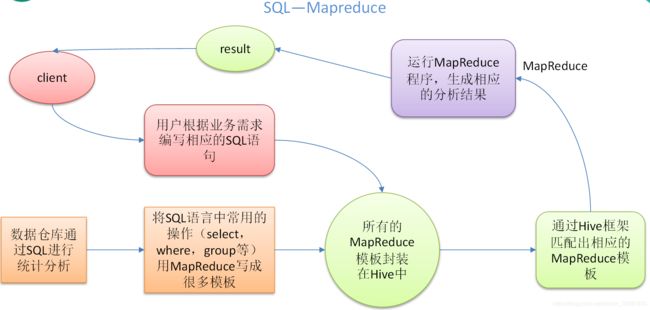
Hive:由Facebook开源用于解决海量结构化日志的数据统计。
Hive是基于Hadoop的一个数据仓库工具,可以将结构化的数据文件映射为一张表,并提供类SQL查询功能。
本质是:将HQL转化成MapReduce程序
1.2 Hive的优缺点
1.2.1 优点
- 操作接口采用类SQL语法,提供快速开发的能力(简单、容易上手)。
- 避免了去写MapReduce,减少开发人员的学习成本。
- Hive的执行延迟比较高,因此Hive常用于数据分析,对实时性要求不高的场合。
- Hive优势在于处理大数据,对于处理小数据没有优势,因为Hive的执行延迟比较高。
- Hive支持用户自定义函数,用户可以根据自己的需求来实现自己的函数。
1.2.2 缺点
1.Hive的HQL表达能力有限
(1)迭代式算法无法表达
(2)数据挖掘方面不擅长
2.Hive的效率比较低
(1)Hive自动生成的MapReduce作业,通常情况下不够智能化
(2)Hive调优比较困难,粒度较粗
1.3 Hive架构原理
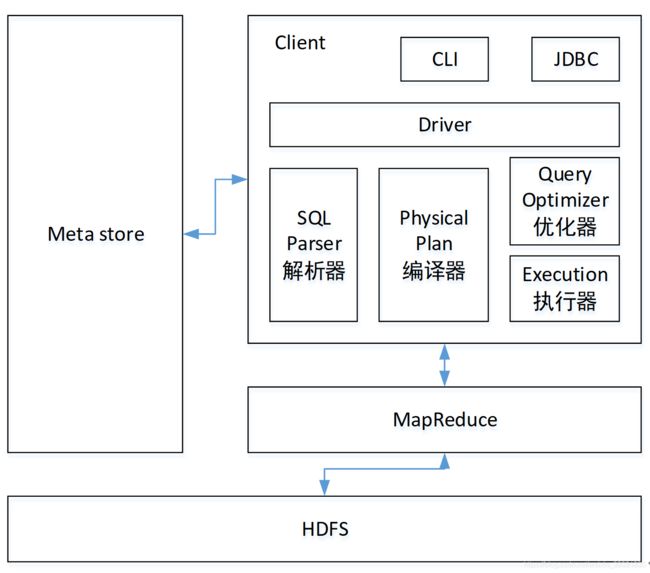
1.用户接口:Client
CLI(hive shell)、JDBC/ODBC(java访问hive)、WEBUI(浏览器访问hive)
2.元数据:Metastore
元数据包括:表名、表所属的数据库(默认是default)、表的拥有者、列/分区字段、表的类型(是否是外部表)、表的数据所在目录等;
默认存储在自带的derby数据库中,推荐使用MySQL存储Metastore
3.Hadoop
使用HDFS进行存储,使用MapReduce进行计算。
4.驱动器:Driver
(1)解析器(SQL Parser):将SQL字符串转换成抽象语法树AST,这一步一般都用第三方工具库完成,比如antlr;对AST进行语法分析,比如表是否存在、字段是否存在、SQL语义是否有误。
(2)编译器(Physical Plan):将AST编译生成逻辑执行计划。
(3)优化器(Query Optimizer):对逻辑执行计划进行优化。
(4)执行器(Execution):把逻辑执行计划转换成可以运行的物理计划。对于Hive来说,就是MR/Spark。
1.4 Hive和数据库的比较
由于 Hive 采用了类似SQL 的查询语言 HQL(Hive Query Language),因此很容易将 Hive 理解为数据库。其实从结构上来看,Hive 和数据库除了拥有类似的查询语言,再无类似之处。本文将从多个方面来阐述 Hive 和数据库的差异。数据库可以用在 Online 的应用中,但是Hive 是为数据仓库而设计的,清楚这一点,有助于从应用角度理解 Hive 的特性。
1.4.1 查询语言
由于SQL被广泛的应用在数据仓库中,因此,专门针对Hive的特性设计了类SQL的查询语言HQL。熟悉SQL开发的开发者可以很方便的使用Hive进行开发。
1.4.2 数据存储位置
Hive 是建立在 Hadoop 之上的,所有 Hive 的数据都是存储在 HDFS 中的。而数据库则可以将数据保存在块设备或者本地文件系统中。
1.4.3 数据更新
由于Hive是针对数据仓库应用设计的,而数据仓库的内容是读多写少的。因此,Hive中不建议对数据的改写,所有的数据都是在加载的时候确定好的。而数据库中的数据通常是需要经常进行修改的,因此可以使用 INSERT INTO … VALUES 添加数据,使用 UPDATE … SET修改数据。
1.4.4 索引
Hive在加载数据的过程中不会对数据进行任何处理,甚至不会对数据进行扫描,因此也没有对数据中的某些Key建立索引。Hive要访问数据中满足条件的特定值时,需要暴力扫描整个数据,因此访问延迟较高。由于 MapReduce 的引入, Hive 可以并行访问数据,因此即使没有索引,对于大数据量的访问,Hive 仍然可以体现出优势。数据库中,通常会针对一个或者几个列建立索引,因此对于少量的特定条件的数据的访问,数据库可以有很高的效率,较低的延迟。由于数据的访问延迟较高,决定了 Hive 不适合在线数据查询。
1.4.5 执行
Hive中大多数查询的执行是通过 Hadoop 提供的 MapReduce 来实现的。而数据库通常有自己的执行引擎。
1.4.6 执行延迟
Hive 在查询数据的时候,由于没有索引,需要扫描整个表,因此延迟较高。另外一个导致 Hive 执行延迟高的因素是 MapReduce框架。由于MapReduce 本身具有较高的延迟,因此在利用MapReduce 执行Hive查询时,也会有较高的延迟。相对的,数据库的执行延迟较低。当然,这个低是有条件的,即数据规模较小,当数据规模大到超过数据库的处理能力的时候,Hive的并行计算显然能体现出优势。
1.4.7 可扩展性
由于Hive是建立在Hadoop之上的,因此Hive的可扩展性是和Hadoop的可扩展性是一致的(世界上最大的Hadoop 集群在 Yahoo!,2009年的规模在4000 台节点左右)。而数据库由于 ACID 语义的严格限制,扩展行非常有限。目前最先进的并行数据库 Oracle 在理论上的扩展能力也只有100台左右。
1.4.8 数据规模
由于Hive建立在集群上并可以利用MapReduce进行并行计算,因此可以支持很大规模的数据;对应的,数据库可以支持的数据规模较小。
2 Hive安装
2.1 Hive安装地址
1.Hive官网地址
http://hive.apache.org/
2.文档查看地址
https://cwiki.apache.org/confluence/display/Hive/GettingStarted
3.下载地址
http://archive.apache.org/dist/hive/
4.github地址
https://github.com/apache/hive
2.2 Hive安装部署
1.Hive安装及配置
(1)把apache-hive-1.2.1-bin.tar.gz上传到linux的/opt/software目录下
(2)解压apache-hive-1.2.1-bin.tar.gz到/opt/module/目录下面
[atguigu@hadoop102 software]$ tar -zxvf apache-hive-1.2.1-bin.tar.gz -C /opt/module/
(3)修改apache-hive-1.2.1-bin.tar.gz的名称为hive
[atguigu@hadoop102 module]$ mv apache-hive-1.2.1-bin/ hive
(4)修改/opt/module/hive/conf目录下的hive-env.sh.template名称为hive-env.sh
[atguigu@hadoop102 conf]$ mv hive-env.sh.template hive-env.sh
(5)配置hive-env.sh文件
(a)配置HADOOP_HOME路径
export HADOOP_HOME=/opt/module/hadoop-2.7.2
(b)配置HIVE_CONF_DIR路径
export HIVE_CONF_DIR=/opt/module/hive/conf
2.Hadoop集群配置
(1)必须启动hdfs和yarn
[atguigu@hadoop102 hadoop-2.7.2]$ sbin/start-dfs.sh
[atguigu@hadoop103 hadoop-2.7.2]$ sbin/start-yarn.sh
(2)在HDFS上创建/tmp和/user/hive/warehouse两个目录并修改他们的同组权限可写
[atguigu@hadoop102 hadoop-2.7.2]$ bin/hadoop fs -mkdir /tmp
[atguigu@hadoop102 hadoop-2.7.2]$ bin/hadoop fs -mkdir -p /user/hive/warehouse
[atguigu@hadoop102 hadoop-2.7.2]$ bin/hadoop fs -chmod g+w /tmp
[atguigu@hadoop102 hadoop-2.7.2]$ bin/hadoop fs -chmod g+w /user/hive/warehouse
3.Hive基本操作
(1)启动hive
[atguigu@hadoop102 hive]$ bin/hive
(2)查看数据库
hive> show databases;
(3)打开默认数据库
hive> use default;
(4)显示default数据库中的表
hive> show tables;
(5)创建一张表
hive> create table student(id int, name string);
(6)显示数据库中有几张表
hive> show tables;
(7)查看表的结构
hive> desc student;
(8)向表中插入数据
hive> insert into student values(1000,“ss”);
(9)查询表中数据
hive> select * from student;
(10)退出hive
hive> quit;
3 Hive数据类型
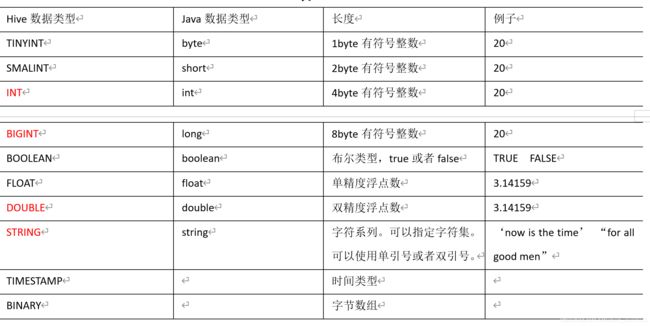
3.1 基本数据类型
3.2 集合数据类型
struct
和C语言中的struct类似,都可以通过“点”符号访问元素内容。
例如,struct(first string,last string)都可以通过字段.first来引用
map
map是一对键值对元素组合,使用数组可以
first:John last:Doe
可以通过['last']访问获取最后一个元素
array
具有相同类型和名称的变量的集合, 数组的元素 编号从0开始
['John','Doe'] [1]可以获取第二个元素
=========================================================
操作实例
- 数据结构
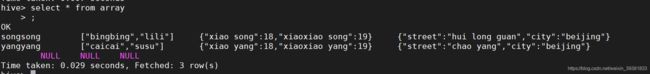
用json表示数据结构为:
{
"name": "songsong",
"friends": ["bingbing" , "lili"] , //列表Array,
"children": { //键值Map,
"xiao song": 18 ,
"xiaoxiao song": 19
}
"address": { //结构Struct,
"street": "hui long guan" ,
"city": "beijing"
}
}
- 创建test.txt
songsong,bingbing_lili,xiao song:18_xiaoxiao song:19,hui long guan_beijing
yangyang,caicai_susu,xiao yang:18_xiaoxiao yang:19,chao yang_beijing
action:Map struct array 里的元素间关系都可以用一个字符表示,这里用“_”
- 创建表
create table array(
name string,
friends array<string>,
children map<string, int>,
address struct<street:string, city:string>
)
row format delimited fields terminated by ','
collection items terminated by '_'
map keys terminated by ':'
lines terminated by '\n';
row format delimited fields terminated by ' , ' --列分隔符
collection items terminated by ' , ' -- map struct 和 array 的分隔符
map key terminated by ' , ' -- map中key和value的分隔符
lines terminated by ' \n ' -- 行分隔符
- 导入文本数据到表
load data local inpath '/data/hivedata/test.txt' into table array;
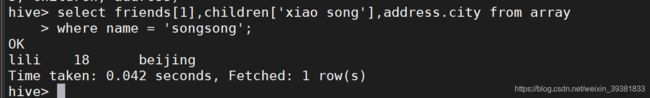
- 访问三种集合里面的数据
select friends[1],children['xiao song'],address.city from array
where name = 'songsong';
3.3 类型转换
Hive的原子数据类型是可以进行隐式转换的,类似于Java的类型转换,例如某表达式使用INT类型,TINYINT会自动转换为INT类型,但是Hive不会进行反向转化,例如,某表达式使用TINYINT类型,INT不会自动转换为TINYINT类型,它会返回错误,除非使用CAST操作。
- 隐式类型转换规则如下
- 任何证书类型都可以转换成为一个范围更广的类型,tinyint —> int , int —> bigint
- 所有整数类型,Float 和 String类型都可以隐式转换成为double
- tinyint 、 smallint 、 int 都可以转换成为float
- Boolean 不可以转
- 可以使用cast操作进行数据类型转换
cast('1',as int) 将把字符串‘1’转换成整数1;
强转失败将返回NULL
4 DDL数据定义
4.1 创建数据库
- 创建一个数据库,数据库默认在HDFS上存储路径为
/usr/hive/warehouse/*.db
- 避免数据库已经存在 增加if not exists 判断
create database if not exits db_hive
- 指定存放地址
create database db_hive2 location '/db_hvie2.db';
4.2 查询数据库
4.2.1 显示数据库
- 显示数据库
show databases;
- 过滤显示数据库
show databases like 'db_hive';
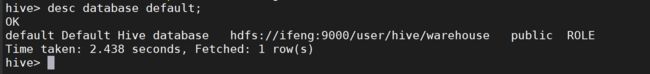
4.2.2 查看数据库详情
desc database default;
desc database extended default;
4.3 修改数据库
alter database : 为某个数据库的dbproperties设置键值对属性
数据库其他元数据信息都是不可更改的,包括数据库名 & 数据库目录
alter database db_hive set dbproperties('createtime'='20210731')
4.4 删除数据库
- 删除空数据库
hive>drop database db_hive2;
- 如果删除的数据库不存在,最好采用 if exists判断数据库是否存在
hive> drop database db_hive;
FAILED: SemanticException [Error 10072]: Database does not exist: db_hive
hive> drop database if exists db_hive2;
- 如果数据库不为空,可以采用cascade命令,强制删除
hive> drop database db_hive;
FAILED: Execution Error, return code 1 from org.apache.hadoop.hive.ql.exec.DDLTask. InvalidOperationException(message:Database db_hive is not empty. One or more tables exist.)
hive> drop database db_hive cascade;
4.5 创建表
- 创建表
CREATE [EXTERNAL] TABLE [IF NOT EXISTS] table_name
[(col_name data_type [COMMENT col_comment], ...)]
[COMMENT table_comment]
[PARTITIONED BY (col_name data_type [COMMENT col_comment], ...)]
[CLUSTERED BY (col_name, col_name, ...)
[SORTED BY (col_name [ASC|DESC], ...)] INTO num_buckets BUCKETS]
[ROW FORMAT row_format]
[STORED AS file_format]
[LOCATION hdfs_path]
- 字段解释说明
-
crate table , if not exits选项可以忽略这个异常
-
external : 外部表 ,建表的同时指定一个指向实际数据的路径(location).Hive创建内部表时,会将数据移动到数据仓库指向的路径;若创建外部表,仅记录数据所在的路径,不对数据的位置做任何改变。
-
comment:注解
-
partitioned by : 分区表
-
clustered by : 分桶表
-
ROW FORMAT
DELIMITED [FIELDS TERMINATED BY char] [COLLECTION ITEMS TERMINATED BY char]
[MAP KEYS TERMINATED BY char] [LINES TERMINATED BY char]
| SERDE serde_name [WITH SERDEPROPERTIES (property_name=property_value, property_name=property_value, ...)]
用户在建表的时候可以自定义SerDe或者使用自带的SerDe。如果没有指定ROW FORMAT 或者ROW FORMAT DELIMITED,将会使用自带的SerDe。在建表的时候,用户还需要为表指定列,用户在指定表的列的同时也会指定自定义的SerDe,Hive通过SerDe确定表的具体的列的数据。
SerDe是Serialize/Deserilize的简称,目的是用于序列化和反序列化。
- strored as 指定存储文件类型
常用的存储类型:sequencefile(二进制序列文件)
textfile(文本)
rcfile(列式存储格式文件)
文件数据是纯文本,可以使用stored as textfiel
数据需要压缩 使用 stored as sequencefile
- location : 指定HDFS存储位置
- like 允许用户复制现有表结构,但不能复制数据
4.5.1 管理表
1.理论
默认创建的表都是所谓的管理表,有时也被称为内部表。因为这种表,Hive会(或多或少地)控制着数据的生命周期。Hive默认情况下会将这些表的数据存储在由配置项hive.metastore.warehouse.dir(例如,/user/hive/warehouse)所定义的目录的子目录下。 当我们删除一个管理表时,Hive也会删除这个表中数据。管理表不适合和其他工具共享数据。
2.案例实操
(1)普通创建表
create table if not exits student2(
id int,name string
)
row format delimited fileds terminated by '\t'
stored as textfile
location '/user/hive/warehouse/student2';
(2)根据查询结果创建表(查询的结果会添加到新创建的表中)
create table if not exists student3 as select id, name from student;
(3)根据已经存在的表结构创建表
create table if not exists student4 like student;
(4)查询表的类型
hive (default)> desc formatted student2;
Table Type: MANAGED_TABLE
4.5.2 外部表
1.理论
因为表是外部表,所以Hive并非认为其完全拥有这份数据。删除该表并不会删除掉这份数据,不过描述表的元数据信息会被删除掉。
2.管理表和外部表的使用场景
每天将收集到的网站日志定期流入HDFS文本文件。在外部表(原始日志表)的基础上做大量的统计分析,用到的中间表、结果表使用内部表存储,数据通过SELECT+INSERT进入内部表。
3.案例实操
创建 部门和员工外部表
- 建表语句
--部门表
create external table if not exists default.dept(
deptno int,
dname string,
loc int
)
row format delimited fields terminated by '\t';
--员工表
create external table if not exists default.emp(
empno int,
cname string,
job string,
mgr int,
hiredate string,
sal double,
comm double,
deptno int
)
row format delimited fields terminated by '\t';
- 查看创建的表
show tables;
- 导入数据
load data local inpath '/data/hivedata/dept.txt' into table dept;
load data local inpath '/data/hivedata/emp.txt' into table emp;
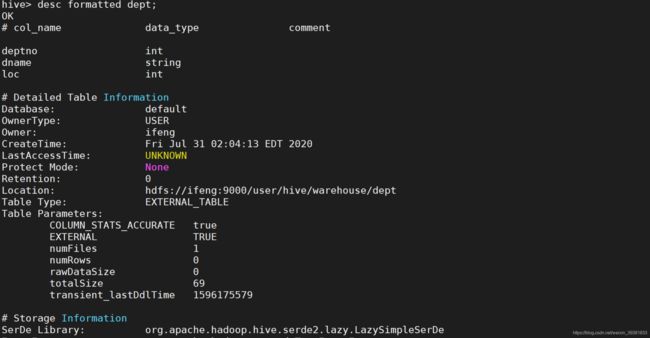
- 查看表格式化数据
desc formatted dept;
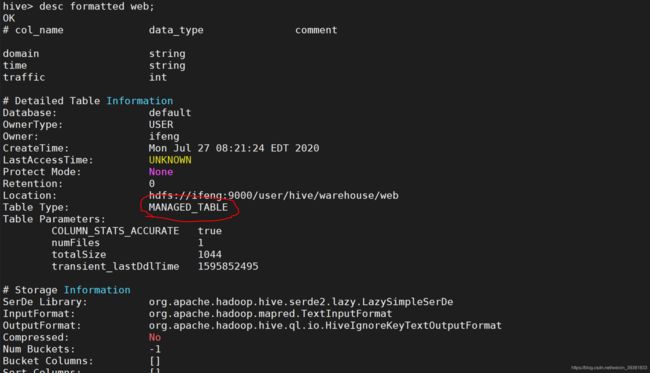
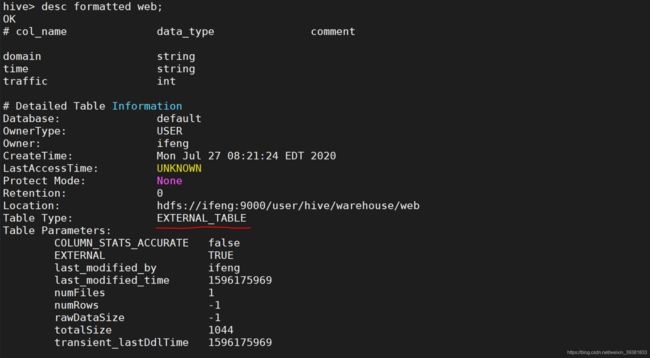
4.5.3 管理表与外部表的相互转换
- 查询表的类型
desc formatted web;
alter table web set tblproperties('EXTERNAL'='TRUE');
alter table web set tblproperties('external'='false');
4.6 分区表
分区表实际上就是对应一个HDFS文件系统上的独立的文件夹,该文件夹下是该分区所有的数据文件。Hive中的分区就是分区目录,把一个大数据集根据业务需要切分成小的数据集。再通过where子句中的表达式选择查询所需的指定的分区,提高效率。
4.6.1 分区表基本操作
1.引入分区表(需要根据日期对日志进行管理)
/user/hive/warehouse/log_partition/20170702/20170702.log
/user/hive/warehouse/log_partition/20170703/20170703.log
/user/hive/warehouse/log_partition/20170704/20170704.log
2.创建分区表语法
create table dept partition(
deptno int,dname string,loc string
)
partitioned by (month string)
row format delimited fields terminated by '\t';
3.加载数据到分区表中
hive (default)> load data local inpath '/opt/module/datas/dept.txt' into table default.dept_partition partition(month='201709');
hive (default)> load data local inpath '/opt/module/datas/dept.txt' into table default.dept_partition partition(month='201708');
hive (default)> load data local inpath '/opt/module/datas/dept.txt' into table default.dept_partition partition(month='201707’);
4.查询分区表中数据
单分区查询
hive (default)> select * from dept_partition where month='201709';
多分区联合查询
hive (default)> select * from dept_partition where month='201709'
union
select * from dept_partition where month='201708'
union
select * from dept_partition where month='201707';
_u3.deptno _u3.dname _u3.loc _u3.month
10 ACCOUNTING NEW YORK 201707
10 ACCOUNTING NEW YORK 201708
10 ACCOUNTING NEW YORK 201709
20 RESEARCH DALLAS 201707
20 RESEARCH DALLAS 201708
20 RESEARCH DALLAS 201709
30 SALES CHICAGO 201707
30 SALES CHICAGO 201708
30 SALES CHICAGO 201709
40 OPERATIONS BOSTON 201707
40 OPERATIONS BOSTON 201708
40 OPERATIONS BOSTON 201709
5.增加分区
创建单个分区
hive (default)> alter table dept_partition add partition(month='201706') ;
同时创建多个分区
hive (default)> alter table dept_partition add partition(month='201705') partition(month='201704');
6.删除分区
删除单个分区
hive (default)> alter table dept_partition drop partition (month='201704');
同时删除多个分区
hive (default)> alter table dept_partition drop partition (month='201705'), partition (month='201706');
7.查看分区表有多少分区
hive> show partitions dept_partition;
8.查看分区表结构
hive> desc formatted dept_partition;
Partition Information
col_name data_type comment
month string
4.6.2 分区表注意事项
- 创建二级分区表
create table dept_partition2(
deptno int,dname,string,loc string
)
partition by (month string,day string)
row format delimited fields terminated by '\t'
- 正常的加载数据
(1)加载数据到二级分区表中
hive (default)> load data local inpath '/opt/module/datas/dept.txt' into table
default.dept_partition2 partition(month='201709', day='13');
(2)查询分区数据
hive (default)> select * from dept_partition2 where month='201709' and day='13';
- 把数据直接上传到分区目录上,让分区表和数据产生关联的三种放生
(1)方式一:上传数据后修复
上传数据
hive (default)> dfs -mkdir -p
/user/hive/warehouse/dept_partition2/month=201709/day=12;
hive (default)> dfs -put /opt/module/datas/dept.txt /user/hive/warehouse/dept_partition2/month=201709/day=12;
查询数据(查询不到刚上传的数据)
hive (default)> select * from dept_partition2 where month='201709' and day='12';
执行修复命令
hive> msck repair table dept_partition2;
再次查询数据
hive (default)> select * from dept_partition2 where month='201709' and day='12';
(2)方式二:上传数据后添加分区
上传数据
hive (default)> dfs -mkdir -p
/user/hive/warehouse/dept_partition2/month=201709/day=11;
hive (default)> dfs -put /opt/module/datas/dept.txt /user/hive/warehouse/dept_partition2/month=201709/day=11;
执行添加分区
hive (default)> alter table dept_partition2 add partition(month='201709',
day='11');
查询数据
hive (default)> select * from dept_partition2 where month='201709' and day='11';
(3)方式三:创建文件夹后load数据到分区
创建目录
hive (default)> dfs -mkdir -p
/user/hive/warehouse/dept_partition2/month=201709/day=10;
上传数据
hive (default)> load data local inpath '/opt/module/datas/dept.txt' into table
dept_partition2 partition(month='201709',day='10');
查询数据
hive (default)> select * from dept_partition2 where month='201709' and day='10';
4.7 修改表
4.7.1 重命名表
alter table table_name rename to new_table_name;
4.7.3 增加/修改/替换列信息
1.语法
更新列
ALTER TABLE table_name CHANGE [COLUMN] col_old_name col_new_name column_type [COMMENT col_comment] [FIRST|AFTER column_name]
增加和替换列
ALTER TABLE table_name ADD|REPLACE COLUMNS (col_name data_type [COMMENT col_comment], ...)
注:ADD是代表新增一字段,字段位置在所有列后面(partition列前),REPLACE则是表示替换表中所有字段。
2.实操案例
(1)查询表结构
hive> desc dept_partition;
(2)添加列
hive (default)> alter table dept_partition add columns(deptdesc string);
(3)查询表结构
hive> desc dept_partition;
(4)更新列
hive (default)> alter table dept_partition change column deptdesc desc int;
(5)查询表结构
hive> desc dept_partition;
(6)替换列
hive (default)> alter table dept_partition replace columns(deptno string, dname
string, loc string);
(7)查询表结构
hive> desc dept_partition;
5 DML数据操作
5.1 数据导入
5.1.1 load to table
load data [local] inpath '/data/hivadata/test.txt' overwrite | into table student [partition(partcol1=val1,...)];
- load data:表示加载数据
- local:从本地加载
- inpath:加载数据路径
- overwriter:覆盖表中已有的数据,否则表示追加
- partition : 上传到指定分区
5.1.2 通过查询语句向表中插入数据(insert)
- 创建一张分区表
create table sutdent(id int,name string) partitioned by (month string)
row format delimited fields terminated by '\t';
- 基本数据插入
insert into table student partition(month='201709') value(1,'ifeng');
- 基本模式插入
insert overwrite table student partition(month='201709')
- 多种模式插入
from student
insert overwriter table student partitionon(month = '201921565')
5.1.3 查询语句中创建表并加载数据(AS select)
create table if not exists student3
as select id,name from student;
5.1.4 创建表时通过Location指定加载数据路径
- 创建表,指定在hdfs上的位置
create table if not exists student5(id int,name string)
row format delimited fields terminated by '\t'
location '/data/test.txt';
2) 上传数据到HDFS
dfs -put /opt/student.txt
/user/hive/warehouse/student5;
5.1.5 Import 数据到指定Hive表中
注意:先用export导出后,再将数据导入
import table student2 partition(month='20200809') from
'/user/hive/warehouse/export/student'
5.2 数据导出
5.2.1 Insert导出
1.将查询的结果导出到本地
hive (default)> insert overwrite local directory '/opt/module/datas/export/student'
select * from student;
2.将查询的结果格式化导出到本地
hive(default)>insert overwrite local directory '/opt/module/datas/export/student1'
ROW FORMAT DELIMITED FIELDS TERMINATED BY '\t' select * from student;
3.将查询的结果导出到HDFS上(没有local)
hive (default)> insert overwrite directory '/user/atguigu/student2'
ROW FORMAT DELIMITED FIELDS TERMINATED BY '\t'
select * from student;
5.2.2 Hadoop命令导出到本地
hive (default)> dfs -get /user/hive/warehouse/student/month=201709/000000_0
/opt/module/datas/export/student3.txt;
5.2.3 Hive Shell 命令导出
基本语法:(hive -f/-e 执行语句或者脚本 > file)
[atguigu@hadoop102 hive]$ bin/hive -e ‘select * from default.student;’ >
/opt/module/datas/export/student4.txt;
5.2.4 Export导出到HDFS上
(defahiveult)> export table default.student to
‘/user/hive/warehouse/export/student’;
5.2.5 Sqoop导出
Sqoop开荒教程
6 查询
https://cwiki.apache.org/confluence/display/Hive/LanguageManual+Select
查询语句语法:
[WITH CommonTableExpression (, CommonTableExpression)*] (Note: Only available
starting with Hive 0.13.0)
SELECT [ALL | DISTINCT] select_expr, select_expr, ...
FROM table_reference
[WHERE where_condition]
[GROUP BY col_list]
[ORDER BY col_list]
[CLUSTER BY col_list
| [DISTRIBUTE BY col_list] [SORT BY col_list]
]
[LIMIT number]
6.3 分组
6.3.1 Group By 语句
Group By 通常回合聚合函数一起使用,按照一个或者多个队列进行分组,然后对每个分组聚合
案例:
- 计算emp表各个部门的平均工资
select t.deptno,avg(t.sal) avg_sak from emp t group by t.deptno;
- 计算emp每个部门每个岗位的最高薪水
select t.deptno,t.jon,max(t.sql) max_sql from emp t group by t.deptno,t.job;
6.3.2 Having语句
- having 与 where不同点
- where针对表中的列发挥作用,查询数据;having针对查询结果中的列发挥作用,筛选数据
- where后面不能跟分组函数
- having只用于group by分组统计
案例
- 求每个部门平均工资
select deptno,avg(asl) from emp group by deptno;
- 求每个部门平均工资 > 2000
select deptno,avg(sal) from emp group by deptno having avg_sql > 2000;
6.4 Join语句
Hive支持通常的SQL JOIN语句,但是只支持等值连接,不支持非等值连接。
案例实操
(1)根据员工表和部门表中的部门编号相等,查询员工编号、员工名称和部门名称;
hive (default)> select e.empno, e.ename, d.deptno, d.dname from emp e join dept d
on e.deptno = d.deptno;
6.4.2 表的别名
1.好处
(1)使用别名可以简化查询。
(2)使用表名前缀可以提高执行效率。
2.案例实操
合并员工表和部门表
hive (default)> select e.empno, e.ename, d.deptno from emp e join dept d on e.deptno
= d.deptno;
6.4.3 内连接
内连接:只有进行连接的两个表中都存在与连接条件相匹配的数据才会被保留下来。
hive (default)> select e.empno, e.ename, d.deptno from emp e join dept d on e.deptno
= d.deptno;
6.4.4 左外连接
左外连接:JOIN操作符左边表中符合WHERE子句的所有记录将会被返回。
hive (default)> select e.empno, e.ename, d.deptno from emp e left join dept d on e.deptno
= d.deptno;
6.4.5 右外连接
右外连接:JOIN操作符右边表中符合WHERE子句的所有记录将会被返回。
hive (default)> select e.empno, e.ename, d.deptno from emp e right join dept d on e.deptno
= d.deptno;
6.4.6 满外连接
满外连接:将会返回所有表中符合WHERE语句条件的所有记录。如果任一表的指定字段没有符合条件的值的话,那么就使用NULL值替代。
hive (default)> select e.empno, e.ename, d.deptno from emp e full join dept d on e.deptno
= d.deptno;
6.4.7 多表连接
注意:连接 n个表,至少需要n-1个连接条件。例如:连接三个表,至少需要两个连接条件。
数据准备
1.创建位置表
create table if not exists default.location(
loc int,
loc_name string
)
row format delimited fields terminated by '\t';
2.导入数据
hive (default)> load data local inpath '/opt/module/datas/location.txt' into table default.location;
3.多表连接查询
hive (default)>SELECT e.ename, d.deptno, l. loc_name
FROM emp e
JOIN dept d
ON d.deptno = e.deptno
JOIN location l
ON d.loc = l.loc;
大多数情况下,Hive会对每对JOIN连接对象启动一个MapReduce任务。本例中会首先启动一个MapReduce job对表e和表d进行连接操作,然后会再启动一个MapReduce job将第一个MapReduce job的输出和表l;进行连接操作。
注意:为什么不是表d和表l先进行连接操作呢?这是因为Hive总是按照从左到右的顺序执行的。
6.4.8 笛卡尔积
1.笛卡尔集会在下面条件下产生
(1)省略连接条件
(2)连接条件无效
(3)所有表中的所有行互相连接
2.案例实操
hive (default)> select empno, dname from emp, dept;
6.4.9 连接谓词中不支持or
hive (default)> select e.empno, e.ename, d.deptno from emp e join dept d on e.deptno
= d.deptno or e.ename=d.ename; 错误的
6.5 排序
6.5.1 全局排序(Order By)
Order By:全局排序,一个Reducer
1.使用 ORDER BY 子句排序
ASC(ascend): 升序(默认)
DESC(descend): 降序
2.ORDER BY 子句在SELECT语句的结尾
3.案例实操
(1)查询员工信息按工资升序排列
hive (default)> select * from emp order by sal;
(2)查询员工信息按工资降序排列
hive (default)> select * from emp order by sal desc;
6.5.2 按照别名排序
按照员工薪水的2倍排序
hive (default)> select ename, sal*2 twosal from emp order by twosal;
6.5.3 多个列排序
按照部门和工资升序排序
hive (default)> select ename, deptno, sal from emp order by deptno, sal ;
6.5.4 每个MapReduce内部排序(Sort By)
Sort By:每个Reducer内部进行排序,对全局结果集来说不是排序。
1.设置reduce个数
hive (default)> set mapreduce.job.reduces=3;
2.查看设置reduce个数
hive (default)> set mapreduce.job.reduces;
3.根据部门编号降序查看员工信息
hive (default)> select * from emp sort by empno desc;
4.将查询结果导入到文件中(按照部门编号降序排序)
hive (default)> insert overwrite local directory '/opt/module/datas/sortby-result'
select * from emp sort by deptno desc;
6.5.5 分区排序(Distribute By)
Distribute By:类似MR中partition,进行分区,结合sort by使用。
注意,Hive要求DISTRIBUTE BY语句要写在SORT BY语句之前。
对于distribute by进行测试,一定要分配多reduce进行处理,否则无法看到distribute by的效果。
案例实操:
(1)先按照部门编号分区,再按照员工编号降序排序。
hive (default)> set mapreduce.job.reduces=3;
hive (default)> insert overwrite local directory '/opt/module/datas/distribute-result' select * from emp distribute by deptno sort by empno desc;
6.5.6 Cluster By
当distribute by和sorts by字段相同时,可以使用cluster by方式。
cluster by除了具有distribute by的功能外还兼具sort by的功能。但是排序只能是升序排序,不能指定排序规则为ASC或者DESC。
1)以下两种写法等价
hive (default)> select * from emp cluster by deptno;
hive (default)> select * from emp distribute by deptno sort by deptno;
注意:按照部门编号分区,不一定就是固定死的数值,可以是20号和30号部门分到一个分区里面去。
6.6 分桶及抽样查询
6.6.1 分桶表数据存储
分区针对的是数据的存储路径
分桶针对的是数据文件
分区提供一个隔离数据和优化查询的便利方式。不过,并非所有的数据集都可形成合理的分区,特别是之前所提到过的要确定合适的划分大小这个疑虑。
分桶是将数据集分解成更容易管理的若干部分的另一个技术。
- 先创建分桶表,通过直接导入数据文件的方式
-- 创建分桶表
create table stu_buck(id int,name string)
clustered by(id)
into 4 buckets
row format delimited fields terminated by '\t';
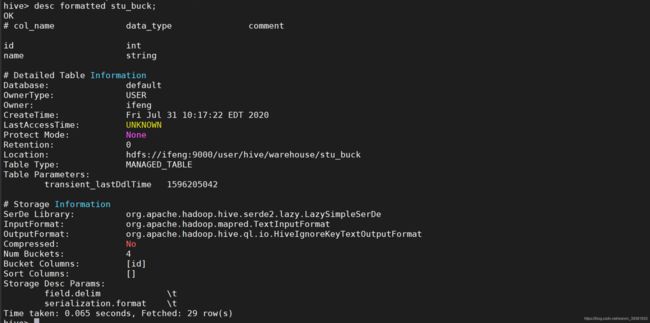
查看表结构
desc formatted stu buck;
load data local inpath '/data/hivedata/student.txt' into table stu_buck;
- 创建分桶表时,数据通过子查询的方式导入
(1)先建一个普通的stu表
create table stu(id int, name string)
row format delimited fields terminated by '\t';
(2)向普通的stu表中导入数据
load data local inpath '/opt/module/datas/student.txt' into table stu;
(3)清空stu_buck表中数据
truncate table stu_buck;
select * from stu_buck;
(4)导入数据到分桶表,通过子查询的方式
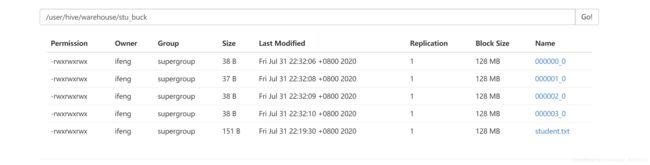
insert into table stu_buck
select id, name from stu;
还是只有一个桶
需要设置一个属性
hive (default)> set hive.enforce.bucketing=true;
hive (default)> set mapreduce.job.reduces=-1;
hive (default)> insert into table stu_buck
select id, name from stu;
6.6.2 分桶的抽样查询
对于非常大的数据集,有时用户需要使用的是一个具有代表性的查询结果而不是全部结果。Hive可以通过对表进行抽样来满足这个需求。
查询表stu_buck中的数据。
hive (default)> select * from stu_buck tablesample(bucket 1 out of 4 on id);
注:tablesample是抽样语句,语法:TABLESAMPLE(BUCKET x OUT OF y) 。
y必须是table总bucket数的倍数或者因子。hive根据y的大小,决定抽样的比例。例如,table总共分了4份,当y=2时,抽取(4/2=)2个bucket的数据,当y=8时,抽取(4/8=)1/2个bucket的数据。
x表示从哪个bucket开始抽取,如果需要取多个分区,以后的分区号为当前分区号加上y。例如,table总bucket数为4,tablesample(bucket 1 out of 2),表示总共抽取(4/2=)2个bucket的数据,抽取第1(x)个和第3(x+y)个bucket的数据。
注意:x的值必须小于等于y的值,否则
FAILED: SemanticException [Error 10061]: Numerator should not be bigger than denominator in sample clause for table stu_buck
6.7 其他常用查询函数
6.7.1 空字段赋值
- 函数说明
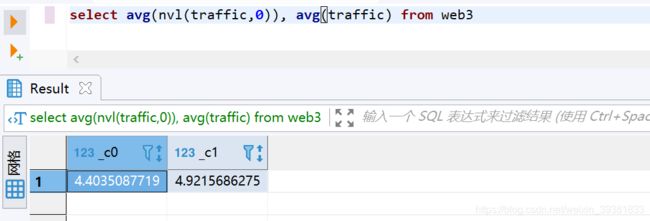
NVL:给值为NULL的数据赋值,它的格式是NVL( string1, replace_with)。它的功能是如果string1为NULL,则NVL函数返回replace_with的值,否则返回string1的值,如果两个参数都为NULL ,则返回NULL。
在处理avg时,null将不参加 需要替换成0
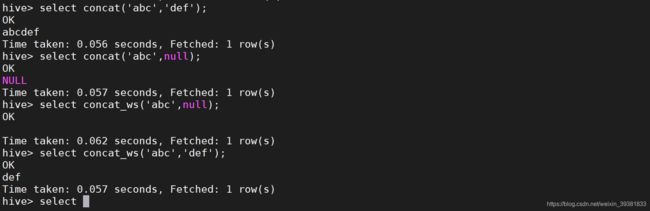
concat(‘abc’,‘def’) = abcdef
concat(‘abc’,‘null’) = null
6.7.2 CASE WHEN
1) 创建表
create table emp_sex(
name string,
dept_id string,
sex string
)
row format delimited fields terminated by '\t';
- 导入数据
vi emp_sex.txt
悟空 A 男
大海 A 男
宋宋 B 男
凤姐 A 女
婷姐 B 女
婷婷 B 女
load data local inpath '/data/datahive/emp_sex.txt' into table emp_sex;
需求:求出不同部门男女个多少人
select
dept_id,
sum(case sex when '男' then 1 else 0 end) male_count,
sum(case sex when '女' then 1 else 0 end) female_count
from
emp_sex
group by
dept_id;
6.7.3 行转列
- 相关函数说明
concat(string A/col,string B/col) : 返回输入字符串连续后的结果
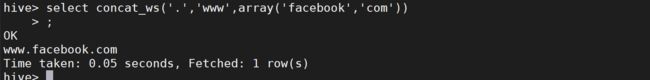
CONCAT_WS(separator, str1, str2,…):它是一个特殊形式的 CONCAT()。第一个参数剩余参数间的分隔符。分隔符可以是与剩余参数一样的字符串。如果分隔符是 NULL,返回值也将为 NULL。这个函数会跳过分隔符参数后的任何 NULL 和空字符串。分隔符将被加到被连接的字符串之间;
COLLECT_SET(col):函数只接受基本数据类型,它的主要作用是将某字段的值进行去重汇总,产生array类型字段。
4.创建本地constellation.txt,导入数据
[atguigu@hadoop102 datas]$ vi constellation.txt
孙悟空 白羊座 A
大海 射手座 A
宋宋 白羊座 B
猪八戒 白羊座 A
凤姐 射手座 A
5.创建hive表并导入数据
create table person_info(
name string,
constellation string,
blood_type string)
row format delimited fields terminated by "\t";
load data local inpath “/opt/module/datas/person_info.txt” into table person_info;
6.按需求查询数据
select
t1.base,
concat_ws('|', collect_set(t1.name)) name
from
(select
name,
concat(constellation, ",", blood_type) base
from
person_info) t1
group by
t1.base;
6.7.4 列转行
- 函数说明
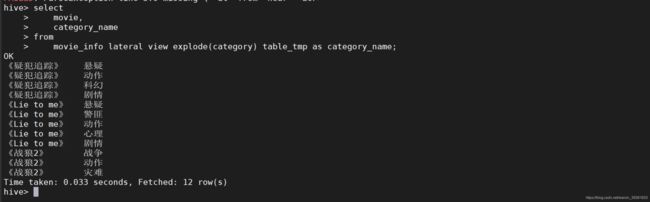
explode(col):将Hive一列中复杂的array‘或者map结构拆成多行
lateral view
用法:lateral view udtf(expression) tableAlias AS columnAlias
解释:用于和split,export 等UDTF一起使用,将一列数据拆分成多个 , 在此基础上可以对拆分后的数据进行聚合
- 案例:分开电影分类
数据准备
vi movie.txt
《疑犯追踪》 悬疑,动作,科幻,剧情
《Lie to me》 悬疑,警匪,动作,心理,剧情
《战狼2》 战争,动作,灾难
创建表并导入数据
create table movie_info(
movie string,
category array<string>)
row format delimited fields terminated by "\t"
collection items terminated by ",";
load data local inpath "/data/hivedata/movie.txt" into table movie_info;
按需查询
select
movie,
category_name
from
movie_info lateral view explode(category) table_tmp as category_name;
6.7.5 窗口函数
- 相关函数说明
over:指定分析函数工作的数据窗口的大小
current now : 当前行
n preceding : 往前N行
n following : 往后N行
unbounded :起点,unbounded preceding 从前面起点 unbounded following 到后面终点
lag(col,n) :往前n行数据
lead(col,n) :往后n行数据
ntile(n) : 把有序分区中的行分发到指定数据的组中
2.数据准备:name,orderdate,cost
jack,2017-01-01,10
tony,2017-01-02,15
jack,2017-02-03,23
tony,2017-01-04,29
jack,2017-01-05,46
jack,2017-04-06,42
tony,2017-01-07,50
jack,2017-01-08,55
mart,2017-04-08,62
mart,2017-04-09,68
neil,2017-05-10,12
mart,2017-04-11,75
neil,2017-06-12,80
mart,2017-04-13,94
3.需求
(1)查询在2017年4月份购买过的顾客及总人数
(2)查询顾客的购买明细及月购买总额
(3)上述的场景,要将cost按照日期进行累加
(4)查询顾客上次的购买时间
(5)查询前20%时间的订单信息
4.创建本地business.txt,导入数据
[atguigu@hadoop102 datas]$ vi business.txt
5.创建hive表并导入数据
create table business(
name string,
orderdate string,
cost int
) ROW FORMAT DELIMITED FIELDS TERMINATED BY ',';
load data local inpath "/opt/module/datas/business.txt" into table business;
6.按需求查询数据
(1)查询在2017年4月份购买过的顾客及总人数
select name,count(*) over ()
from business
where substring(orderdate,1,7) = '2017-04'
group by name;
(2)查询顾客的购买明细及月购买总额
select name,orderdate,cost,sum(cost) over(partition by month(orderdate)) from
business;
(3)上述的场景,要将cost按照日期进行累加
select name,orderdate,cost,
sum(cost) over() as sample1,--所有行相加
sum(cost) over(partition by name) as sample2,--按name分组,组内数据相加
sum(cost) over(partition by name order by orderdate) as sample3,--按name分组,组内数据累加
sum(cost) over(partition by name order by orderdate rows between UNBOUNDED PRECEDING and current row ) as sample4 ,--和sample3一样,由起点到当前行的聚合
sum(cost) over(partition by name order by orderdate rows between 1 PRECEDING and current row) as sample5, --当前行和前面一行做聚合
sum(cost) over(partition by name order by orderdate rows between 1 PRECEDING AND 1 FOLLOWING ) as sample6,--当前行和前边一行及后面一行
sum(cost) over(partition by name order by orderdate rows between current row and UNBOUNDED FOLLOWING ) as sample7 --当前行及后面所有行
from business;
(4)查看顾客上次的购买时间
select name,orderdate,cost,
lag(orderdate,1,'1900-01-01') over(partition by name order by orderdate ) as time1, lag(orderdate,2) over (partition by name order by orderdate) as time2
from business;
(5)查询前20%时间的订单信息
select * from (
select name,orderdate,cost, ntile(5) over(order by orderdate) sorted
from business
) t
where sorted = 1;
6.7.6 OLAP函数
hive> select * from OLAP;
OK
北京 北京 丰台区 1251
北京 北京 海淀区 1896
北京 北京 通州区 427
北京 北京 东城区 1310
北京 北京 西城区 1057
北京 北京 朝阳区 3099
广东 深圳 龙岗区 2484
广东 深圳 盐田区 334
广东 深圳 南山区 1195
广东 深圳 宝安区 2453
广东 深圳 龙华区 86
广东 深圳 福田区 1027
广东 深圳 罗湖区 1155
上海 上海 虹口区 419
上海 上海 长宁区 525
上海 上海 崇明区 478
上海 上海 静安区 879
上海 上海 金山区 265
上海 上海 徐汇区 990
上海 上海 嘉定区 635
NULL NULL NULL
Time taken: 0.038 seconds, Fetched: 21 row(s)
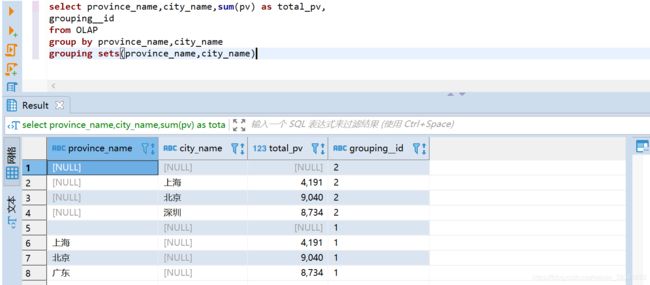
GROUPING SETS
在一个grouping sets查询中,根据不同的维度进行聚合,等价于将不同维度的group by 结果进行union all
select province_name,city_name,sum(pv) as total_pv,
grouping__id
from OLAP
group by province_name,city_name
grouping sets(province_name,city_name)
等价于
select null as province_name,city_name,sum(pv) as total_pv,
2 as grouping__id
from OLAP
group by city_name
union all
select province_name,null as city_name,sum(pv) as total_pv,
1 as grouping__id
from OLAP
group by province_name
CUBE
select province_name,city_name,sum(pv) as total_pv,
grouping__id
from OLAP
group by province_name,city_name
with cube;
等价于
select null as province_name,null as city_name,sum(pv) as total_pv ,0 as grouping__id from OLAP
union all
select province_name,null as city_name,sum(pv) as total_pv , 1 as grouping__id from OLAP group by province_name
union all
select null as province_name,city_name,sum(pv) as total_pv , 1 as grouping__id from OLAP group by city_name
union all
select province_name, city_name,sum(pv) as total_pv , 1 as grouping__id from OLAP group by province_name,city_name
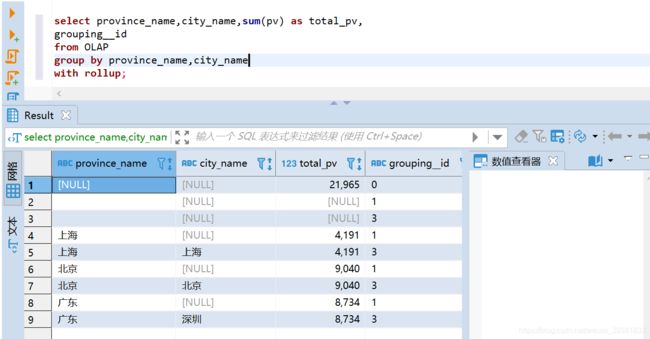
ROLLUP
--以province_name维度进行层级聚合:
select province_name,city_name,sum(pv) as total_pv,
grouping__id
from OLAP
group by province_name,city_name
with rollup;