数据结构第二课 -----线性表之顺序表
作者前言
✨✨✨✨✨✨
作者介绍:
作者id:老秦包你会,
简单介绍:
喜欢学习C语言和python等编程语言,是一位爱分享的博主,有兴趣的小可爱可以来互讨
个人主页::小小页面
gitee页面:秦大大
一个爱分享的小博主 欢迎小可爱们前来借鉴
顺序表
- **作者前言**
- 线性表
- 顺序表
- 动态顺序表的使用
-
- 动态顺序表开辟扩大问题
- 顺序表的初始化
- 顺序表的销毁
- 顺序表的尾部插入
- 顺序表的头部插入
- 顺序表尾部删除
- 顺序表的头部删除
- 顺序表的随机插入
- 顺序表的随机删除
- 顺序表的查找
- 顺序表的菜单操作
- 总结
线性表
线性表(linear list)是n个具有相同特性的数据元素的有限序列。 线性表是一种在实际中广泛使
用的数据结构,常见的线性表:顺序表、链表、栈、队列、字符串…
线性表在逻辑上是线性结构,也就是说是连续的一条直线,但是在物理结构上并不一定,线性表在物理上存储时,通常以数组和链式结构的形式存储
顺序表
顺序表是用一段物理地址连续的存储单元,依次存储数据元素的线性结构,一般情况下采用数组存储,在数组上完成数据的增删改查
顺序表一般分为两种:
- 静态顺序表:使用定长数组存储元素。
#include
一般静态的顺序表用处不大,这里主要介绍动态顺序表
2. 动态顺序表: 使用动态开辟的数组存储。
#include动态顺序表的使用
动态顺序表开辟扩大问题
在使用动态顺序表的大小,一般都是先开辟一定数量的空间,如果开辟的空间不够用时我们就可以利用realloc扩大空间,我们时常为扩大多少空间烦恼,在顺序表中是没有规定扩大多少,一个个扩大或几千或者几万的扩大都是可以的,但是为了节省空间,和减少扩大频率,我们默认一般都是把目前的空间扩大两倍,比如定义大小为100 下次扩大为200,下次为400,
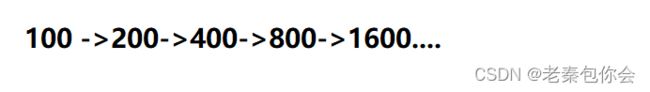
遇到问题就要具体分析,空间的扩大没有限制,按实际情况来
顺序表的初始化
//初始化
void SLinit(SeList* SL)
{
//方式1
/*SL->Sel = NULL;
SL->count = 0;
SL->capacity = 0;*/
//方式2
SL->Sel = calloc(SIZE, sizeof(SLDatatype));
SL->count = 0;
SL->capacity = SIZE;
}
初始化有两种一种是没有给空间的初始化,一种是给空间的初始化。所以我们可以二选一
顺序表的销毁
因为我们是动态开辟。所以我们要使用free来释放空间,否则就会可能造成内存泄漏,这里用于结束顺序表
//销毁
void Desstroy(SeList* SL)
{
free(SL->Sel);
SL->Sel = NULL;
SL->count = 0;
SL->capacity = 0;
}
顺序表的尾部插入
思路:第一步先判断空间是否满了。没满直接在最后面插入,满了就要先扩容,再插入,我们需要注意的是SL->capacity的个数是否为0
//尾插
void SLPushBack(SeList* SL, SLDatatype elemest)
{
//扩大空间
if (SL->capacity == SL->count)
{
//扩2倍
size_t NewSize = ((SL->capacity * 2) > 0 ? (SL->capacity * 2) : 4);
SLDatatype * mdt = realloc(SL->Sel, sizeof(SLDatatype) * NewSize);
if (mdt != NULL)
{
SL->Sel = mdt;
SL->capacity = SL->capacity * 2;
}
else
{
perror("SLPushBack _ realloc");
return;
}
}
SL->Sel[SL->count] = elemest;
SL->count++;
}
这里我们只要的知识还是顺序表,这个过程我们要使用到realloc函数,这个函数主要的作用是扩大动态开辟的空间,扩大的方式有两种,一种是原地扩容(效率高),一种是异地扩容(效率低,会找到一块符合条件的空间开辟,然后把原来的数据拷贝过来,free掉原来的地址)realloc是可以对NULL进行扩容相当于malloc
代码如下:
#include这里就可以简单的判断出是原地扩容还是异地扩容了,
顺序表的头部插入
思路:第一步先判断空间是否满了。没满直接在前面插入,满了就要先扩容,再插入,我们需要注意的是SL->capacity的个数是否为0
//扩大空间
void capacityadd(SeList* SL)
{
//扩大空间
if (SL->capacity == SL->count)
{
//扩2倍
size_t NewSize = ((SL->capacity * 2) > 0 ? (SL->capacity * 2) : 4);
SLDatatype* mdt = realloc(SL->Sel, sizeof(SLDatatype) * NewSize);
if (mdt != NULL)
{
SL->Sel = mdt;
SL->capacity = SL->capacity * 2;
}
else
{
perror("SLPushBack _ realloc");
return;
}
}
}
// 头插
void SLPushFront(SeList* SL, SLDatatype elemest)
{
capacityadd(SL);
// 往后移动
for (int i = SL->count; i > 0; i--)
{
SL->Sel[i] = SL->Sel[i - 1];
}
//插入
SL->Sel[0] = elemest;
SL->count++;
}
在这里的时间复杂度是O(n),但是我们如果插入n个数据,时间复杂度就是O(n^2),插入的数量越多时间复杂度就越高
顺序表尾部删除
思路:要判断顺序表的存储的数据是否为0,不判断可能SL->capacity为负数,后面插入数据就有可能会越界访问
//尾删
void SLPopBack(SeList* SL)
{
if (SL->count)
{
SL->count--;
}
else
{
return;
}
}
这里我们不需要把空间删除我们只需把SL->capacity减1,就可以下次尾插或者头插就覆盖掉这个数据
我们还可以使用assert函数来判断
顺序表的头部删除
思路:就是我们只需要把后面的往前覆盖就行,我们还要判断是否是SL->count为0
// 头删
void SLPopFront(SeList* SL)
{
assert(SL && SL->count);
int idx = 0;
while (idx < SL->count - 1)
{
SL->Sel[idx] = SL->Sel[idx + 1];
idx++;
}
SL->count--;
}
顺序表的随机插入
这里插入我们要注意顺序表的空间是连续的,存储数据也是连续的,不可以跳过一两个空间存储数据
只能紧挨这其他数据
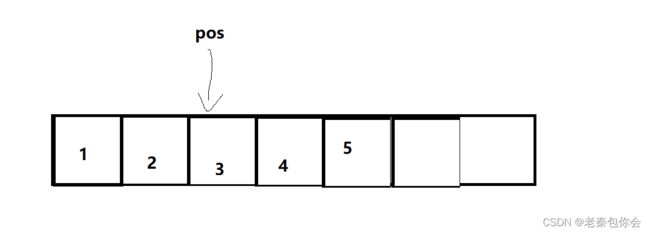
/随机插入
void SLInsert(SeList* SL,int pos, SLDatatype elemest)
{
assert(SL && pos >= 0 && pos <= SL->count);
//判断容量是否正常
capacityadd(SL);
//往后移
int i = SL->count - 1;
while (i >= pos)
{
SL->Sel[i + 1] = SL->Sel[i];
}
SL->Sel[pos] = elemest;
SL->count++;
}
顺序表的随机删除
和上面的思路是一样的
//随机删除
void SLErase(SeList* SL, int pos, SLDatatype elemest)
{
assert(SL && pos >= 0 && pos < SL->count);
//覆盖
int i = pos;
while (i < SL->count - 1)
{
SL->Sel[i] = SL->Sel[i + 1];
i++;
}
SL->count--;
}
顺序表的查找
//查找
int SLFind(SeList* SL, SLDatatype elemest)
{
assert(SL);
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < SL->count; i++)
{
if (SL->Sel[i] == elemest)
{
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
顺序表的菜单操作
void menu()
{
printf("****************************\n");
printf("**** 0.exit 1.pushback ***\n");
printf("**** 2.pushfront 3.popback**\n");
printf("**** 4.popfront 5.inser **\n");
printf("**** 6.ereat 7.print **\n");
printf("**** 8.find **\n");
printf("***************************/\n");
}
int main()
{
/*Test();*/
int input = 0;
printf("是否开始:1/0:");
scanf("%d", &input);
SeList S1;
SLinit(&S1);
do
{
menu();
int select = 0;
printf("请选择你的决定:>");
scanf("%d", &select);
if (select == 0)
{
printf("退出程序\n");
break;
}
else if (select == 1)
{
int elemest = 0;
printf("请输入你要尾插数据个数和数据:>");
scanf("%d", &elemest);
while (elemest)
{
int data = 0;
scanf("%d", &data);
SLPushBack(&S1, data);
elemest--;
}
}
else if (select == 2)
{
int elemest = 0;
printf("请输入你要头插数据个数和数据:>");
scanf("%d", &elemest);
while (elemest)
{
int data = 0;
scanf("%d", &data);
SLPushFront(&S1, data);
elemest--;
}
}
else if (select == 3)
{
int elemest = 0;
printf("请输入你要尾部删除数据个数:>");
scanf("%d", &elemest);
while (elemest)
{
SLPopBack(&S1);
elemest--;
}
}
else if (select == 4)
{
int elemest = 0;
printf("请输入你要头部删除数据个数:>");
scanf("%d", &elemest);
while (elemest)
{
SLPopFront(&S1);
elemest--;
}
}
else if (select == 5)
{
int position = 0;
int elemest = 0;
printf("请输入你要插入的位置和数据:>");
scanf("%d %d", &position, &elemest);
SLInsert(&S1, position, elemest);
}
else if (select == 6)
{
int position = 0;
printf("请输入你要删除的位置:>");
scanf("%d", &position);
SLErase(&S1, position);
continue;
}
else if (select == 7)
{
SLPrint(&S1);
}
else if (select == 8)
{
int position = 0;
printf("请输入你要查找的数据:>");
scanf("%d", &position);
int a = SLFind(&S1, position);
if (a == -1)
{
printf("找不到\n");
}
else
{
printf("下标为%d\n", a);
}
continue;
}
else
{
printf("输入有误,请重新输入\n");
}
} while (input);
SLDesstroy(&S1);
return 0;
}
总结
这里主要介绍了顺序表,有不懂的小可爱可以私聊我