MNIST手写数字识别
MNIST是一个手写体数字的图片数据集,该数据集由美国国家标准与技术研究所(National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST))发起整理,其包含 60,000 张训练图像和 10,000 张测试图像,每张图片的尺寸为 28 x 28

线性回归
我们尝试通过 线性回归模型 识别手写数字,输入的图片是 28 x 28像素,我们可以将其看为 784 个变量,即:
y = a 1 x 1 + a 2 x 2 + . . . + a n x n y = a_1x_1+a_2x_2+...+a_nx_n y=a1x1+a2x2+...+anxn
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import tensorflow as tf
# 计算梯度,并更新 [a1,a2,...,an],b 值
def gradient(a, b, x_array, y_array, learning_rate):
a_gradient = tf.zeros([784, 1])
b_gradient = 0
length = len(x_array)
# 计算梯度
for i in range(0, length):
x = x_array[i]
y = y_array[i]
base_gradient = (2 / length) * (np.dot(x, a) + b - y)[0]
# print("base_gradient", base_gradient)
a_gradient += base_gradient * tf.reshape(x, [784, 1])
b_gradient += base_gradient
# 更新 a、b 值
new_a = a - learning_rate * a_gradient
new_b = b - learning_rate * b_gradient
return [new_a, new_b]
# 计算损失
def computer_loss(a, b, x_array, y_array):
length = len(x_array)
loss = 0
# 计算梯度
for i in range(0, length):
x = x_array[i]
y = y_array[i]
loss += (np.dot(x, a) + b - y) ** 2
loss /= length
return loss
# 计算准确率
def computer_accuracy(a, b, x_array, y_array):
accuracy = 0
length = len(x_array)
for i in range(0, length):
x = x_array[i]
y = np.dot(x, a) + b
y = round(y[0])
if y == y_array[i]:
accuracy += 1
return accuracy / length
mnist = tf.keras.datasets.mnist
(train_data, train_label), (test_data, test_label) = mnist.load_data()
train_size = len(train_data)
test_size = len(test_data)
# 手写数字图片是 28x28 的 Tensor,需要将其转换为 1x784
train_data_reshape = tf.reshape(train_data, [train_size, 784])
# 将 int 转换为 float,否则会有计算问题
train_data_reshape = tf.cast(train_data_reshape, dtype=tf.dtypes.float32)
print("train_data_reshape shape", np.shape(train_data_reshape))
# 对数据进行归一化处理
train_data_reshape = train_data_reshape / tf.constant(255.0, shape=[train_size, 784])
print("train_data_reshape", train_data_reshape)
test_data_reshape = tf.reshape(test_data, [test_size, 784])
test_data_reshape = tf.cast(test_data_reshape, dtype=tf.dtypes.float32)
train_data_reshape = test_data_reshape / tf.constant(255.0, shape=[test_size, 784])
# 假设 y = a1x1 + a2x2 +...+ anxn +b 且 x shape [1,784],则 a shape 为 [784,1]
a = tf.random.normal([784, 1])
b = 0
loss_list = list()
accuracy_list = list()
for i in range(0, 1000):
[a, b] = gradient(a, b, train_data_reshape, train_label, 0.01)
if i % 10 == 0:
loss = computer_loss(a, b, train_data_reshape, train_label)
accuracy = computer_accuracy(a, b, test_data_reshape, test_label)
print("loss = {} accuracy = {}".format(loss, accuracy))
loss_list.append(loss)
accuracy_list.append(accuracy)
print("a = {} b = {}".format(a, b))
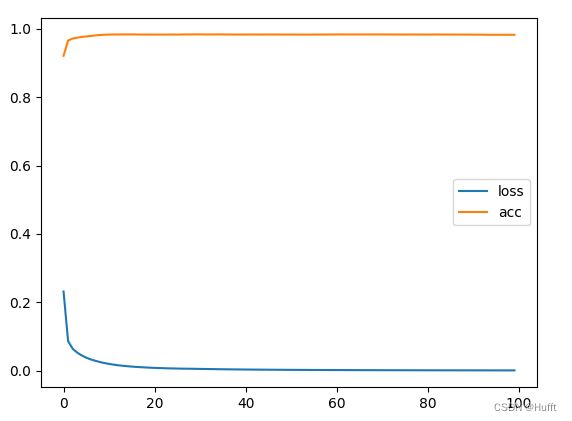
l1 = plt.plot(loss_list, label="loss")
l2 = plt.plot(accuracy_list, label="accuracy")
plt.legend()
plt.show()

可以看出损失收敛在10左右,准确率只有15%左右,这是因为该模型存在两个问题:
- 如果预测的数据是 2.5,那实际值应该是2还是3呢?所以应该通过概率来解决该问题,它需要输出多个结果,例如:1的概率为0.999,2的概率为0.0001,3的概率为0.0001等,最终所有结果的概率综合为1。我们称这样的问题为
分类问题。 - 图片像素与数字并非线性关系,而是复杂的非线性关系
非线性分类
多输出问题
对于多个结果我们可以考虑使用矩阵的形式,例如 1x4 阶矩阵,需要输出 2 个结果,则可以进行如下运算:
[ a b c d ] ∗ [ 1 5 2 6 3 7 4 8 ] = [ 1 a + 2 b + 3 c + 4 d 5 a + 6 b + 7 c + 8 d ] {\begin{bmatrix} a&b&c&d\\ \end{bmatrix}} * {\begin{bmatrix} 1&5\\ 2&6\\ 3&7\\ 4&8\\ \end{bmatrix}} = {\begin{bmatrix} 1a+2b+3c+4d&5a+6b+7c+8d\\ \end{bmatrix}} [abcd]∗ 12345678 =[1a+2b+3c+4d5a+6b+7c+8d]
手写数字需要10个结果,即 [10] 矩阵,每列的值代表数字 n 的概率,例如表示1的概率为0.999:
[ 0.999 0.0001 0.0001 0.0001 0.0001 0.0001 0.0001 0.0001 0.0001 0.0001 ] {\begin{bmatrix} 0.999 & 0.0001 & 0.0001& 0.0001& 0.0001& 0.0001& 0.0001& 0.0001& 0.0001& 0.0001 \end{bmatrix}} [0.9990.00010.00010.00010.00010.00010.00010.00010.00010.0001]
因为 x x x 为 [ n , 784 ] [n,784] [n,784] 矩阵,所以应该给 x x x 点乘一个 [ 784 , 10 ] [784,10] [784,10] 矩阵,由此多个输出问题得以解决。
非线性问题
我们需要针对线性模型中增加非线性因子,使其变为非线性,这里采用ReLU函数:

即 y = r e l u ( a x + b ) y = relu(a x + b) y=relu(ax+b),其中 a = [ 784 , 10 ] a = [784,10] a=[784,10], y = [ 10 ] y = [10] y=[10]
# 线性回归模型识别手写数字
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import tensorflow as tf
np.set_printoptions(edgeitems=10, linewidth=200)
mnist = tf.keras.datasets.mnist
(train_data, train_label), (test_data, test_label) = mnist.load_data()
train_size = len(train_data)
test_size = len(test_data)
# 将 numpy.ndarray 类型数据转换为 Tensor
train_data = tf.convert_to_tensor(train_data, dtype=tf.dtypes.float32)
# 手写数字图片是 28x28 的 Tensor,需要将其转换为 1x784
train_data = tf.reshape(train_data, [train_size, 784])
# 对数据进行归一化处理
train_data = train_data / 255.
print("train_data", train_data)
# 对 label 进行 one_hot 编码
train_label = tf.convert_to_tensor(train_label, dtype=tf.dtypes.int8)
train_label = tf.one_hot(train_label, 10)
# 沿着第一个维度切片,将 train_data、train_label 转换为 tf.data.Dataset 对象,并按60个合为一个数据集
train_batch = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((train_data, train_label)).batch(60)
print("train_batch", train_batch)
# 准备测试集数据
test_data = tf.convert_to_tensor(test_data, dtype=tf.dtypes.float32)
test_data = tf.reshape(test_data, [test_size, 784])
test_data = test_data / 255
test_label = tf.one_hot(test_label, 10)
model = tf.keras.Sequential([
tf.keras.layers.Dense(10, activation='relu')
])
optimizer = tf.optimizers.SGD(learning_rate=0.01)
def computer_acc():
# 预测测试集结果
test_out = model.predict(test_data)
# 将概率最大置1,其他置0
max_val = tf.reduce_max(test_out, axis=1)
max_val = tf.reshape(max_val, [-1, 1])
test_out = tf.where(tf.equal(test_out, max_val), tf.ones_like(test_out), tf.zeros_like(test_out))
# 降维,判断整行数据是否相等
acc = tf.reduce_all(tf.equal(test_out, test_label), axis=1)
return tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(acc, tf.float32))
loss_list = list()
acc_list = list()
for i in range(0, 1000):
for (x, y) in train_batch:
# -1 表示自动推断
x = tf.reshape(x, (-1, 784))
with tf.GradientTape() as tape:
out = model(x)
loss = tf.reduce_sum(tf.square(out - y) / x.shape[0])
# 计算梯度
gradient = tape.gradient(loss, model.trainable_variables)
# 反向传递
optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(gradient, model.trainable_variables))
if i % 10 == 0:
loss_list.append(loss)
acc = computer_acc()
acc_list.append(acc)
print("i = {} loss = {} acc = {}".format(i, loss, acc))
l1 = plt.plot(loss_list, label="loss")
l2 = plt.plot(acc_list, label="acc")
plt.legend()
plt.show()
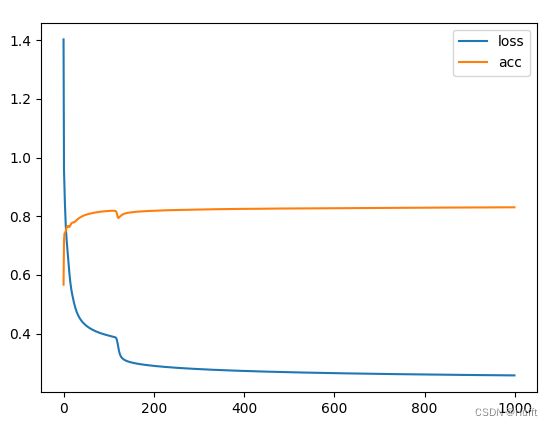
最终准确率收敛在了 84% 左右,原因是增加一个非线性因素可能不够,所以我们需要增加多个,使其可以拟合更复杂的非线性函数:
o u t 1 = r e l u ( a 1 x + b ) out_1 = relu(a_1 x + b) out1=relu(a1x+b),其中 a 1 = [ 784 , 512 ] a_1 = [784,512] a1=[784,512], o u t 1 = [ 512 ] out_1 = [512] out1=[512]
o u t 2 = r e l u ( a 2 o u t 1 + b ) out_2 = relu(a_2 out_1 + b) out2=relu(a2out1+b),其中 a 1 = [ 512 , 256 ] a_1 = [512,256] a1=[512,256], o u t 1 = [ 256 ] out_1 = [256] out1=[256]
o u t 3 = r e l u ( a 3 o u t 2 + b ) out_3 = relu(a_3 out_2 + b) out3=relu(a3out2+b),其中 a 1 = [ 256 , 10 ] a_1 = [256,10] a1=[256,10], o u t 3 = [ 10 ] out_3 = [10] out3=[10]
model = tf.keras.Sequential([
tf.keras.layers.Dense(512, activation='relu'),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(256, activation='relu'),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(10)
])