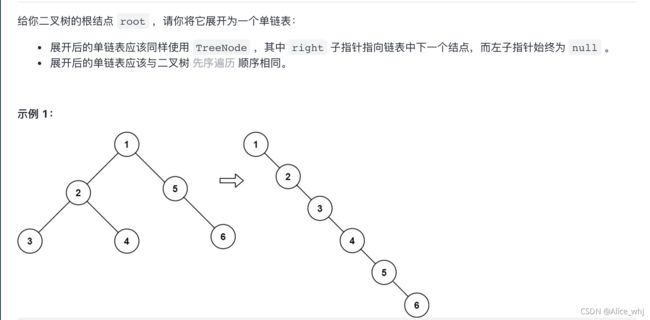
leetcode上再复习一遍
再做一遍
求一个数组中连续子向量的最大和
有一个链表,奇数位升序偶数位降序,如何将链表变成升序?
leetcode:
面试题 17.09. 第 k 个数
剑指 Offer II 062. 实现前缀树
掷骰子模拟
1838. 最高频元素的频数
剑指 Offer II 099. 最小路径之和
- 二叉树的最近公共祖先
华为机试题
华为机试题2
面试题|求华为机考第三题思路
玩牌
玩牌高手
华为9月8号机考第二题求助思路
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/maximum-subarray/
public class TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
TreeNode() {}
TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
this.val = val;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
}
先序遍历——栈
TreeNode这种有儿子节点的,,获取到一个node,相当于获取了其所有子孙后代。
将数列组成一棵树,采用递归!!!
我的实现
public void flatten(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null){
return;
}
Stack stack = new Stack<>();
Queue queue = new ArrayDeque<>();
TreeNode station = root;
while (stack.size() >0 || Objects.nonNull(station) ){
while (Objects.nonNull(station)){
stack.push(station);
queue.add(station.val);
station = station.left;
}
TreeNode temp = stack.pop();
station = temp.right;
}
if(queue.size() == 1){
return;
}
queue.poll();
root.left = null;
root.right = null;
toTree(root,queue);
return;
}
public void toTree(TreeNode root,Queue queue){
if(Objects.isNull(root)){
return;
}
root.right = new TreeNode(queue.poll(),null,null);
if(!queue.isEmpty()){
toTree(root.right,queue);
}
}
端点,就是只和其他一个点相连的点肯定不是,,除非总共只有一个或两个节点。
然后每个节点的年龄为其所有关联节点的年龄的最大值加一。最后找到除端点外年龄最小的。
迭代思想。
首先根据各边形成映射,即某个点和相连点点映射Map

1.1.假如{A:[B,C]}计算A的年龄通过BC,2而计算B的年龄又通过A会形成循环,,如果这次遍历的目的是计算A。。则计算B时就要排除A
1.2.孩子中最大值
1.3端点年龄为1
2.剪枝法
通过一次次去端点找到最后剩下的一个或两个节点

2.1
第一次遍历找端点,,都找完再一起删除,,如果找一个删一个则又会生成新的端点。
2.2 因为最终可能是一个或两个,,则在2处判断下
public class CBTInserter {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] edge = new int[][]{{0,1},{1,2},{2,3}};
List list = findMinHeightTrees1(4,edge);
}
public static List findMinHeightTrees1(int n, int[][] edges){
if(n==1){
return Collections.singletonList(0);
}
if(n==2){
List r = new LinkedList<>();
r.add(0);
r.add(1);
return r;
}
//整理
Map> map = toMap(n,edges);
while (map.size()>=2){
if(map.size() == 2 ){
Object[] leys = map.keySet().toArray();
if(map.get(Integer.valueOf(leys[0]+"")).size() == 1 && map.get(Integer.valueOf(leys[1]+"")).size() == 1 ){
break;
}
}
Set remove = new HashSet<>();
for(Integer key:map.keySet()){
if(map.get(key).size() == 1){
remove.add(key);
}
}
for(Integer a:remove){
Object v = map.get(a).toArray()[0];
map.get(Integer.valueOf(v+"")) .remove(a);
map.remove(a);
}
}
List result = new LinkedList<>();
result.addAll(map.keySet());
return result;
}
public static List findMinHeightTrees(int n, int[][] edges) {
if(n==1){
return Collections.singletonList(0);
}
if(n==2){
List r = new LinkedList<>();
r.add(0);
r.add(1);
return r;
}
//整理
Map> map = toMap(n,edges);
//递归
List result = new LinkedList<>();
int min = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for(int i=0;i> toMap(int n, int[][] edges){
Map> map = new HashMap<>(n);
for(int[] edge:edges){
Integer a = edge[0];
int b = edge[1];
for(int i=0;i<2;i++){
Set set = map.get(a);
if(Objects.isNull(set)){
Set set1 = new HashSet<>();
set1.add(b);
map.put(a,set1);
} else {
set.add(b) ;
}
int temp = a;
a=b;
b =temp;
}
}
return map;
}
public static int maxAge(Map> map,Integer self,Integer father){
Set childs = map.get(self);
if(childs.size() == 1){
return 1;
}
int age = 0;
for(Integer child:childs){
if(child != father){
age = Math.max(age,maxAge(map,child,self));
}
}
return age + 1;
}
}
???面试题 04.05. 合法二叉搜索树
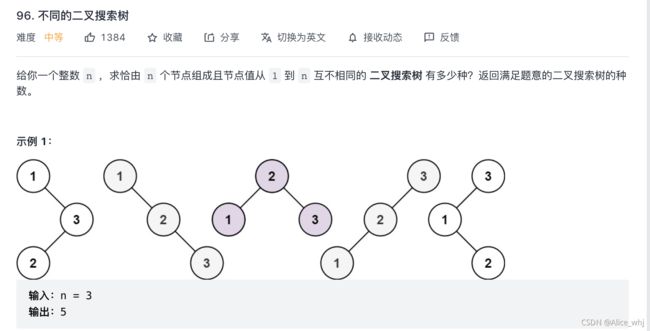
结题思路:假设n个节点存在二叉排序树的个数是G(n),1为根节点,2为根节点,…,n为根节点,当1为根节点时,其左子树节点个数为0,右子树节点个数为n-1,同理当2为根节点时,其左子树节点个数为1,右子树节点为n-2,所以可得G(n) = G(0)G(n-1)+G(1)(n-2)+…+G(n-1)*G(0)
public static int numTrees(int n) {
if(n<=2){
return n;
}
return cal(n);
}
public static int cal(int n){
if(n0 || n1){
return 1;
}
if(n==2){
return 2;
}
int sum = 0;
for(int i=0;i
}
return sum;
}
二叉搜索树关键的性质是根节点的值大于左子树所有节点的值,小于右子树所有节点的值,且左子树和右子树也同样为二叉搜索树。因此在生成所有可行的二叉搜索树的时候,假设当前序列长度为 nn,如果我们枚举根节点的值为 ii,那么根据二叉搜索树的性质我们可以知道左子树的节点值的集合为 [1 \ldots i-1][1…i−1],右子树的节点值的集合为 [i+1 \ldots n][i+1…n]。而左子树和右子树的生成相较于原问题是一个序列长度缩小的子问题,因此我们可以想到用回溯的方法来解决这道题目。
我们定义 generateTrees(start, end) 函数表示当前值的集合为 [\textit{start},\textit{end}][start,end],返回序列 [\textit{start},\textit{end}][start,end] 生成的所有可行的二叉搜索树。按照上文的思路,我们考虑枚举 [\textit{start},\textit{end}][start,end] 中的值 ii 为当前二叉搜索树的根,那么序列划分为了 [\textit{start},i-1][start,i−1] 和 [i+1,\textit{end}][i+1,end] 两部分。我们递归调用这两部分,即 generateTrees(start, i - 1) 和 generateTrees(i + 1, end),获得所有可行的左子树和可行的右子树,那么最后一步我们只要从可行左子树集合中选一棵,再从可行右子树集合中选一棵拼接到根节点上,并将生成的二叉搜索树放入答案数组即可。
递归的入口即为 generateTrees(1, n),出口为当 \textit{start}>\textit{end}start>end 的时候,当前二叉搜索树为空,返回空节点即可。
public List generateTrees(int n) {
if(n<=0){
return null;
}
return generateTree(1,n);
}
public List generateTree(int start,int end){
if(start>end){
return null;
}
if(start == end){
List one = new ArrayList<>();
TreeNode node = new TreeNode(start);
one.add(node);
return one;
}
List result = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i=start;i<=end;i++){
List left = generateTree(start,i-1);
List right = generateTree(i+1,end) ;
if(left == null && right == null){
TreeNode node = new TreeNode(i);
result.add(node);
} else if(left == null){
for(TreeNode r:right) {
TreeNode node = new TreeNode(i);
node.right = r;
result.add(node);
}
} else if(right == null){
for(TreeNode l:left) {
TreeNode node = new TreeNode(i);
node.left = l;
result.add(node);
}
} else {
for(TreeNode r:right) {
for(TreeNode l:left){
TreeNode node = new TreeNode(i);
node.right = r;
node.left =l;
result.add(node);
}
}
}
}
return result;
}
我的解法:
class Solution {
public long maxTaxiEarnings(int n, int[][] rides) {
Map> map = pos(rides);
return cal(n,rides,map);
}
public long cal(int i,int[][] rides,Map> map){
if(i==1){
return 0;
}
long max = cal(i-1,rides,map);
if(map.containsKey(i)){
Set set = map.get(i);
for(Integer k:set){
long temp = (i-rides[k][0]+rides[k][2])+cal(rides[k][0],rides,map);
max = Math.max(max,temp);
}
}
return max;
}
public Map> pos(int[][] rides){
Map> map = new HashMap<>();
for(int i=0;i set = new HashSet<>();
set.add(i);
map.put(end,set);
}
}
return map;
}
}
我的解法超时了
后来换了一下遍历顺序,从低到高并做了存储,以减少重复计算
public static long maxTaxiEarnings2(int n, int[][] rides){
Map
int[] posMax = new int[n+1];
long max = 0;
for(int i=2;i
if(map.containsKey(i)){
Set set = map.get(i);
for(int p:set){
posMax[i] = Math.max(posMax[i],(rides[p][1]-rides[p][0]+rides[p][2]+posMax[rides[p][0]])) ;
}
max = Math.max(max,posMax[i]);
}
}
return max;
}
跑过了大部分case,在n=90000的case上报错了。与结果不符
看了某个别人的提交,正确,没搞懂区别
public static long maxTaxiEarnings1(int n, int[][] rides) {
long[] dp = new long[n+1];
List
for(int[] ride : rides) {
if(hash[ride[1]] == null) {
hash[ride[1]] = new ArrayList<>();
}
hash[ride[1]].add(ride);
}
long max = 0;
for(int i = 2; i < n+1; ++i) {
dp[i] = dp[i - 1];
if(hash[i] != null) {
for(int[] b : hash[i]) {
dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i], i - b[0] + b[2] + dp[b[0]]);
}
}
max = Math.max(max, dp[i]);
}
return max;
}

我的做法就是寻找从第二个到倒数第二个元素,以及元素缝隙依次遍历作为中心,向两边扩散取值看是否相等。

public String longestPalindrome(String s) {
int len = s.length();
if (len < 2) {
return s;
}
int maxLen = 1;
int begin = 0;
// dp[i][j] 表示 s[i..j] 是否是回文串
boolean[][] dp = new boolean[len][len];
// 初始化:所有长度为 1 的子串都是回文串
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
dp[i][i] = true;
}
char[] charArray = s.toCharArray();
// 递推开始
// 先枚举子串长度
for (int L = 2; L <= len; L++) {
// 枚举左边界,左边界的上限设置可以宽松一些
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
// 由 L 和 i 可以确定右边界,即 j - i + 1 = L 得
int j = L + i - 1;
// 如果右边界越界,就可以退出当前循环
if (j >= len) {
break;
}
if (charArray[i] != charArray[j]) {
dp[i][j] = false;
} else {
if (j - i < 3) {
dp[i][j] = true;
} else {
dp[i][j] = dp[i + 1][j - 1];
}
}
// 只要 dp[i][L] == true 成立,就表示子串 s[i..L] 是回文,此时记录回文长度和起始位置
if (dp[i][j] && j - i + 1 > maxLen) {
maxLen = j - i + 1;
begin = i;
}
}
}
return s.substring(begin, begin + maxLen);
}
class LRUCache {
private Integer capacity = 0;
private List sort = new ArrayList<>();
private HashMap map = new HashMap<>();
public LRUCache(int capacity) {
if(capacity <0) capacity =0;
this.capacity = capacity;
}
public int get(int key) {
if(!map.containsKey(key)){
return -1;
}
sort.remove((Integer)key);
sort.add((Integer)key);
return map.get(key);
}
public void put(int key, int value) {
if(map.containsKey(key)){
sort.remove((Integer)key);
sort.add((Integer)key);
map.put(key,value);
return;
}
if(sort.size() >= capacity){
Integer ke = sort.remove(0);
map.remove(ke);
}
sort.add(key);
map.put(key,value);
}
}
这种方法在链表中寻找指定元素时时间复杂度时O(n),
维护顺序肯定要用链表,,寻找链表中元素想达到O(1)的时间复杂度,那么如何实现呢,,借助hashmap,map中value的值为node 节点
自己实现的双向链表
public class LRUCache {
class DLinkedNode {
int key;
int value;
DLinkedNode prev;
DLinkedNode next;
public DLinkedNode() {}
public DLinkedNode(int _key, int _value) {key = _key; value = _value;}
}
private Map cache = new HashMap();
private int size;
private int capacity;
private DLinkedNode head, tail;
public LRUCache(int capacity) {
this.size = 0;
this.capacity = capacity;
// 使用伪头部和伪尾部节点
head = new DLinkedNode();
tail = new DLinkedNode();
head.next = tail;
tail.prev = head;
}
public int get(int key) {
DLinkedNode node = cache.get(key);
if (node == null) {
return -1;
}
// 如果 key 存在,先通过哈希表定位,再移到头部
moveToHead(node);
return node.value;
}
public void put(int key, int value) {
DLinkedNode node = cache.get(key);
if (node == null) {
// 如果 key 不存在,创建一个新的节点
DLinkedNode newNode = new DLinkedNode(key, value);
// 添加进哈希表
cache.put(key, newNode);
// 添加至双向链表的头部
addToHead(newNode);
++size;
if (size > capacity) {
// 如果超出容量,删除双向链表的尾部节点
DLinkedNode tail = removeTail();
// 删除哈希表中对应的项
cache.remove(tail.key);
--size;
}
}
else {
// 如果 key 存在,先通过哈希表定位,再修改 value,并移到头部
node.value = value;
moveToHead(node);
}
}
private void addToHead(DLinkedNode node) {
node.prev = head;
node.next = head.next;
head.next.prev = node;
head.next = node;
}
private void removeNode(DLinkedNode node) {
node.prev.next = node.next;
node.next.prev = node.prev;
}
private void moveToHead(DLinkedNode node) {
removeNode(node);
addToHead(node);
}
private DLinkedNode removeTail() {
DLinkedNode res = tail.prev;
removeNode(res);
return res;
}
}
sql
不会这个

反转链表

我的思路:
难点一:遍历到要反转的临界节点,反转完的链表与原链表连接
难点二:反转
反转的话,由于不是双链表,一旦next被修改,就无法通过链路找到原本的next了,可以用多个指针。
我的解法:
public static ListNode reverseBetween(ListNode head, int left, int right) {
if(left==right){
return head;
}
ListNode one = null;
ListNode tow = new ListNode();
tow.next = head;
ListNode A = new ListNode();
A.next = head;
ListNode B = new ListNode();
B.next = A.next.next;
ListNode C = new ListNode();
C.next = B.next.next;
int index = 1;
while (Objects.nonNull(B.next) && index < right){
if(index < left){
if(Objects.isNull(one)){
one = new ListNode();
one.next = head;
} else {
one.next = one.next.next;
}
tow.next = tow.next.next;
A.next = A.next.next;
B.next = B.next.next;
C.next = C.next.next;
} else if(index >= left){
B.next.next = A.next;
if(!(index+1 == right)){
A.next = B.next;
B.next = C.next;
C.next = Objects.isNull(C.next.next)?null:C.next.next;
}
}
index++;
}
if(Objects.isNull(one)){
tow.next.next = C.next;
return B.next;
} else {
one.next.next =B.next;
tow.next.next = C.next;
return head;
}
}

一看本题就知道要用递归,,4个分段分别满足条件,相当于第一个分段满足条件后,剩余字符串求满足三个分段的,,每个分段字数为1-3,分段数为4,即我完成前三个分段后直接判断最后一个分段是否满足条件即可。且最终的值要能被记录,且对边界条件要判断。
以下是我的解法;太长了,,
class Solution {
public List restoreIpAddresses(String s) {
char[] list = s.toCharArray();
List strings = new ArrayList<>();
test(list,0,4,"",strings);
List result= new ArrayList<>();
for(String l:strings){
char[] chars = l.toCharArray();
StringBuffer stringBuffer = new StringBuffer();
int last = 0;
for(int i=0;i<3;i++){
int len = chars[i]-48;
stringBuffer.append(Arrays.copyOfRange(list,last,last+len));
stringBuffer.append(".");
last=last+len;
}
stringBuffer.append(Arrays.copyOfRange(list,last,list.length));
result.add(stringBuffer.toString());
}
return result;
}
public void test(char[] list, int index, int count, String result,List strings) {
if (count >= 1 && index >= list.length ) {
return;
}
if(count == 1 && index < list.length-3){
return;
}
if(count == 1){
if(index == list.length-3 && list[index]-48 !=0 && ((list[index] - 48) * 100 + (list[index + 1] - 48) * 10 + list[index+2] - 48) <= 255){
strings.add(result+3);
return;
}
if(index == list.length-2 && list[index]-48 !=0){
strings.add(result+2);
return;
}
if(index == list.length-1){
strings.add(result+1);
return;
}
return;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= 3; i++) {
if (i == 1) {
test(list, index + 1, count - 1, result + 1,strings);
} else if (i == 2) {
if (list[index]-48 != 0 && index + 1 < list.length) {
test(list, index + 2, count - 1, result + 2,strings);
}
} else {
if (list[index]-48 != 0 && index + 2 < list.length && ((list[index] - 48) * 100 + (list[index + 1] - 48) * 10 + list[index] - 48) <= 255)
test(list, index + 3, count - 1, result + 3,strings);
}
}
}
}
算法: 在数组中找到左边数都比它小, 右边数都比它大的数
在无序不重复数组中寻找满足如下条件的值:
该值左边的数均不大于它
该值右边的数均不小于它
我的做法:
//不重复数组,找出所有左边比他小,右边比他大的所有数
public static int[] midValue(int[] nums){
if(Objects.isNull(nums) || nums.length<3){
return null;
}
Set smallSet = new HashSet<>();
Set bigSet = new HashSet<>();
int max = nums[0];
for(int i=1;i0){
smallSet.add(i);
max = nums[i];
}
}
int min = nums[nums.length-1];
for(int j=nums.length-2;j>0;j--){
if(nums[j]-min<0){
bigSet.add(j);
min = nums[j];
}
}
if(smallSet.isEmpty() || bigSet.isEmpty()){
return null;
}
smallSet.retainAll(bigSet);
int[] result = new int[smallSet.size()];
int t=0;
for(Integer k:smallSet){
result[t++] = nums[k];
}
return result;
}
一个链表中奇数位递增,偶数位递减,排序成递增,不能用额外空间
我的做法,先拆再合,拆用双指针
public static Node sort(Node head){
if(Objects.isNull(head)){
return null;
}
Node oneHead = new Node();
Node one = oneHead;
Node two = new Node();
Node k1 = head;
Node k2 = head.next;
while (Objects.nonNull(k2)){
one.next = k1;
k1 = k2.next;
k2.next = two.next;
two.next = k2;
one = one.next;
if(Objects.isNull(k1)){
break;
}
k2=k1.next;
}
if(Objects.isNull(k1)){
one.next = null;
} else {
one.next = k1;
k1.next = null;
}
return merge(oneHead.next,two.next);
}
public Node merge(Node one,Node two){
Node head = new Node();
Node node = head;
while (Objects.nonNull(one) || Objects.nonNull(two)){
if(Objects.isNull(one)){
node.next = two;
break;
}
if(Objects.isNull(two)){
node.next = one;
break;
}
if(one.data<=two.data){
node.next = one;
one = one.next;
} else {
node.next = two;
two = two.next;
}
node = node.next;
}
return head.next;
}
栈用递归方式反转
public void reverse(Stack stack){
if(stack.size()==0 || stack.size()==1){
return;
}
int temp1 = stack.pop();
reverse(stack);
int temp2 = stack.pop();
reverse(stack);
stack.push(temp1);
reverse(stack);
stack.push(temp2);
}
验证括号是否成对
public boolean test(String str){
if(StringUtils.isEmpty(str) || str.length()%2==1){
return false;
}
char[] chars = str.toCharArray();
int num = 0;
for(char c:chars){
if(c == '('){
num++;
} else {
if(num ==0){
return false;
} else {
num--;
}
}
}
return num==0;
}
链表反转,一个LRU,二叉树镜像左右反转
public TreeNode mirrorTree(TreeNode root) {
if(Objects.isNull(root)){
return null;
}
TreeNode result = new TreeNode(root.val);
result.left = mirrorTree(root.right);
result.right = mirrorTree(root.left);
return result;
}