【计算机视觉】如何可视化卷积神经网络的特征图(含源代码)
文章目录
- 一、特征图(Feature Map)
- 二、可视化特征图
-
- 2.1 原图
- 2.2 一个特征图的可视化
- 2.3 多个通道特征图
一、特征图(Feature Map)
特征图(Feature Map)是深度学习卷积神经网络(CNN)中的重要概念。它是卷积层的输出,是对输入图像进行卷积运算后产生的图像。
以下是关于特征图的一些关键信息:
- 特征提取:特征图是通过卷积层从原始输入图像中提取的信息。这些信息代表了不同的特征,如边缘、纹理、形状等。
- 深度层次:卷积神经网络通常包括多个卷积层,每个卷积层生成一组特征图。随着网络的深度增加,特征图的抽象程度逐渐提高。
- 空间维度:特征图通常比输入图像的空间维度小,因为卷积运算会减小图像的空间分辨率。每个特征图对应卷积核在输入图像上的一个感受野(receptive field)。
- 通道数:每个卷积层可以生成多个特征图,这些特征图在通道维度上不同。通常,一个卷积层的输出特征图数量由卷积核的数量决定。
- 特征图可视化:特征图通常以热力图的形式进行可视化,其中不同颜色表示不同的特征激活强度。这有助于理解卷积神经网络对输入数据的响应。
- 特征图在分类中的作用:在图像分类任务中,深度学习模型的最后一层通常包含全连接层,它将特征图转化为类别概率。通过训练,模型能够自动学习如何从特征图中提取图像中的有用信息,以便进行分类。
特征图的生成是卷积神经网络的核心过程,它使深度学习模型能够有效地理解和表示复杂的图像数据,从而实现各种计算机视觉任务,如图像分类、目标检测和分割。
二、可视化特征图
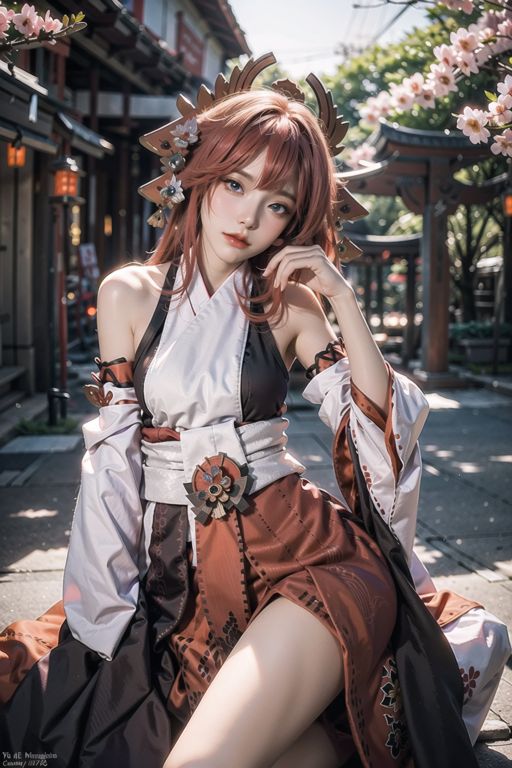
2.1 原图
from PIL import Image
image_path = './images/6.png'
image = Image.open(image_path)
image.show()
使用PIL库打开图像文件,并调用show()方法来显示图像。这是一种基本的图像显示方法。
2.2 一个特征图的可视化
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from PIL import Image
import torchvision.transforms as transforms
# 加载RGB图像
image_path = './images/6.png'
image = Image.open(image_path)
# 将图像转换为PyTorch张量并进行必要的预处理
transform = transforms.Compose([transforms.Resize((224, 224)),
transforms.ToTensor()])
input_image = transform(image).unsqueeze(0) # 添加一个批次维度
# 创建一个卷积层(示例卷积核)
conv_layer = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=3, out_channels=1, kernel_size=3, padding=1)
# 进行卷积操作
output_feature_map = conv_layer(input_image)
# 获取特征图数据
feature_map_data = output_feature_map[0, 0].detach().numpy()
# 使用Matplotlib绘制特征图的热力图
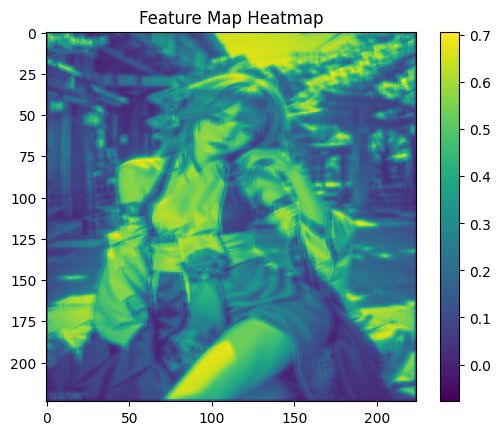
plt.imshow(feature_map_data, cmap="viridis")
plt.title("Feature Map Heatmap")
plt.colorbar()
plt.show()
这段代码演示了如何使用PyTorch和Matplotlib来创建和可视化一个卷积神经网络(CNN)的特征图。下面是代码的解读:
首先,通过PIL库的Image.open()函数加载一张RGB图像,该图像被存储在image_path路径中。
然后,使用torchvision.transforms来对图像进行必要的预处理。这包括将图像的大小调整为 (224, 224) 像素,并将其转换为PyTorch张量。unsqueeze(0)用于为图像添加一个批次维度,因为卷积层通常期望输入为批次数据。
接下来,创建了一个卷积层(nn.Conv2d),该卷积层定义了输入通道数(in_channels,这里是3,对应于RGB通道)、输出通道数(out_channels,这里是1,通常用于示例目的),卷积核的大小(kernel_size,这里是3x3),以及填充(padding,这里是1,以保持输出特征图的大小与输入相同)。
进行卷积操作,通过将卷积层应用于输入图像,以生成特征图。
从特征图中获取数据,通过output_feature_map提取第一个批次的第一个通道的特征图数据,然后使用.detach().numpy()将其转换为NumPy数组。
最后,使用Matplotlib绘制特征图的热力图,其中plt.imshow()用于显示特征图数据,cmap="viridis"指定了颜色映射,plt.title()用于设置标题,plt.colorbar()添加了颜色条以显示特征激活的强度。
这段代码的输出将是原始图像的特征图的热力图,显示了卷积层中特定通道的激活情况,这有助于理解卷积神经网络在图像中检测到的不同特征。
2.3 多个通道特征图
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from PIL import Image
import torchvision.transforms as transforms
# 加载RGB图像
image_path = './images/6.png'
image = Image.open(image_path)
# 将图像转换为PyTorch张量并进行必要的预处理
transform = transforms.Compose([transforms.Resize((224, 224)),
transforms.ToTensor()])
input_image = transform(image).unsqueeze(0) # 添加一个批次维度
# 创建一个卷积层,输出多个特征图
conv_layer = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=3, out_channels=5, kernel_size=3, padding=1)
# 进行卷积操作
output_feature_maps = conv_layer(input_image)
# 获取每个特征图的数据
feature_map_data_list = [output_feature_maps[0, i].detach().numpy() for i in range(output_feature_maps.shape[1])]
# 可视化每个特征图的热力图
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 6))
for i, feature_map_data in enumerate(feature_map_data_list):
plt.subplot(1, 5, i + 1)
plt.imshow(feature_map_data, cmap="viridis")
plt.title(f"Feature Map {i + 1}")
plt.axis('off')
plt.show()