鲸鱼优化算法WOA求解旅行商TSP优化问题(2022.6.2)
鲸鱼优化算法WOA求解旅行商TSP优化问题(2022.6.2)
- 引言
- 1、鲸鱼优化算法WOA
-
- 1.1 WOA算法原理介绍
-
- 1.1.1 包围猎物
- 1.1.2 气泡网式攻击猎物(开发阶段)
- 1.1.3 寻找猎物(探索阶段)
- 1.2 WOA算法流程
- 1.3 WOA官方源码
- 2、WOA源码测试运行(Matlab)
-
- 2.1 WOA代码简介
-
- 2.1.1 Get_Functions_details.m
- 2.1.2 func_plot.m
- 2.1.3 initialization.m
- 2.1.4 WOA.m
- 2.1.5 main.m(运行文件)
- 2.2 运行结果(函数F1~F23)
- 3、WOA求解TSP(C++ or Python)
-
- 3.1 WOA求解TSP(C++)
-
- 3.1.1 C++代码(main.cpp)
- 3.1.2 运行结果
- 3.2 WOA求解TSP(Python)
-
- 3.2.1 Python代码(WOA.py)
- 3.2.2 运行结果
- 4、总结
引言
作为世界上最大的哺乳动物,一条成年鲸鱼的身长可达到30m,体重能达到180t。鲸鱼大多被认为是食肉动物,它们从不睡觉,因为必须从海洋表面呼吸。事实证明,鲸鱼可以像人类一样思考、学习、判断、交流,它们也被认为是具有情感的高智商动物。另一件有趣的事情是鲸鱼的社交行为:它们独居或群居,但大多是处于群体当中。成年座头鲸(Megaptera novaeangliae)几乎和校车一样大。它们最喜欢的猎物是磷虾和小鱼群。
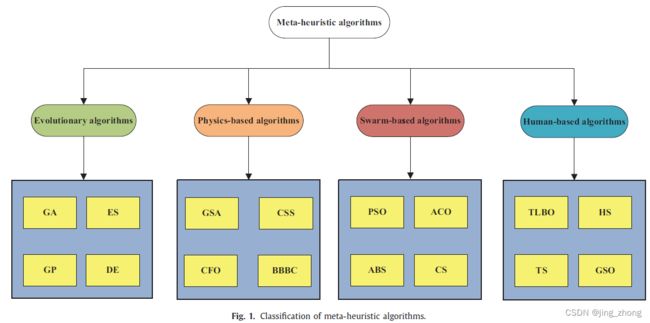
1、鲸鱼优化算法WOA

|

|
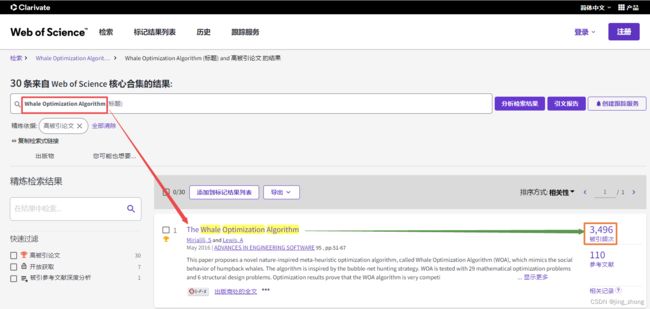
2016年,来自澳大利亚的两位研究人员Mirjalili Seyedali和Lewis Andrew通过模拟自然界生物座头鲸的社会行为,提出了一种元启发式的优化算法——鲸鱼优化算法WOA,撰写的论文在Advances in Engineering Software期刊上在线发表,被SCI收录,引起了学者们的广泛关注,迄今为止论文的被引频次高达3496。

算法的核心在于座头鲸的气泡网式捕捉策略,算法利用三个操作算子来模拟座头鲸对猎物的搜索、包围猎物和气泡网觅食行为。经过29个数学优化问题和6个结构设计问题的实际测试,结果证明,与其他传统的元启发式算法相比,WOA具有十分明显的计算优势。(注:WOA算法源代码已公开,可点击下载)
1.1 WOA算法原理介绍
1.1.1 包围猎物
座头鲸能够识别猎物位置并且对其进行转圈包围,WOA算法假设当前最优的候选位置就是目标猎物或者说更接近最优猎物的位置,在定义了最好的搜索智能体后,其他的搜索智能体就会向着最好的搜索智能体来尝试更新它们的位置,这个行为可以用下列方程来表示:
D ⃗ = ∣ C ⃗ ⋅ X ∗ ⃗ ( t ) − X ⃗ ( t ) ∣ (公式1) \vec{D}=|\vec{C}\cdot \vec{X^{*}}(t)-\vec{X}(t)| \tag{公式1} D=∣C⋅X∗(t)−X(t)∣(公式1) X ⃗ ( t + 1 ) = X ∗ ⃗ ( t ) − A ⃗ ⋅ D ⃗ (公式2) \vec{X}(t+1)=\vec{X^{*}}(t)-\vec{A}\cdot \vec{D} \tag{公式2} X(t+1)=X∗(t)−A⋅D(公式2)
其中, t t t 表示当前代数; A ⃗ \vec{A} A 和 C ⃗ \vec{C} C 是系数向量; X ∗ X^{*} X∗ 是目前为止所获取最优解的位置向量; X ⃗ \vec{X} X是位置向量; ∣ ∣ | | ∣∣ 是绝对值; ⋅ \cdot ⋅ 是点积,对应元素逐点相乘。
A ⃗ = 2 a ⃗ ⋅ r ⃗ − a ⃗ (公式3) \vec{A}=2\vec{a}\cdot \vec{r} -\vec{a} \tag{公式3} A=2a⋅r−a(公式3) C ⃗ = 2 ⋅ r ⃗ (公式4) \vec{C}=2\cdot{\vec{r}} \tag{公式4} C=2⋅r(公式4)
a ⃗ \vec{a} a 随着代数的增加线性递减,取值范围为[2,1]; r ⃗ \vec{r} r 是一个取值范围在[0,1]的随机向量。
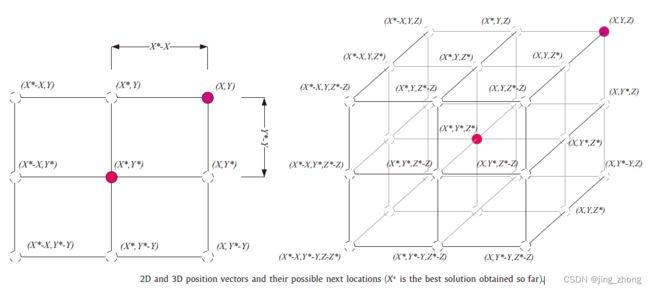
如上图所示,无论是二维空间还是三维空间,通过对当前位置调整 A ⃗ \vec{A} A 和 C ⃗ \vec{C} C的值可到达最好个体周围的不同位置,因此,公式2可用来根据当前最优解的邻域对一些搜索个体的位置进行更新,这样来实现对猎物的包围。
1.1.2 气泡网式攻击猎物(开发阶段)
为了对座头鲸的气泡网攻击猎物方法进行建模,故而设计了以下两种方法,如下图所示。

- 收缩环绕机制:这个行为可通过减小公式3中 a ⃗ \vec{a} a 的值来实现,当a随着代数增加从2逐渐下降到0, A ⃗ \vec{A} A的取值范围,为[-a,a]。如果设定 A ⃗ \vec{A} A 的随机值在[-1,1],那么一个搜索个体的新位置就会位于其原来位置和当前最优个体位置之间。上图中(a)展示了2维空间 0 ≤ A ≤ 1 0≤A≤1 0≤A≤1 时从 ( X , Y ) (X,Y) (X,Y) 向 ( X ∗ , Y ∗ ) (X^{*},Y^{*}) (X∗,Y∗) 的可能搜索位置。
- 螺旋线更新位置:如上图中(b)所示,首先计算鲸鱼所在位置 ( X , Y ) (X,Y) (X,Y)到猎物所在位置 ( X ∗ , Y ∗ ) (X^{*},Y^{*}) (X∗,Y∗)的距离,然后在鲸鱼和猎物的位置之间建立一个螺旋方程来模拟座头鲸的螺旋形运动,如下所示: X ⃗ ( t + 1 ) = D ′ ⃗ ⋅ e b l ⋅ c o s ( 2 π l ) + X ∗ ⃗ ( t ) (公式5) \vec{X}(t+1)=\vec{D^{'}} \cdot e^{bl} \cdot cos(2\pi l) + \vec{X^{*}}(t) \tag{公式5} X(t+1)=D′⋅ebl⋅cos(2πl)+X∗(t)(公式5) 式中, D ′ ⃗ = X ∗ ⃗ ( t ) − X ⃗ ( t ) \vec{D^{'}}=\vec{X^{*}}(t) -\vec{X}(t) D′=X∗(t)−X(t) 表示第 i i i 代鲸鱼到目前最优猎物的距离; b b b 是一个定义对数螺旋线形状的常数; l l l 是一个取值范围在[-1,1]区间的随机数。
注意到座头鲸在围绕猎物游动时会同时进行缩小包围圈和螺旋形位置更新这两种行为,为了建模这个同时进行的行为,假设在优化期间存在50%的概率在缩小包围圈和螺旋形更新位置这两个行为中做一个随机选择,数学模型如下:
X ⃗ ( t + 1 ) = { X ∗ ⃗ ( t ) − A ⃗ ⋅ D ⃗ p < 0.5 D ′ ⃗ ⋅ e b l ⋅ c o s ( 2 π l ) + X ∗ ⃗ ( t ) p ≥ 0.5 (公式6) \vec{X}(t+1)=\left\{\begin{matrix} \vec{X^{*}}(t)-\vec{A}\cdot \vec{D} & p < 0.5 \\ \vec{D^{'}} \cdot e^{bl} \cdot cos(2\pi l) + \vec{X^{*}}(t) &p \geq 0.5 \\ \end{matrix}\right. \tag{公式6} X(t+1)={X∗(t)−A⋅DD′⋅ebl⋅cos(2πl)+X∗(t)p<0.5p≥0.5(公式6) 其中,随机概率 p ∈ [ 0 , 1 ] p∈[0,1] p∈[0,1]。
1.1.3 寻找猎物(探索阶段)
座头鲸在寻找猎物时是按照随机的方式根据彼此的位置进行搜索,使用具有小于-1或者大于1的随机值 A ⃗ \vec{A} A来迫使搜索个体向远离参考鲸鱼个体的方向移动,根据随机选择的个体进行距离更新而不是选择最优个体, A ⃗ > 1 \vec{A}>1 A>1强调在探索阶段WOA算法可进行全局搜索,具体公式如下:
D ⃗ = ∣ C ⃗ ⋅ X r a n d ⃗ ( t ) − X ⃗ ( t ) ∣ (公式7) \vec{D}=|\vec{C}\cdot \vec{X_{rand}}(t)-\vec{X}(t)| \tag{公式7} D=∣C⋅Xrand(t)−X(t)∣(公式7) X ⃗ ( t + 1 ) = X r a n d ⃗ ( t ) − A ⃗ ⋅ D ⃗ (公式8) \vec{X}(t+1)=\vec{X_{rand}}(t)-\vec{A}\cdot \vec{D} \tag{公式8} X(t+1)=Xrand(t)−A⋅D(公式8)
式中, X r a n d ( t ) X_{rand}(t) Xrand(t)表示从当前代(第t代)随机选择的座鱼鲸个体的位置向量。

1.2 WOA算法流程
WOA算法的伪代码和计算流程如下图所示。

|

|
1.3 WOA官方源码

在WOA官网中给出了源代码Source Codes of WOA和工具箱Source Codes of WOA toolbox的下载地址,下载至本地并解压,如下图所示。


|
|
2、WOA源码测试运行(Matlab)
测试运行环境为Matlab R2021a 64位

2.1 WOA代码简介
WOA代码共包含5个.m脚本文件:Get_Functions_details.m、func_plot.m、initialization.m、WOA.m和main.m,其中前两个包含23个函数的定义,initialization.m是种群初始化文件,WOA.m中执行WOA算法整个流程,main.m本质是调用WOA.m执行,可进行传参,设定目标函数(F1~F23)后即可运行。23个经典数学函数的表达式、自变量维度、变量范围、最小值的详细信息如下所示:


2.1.1 Get_Functions_details.m
%_________________________________________________________________________%
% Whale Optimization Algorithm (WOA) source codes demo 1.0 %
% %
% Developed in MATLAB R2011b(7.13) %
% %
% Author and programmer: Seyedali Mirjalili %
% %
% e-Mail: ali.mirjalili@gmail.com %
% seyedali.mirjalili@griffithuni.edu.au %
% %
% Homepage: http://www.alimirjalili.com %
% %
% Main paper: S. Mirjalili, A. Lewis %
% The Whale Optimization Algorithm, %
% Advances in Engineering Software , in press, %
% DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.advengsoft.2016.01.008 %
% %
%_________________________________________________________________________%
% This function containts full information and implementations of the benchmark
% functions in Table 1, Table 2, and Table 3 in the paper
% lb is the lower bound: lb=[lb_1,lb_2,...,lb_d]
% up is the uppper bound: ub=[ub_1,ub_2,...,ub_d]
% dim is the number of variables (dimension of the problem)
function [lb,ub,dim,fobj] = Get_Functions_details(F)
switch F
case 'F1'
fobj = @F1;
lb=-100;
ub=100;
dim=30;
case 'F2'
fobj = @F2;
lb=-10;
ub=10;
dim=30;
case 'F3'
fobj = @F3;
lb=-100;
ub=100;
dim=30;
case 'F4'
fobj = @F4;
lb=-100;
ub=100;
dim=30;
case 'F5'
fobj = @F5;
lb=-30;
ub=30;
dim=30;
case 'F6'
fobj = @F6;
lb=-100;
ub=100;
dim=30;
case 'F7'
fobj = @F7;
lb=-1.28;
ub=1.28;
dim=30;
case 'F8'
fobj = @F8;
lb=-500;
ub=500;
dim=30;
case 'F9'
fobj = @F9;
lb=-5.12;
ub=5.12;
dim=30;
case 'F10'
fobj = @F10;
lb=-32;
ub=32;
dim=30;
case 'F11'
fobj = @F11;
lb=-600;
ub=600;
dim=30;
case 'F12'
fobj = @F12;
lb=-50;
ub=50;
dim=30;
case 'F13'
fobj = @F13;
lb=-50;
ub=50;
dim=30;
case 'F14'
fobj = @F14;
lb=-65.536;
ub=65.536;
dim=2;
case 'F15'
fobj = @F15;
lb=-5;
ub=5;
dim=4;
case 'F16'
fobj = @F16;
lb=-5;
ub=5;
dim=2;
case 'F17'
fobj = @F17;
lb=[-5,0];
ub=[10,15];
dim=2;
case 'F18'
fobj = @F18;
lb=-2;
ub=2;
dim=2;
case 'F19'
fobj = @F19;
lb=0;
ub=1;
dim=3;
case 'F20'
fobj = @F20;
lb=0;
ub=1;
dim=6;
case 'F21'
fobj = @F21;
lb=0;
ub=10;
dim=4;
case 'F22'
fobj = @F22;
lb=0;
ub=10;
dim=4;
case 'F23'
fobj = @F23;
lb=0;
ub=10;
dim=4;
end
end
% F1
function o = F1(x)
o=sum(x.^2);
end
% F2
function o = F2(x)
o=sum(abs(x))+prod(abs(x));
end
% F3
function o = F3(x)
dim=size(x,2);
o=0;
for i=1:dim
o=o+sum(x(1:i))^2;
end
end
% F4
function o = F4(x)
o=max(abs(x));
end
% F5
function o = F5(x)
dim=size(x,2);
o=sum(100*(x(2:dim)-(x(1:dim-1).^2)).^2+(x(1:dim-1)-1).^2);
end
% F6
function o = F6(x)
o=sum(abs((x+.5)).^2);
end
% F7
function o = F7(x)
dim=size(x,2);
o=sum([1:dim].*(x.^4))+rand;
end
% F8
function o = F8(x)
o=sum(-x.*sin(sqrt(abs(x))));
end
% F9
function o = F9(x)
dim=size(x,2);
o=sum(x.^2-10*cos(2*pi.*x))+10*dim;
end
% F10
function o = F10(x)
dim=size(x,2);
o=-20*exp(-.2*sqrt(sum(x.^2)/dim))-exp(sum(cos(2*pi.*x))/dim)+20+exp(1);
end
% F11
function o = F11(x)
dim=size(x,2);
o=sum(x.^2)/4000-prod(cos(x./sqrt([1:dim])))+1;
end
% F12
function o = F12(x)
dim=size(x,2);
o=(pi/dim)*(10*((sin(pi*(1+(x(1)+1)/4)))^2)+sum((((x(1:dim-1)+1)./4).^2).*...
(1+10.*((sin(pi.*(1+(x(2:dim)+1)./4)))).^2))+((x(dim)+1)/4)^2)+sum(Ufun(x,10,100,4));
end
% F13
function o = F13(x)
dim=size(x,2);
o=.1*((sin(3*pi*x(1)))^2+sum((x(1:dim-1)-1).^2.*(1+(sin(3.*pi.*x(2:dim))).^2))+...
((x(dim)-1)^2)*(1+(sin(2*pi*x(dim)))^2))+sum(Ufun(x,5,100,4));
end
% F14
function o = F14(x)
aS=[-32 -16 0 16 32 -32 -16 0 16 32 -32 -16 0 16 32 -32 -16 0 16 32 -32 -16 0 16 32;,...
-32 -32 -32 -32 -32 -16 -16 -16 -16 -16 0 0 0 0 0 16 16 16 16 16 32 32 32 32 32];
for j=1:25
bS(j)=sum((x'-aS(:,j)).^6);
end
o=(1/500+sum(1./([1:25]+bS))).^(-1);
end
% F15
function o = F15(x)
aK=[.1957 .1947 .1735 .16 .0844 .0627 .0456 .0342 .0323 .0235 .0246];
bK=[.25 .5 1 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16];bK=1./bK;
o=sum((aK-((x(1).*(bK.^2+x(2).*bK))./(bK.^2+x(3).*bK+x(4)))).^2);
end
% F16
function o = F16(x)
o=4*(x(1)^2)-2.1*(x(1)^4)+(x(1)^6)/3+x(1)*x(2)-4*(x(2)^2)+4*(x(2)^4);
end
% F17
function o = F17(x)
o=(x(2)-(x(1)^2)*5.1/(4*(pi^2))+5/pi*x(1)-6)^2+10*(1-1/(8*pi))*cos(x(1))+10;
end
% F18
function o = F18(x)
o=(1+(x(1)+x(2)+1)^2*(19-14*x(1)+3*(x(1)^2)-14*x(2)+6*x(1)*x(2)+3*x(2)^2))*...
(30+(2*x(1)-3*x(2))^2*(18-32*x(1)+12*(x(1)^2)+48*x(2)-36*x(1)*x(2)+27*(x(2)^2)));
end
% F19
function o = F19(x)
aH=[3 10 30;.1 10 35;3 10 30;.1 10 35];cH=[1 1.2 3 3.2];
pH=[.3689 .117 .2673;.4699 .4387 .747;.1091 .8732 .5547;.03815 .5743 .8828];
o=0;
for i=1:4
o=o-cH(i)*exp(-(sum(aH(i,:).*((x-pH(i,:)).^2))));
end
end
% F20
function o = F20(x)
aH=[10 3 17 3.5 1.7 8;.05 10 17 .1 8 14;3 3.5 1.7 10 17 8;17 8 .05 10 .1 14];
cH=[1 1.2 3 3.2];
pH=[.1312 .1696 .5569 .0124 .8283 .5886;.2329 .4135 .8307 .3736 .1004 .9991;...
.2348 .1415 .3522 .2883 .3047 .6650;.4047 .8828 .8732 .5743 .1091 .0381];
o=0;
for i=1:4
o=o-cH(i)*exp(-(sum(aH(i,:).*((x-pH(i,:)).^2))));
end
end
% F21
function o = F21(x)
aSH=[4 4 4 4;1 1 1 1;8 8 8 8;6 6 6 6;3 7 3 7;2 9 2 9;5 5 3 3;8 1 8 1;6 2 6 2;7 3.6 7 3.6];
cSH=[.1 .2 .2 .4 .4 .6 .3 .7 .5 .5];
o=0;
for i=1:5
o=o-((x-aSH(i,:))*(x-aSH(i,:))'+cSH(i))^(-1);
end
end
% F22
function o = F22(x)
aSH=[4 4 4 4;1 1 1 1;8 8 8 8;6 6 6 6;3 7 3 7;2 9 2 9;5 5 3 3;8 1 8 1;6 2 6 2;7 3.6 7 3.6];
cSH=[.1 .2 .2 .4 .4 .6 .3 .7 .5 .5];
o=0;
for i=1:7
o=o-((x-aSH(i,:))*(x-aSH(i,:))'+cSH(i))^(-1);
end
end
% F23
function o = F23(x)
aSH=[4 4 4 4;1 1 1 1;8 8 8 8;6 6 6 6;3 7 3 7;2 9 2 9;5 5 3 3;8 1 8 1;6 2 6 2;7 3.6 7 3.6];
cSH=[.1 .2 .2 .4 .4 .6 .3 .7 .5 .5];
o=0;
for i=1:10
o=o-((x-aSH(i,:))*(x-aSH(i,:))'+cSH(i))^(-1);
end
end
function o=Ufun(x,a,k,m)
o=k.*((x-a).^m).*(x>a)+k.*((-x-a).^m).*(x<(-a));
end
2.1.2 func_plot.m
%_________________________________________________________________________%
% Whale Optimization Algorithm (WOA) source codes demo 1.0 %
% %
% Developed in MATLAB R2011b(7.13) %
% %
% Author and programmer: Seyedali Mirjalili %
% %
% e-Mail: ali.mirjalili@gmail.com %
% seyedali.mirjalili@griffithuni.edu.au %
% %
% Homepage: http://www.alimirjalili.com %
% %
% Main paper: S. Mirjalili, A. Lewis %
% The Whale Optimization Algorithm, %
% Advances in Engineering Software , in press, %
% DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.advengsoft.2016.01.008 %
% %
%_________________________________________________________________________%
% This function draw the benchmark functions
function func_plot(func_name)
[lb,ub,dim,fobj]=Get_Functions_details(func_name);
switch func_name
case 'F1'
x=-100:2:100; y=x; %[-100,100]
case 'F2'
x=-100:2:100; y=x; %[-10,10]
case 'F3'
x=-100:2:100; y=x; %[-100,100]
case 'F4'
x=-100:2:100; y=x; %[-100,100]
case 'F5'
x=-200:2:200; y=x; %[-5,5]
case 'F6'
x=-100:2:100; y=x; %[-100,100]
case 'F7'
x=-1:0.03:1; y=x %[-1,1]
case 'F8'
x=-500:10:500;y=x; %[-500,500]
case 'F9'
x=-5:0.1:5; y=x; %[-5,5]
case 'F10'
x=-20:0.5:20; y=x;%[-500,500]
case 'F11'
x=-500:10:500; y=x;%[-0.5,0.5]
case 'F12'
x=-10:0.1:10; y=x;%[-pi,pi]
case 'F13'
x=-5:0.08:5; y=x;%[-3,1]
case 'F14'
x=-100:2:100; y=x;%[-100,100]
case 'F15'
x=-5:0.1:5; y=x;%[-5,5]
case 'F16'
x=-1:0.01:1; y=x;%[-5,5]
case 'F17'
x=-5:0.1:5; y=x;%[-5,5]
case 'F18'
x=-5:0.06:5; y=x;%[-5,5]
case 'F19'
x=-5:0.1:5; y=x;%[-5,5]
case 'F20'
x=-5:0.1:5; y=x;%[-5,5]
case 'F21'
x=-5:0.1:5; y=x;%[-5,5]
case 'F22'
x=-5:0.1:5; y=x;%[-5,5]
case 'F23'
x=-5:0.1:5; y=x;%[-5,5]
end
L=length(x);
f=[];
for i=1:L
for j=1:L
if strcmp(func_name,'F15')==0 && strcmp(func_name,'F19')==0 && strcmp(func_name,'F20')==0 && strcmp(func_name,'F21')==0 && strcmp(func_name,'F22')==0 && strcmp(func_name,'F23')==0
f(i,j)=fobj([x(i),y(j)]);
end
if strcmp(func_name,'F15')==1
f(i,j)=fobj([x(i),y(j),0,0]);
end
if strcmp(func_name,'F19')==1
f(i,j)=fobj([x(i),y(j),0]);
end
if strcmp(func_name,'F20')==1
f(i,j)=fobj([x(i),y(j),0,0,0,0]);
end
if strcmp(func_name,'F21')==1 || strcmp(func_name,'F22')==1 ||strcmp(func_name,'F23')==1
f(i,j)=fobj([x(i),y(j),0,0]);
end
end
end
surfc(x,y,f,'LineStyle','none');
end
2.1.3 initialization.m
%_________________________________________________________________________%
% Whale Optimization Algorithm (WOA) source codes demo 1.0 %
% %
% Developed in MATLAB R2011b(7.13) %
% %
% Author and programmer: Seyedali Mirjalili %
% %
% e-Mail: ali.mirjalili@gmail.com %
% seyedali.mirjalili@griffithuni.edu.au %
% %
% Homepage: http://www.alimirjalili.com %
% %
% Main paper: S. Mirjalili, A. Lewis %
% The Whale Optimization Algorithm, %
% Advances in Engineering Software , in press, %
% DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.advengsoft.2016.01.008 %
% %
%_________________________________________________________________________%
% This function initialize the first population of search agents
function Positions=initialization(SearchAgents_no,dim,ub,lb)
Boundary_no= size(ub,2); % numnber of boundaries
% If the boundaries of all variables are equal and user enter a signle
% number for both ub and lb
if Boundary_no==1
Positions=rand(SearchAgents_no,dim).*(ub-lb)+lb;
end
% If each variable has a different lb and ub
if Boundary_no>1
for i=1:dim
ub_i=ub(i);
lb_i=lb(i);
Positions(:,i)=rand(SearchAgents_no,1).*(ub_i-lb_i)+lb_i;
end
end
2.1.4 WOA.m
%_________________________________________________________________________%
% Whale Optimization Algorithm (WOA) source codes demo 1.0 %
% %
% Developed in MATLAB R2011b(7.13) %
% %
% Author and programmer: Seyedali Mirjalili %
% %
% e-Mail: ali.mirjalili@gmail.com %
% seyedali.mirjalili@griffithuni.edu.au %
% %
% Homepage: http://www.alimirjalili.com %
% %
% Main paper: S. Mirjalili, A. Lewis %
% The Whale Optimization Algorithm, %
% Advances in Engineering Software , in press, %
% DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.advengsoft.2016.01.008 %
% %
%_________________________________________________________________________%
% The Whale Optimization Algorithm
function [Leader_score,Leader_pos,Convergence_curve]=WOA(SearchAgents_no,Max_iter,lb,ub,dim,fobj)
% initialize position vector and score for the leader
Leader_pos=zeros(1,dim);
Leader_score=inf; %change this to -inf for maximization problems
%Initialize the positions of search agents
Positions=initialization(SearchAgents_no,dim,ub,lb);
Convergence_curve=zeros(1,Max_iter);
t=0;% Loop counter
% Main loop
while t<Max_iter
for i=1:size(Positions,1)
% Return back the search agents that go beyond the boundaries of the search space
Flag4ub=Positions(i,:)>ub;
Flag4lb=Positions(i,:)<lb;
Positions(i,:)=(Positions(i,:).*(~(Flag4ub+Flag4lb)))+ub.*Flag4ub+lb.*Flag4lb;
% Calculate objective function for each search agent
fitness=fobj(Positions(i,:));
% Update the leader
if fitness<Leader_score % Change this to > for maximization problem
Leader_score=fitness; % Update alpha
Leader_pos=Positions(i,:);
end
end
a=2-t*((2)/Max_iter); % a decreases linearly fron 2 to 0 in Eq. (2.3)
a2=-1+t*((-1)/Max_iter);% a2 linearly dicreases from -1 to -2 to calculate t in Eq. (3.12)
% Update the Position of search agents
for i=1:size(Positions,1)
r1=rand(); % r1 is a random number in [0,1]
r2=rand(); % r2 is a random number in [0,1]
A=2*a*r1-a; % Eq. (2.3) in the paper
C=2*r2; % Eq. (2.4) in the paper
b=1; % parameters in Eq. (2.5)
l=(a2-1)*rand+1; % parameters in Eq. (2.5)
p = rand(); % p in Eq. (2.6)
for j=1:size(Positions,2)
if p<0.5
if abs(A)>=1
rand_leader_index = floor(SearchAgents_no*rand()+1);
X_rand = Positions(rand_leader_index, :);
D_X_rand=abs(C*X_rand(j)-Positions(i,j)); % Eq. (2.7)
Positions(i,j)=X_rand(j)-A*D_X_rand; % Eq. (2.8)
elseif abs(A)<1
D_Leader=abs(C*Leader_pos(j)-Positions(i,j)); % Eq. (2.1)
Positions(i,j)=Leader_pos(j)-A*D_Leader; % Eq. (2.2)
end
elseif p>=0.5
distance2Leader=abs(Leader_pos(j)-Positions(i,j));
Positions(i,j)=distance2Leader*exp(b.*l).*cos(l.*2*pi)+Leader_pos(j); % Eq. (2.5)
end
end
end
t=t+1;
Convergence_curve(t)=Leader_score;
[t Leader_score]
end
2.1.5 main.m(运行文件)
%_________________________________________________________________________%
% Whale Optimization Algorithm (WOA) source codes demo 1.0 %
% %
% Developed in MATLAB R2011b(7.13) %
% %
% Author and programmer: Seyedali Mirjalili %
% %
% e-Mail: ali.mirjalili@gmail.com %
% seyedali.mirjalili@griffithuni.edu.au %
% %
% Homepage: http://www.alimirjalili.com %
% %
% Main paper: S. Mirjalili, A. Lewis %
% The Whale Optimization Algorithm, %
% Advances in Engineering Software , in press, %
% DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.advengsoft.2016.01.008 %
% %
%_________________________________________________________________________%
% You can simply define your cost in a seperate file and load its handle to fobj
% The initial parameters that you need are:
%__________________________________________
% fobj = @YourCostFunction
% dim = number of your variables
% Max_iteration = maximum number of generations
% SearchAgents_no = number of search agents
% lb=[lb1,lb2,...,lbn] where lbn is the lower bound of variable n
% ub=[ub1,ub2,...,ubn] where ubn is the upper bound of variable n
% If all the variables have equal lower bound you can just
% define lb and ub as two single number numbers
% To run WOA: [Best_score,Best_pos,WOA_cg_curve]=WOA(SearchAgents_no,Max_iteration,lb,ub,dim,fobj)
%__________________________________________
clear all
clc
SearchAgents_no=30; % Number of search agents
Function_name='F1'; % Name of the test function that can be from F1 to F23 (Table 1,2,3 in the paper)
Max_iteration=500; % Maximum numbef of iterations
% Load details of the selected benchmark function
[lb,ub,dim,fobj]=Get_Functions_details(Function_name);
[Best_score,Best_pos,WOA_cg_curve]=WOA(SearchAgents_no,Max_iteration,lb,ub,dim,fobj);
figure('Position',[269 240 660 290])
%Draw search space
subplot(1,2,1);
func_plot(Function_name);
title('Parameter space')
xlabel('x_1');
ylabel('x_2');
zlabel([Function_name,'( x_1 , x_2 )'])
%Draw objective space
subplot(1,2,2);
semilogy(WOA_cg_curve,'Color','r')
title('Objective space')
xlabel('Iteration');
ylabel('Best score obtained so far');
axis tight
grid on
box on
legend('WOA')
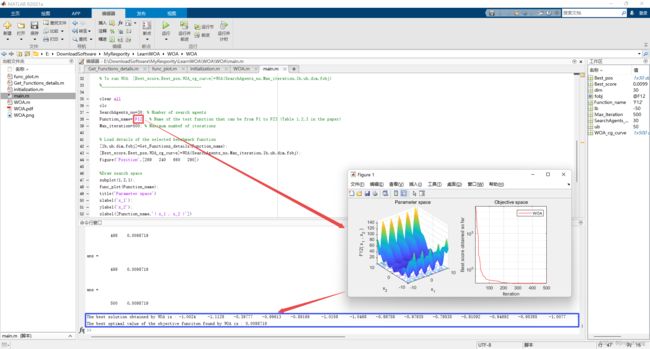
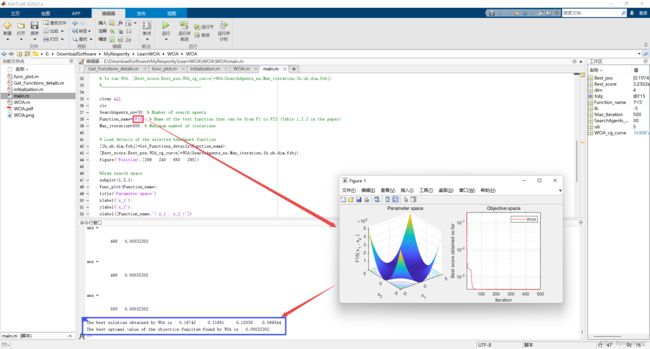
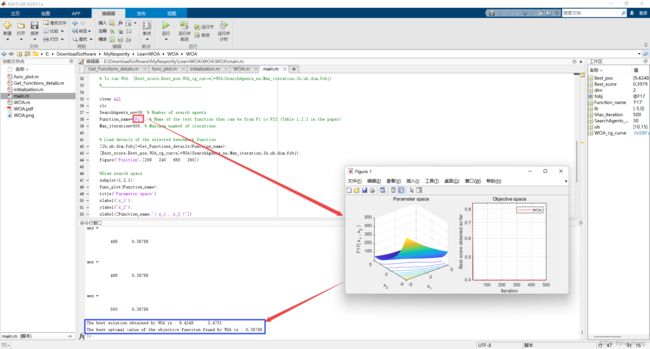
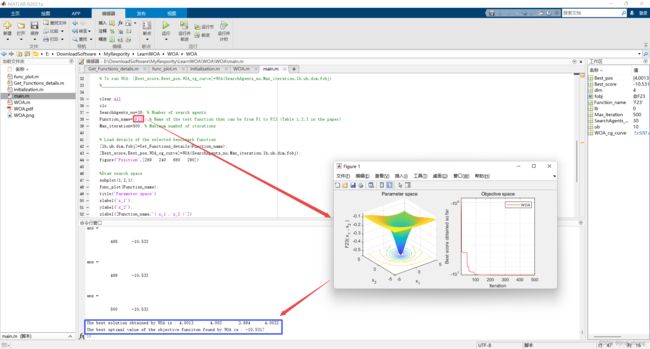
display(['The best solution obtained by WOA is : ', num2str(Best_pos)]);
display(['The best optimal value of the objective funciton found by WOA is : ', num2str(Best_score)]);
2.2 运行结果(函数F1~F23)

|

|

|

|

|
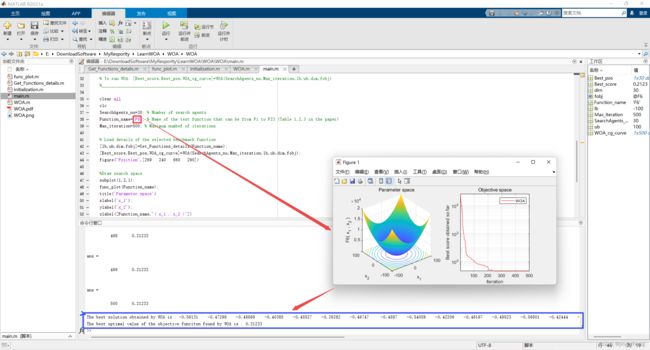
|

|
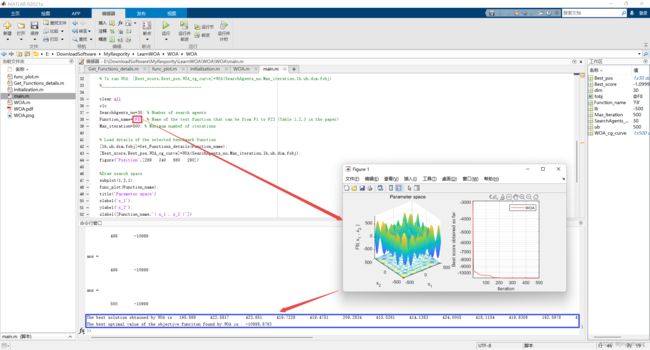
|

|
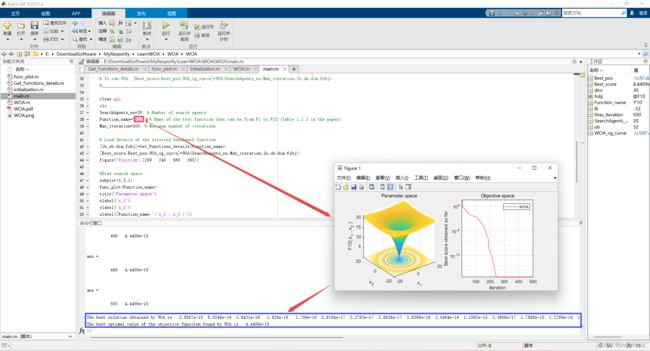
|
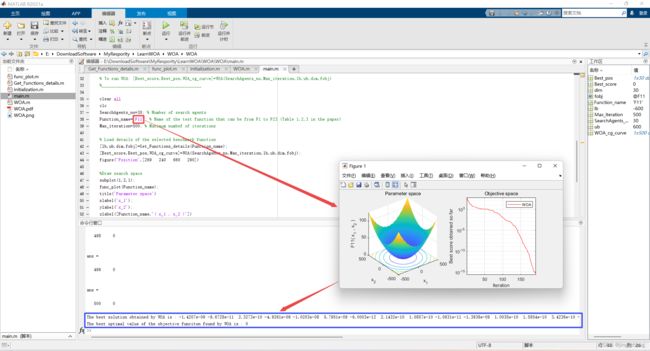
|
|

|

|
|

|
|

|

|

|

|

|
|
3、WOA求解TSP(C++ or Python)
3.1 WOA求解TSP(C++)
在利用优化算法求解TSP问题时,关键在于构造问题的有效解、确定目标函数、求解最大值或最小值,在相关算子的作用下使得个体在解空间不断搜寻,进而找到相对较优的满意解。
这里用到的C++环境为gcc 8.1.0 ,编写代码所使用的IDE为CodeBlocks。


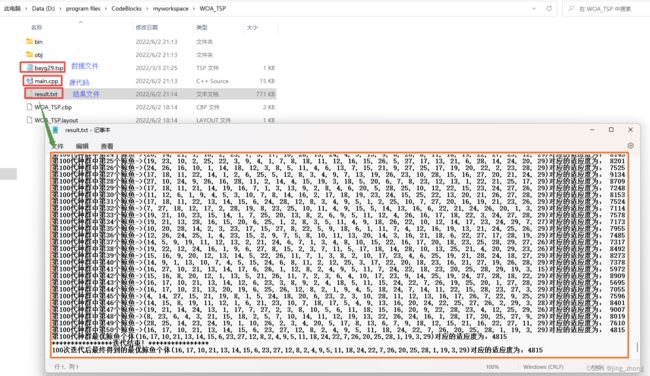
3.1.1 C++代码(main.cpp)
main.cpp
#include 3.1.2 运行结果

3.2 WOA求解TSP(Python)
这里用到的Python环境为Python 3.8,安装的依赖包有numpy和matplotlib,使用的IDE为PyCharm。

3.2.1 Python代码(WOA.py)
import random
import numpy as np
import math
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
class City(object): # 城市类
def __init__(self, ID, CoordinateX, CoordinateY):
self.ID = ID
self.CoordinateX = CoordinateX
self.CoordinateY = CoordinateY
def shuchu(self):
print(self.ID, self.CoordinateX, self.CoordinateY)
def getDistanceOfTwoCity(city1, city2): # 计算两个城市距离的函数
return math.sqrt((pow((city1.CoordinateX - city2.CoordinateX), 2) + pow((city1.CoordinateY - city2.CoordinateY), 2)) / 10.0)
def ReplaceContinueousSpace(str): # 替换字符串中的空格,并以逗号分隔符连接
n = len(str)
newstr = ''
for i in range(n):
if str[i] != ' ':
newstr += str[i]
if i+1 < n and str[i+1] == ' ':
newstr += ','
return newstr
Distances = [] # 城市距离矩阵
class CityGraph(object): # 城市群类
def __init__(self, filename):
self.Citys = [] # 所有的城市
self.n = 0 # 城市的数量
self.readDataFile(filename)
self.computeDistances()
def readDataFile(self, filename): # 读取城市数据文件函数
f = open(filename)
line = f.readline()
while line:
line_str = line.strip('\n')
city_linestr = ReplaceContinueousSpace(line_str).split(',')
city_i = City(int(city_linestr[0]), float(city_linestr[1]), float(city_linestr[2]))
self.Citys.append(city_i)
line = f.readline()
f.close()
self.n = len(self.Citys)
def computeDistances(self): # 得到城市距离矩阵的函数
for i in range(0, self.n):
dist_i = []
for j in range(0, self.n):
dist_ij = getDistanceOfTwoCity(self.Citys[i], self.Citys[j])
dist_i.append(dist_ij)
Distances.append(dist_i)
def shuchu(self): # 输出城市群信息的函数
print('城市ID-----城市横坐标X-----城市纵坐标Y')
for i in range(self.n):
self.Citys[i].shuchu()
print('----------各城市间的距离矩阵---------')
for i in range(0,self.n):
for j in range(0, self.n):
print(round(Distances[i][j],3), end=',')
print('\n')
# The Whale Optimization Algorithm By jing_zhong 2022.6.2
class WOA(object):
def __init__(self, population_size=50, dimension=29, lb=1, ub=29, Max_iteration = 100):
self.dimension = dimension # 每个鲸鱼个体位置的维度
self.lb = lb # 鲸鱼个体位置的下边界
self.ub = ub # 鲸鱼个体位置的上边界
self.PopSize = population_size # 鲸鱼种群大小
self.Max_iter = Max_iteration # 最大迭代次数
self.Population = [] # 鲸鱼种群
self.BestGeti = [] # 最优鲸鱼个体
self.BestFitness = -100 # 最优鲸鱼个体的适应度
self.Convergence_curve = [] # 各代鲸鱼种群最优适应度集合,用于绘制收敛曲线
def Init_Population(self): # 种群初始化,评价所有鲸鱼个体的适应度,获得最优个体
self.Population = []
for i in range(0, self.PopSize):
geti_i = []
for j in range(0, self.dimension):
xj = j + 1
geti_i.append(xj)
random.shuffle(geti_i)
self.Population.append(geti_i)
self.BestGeti = self.Population[0]
self.BestFitness = self.Evaluate(self.Population[0])
for i in range(0,self.PopSize):
fitness_i = self.Evaluate(self.Population[i])
print('种群初始化第 {} 个服务链座鱼鲸个体 {} 的适应度为 {}'.format(i + 1, self.Population[i], fitness_i))
if fitness_i < self.BestFitness:
self.BestGeti = self.Population[i]
self.BestFitness = fitness_i
print('\n初始化种群最优服务链座鱼鲸个体 {} 的适应度为 {}'.format(self.BestGeti, self.BestFitness))
def Valid_Geti(self,geti):
for j in range(0, self.dimension):
if geti[j] > self.lb and geti[j] < self.ub:
geti[j] = int(math.floor(geti[j]))
else:
geti[j] = random.randint(int(self.lb), int(self.ub))
# 调整鲸鱼个体解的有效性
n = len(geti)
std_geti = [] # 标准的一个全排列
std_flag = [] # 标记是否需要修改
Count = [] # 统计出现的次数
for i in range(0, n):
std_geti.append(i + 1)
Count.append(0)
std_flag.append(True)
for i in range(0, n):
findNum = std_geti[i]
count = 0
for j in range(0, n):
if (findNum == geti[j]):
count = count + 1
if count > 1:
std_flag[j] = False
Count[i] = count
for i in range(0, n):
if Count[i] == 0:
for j in range(0, n):
if std_flag[j] == False:
geti[j] = std_geti[i]
std_flag[j] = True
break
def Evaluate(self, geti): # 鲸鱼个体适应度评价函数
sumDist = 0
n = len(geti)
for i in range(0, n-1):
sumDist += Distances[geti[i]-1][geti[i+1]-1]
sumDist += Distances[geti[n-1]-1][geti[0]-1]
return int(sumDist)
def Start(self):
self.Init_Population() # 初始化鲸鱼种群
t = 0
while t < self.Max_iter:
a = 2 - t * (2 / self.Max_iter) # a decreases linearly fron 2 to 0
a2 = -1 + t * ((-1) / self.Max_iter) # a2 linearly dicreases from -1 to -2 to calculate t
for i in range(0, self.PopSize):
r1 = random.random() # r1 is a random number in [0,1]
r2 = random.random() # r2 is a random number in [0,1]
A = 2 * a * r1 - a
C = 2 * r2
b = 1
l = (a2 - 1) * random.random() +1
p = random.random()
for j in range(0,self.dimension):
if p < 0.5:
if abs(A) >= 1:
rand_leader_index = math.floor(self.PopSize * random.random())
X_rand = self.Population[rand_leader_index]
D_X_rand = abs(C * X_rand[j] - self.Population[i][j])
self.Population[i][j] = X_rand[j] - A * D_X_rand
else:
D_Leader = abs(C * self.BestGeti[j] - self.Population[i][j])
self.Population[i][j] = self.BestGeti[j] - A * D_Leader
else:
distance2Leader = abs(self.BestGeti[j] - self.Population[i][j])
self.Population[i][j] = distance2Leader * np.exp(b * l) * np.cos(l * 2 * math.pi) + self.BestGeti[j]
t = t + 1
self.Convergence_curve.append(self.BestFitness)
for i in range(0,self.PopSize):
self.Valid_Geti(self.Population[i]) # Return back the search agents that go beyond the boundaries of the search space
fitness_i = self.Evaluate(self.Population[i])
if fitness_i < self.BestFitness:
self.BestGeti = self.Population[i]
self.BestFitness = fitness_i
print('第 {} 代种群第 {} 个座鱼鲸个体 {} 的适应度为 {}'.format(t + 1, i+1, self.Population[i], fitness_i))
print('第 {} 代种群 最优座鱼鲸个体 {} 的适应度为 {}'.format(t + 1, self.BestGeti, self.BestFitness))
print('{} 次迭代后WOA种群最优座鱼鲸个体 {} 的适应度值为 {}'.format(self.Max_iter, self.BestGeti, self.BestFitness))
if __name__ == "__main__":
filename = 'bayg29.tsp'
citygraph = CityGraph(filename)
citygraph.shuchu()
woa = WOA(50, 29, 1, 29, 500)
woa.Start()
epochs = range(len(woa.Convergence_curve))
plt.figure()
plt.plot(epochs, woa.Convergence_curve, "b", label="woa")
plt.title('WOA_ServiceChain')
plt.xlabel("Epochs")
plt.ylabel("Fitness")
plt.legend()
plt.show()
3.2.2 运行结果

4、总结

WOA作为一种新型的启发式优化算法,通过对座头鲸的捕食行为进行数学建模,螺旋式上升和收缩包围机制易于理解,算法的执行时间短,求解速度快且效率高,在云计算、无线传感网、图像处理、交通、电力等领域都有了较为广泛的应用,对于求解旅行商、资源分配、组合优化等问题十分有效。
 |
 |
 |