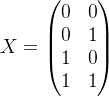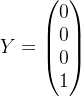简单的二层BP神经网络-实现逻辑与门(Matlab和Python)
该程序主要是设计一个2层的神经网络,通过BP算法实现与门逻辑。
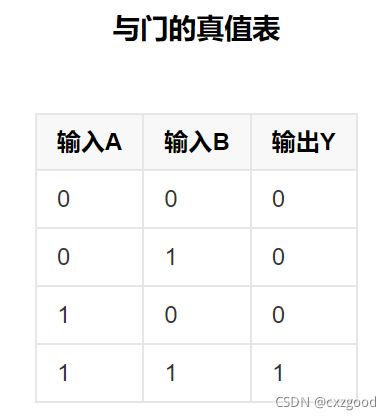
一、逻辑与门
二、二层的神经网络
三、数学推导
根据真值表可知,输入输出的对应逻辑关系。
故设输入X,输出Y为
权值W1为2*2矩阵,W2为2*1矩阵
(1). 前向计算过程
第1个神经元输出为:![]()
第2个神经元输出为:![]()
其中:![]()
(2). 反向传播过程
公式由链式求导法则得出,这里不做推导。结果如下:
第2个神经元误差为:
![]()
第1个神经元误差为:![]()
其中:![]()
权值W2的偏导数为:![]()
权值W1的偏导数为:![]()
(3). 梯度下降算法更新权值
![]()
四、程序
Matlab代码:
clear all;clc
%数据初始化
X = [0 0;0 1; 1 0;1 1];
Y = [0;0;0;1];
w1 = 3 * rand(2,2) - 0.5;
w2 = 3 * rand(2,1) - 0.5;
W1 = w1;
W2 = w2;
m = length(Y);
alpha = 5; %learning_rate
number_iters = 50000; %number_of_training_iterations
%迭代
for i=1:number_iters
%Forward Propagation
a0 = X; %4*2
a1 = X * W1; %4*2
z1 = sigmoid(a1); %4*2
a2 = z1 * W2; %4*1
z2 = sigmoid(a2); %4*1
%Back Propagation
error2 = Y - z2; %4*1
delta2 = error2.* sigmoidGradient(a2); %4*1
error1 = delta2 * W2'; %4*2
delta1 = error1.* sigmoidGradient(a1); %4*2
W1_adjustment = X' * delta1; %2*2
W2_adjustment = z1' * delta2; %2*1
W1 = W1 + alpha * W1_adjustment; %2*2
W2 = W2 + alpha * W2_adjustment; %2*1
%Cost Function
J(i) = (1/m) * sum(Y - z2)^2;
end
%绘制代价函数曲线
plot(J);
xlabel('number of iterations')
ylabel('Costfunction in the output layer');
%输出随机初始值
fprintf('Stage 1) Random starting synaptic weights:\n');
disp(w1);
disp(w2);
%输出训练后参数值
fprintf('Stage 2) New synaptic weights after training:\n');
disp(W1);
disp(W2);
%预测
fprintf('Stage 3) Considering a new situation [0 0;0 1; 1 0;1 1] -> ?:\n');
x = [0 0;0 1; 1 0;1 1];
y = sigmoid(sigmoid(x * W1) * W2);
%取整
% [a,b]=size(y);
% for i=1:a
% for j=1:b
% if y(i,j)>0.5
% y(i,j)=1;
% else y(i,j)=0;
% end
% end
% end
disp(y);
输出结果:
Stage 3) Considering a new situation [0 0;0 1; 1 0;1 1] -> ?:
0.0002
0.0044
0.0056
0.9950代价函数图像:
Python代码:
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from numpy import exp, array, random, dot
class NeuronLayer():
def __init__(self, number_of_neurons, number_of_inputs_per_neuron):
self.synaptic_weights = 3 * random.random((number_of_inputs_per_neuron, number_of_neurons)) - 0.5
class NeuralNetwork():
def __init__(self, layer1, layer2):
self.layer1 = layer1
self.layer2 = layer2
self.learning_rate = 10
# The Sigmoid function, which describes an S shaped curve.
# We pass the weighted sum of the inputs through this function to
# normalise them between 0 and 1.
def __sigmoid(self, x):
return 1 / (1 + exp(-x))
# The derivative of the Sigmoid function.
# This is the gradient of the Sigmoid curve.
# It indicates how confident we are about the existing weight.
def __sigmoid_derivative(self, x):
return x * (1 - x)
# We train the neural network through a process of trial and error.
# Adjusting the synaptic weights each time.
def train(self, training_set_inputs, training_set_outputs, number_of_training_iterations):
for iteration in range(number_of_training_iterations):
# Pass the training set through our neural network
output_from_layer_1, output_from_layer_2 = self.think(training_set_inputs)
# Calculate the error for layer 2 (The difference between the desired output
# and the predicted output).
layer2_error = training_set_outputs - output_from_layer_2
layer2_delta = layer2_error * self.__sigmoid_derivative(output_from_layer_2)
# Calculate the error for layer 1 (By looking at the weights in layer 1,
# we can determine by how much layer 1 contributed to the error in layer 2).
layer1_error = layer2_delta.dot(self.layer2.synaptic_weights.T)
layer1_delta = layer1_error * self.__sigmoid_derivative(output_from_layer_1)
# Calculate how much to adjust the weights by
layer1_adjustment = training_set_inputs.T.dot(layer1_delta)
layer2_adjustment = output_from_layer_1.T.dot(layer2_delta)
# Adjust the weights.
self.layer1.synaptic_weights += layer1_adjustment * self.learning_rate
self.layer2.synaptic_weights += layer2_adjustment * self.learning_rate
# The neural network thinks.
def think(self, inputs):
output_from_layer1 = self.__sigmoid(dot(inputs, self.layer1.synaptic_weights))
output_from_layer2 = self.__sigmoid(dot(output_from_layer1, self.layer2.synaptic_weights))
return output_from_layer1, output_from_layer2
# The neural network prints its weights
def print_weights(self):
print(" Layer 1 (2 neurons, each with 2 inputs):")
print(self.layer1.synaptic_weights)
print(" Layer 2 (1 neuron, with 2 inputs):")
print(self.layer2.synaptic_weights)
if __name__ == "__main__":
#Seed the random number generator
# random.seed(2)
# Create layer 1 (2 neurons, each with 2 inputs)
layer1 = NeuronLayer(2, 2)
# Create layer 2 (a single neuron with 2 inputs)
layer2 = NeuronLayer(1, 2)
# Combine the layers to create a neural network
neural_network = NeuralNetwork(layer1, layer2)
print("Stage 1) Random starting synaptic weights: ")
neural_network.print_weights()
# The training set. We have 4 examples, each consisting of 2 input values
# and 1 output value.
training_set_inputs = array([[0, 0], [0, 1], [1, 0], [1, 1]])
training_set_outputs = array([[0, 0, 0, 1]]).T
# Train the neural network using the training set.
# Do it 60,000 times and make small adjustments each time.
neural_network.train(training_set_inputs, training_set_outputs, 60000)
print("Stage 2) New synaptic weights after training: ")
neural_network.print_weights()
# Test the neural network with a new situation.
print("Stage 3) Considering a new situation [0,1] -> ?: ")
hidden_state, output = neural_network.think(array([0, 1]))
print(output)
输出结果:
Stage 3) Considering a new situation [ , ] -> ?:
[9.78921931e-05]
[0.00284118]
[0.0036443]
[0.99679971]五、总结
BP神经网络作为最基础的机器学习之一,是机器学习初学者的必经之路。作者在学习的过程中,得到很多前辈们的经验帮助,特此将代码整理出来,反馈于各位。
注:代码来源于网络搜集及自己的修改,如侵可删。