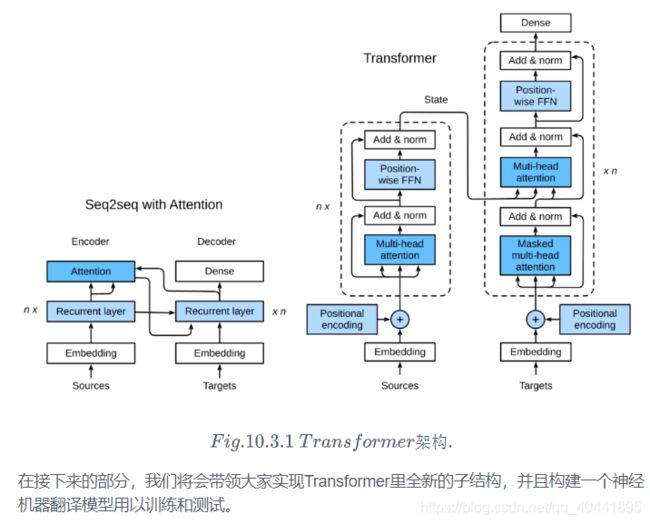
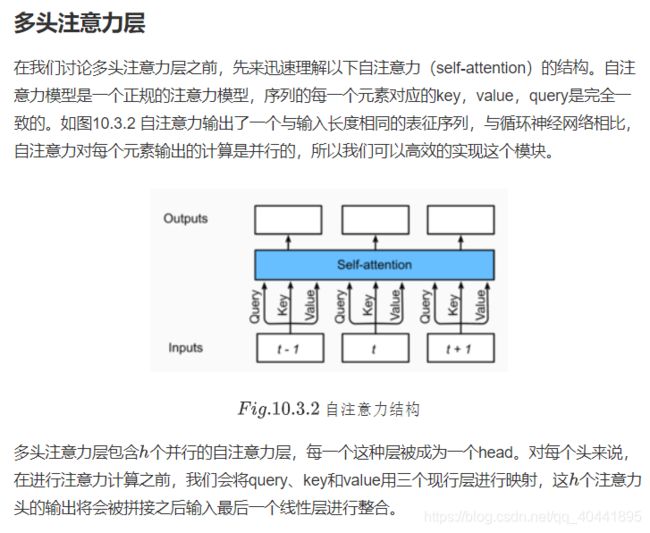
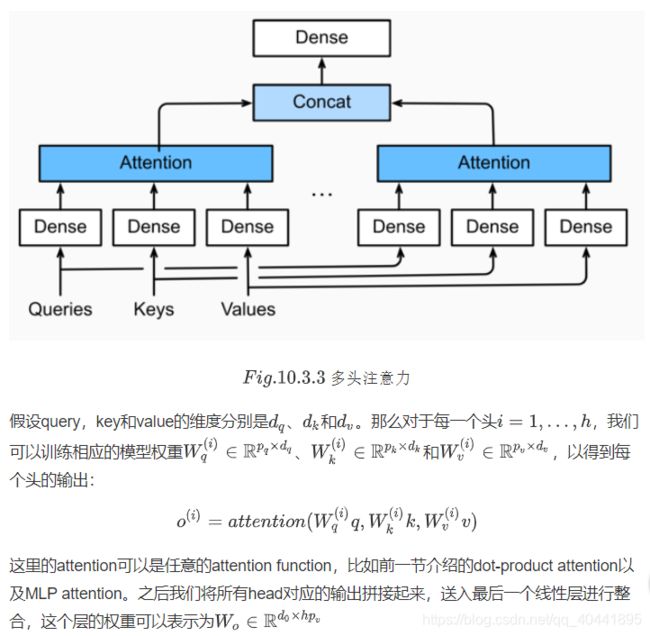
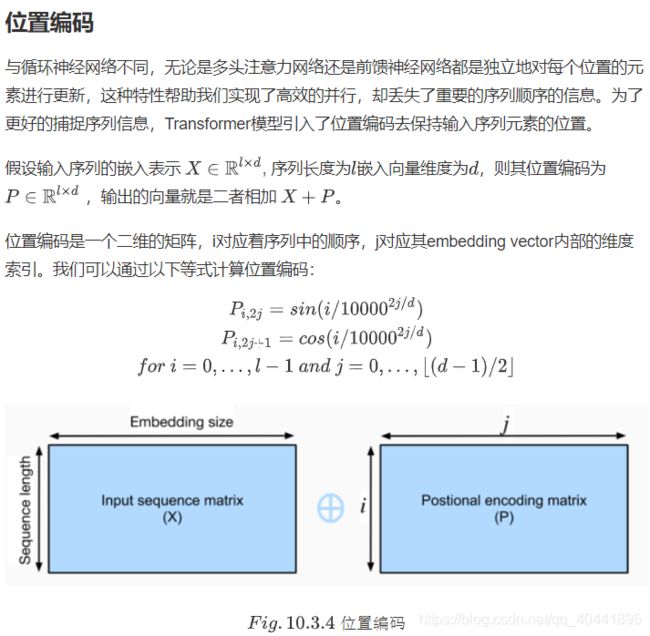
transformer
import os
import math
import numpy as np
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import sys
sys.path.append('/home/kesci/input/d2len9900')
import d2l
以下是复制了上一小节中 masked softmax 实现,这里就不再赘述了。
def SequenceMask(X, X_len,value=-1e6):
maxlen = X.size(1)
X_len = X_len.to(X.device)
#print(X.size(),torch.arange((maxlen),dtype=torch.float)[None, :],'\n',X_len[:, None] )
mask = torch.arange((maxlen), dtype=torch.float, device=X.device)
mask = mask[None, :] < X_len[:, None]
#print(mask)
X[~mask]=value
return X
def masked_softmax(X, valid_length):
# X: 3-D tensor, valid_length: 1-D or 2-D tensor
softmax = nn.Softmax(dim=-1)
if valid_length is None:
return softmax(X)
else:
shape = X.shape
if valid_length.dim() == 1:
try:
valid_length = torch.FloatTensor(valid_length.numpy().repeat(shape[1], axis=0))#[2,2,3,3]
except:
valid_length = torch.FloatTensor(valid_length.cpu().numpy().repeat(shape[1], axis=0))#[2,2,3,3]
else:
valid_length = valid_length.reshape((-1,))
# fill masked elements with a large negative, whose exp is 0
X = SequenceMask(X.reshape((-1, shape[-1])), valid_length)
return softmax(X).reshape(shape)
# Save to the d2l package.
class DotProductAttention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, dropout, **kwargs):
super(DotProductAttention, self).__init__(**kwargs)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(dropout)
# query: (batch_size, #queries, d)
# key: (batch_size, #kv_pairs, d)
# value: (batch_size, #kv_pairs, dim_v)
# valid_length: either (batch_size, ) or (batch_size, xx)
def forward(self, query, key, value, valid_length=None):
d = query.shape[-1]
# set transpose_b=True to swap the last two dimensions of key
scores = torch.bmm(query, key.transpose(1,2)) / math.sqrt(d)
attention_weights = self.dropout(masked_softmax(scores, valid_length))
return torch.bmm(attention_weights, value)
class MultiHeadAttention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_size, hidden_size, num_heads, dropout, **kwargs):
super(MultiHeadAttention, self).__init__(**kwargs)
self.num_heads = num_heads
self.attention = DotProductAttention(dropout)
self.W_q = nn.Linear(input_size, hidden_size, bias=False)
self.W_k = nn.Linear(input_size, hidden_size, bias=False)
self.W_v = nn.Linear(input_size, hidden_size, bias=False)
self.W_o = nn.Linear(hidden_size, hidden_size, bias=False)
def forward(self, query, key, value, valid_length):
# query, key, and value shape: (batch_size, seq_len, dim),
# where seq_len is the length of input sequence
# valid_length shape is either (batch_size, )
# or (batch_size, seq_len).
# Project and transpose query, key, and value from
# (batch_size, seq_len, hidden_size * num_heads) to
# (batch_size * num_heads, seq_len, hidden_size).
query = transpose_qkv(self.W_q(query), self.num_heads)
key = transpose_qkv(self.W_k(key), self.num_heads)
value = transpose_qkv(self.W_v(value), self.num_heads)
if valid_length is not None:
# Copy valid_length by num_heads times
device = valid_length.device
valid_length = valid_length.cpu().numpy() if valid_length.is_cuda else valid_length.numpy()
if valid_length.ndim == 1:
valid_length = torch.FloatTensor(np.tile(valid_length, self.num_heads))
else:
valid_length = torch.FloatTensor(np.tile(valid_length, (self.num_heads,1)))
valid_length = valid_length.to(device)
output = self.attention(query, key, value, valid_length)
output_concat = transpose_output(output, self.num_heads)
return self.W_o(output_concat)
def transpose_qkv(X, num_heads):
# Original X shape: (batch_size, seq_len, hidden_size * num_heads),
# -1 means inferring its value, after first reshape, X shape:
# (batch_size, seq_len, num_heads, hidden_size)
X = X.view(X.shape[0], X.shape[1], num_heads, -1)
# After transpose, X shape: (batch_size, num_heads, seq_len, hidden_size)
X = X.transpose(2, 1).contiguous()
# Merge the first two dimensions. Use reverse=True to infer shape from
# right to left.
# output shape: (batch_size * num_heads, seq_len, hidden_size)
output = X.view(-1, X.shape[2], X.shape[3])
return output
# Saved in the d2l package for later use
def transpose_output(X, num_heads):
# A reversed version of transpose_qkv
X = X.view(-1, num_heads, X.shape[1], X.shape[2])
X = X.transpose(2, 1).contiguous()
return X.view(X.shape[0], X.shape[1], -1)
cell = MultiHeadAttention(5, 9, 3, 0.5)
X = torch.ones((2, 4, 5))
valid_length = torch.FloatTensor([2, 3])
cell(X, X, X, valid_length).shape
# Save to the d2l package.
class PositionWiseFFN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_size, ffn_hidden_size, hidden_size_out, **kwargs):
super(PositionWiseFFN, self).__init__(**kwargs)
self.ffn_1 = nn.Linear(input_size, ffn_hidden_size)
self.ffn_2 = nn.Linear(ffn_hidden_size, hidden_size_out)
def forward(self, X):
return self.ffn_2(F.relu(self.ffn_1(X)))
与多头注意力层相似,FFN层同样只会对最后一维的大小进行改变;除此之外,对于两个完全相同的输入,FFN层的输出也将相等。
ffn = PositionWiseFFN(4, 4, 8)
out = ffn(torch.ones((2,3,4)))
print(out, out.shape)
layernorm = nn.LayerNorm(normalized_shape=2, elementwise_affine=True)
batchnorm = nn.BatchNorm1d(num_features=2, affine=True)
X = torch.FloatTensor([[1,2], [3,4]])
print('layer norm:', layernorm(X))
print('batch norm:', batchnorm(X))
# Save to the d2l package.
class AddNorm(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, hidden_size, dropout, **kwargs):
super(AddNorm, self).__init__(**kwargs)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(dropout)
self.norm = nn.LayerNorm(hidden_size)
def forward(self, X, Y):
return self.norm(self.dropout(Y) + X)
由于残差连接,X和Y需要有相同的维度。
add_norm = AddNorm(4, 0.5)
add_norm(torch.ones((2,3,4)), torch.ones((2,3,4))).shape
class PositionalEncoding(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, embedding_size, dropout, max_len=1000):
super(PositionalEncoding, self).__init__()
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(dropout)
self.P = np.zeros((1, max_len, embedding_size))
X = np.arange(0, max_len).reshape(-1, 1) / np.power(
10000, np.arange(0, embedding_size, 2)/embedding_size)
self.P[:, :, 0::2] = np.sin(X)
self.P[:, :, 1::2] = np.cos(X)
self.P = torch.FloatTensor(self.P)
def forward(self, X):
if X.is_cuda and not self.P.is_cuda:
self.P = self.P.cuda()
X = X + self.P[:, :X.shape[1], :]
return self.dropout(X)
测试
下面我们用PositionalEncoding这个类进行一个小测试,取其中的四个维度进行可视化。 我们可以看到,第4维和第5维有相同的频率但偏置不同。第6维和第7维具有更低的频率;因此positional encoding对于不同维度具有可区分性。
import numpy as np
pe = PositionalEncoding(20, 0)
Y = pe(torch.zeros((1, 100, 20))).numpy()
d2l.plot(np.arange(100), Y[0, :, 4:8].T, figsize=(6, 2.5),
legend=["dim %d" % p for p in [4, 5, 6, 7]])
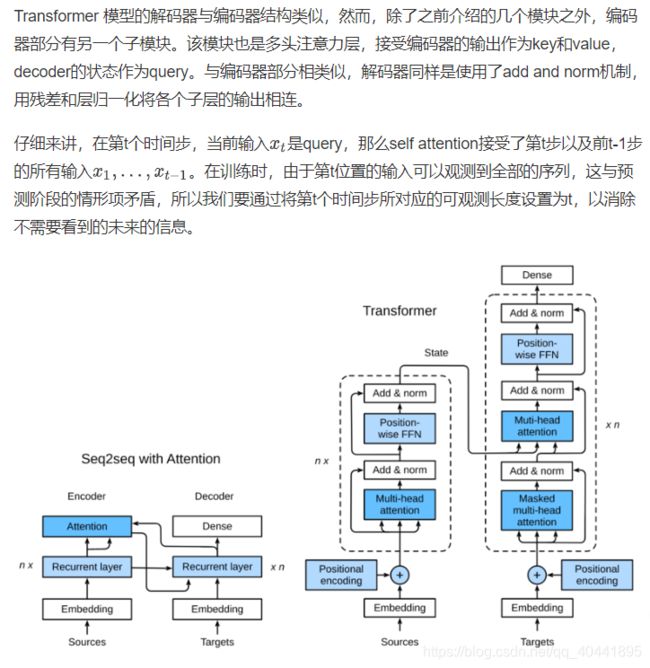
编码器
我们已经有了组成Transformer的各个模块,现在我们可以开始搭建了!编码器包含一个多头注意力层,一个position-wise FFN,和两个 Add and Norm层。对于attention模型以及FFN模型,我们的输出维度都是与embedding维度一致的,这也是由于残差连接天生的特性导致的,因为我们要将前一层的输出与原始输入相加并归一化。
class EncoderBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, embedding_size, ffn_hidden_size, num_heads,
dropout, **kwargs):
super(EncoderBlock, self).__init__(**kwargs)
self.attention = MultiHeadAttention(embedding_size, embedding_size, num_heads, dropout)
self.addnorm_1 = AddNorm(embedding_size, dropout)
self.ffn = PositionWiseFFN(embedding_size, ffn_hidden_size, embedding_size)
self.addnorm_2 = AddNorm(embedding_size, dropout)
def forward(self, X, valid_length):
Y = self.addnorm_1(X, self.attention(X, X, X, valid_length))
return self.addnorm_2(Y, self.ffn(Y))
# batch_size = 2, seq_len = 100, embedding_size = 24
# ffn_hidden_size = 48, num_head = 8, dropout = 0.5
X = torch.ones((2, 100, 24))
encoder_blk = EncoderBlock(24, 48, 8, 0.5)
encoder_blk(X, valid_length).shape
class TransformerEncoder(d2l.Encoder):
def __init__(self, vocab_size, embedding_size, ffn_hidden_size,
num_heads, num_layers, dropout, **kwargs):
super(TransformerEncoder, self).__init__(**kwargs)
self.embedding_size = embedding_size
self.embed = nn.Embedding(vocab_size, embedding_size)
self.pos_encoding = PositionalEncoding(embedding_size, dropout)
self.blks = nn.ModuleList()
for i in range(num_layers):
self.blks.append(
EncoderBlock(embedding_size, ffn_hidden_size,
num_heads, dropout))
def forward(self, X, valid_length, *args):
X = self.pos_encoding(self.embed(X) * math.sqrt(self.embedding_size))
for blk in self.blks:
X = blk(X, valid_length)
return X
# test encoder
encoder = TransformerEncoder(200, 24, 48, 8, 2, 0.5)
encoder(torch.ones((2, 100)).long(), valid_length).shape
解码器
class DecoderBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, embedding_size, ffn_hidden_size, num_heads,dropout,i,**kwargs):
super(DecoderBlock, self).__init__(**kwargs)
self.i = i
self.attention_1 = MultiHeadAttention(embedding_size, embedding_size, num_heads, dropout)
self.addnorm_1 = AddNorm(embedding_size, dropout)
self.attention_2 = MultiHeadAttention(embedding_size, embedding_size, num_heads, dropout)
self.addnorm_2 = AddNorm(embedding_size, dropout)
self.ffn = PositionWiseFFN(embedding_size, ffn_hidden_size, embedding_size)
self.addnorm_3 = AddNorm(embedding_size, dropout)
def forward(self, X, state):
enc_outputs, enc_valid_length = state[0], state[1]
# state[2][self.i] stores all the previous t-1 query state of layer-i
# len(state[2]) = num_layers
# If training:
# state[2] is useless.
# If predicting:
# In the t-th timestep:
# state[2][self.i].shape = (batch_size, t-1, hidden_size)
# Demo:
# love dogs ! [EOS]
# | | | |
# Transformer
# Decoder
# | | | |
# I love dogs !
if state[2][self.i] is None:
key_values = X
else:
# shape of key_values = (batch_size, t, hidden_size)
key_values = torch.cat((state[2][self.i], X), dim=1)
state[2][self.i] = key_values
if self.training:
batch_size, seq_len, _ = X.shape
# Shape: (batch_size, seq_len), the values in the j-th column are j+1
valid_length = torch.FloatTensor(np.tile(np.arange(1, seq_len+1), (batch_size, 1)))
valid_length = valid_length.to(X.device)
else:
valid_length = None
X2 = self.attention_1(X, key_values, key_values, valid_length)
Y = self.addnorm_1(X, X2)
Y2 = self.attention_2(Y, enc_outputs, enc_outputs, enc_valid_length)
Z = self.addnorm_2(Y, Y2)
return self.addnorm_3(Z, self.ffn(Z)), state
decoder_blk = DecoderBlock(24, 48, 8, 0.5, 0)
X = torch.ones((2, 100, 24))
state = [encoder_blk(X, valid_length), valid_length, [None]]
decoder_blk(X, state)[0].shape
对于Transformer解码器来说,构造方式与编码器一样,除了最后一层添加一个dense layer以获得输出的置信度分数。下面让我们来实现一下Transformer Decoder,除了常规的超参数例如vocab_size embedding_size 之外,解码器还需要编码器的输出 enc_outputs 和句子有效长度 enc_valid_length。
class TransformerDecoder(d2l.Decoder):
def __init__(self, vocab_size, embedding_size, ffn_hidden_size,
num_heads, num_layers, dropout, **kwargs):
super(TransformerDecoder, self).__init__(**kwargs)
self.embedding_size = embedding_size
self.num_layers = num_layers
self.embed = nn.Embedding(vocab_size, embedding_size)
self.pos_encoding = PositionalEncoding(embedding_size, dropout)
self.blks = nn.ModuleList()
for i in range(num_layers):
self.blks.append(
DecoderBlock(embedding_size, ffn_hidden_size, num_heads,
dropout, i))
self.dense = nn.Linear(embedding_size, vocab_size)
def init_state(self, enc_outputs, enc_valid_length, *args):
return [enc_outputs, enc_valid_length, [None]*self.num_layers]
def forward(self, X, state):
X = self.pos_encoding(self.embed(X) * math.sqrt(self.embedding_size))
for blk in self.blks:
X, state = blk(X, state)
return self.dense(X), state
训练
import zipfile
import torch
import requests
from io import BytesIO
from torch.utils import data
import sys
import collections
class Vocab(object): # This class is saved in d2l.
def __init__(self, tokens, min_freq=0, use_special_tokens=False):
# sort by frequency and token
counter = collections.Counter(tokens)
token_freqs = sorted(counter.items(), key=lambda x: x[0])
token_freqs.sort(key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True)
if use_special_tokens:
# padding, begin of sentence, end of sentence, unknown
self.pad, self.bos, self.eos, self.unk = (0, 1, 2, 3)
tokens = ['', '', '', '']
else:
self.unk = 0
tokens = ['']
tokens += [token for token, freq in token_freqs if freq >= min_freq]
self.idx_to_token = []
self.token_to_idx = dict()
for token in tokens:
self.idx_to_token.append(token)
self.token_to_idx[token] = len(self.idx_to_token) - 1
def __len__(self):
return len(self.idx_to_token)
def __getitem__(self, tokens):
if not isinstance(tokens, (list, tuple)):
return self.token_to_idx.get(tokens, self.unk)
else:
return [self.__getitem__(token) for token in tokens]
def to_tokens(self, indices):
if not isinstance(indices, (list, tuple)):
return self.idx_to_token[indices]
else:
return [self.idx_to_token[index] for index in indices]
def load_data_nmt(batch_size, max_len, num_examples=1000):
"""Download an NMT dataset, return its vocabulary and data iterator."""
# Download and preprocess
def preprocess_raw(text):
text = text.replace('\u202f', ' ').replace('\xa0', ' ')
out = ''
for i, char in enumerate(text.lower()):
if char in (',', '!', '.') and text[i-1] != ' ':
out += ' '
out += char
return out
with open('/home/kesci/input/fraeng6506/fra.txt', 'r') as f:
raw_text = f.read()
text = preprocess_raw(raw_text)
# Tokenize
source, target = [], []
for i, line in enumerate(text.split('\n')):
if i >= num_examples:
break
parts = line.split('\t')
if len(parts) >= 2:
source.append(parts[0].split(' '))
target.append(parts[1].split(' '))
# Build vocab
def build_vocab(tokens):
tokens = [token for line in tokens for token in line]
return Vocab(tokens, min_freq=3, use_special_tokens=True)
src_vocab, tgt_vocab = build_vocab(source), build_vocab(target)
# Convert to index arrays
def pad(line, max_len, padding_token):
if len(line) > max_len:
return line[:max_len]
return line + [padding_token] * (max_len - len(line))
def build_array(lines, vocab, max_len, is_source):
lines = [vocab[line] for line in lines]
if not is_source:
lines = [[vocab.bos] + line + [vocab.eos] for line in lines]
array = torch.tensor([pad(line, max_len, vocab.pad) for line in lines])
valid_len = (array != vocab.pad).sum(1)
return array, valid_len
src_vocab, tgt_vocab = build_vocab(source), build_vocab(target)
src_array, src_valid_len = build_array(source, src_vocab, max_len, True)
tgt_array, tgt_valid_len = build_array(target, tgt_vocab, max_len, False)
train_data = data.TensorDataset(src_array, src_valid_len, tgt_array, tgt_valid_len)
train_iter = data.DataLoader(train_data, batch_size, shuffle=True)
return src_vocab, tgt_vocab, train_iter
import os
import d2l
# 平台暂时不支持gpu,现在会自动使用cpu训练,gpu可以用了之后会使用gpu来训练
os.environ["CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES"] = "1"
embed_size, embedding_size, num_layers, dropout = 32, 32, 2, 0.05
batch_size, num_steps = 64, 10
lr, num_epochs, ctx = 0.005, 250, d2l.try_gpu()
print(ctx)
num_hiddens, num_heads = 64, 4
src_vocab, tgt_vocab, train_iter = load_data_nmt(batch_size, num_steps)
encoder = TransformerEncoder(
len(src_vocab), embedding_size, num_hiddens, num_heads, num_layers,
dropout)
decoder = TransformerDecoder(
len(src_vocab), embedding_size, num_hiddens, num_heads, num_layers,
dropout)
model = d2l.EncoderDecoder(encoder, decoder)
d2l.train_s2s_ch9(model, train_iter, lr, num_epochs, ctx)
model.eval()
for sentence in ['Go .', 'Wow !', "I'm OK .", 'I won !']:
print(sentence + ' => ' + d2l.predict_s2s_ch9(
model, sentence, src_vocab, tgt_vocab, num_steps, ctx))