leetcode图论刷题总结
文章目录
- 理论
-
- 1. 基本概念
-
- 1.1 顶点
- 1.2 边
- 1.3 度
- 1.4 无向图和有向图
- 1.5 无权图和带权图
- 2. 图的存储
-
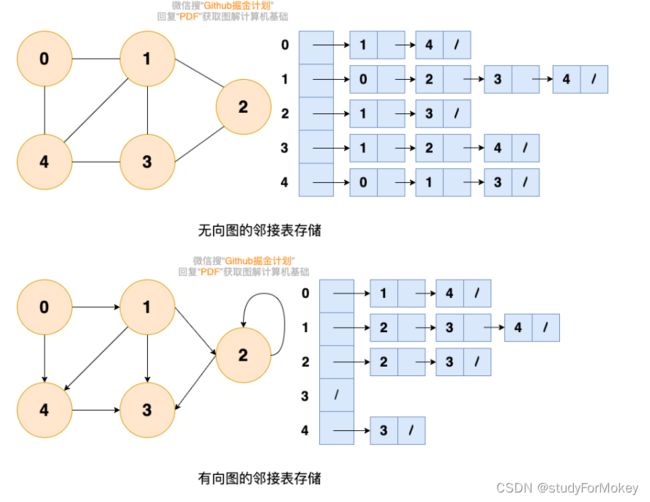
- 2.1 邻接矩阵存储
- 2.2 邻接表存储
- 3. 图的搜索
-
- 3.1 深度优先 DFS
- 3.2 广度优先 BFS
- T841. 钥匙和房间 (有向图找一条路径、DFS) **
- T797. 所有可能的路径(有向图找所有路径:DFS、回溯) **
- T127. 单词接龙 (无向图求最短路径、BFS) ***
- T200. 岛屿数量(无向图:DFS/BFS)*
- T417. 太平洋大西洋水流问题(无向图:多源BFS)****
- T1020. 飞地的数量 (无向图:DFS/多源BFS) ***
- 剑指 Offer II 105. 岛屿的最大面积(无向图:DFS) **
- T207. 课程表(拓扑排序判断是否为有向无环图:邻接表+BFS)
- T684. 冗余连接(无向图中找环:邻接表BFS/并查集)
- 华为机考题:循环依赖(有向图中找环并输出节点)
- T130. 被围绕的区域
理论
1. 基本概念
1.1 顶点
图中的数据元素,我们称之为顶点,图至少有一个顶点(非空有穷集合)
1.2 边
顶点之间的关系用边表示。
1.3 度
度表示一个顶点包含多少条边,在有向图中,还分为出度和入度,出度表示从该顶点出去的边的条数,入度表示进入该顶点的边的条数。
1.4 无向图和有向图
边表示的是顶点之间的关系,有的关系是双向的,比如同学关系,A是B的同学,那么B也肯定是A的同学,那么在表示A和B的关系时,就不用关注方向,用不带箭头的边表示,这样的图就是无向图。有的关系是有方向的,比如父子关系,师生关系,微博的关注关系,A是B的爸爸,但B肯定不是A的爸爸,A关注B,B不一定关注A。在这种情况下,我们就用带箭头的边表示二者的关系,这样的图就是有向图。
1.5 无权图和带权图
对于一个关系,如果我们只关心关系的有无,而不关心关系有多强,那么就可以用无权图表示二者的关系。对于一个关系,如果我们既关心关系的有无,也关心关系的强度,比如描述地图上两个城市的关系,需要用到距离,那么就用带权图来表示,带权图中的每一条边一个数值表示权值,代表关系的强度。
2. 图的存储
2.1 邻接矩阵存储
2.2 邻接表存储
3. 图的搜索
3.1 深度优先 DFS
深度优先搜索就是“一条路走到黑”,从源顶点开始,一直走到没有后继节点,才回溯到上一顶点,然后继续“一条路走到黑”
3.2 广度优先 BFS
广度优先搜索就像水面上的波纹一样一层一层向外扩展
T841. 钥匙和房间 (有向图找一条路径、DFS) **
- 思路分析
有向图
首先必须从0号房间开始搜索,一直搜,不需要回溯(只要找到一条路径就可以),深度为len返回true
class Solution {
//不需要回溯:只要找到一条符合的路径即可
boolean[] visited;//记录是否访问过
int deep;//记录访问深度
public boolean canVisitAllRooms(List<List<Integer>> rooms) {
int len = rooms.size();
visited = new boolean[len];//false
dfs(rooms,0);//从0号房间开始
if(deep == len){return true;}
return false;
}
public void dfs(List<List<Integer>> rooms,int index){
visited[index] = true;
deep++;//遍历依次深度就加1,由于设置的是没访问过的才会递归dfs,因此只要递归次数达到len,就说明满足条件
for(int i:rooms.get(index)){//从该房间往可能的房间方向遍历
if(visited[i]!=true){//访问的不需要再访问
dfs(rooms,i);
}
}
}
}
T797. 所有可能的路径(有向图找所有路径:DFS、回溯) **
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> allPathsSourceTarget(int[][] graph) {
path.add(0);//0号房间需要手动加进去
dfs(graph,0);
return res;
}
public void dfs(int[][] graph, int index){
//终止条件
if(index == graph.length-1){//审题:终点必然是n-1
res.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
return;
}
for(int i=0;i<graph[index].length;i++){//遍历graph每个元素
path.add(graph[index][i]);
dfs(graph,graph[index][i]);
path.removeLast();//回溯
}
return;
}
}
T127. 单词接龙 (无向图求最短路径、BFS) ***
class Solution {
public int ladderLength(String beginWord, String endWord, List<String> wordList) {
HashSet<String> wordSet = new HashSet<>(wordList);//把wordlist的单词放入hash表中
if(!wordSet.contains(endWord)){return 0;}//特殊情况:不存在目标单词
Queue<String> que = new LinkedList<>();
que.offer(beginWord);
Map<String,Integer> map = new HashMap<>();//单词:路径长度
map.put(beginWord,1);
while(!que.isEmpty()){
String word = que.poll();
int path = map.get(word);//取出第一个单词和其路径长度
//对单词的每个字符进行修改遍历
for(int i=0;i<word.length();i++){
//修改字符
char[] chars = word.toCharArray();
for(char c='a';c<='z';c++){
chars[i] = c;
String newWord = String.valueOf(chars);//char变成string
if(newWord.equals(endWord)){
return path+1;//如果新单词与目标一致,返回结果
}
if(wordSet.contains(newWord) && !map.containsKey(newWord)){//存在该单词,且未使用过
map.put(newWord,path+1);
que.offer(newWord);
}
}
}
}
return 0;
}
}
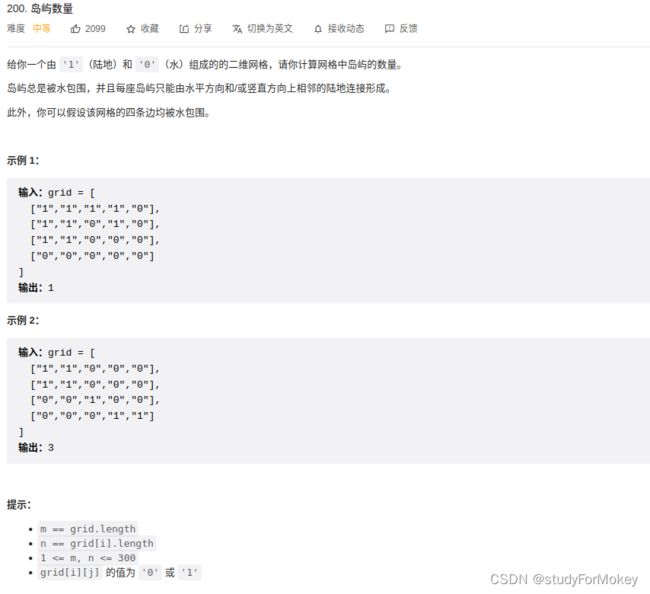
T200. 岛屿数量(无向图:DFS/BFS)*
- 思路分析
遇到陆地就开始向四个方向搜索,直到遇到海洋就停止,搜索过的就做个标记;
岛屿数量就是dfs了多少次
class Solution {
public int numIslands(char[][] grid) {
int count = 0;
for(int m=0;m<grid.length;m++){
for(int n=0;n<grid[0].length;n++){
if(grid[m][n] == '1'){
dfs(grid,m,n);
count++;
}
}
}
return count;
}
void dfs(char[][] grid,int r,int c){
//判断是否在表格中
if(r<0||c<0||r>=grid.length||c>=grid[0].length){
return;
}
//遇到非岛屿的
if(grid[r][c] != '1') return;
//记录遍历过的
grid[r][c] = '2';
//遍历四个方向
dfs(grid,r-1,c);
dfs(grid,r+1,c);
dfs(grid,r,c-1);
dfs(grid,r,c+1);
}
}
class Solution {
public int numIslands(char[][] grid) {
int count = 0;
for(int i=0;i<grid.length;i++){
for(int j=0;j<grid[0].length;j++){
if(grid[i][j] == '1'){
bfs(grid,i,j);
count++;
}
}
}
return count;
}
public void bfs(char[][] grid,int i,int j){
Queue<int[]> que = new LinkedList<>();
que.offer(new int[]{i,j});
while(!que.isEmpty()){
int[] temp = que.poll();
i = temp[0];
j = temp[1];
if(i>=0&&i<grid.length&&j>=0&&j<grid[0].length && grid[i][j] == '1'){
grid[i][j] = '0';
bfs(grid,i+1,j);
bfs(grid,i-1,j);
bfs(grid,i,j+1);
bfs(grid,i,j-1);
}
}
}
}
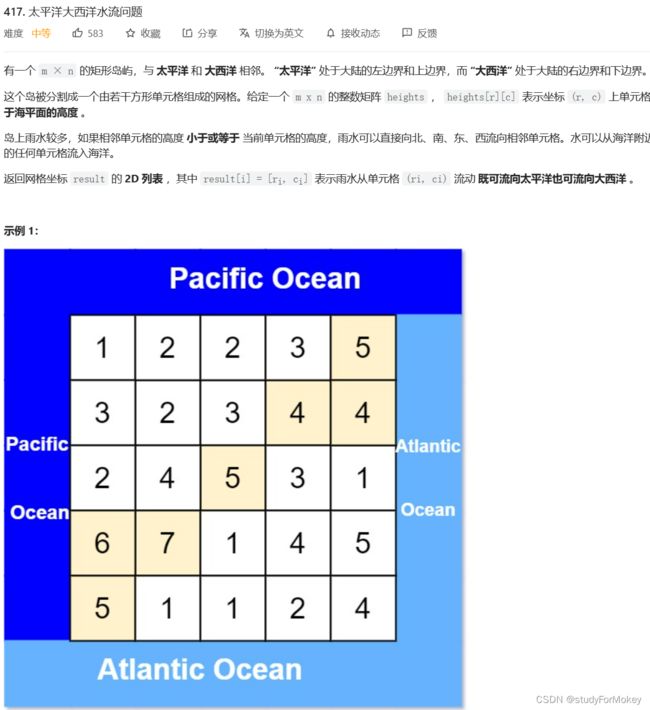
T417. 太平洋大西洋水流问题(无向图:多源BFS)****
- 思路分析
题目翻译: 某个点出发,能从四个方向到达比它小的点,求整个集合中能够到达左上边界(太平洋) 右下边界(大西洋)的有哪些点
思路解决: 遍历所有点太麻烦,直接从边界点出发,能够到达比它大的点,能够到达的就标记为true;分别从太平洋和大西洋出发,进行两次bfs,最终看结果res中两次标记为true的点就是所求。
从结果开始遍历!
BFS思路:以队列为基础,队列存放点坐标。传入点坐标,只要队列非空,就取点坐标,进行四个方向移动,更新,符合条件的入队。 - 代码实现
class Solution {
static int[][] dirs = {{-1,0},{1,0},{0,-1},{0,1}};//移动的四个方向
static int m;
static int n;
static int[][] nums;
//反向推导:从边界出发,水往高处流,能到达就记为true
public List<List<Integer>> pacificAtlantic(int[][] heights) {
m = heights.length;
n = heights[0].length;//行和列
nums = heights;
boolean[][] pacific = new boolean[m][n];//能否到达太平洋
boolean[][] atlantic = new boolean[m][n];//记录能否到达大西洋
//记录能否到达太平洋
for(int i=0;i<m;i++){
bfs(i,0,pacific);
}
for(int j=1;j<n;j++){
bfs(0,j,pacific);
}
//记录能否到达大西洋
for(int i=0;i<m;i++){
bfs(i,n-1,atlantic);
}
for(int j=0;j<n-1;j++){
bfs(m-1,j,atlantic);
}
//算结果:遍历所有的节点,能够同时到达太平洋和大西洋的就add
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i=0;i<m;i++){
for(int j=0;j<n;j++){
if(pacific[i][j] && atlantic[i][j]){
List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();
path.add(i);
path.add(j);
res.add(path);
}
}
}
return res;
}
//广度优先搜索的逻辑
//取出其中一个点
//往四个方向移动,判断条件是否符合
//入队
public static void bfs(int row,int col,boolean[][] ocean){
if(ocean[row][col]){return;}
ocean[row][col] = true;
Queue<int[]> que = new LinkedList<>();//x,y坐标
que.offer(new int[]{row,col});
while(!que.isEmpty()){
int[] temp = que.poll();
for(int[] dir:dirs){//往四个方向移动
//计算新坐标
int newRow = temp[0] + dir[0];
int newCol = temp[1] + dir[1];
//判断是否符合条件:边界条件+高度+未处理过
if(newRow>=0&&newRow<m&&newCol>=0&&newCol<n&& nums[temp[0]][temp[1]]<=nums[newRow][newCol]&& !ocean[newRow][newCol]){
ocean[newRow][newCol] = true;
que.offer(new int[]{newRow,newCol});
}
}
}
}
}
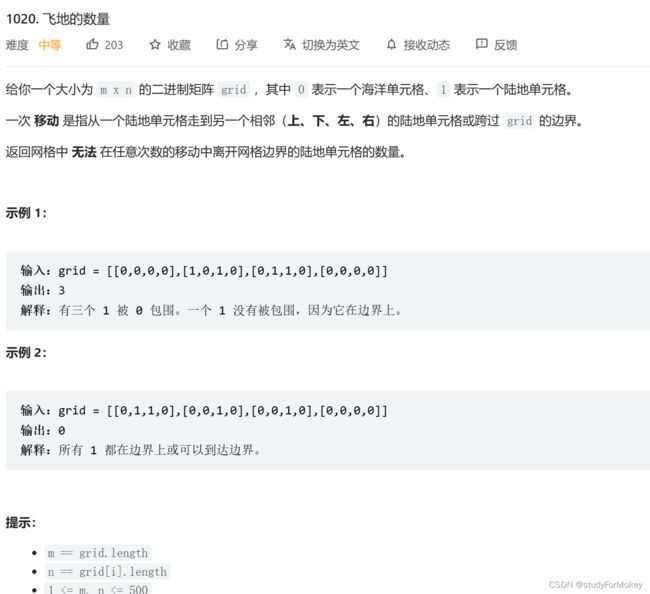
T1020. 飞地的数量 (无向图:DFS/多源BFS) ***
- 解法1:DFS搜索
class Solution {
//从边界搜,如果遇到1,就设置为true;最终grid==1,false的就是飞地
public static int[][] dirs = {{-1,0},{1,0},{0,-1},{0,1}};
public static int m,n;
public static boolean[][] visited;
public int numEnclaves(int[][] grid) {
int count = 0;
m = grid.length;
n = grid[0].length;
visited = new boolean[m][n];
//从边界开始搜
//左右两个边界
for(int i=0;i<m;i++){
dfs(grid,i,0);
dfs(grid,i,n-1);
}
//上下两个边界
for(int j=0;j<n;j++){
dfs(grid,0,j);
dfs(grid,m-1,j);
}
for(int i=0;i<m;i++){
for(int j=0;j<n;j++){
if(!visited[i][j] && grid[i][j]==1){
count++;
}
}
}
return count;
}
public static void dfs(int[][] grid,int i,int j){
if(i<0 || i>=m || j<0 || j>=n || grid[i][j] == 0 || visited[i][j] ){
return;//终止条件
}
visited[i][j] = true;
for(int[] dir:dirs){
dfs(grid,i+dir[0],j+dir[1]);
}
}
}
- 解法2:多源BFS
class Solution {
//从边界搜,如果遇到1,就设置为true;最终grid==1,false的就是飞地
public static int[][] dirs = {{-1,0},{1,0},{0,-1},{0,1}};
public static int m,n;
public static boolean[][] visited;
public int numEnclaves(int[][] grid) {
int count = 0;
m = grid.length;
n = grid[0].length;
visited = new boolean[m][n];
Queue<int[]> que = new LinkedList<>();
//从边界开始搜
for(int i=0;i<m;i++){
for(int j=0;j<n;j++){
if(i==0||i==m-1||j==0||j==n-1){
if(grid[i][j]==0) continue;
visited[i][j] = true;
que.offer(new int[]{i,j});
}
}
}
while(!que.isEmpty()){
int[] temp = que.poll();
for(int[] dir:dirs){
int newX = temp[0] + dir[0];
int newY = temp[1] + dir[1];
if(newX>=0 && newX<m && newY>=0 && newY<n && !visited[newX][newY] && grid[newX][newY]==1){
visited[newX][newY] = true;
que.offer(new int[]{newX,newY});
}
}
}
for(int i=0;i<m;i++){
for(int j=0;j<n;j++){
if(!visited[i][j] && grid[i][j]==1){
count++;
}
}
}
return count;
}
}
剑指 Offer II 105. 岛屿的最大面积(无向图:DFS) **
class Solution {
public int maxAreaOfIsland(int[][] grid) {
int res = 0;
for(int i=0;i<grid.length;i++){
for(int j=0;j<grid[0].length;j++){
if(grid[i][j] == 1){
res = Math.max(dfs(grid,i,j),res);
}
}
}
return res;
}
public int dfs(int[][] grid,int row,int col){
if(row<0 || col<0 || row>=grid.length || col >= grid[0].length||grid[row][col]!=1){
return 0;
}
grid[row][col] = 0;
int res = 1;
res = res + dfs(grid,row+1,col) + dfs(grid,row-1,col) +
dfs(grid,row,col+1) + dfs(grid,row,col-1);
return res;
}
}
T207. 课程表(拓扑排序判断是否为有向无环图:邻接表+BFS)
- 入度表BFS
class Solution {
//BFS 构造一个有向图
//1.统计每个点的入度
//2.度为0的入队
//3.出队:课程数-1,相连的节点的度减去1,若度为0就入度
public boolean canFinish(int numCourses, int[][] prerequisites) {
int[] indegree = new int[numCourses];//统计入度
List<List<Integer>> joinList = new ArrayList<>();//记录相连的课程,索引代表当前课程
for(int i=0;i<numCourses;i++){
joinList.add(new ArrayList<>());
}
for(int[] item:prerequisites){
indegree[item[0]]++;//入度数
joinList.get(item[1]).add(item[0]);//相连的节点
}
Queue<Integer> que = new LinkedList<>();
for(int i=0;i<indegree.length;i++){
if(indegree[i]==0){
que.add(i);//度为0 入队
}
}
while(!que.isEmpty()){
int temp = que.poll();
numCourses--;
for(int item:joinList.get(temp)){
indegree[item]--;
if(indegree[item]==0){
que.add(item);
}
}
}
return numCourses==0;
}
}
T684. 冗余连接(无向图中找环:邻接表BFS/并查集)
- 解法1:邻接表,入度表,BFS
参考题:课程表,不同的是度数为1入队。每次把1的出队,并且删除掉与其相连的边,最终剩下的结果中,两边入度都大于1的为所求
class Solution {
public int[] findRedundantConnection(int[][] edges) {
int size = edges.length;
int[] indegree = new int[size];//构造入度表 下标0表示1
List<List<Integer>> joinList = new ArrayList<>();//邻接表
for(int i=0;i<size;i++){
joinList.add(new ArrayList<>());
}
for(int[] item:edges){//下标统一做减1处理
indegree[item[0]-1]++;
indegree[item[1]-1]++;
joinList.get(item[0]-1).add(item[1]-1);
joinList.get(item[1]-1).add(item[0]-1);
}
Queue<Integer> que = new LinkedList<>();
for(int i=0;i<size;i++){
if(indegree[i]==1){
que.offer(i);//度为1 就入队
}
}
while(!que.isEmpty()){
int item = que.poll();
for(int i:joinList.get(item)){
indegree[i]--;
if(indegree[i]==1){
que.offer(i);
}
}
}
//前边是找环的思路 同题 课程表
//从后往前遍历:如果两个相连的点度数都大于1
for(int i=size-1;i>=0;i--){
if(indegree[edges[i][0]-1]>1&&indegree[edges[i][1]-1]>1){
return edges[i];
}
}
return new int[0];
}
}
华为机考题:循环依赖(有向图中找环并输出节点)
为了方便对原题修改了一下
//输入:
8 (模块名称:模块里的函数)
A a1 a2 a3
B b1 b2 b3
C c1 c2 c3
D d1 d2 d3
E e1 e2 e3
F f1 f2 f3
H h1 h2
G g1 g2 g3
5 (主函数:需要用到的函数,即a1依赖b1,b2)
a1 b1 b2
c2 a3
d2 e1
e1 b1 f2 g3
b2 b1 c2 d1 h1
//输出:
A B C D E
package HuaWei;
/**
* 循环依赖 思路不算难 但是过程很繁琐 java构建输入太过于复杂
* 考察的是:在一个有向图中找环,并输出环的节点。
* 解决方法:构建一个邻接表,利用dfs搜索,用res记录路径
* https://blog.csdn.net/zhilamou7549/article/details/107092998思路见此
* 为了简化,此题不再做起点要求,对整个图进行搜索找环,并且规定起始点为A
*/
import java.util.*;
public class Solution7 {
static List<List<String>> res = new ArrayList<>();
static List<String> path = new LinkedList<>();
static String[] numToStr;
static boolean result;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int m = Integer.parseInt(sc.nextLine());
numToStr = new String[m];
int tempSize = m;
int index = 0;
TreeMap<String,List<String>> map = new TreeMap<>();//模块以及其对应的函数
while(m>0){
String[] line = sc.nextLine().split(" ");
numToStr[index] = line[0];
index++;
List<String> list = new LinkedList<>();
for(int i=1;i<line.length;i++){
list.add(line[i]);
}
map.put(line[0],list);//模块名:对应函数的名字
m--;
}
int n = Integer.parseInt(sc.nextLine());
TreeMap<String,Set<String>> relation = new TreeMap<>();//各个模块之间的依赖关系
while(n>0) {
String[] parts = sc.nextLine().split(" ");
Set<String> value = new HashSet<>();
String key = null;
for (Map.Entry<String, List<String>> entry : map.entrySet()) {
List<String> temp = entry.getValue();
for (String str : temp) {
if (parts[0].equals(str)) {//找到和parts[0]对应的函数 对应的模块 作为key
key = entry.getKey();
}
}
}
for (int i = 1; i < parts.length; i++) {//寻找value
for (Map.Entry<String, List<String>> entry : map.entrySet()) {
List<String> temp = entry.getValue();
for (String str : temp) {
if (parts[i].equals(str)) {//找到和parts[0]对应的函数 对应的模块 作为key
if(!entry.getKey().equals(key)){
value.add(entry.getKey());//给value赋值 记得去重
}
}
}
}
}
relation.put(key, value);
n--;
}
// System.out.println(map);
// System.out.println(relation);
// String target = sc.nextLine();//起点模块
//处理逻辑:默认模块名从A开始排序了
//1.构建邻接表
//行表示当前模块,列表示对应模块,若行依赖于列,值为1
int[][] matrix = new int[tempSize][tempSize];
for(Map.Entry<String,Set<String>> entry: relation.entrySet()){
int row = entry.getKey().charAt(0) - 'A';
for(String str: entry.getValue()){
int col = str.charAt(0) - 'A';
matrix[row][col] = 1;
}
}
// System.out.println(matrix);
//2.dfs处理
boolean[] visited = new boolean[matrix.length];
for(int i=0;i<matrix.length;i++){
for (int j = 0; j < matrix.length; j++) {
//遇到值为1就进行搜索. 如果两次出现visited都为true说明出现了环
if(matrix[i][j]!=0){
Arrays.fill(visited,false);
visited[j] = true;
dfs(matrix,visited,i,j);
}
}
}
if(result){
System.out.println("yes");
Set<String> set = new HashSet<>();
for(List<String> list:res){
for(String str:list){
set.add(str);
}
}
String[] strResult = new String[set.size()];
int i = 0;
for(String str:set){
strResult[i] = str;
i++;
}
Arrays.sort(strResult);
for(int j=0;j<strResult.length;j++){
System.out.print(strResult[j]+" ");
}
}else{
System.out.println("No!");
}
// System.out.println(res);
}
public static void dfs(int[][] matrix,boolean[] visited,int start,int cur_node){
for(int col=0;col<matrix.length;col++){
if(matrix[cur_node][col]!=0&&!visited[col]){
if(col == start){//找到环了
res.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
result = true;
return;
}
visited[col] = true;
path.add(numToStr[col]);
dfs(matrix,visited,start,col);
visited[col] = false;
path.remove(numToStr[col]);
}
}
}
}