coco标注信息与labelme标注信息的详解、相互转换及可视化
coco标注信息与labelme标注信息的详解、相互转换及可视化
引言
在做实例分割或语义分割的时候,我们通常要用labelme进行标注,labelme标注的json文件与coco数据集已经标注好的json文件的格式和内容有差异。如果要用coco数据集的信息,就要对json文件进行修改和转换。本博客提供两种格式的具体内容及含义以及两种格式相互转换的代码,并对两种格式的json标注信息进行可视化。
1.coco格式的json标注信息详解及可视化
从coco官网下载coco的数据集里面,关于实例的标注信息在“annotations_trainval2017.zip”压缩文件里面的“instances_train2017.json”和“instances_val2017.json”里面,分别是训练集和验证集的标注信息。
下载地址:
![]()
训练集图片:http://images.cocodataset.org/zips/train2017.zip 验证集图片:http://images.cocodataset.org/zips/val2017.zip 测试集图片:http://images.cocodataset.org/zips/test2017.zip 训练集、验证集标注信息:http://images.cocodataset.org/annotations/annotations_trainval2017.zip http://images.cocodataset.org/annotations/stuff_annotations_trainval2017.zip http://images.cocodataset.org/annotations/panoptic_annotations_trainval2017.zip
![]()
由于“instances_train2017.json”里面把所有训练集图片的标注信息整合到一个文件了,文件非常大,不太好查看内部具体内容。我从这个文件中提取出一张图片的信息保存成一个新的json文件。
json文件内主要字段:
代码如下:
![]()
从coco标注json中提取单张图片的标注信息
得到一张图片的标注信息如下,包含5大部分的字段信息。
"info"的value是一个dict,存储数据集的一些基本信息,我们不需要关注;
"licenses"的value是一个list,存储license信息,我们不需要关注;
"categories"的value是一个list,存储数据集的类别信息,包括类别的超类、类别id、类别名称;
“images”的value是一个list,存储这张图片的基本信息,包括图片名、长、宽、id等重要信息;
"annotations"的value是一个list,存储这张图片的标注信息,非常重要,list中的每一个元素是一个dict,也即一个标注对象(instance)的信息。包括的字段有"segmentation":标注点的坐标,从第一个的x,y坐标一直到最后一个点的x,y坐标;"area"是标注的闭合多边形的面积; "iscrowd"表示对象之间是否有重叠;"image_id"是图片的id;“bbox”是instance的边界框的左上角的x,y,边界框的宽和高;"category_id"是这个instance对应的类别id;"id"表示此instance标注信息在所有instance标注信息中的id。
![]()
{
"info": {
"description": "COCO 2017 Dataset",
"url": "http://cocodataset.org",
"version": "1.0",
"year": 2017,
"contributor": "COCO Consortium",
"date_created": "2017/09/01"
},
"licenses": [
{
"url": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/2.0/",
"id": 1,
"name": "Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike License"
},
{
"url": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/2.0/",
"id": 2,
"name": "Attribution-NonCommercial License"
},
...(太长,省略)
],
"categories": [
{
"supercategory": "person",
"id": 1,
"name": "person"
},
...(太长,省略)
],
"images": [
{
"license": 2,
"file_name": "000000000049.jpg",
"coco_url": "http://images.cocodataset.org/train2017/000000000049.jpg",
"height": 500,
"width": 381,
"date_captured": "2013-11-14 20:00:23",
"flickr_url": "http://farm4.staticflickr.com/3250/2883102207_bcba5527a7_z.jpg",
"id": 49
}
],
"annotations": [
{
"segmentation": [
[
181.59,
363.43,
...(太长,省略)
]
],
"area": 8451.22405,
"iscrowd": 0,
"image_id": 49,
"bbox": [
162.57,
226.56,
130.41,
184.43
],
"category_id": 19,
"id": 56407
},
...(太长,省略)
]
}
![]()
我们对这个新coco格式的json文件进行可视化:
![]()
coco格式的json文件可视化instance的mask
可视化结果如下:
2.labelme格式的json标注信息详解及可视化
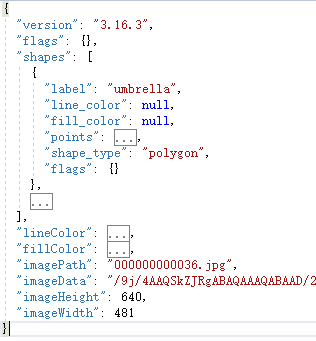
labelme标注工具标注的json格式与coco的格式有差异:
重点关注的是:
"shapes":存储标注instance的闭合多边形的信息,重点关注:label:类别名称;points:闭合多边形的每个点的x,y坐标;
"line_color":闭合多边形的边界线颜色;
"fill_color":闭合多边形的填充颜色;
"imagePath":图片名称;
"imageData":图片路径(加密后);
"imageHeight":图片高;
"imageWidth":图片宽;
利用labelme提供的接口将标注好的json进行可视化代码:
![]()
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
"""
@author: Taoting
将用labeime标注格式的json进行可视化
"""
import json
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import skimage.io as io
from labelme import utils
def main():
json_path = './PATH/TO/JSON'
data = json.load(open(json_path))
img = io.imread('%s/%s'%('./PATH/TO/IMAGE',data['imagePath']))
lab, lab_names = utils.labelme_shapes_to_label(img.shape, data['shapes'])
captions = ['%d: %s' % (l, name) for l, name in enumerate(lab_names)]
lab_ok = utils.draw_label(lab, img, captions)
plt.subplot(121)
plt.imshow(img)
plt.subplot(122)
plt.imshow(lab_ok)
plt.show()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
![]()
可视化结果:
可以看到右图中的mask的可视化效果
结合1和2中的两种格式的json,我们只需要针对格式的差异对json文件做修改,就能将格式进行互相转换。
3.coco格式的json转labelme格式的json
直接上代码:
![]()
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
@author: Taoting
将用coco格式的json转化成labeime标注格式的json
"""
import json
import cv2
import numpy as np
import os
#用一个labelme格式的json作为参考,因为很多信息都是相同的,不需要修改。
def reference_labelme_json():
ref_json_path = 'reference_labelme.json'
data=json.load(open(ref_json_path))
return data
def labelme_shapes(data,data_ref):
shapes = []
label_num = {'person':0,'bicycle':0,'car':0,'motorcycle':0,'bus':0,'train':0,'truck':0}#根据你的数据来修改
for ann in data['annotations']:
shape = {}
class_name = [i['name'] for i in data['categories'] if i['id'] == ann['category_id']]
#label要对应每一类从_1开始编号
label_num[class_name[0]] += 1
shape['label'] = class_name[0] + '_' + str(label_num[class_name[0]])
shape['line_color'] = data_ref['shapes'][0]['line_color']
shape['fill_color'] = data_ref['shapes'][0]['fill_color']
shape['points'] = []
# ~ print(ann['segmentation'])
if not type(ann['segmentation']) == list:
continue
else:
x = ann['segmentation'][0][::2]#奇数个是x的坐标
y = ann['segmentation'][0][1::2]#偶数个是y的坐标
for j in range(len(x)):
shape['points'].append([x[j], y[j]])
shape['shape_type'] = data_ref['shapes'][0]['shape_type']
shape['flags'] = data_ref['shapes'][0]['flags']
shapes.append(shape)
return shapes
def Coco2labelme(json_path,data_ref):
with open(json_path,'r') as fp:
data = json.load(fp) # 加载json文件
data_labelme={}
data_labelme['version'] = data_ref['version']
data_labelme['flags'] = data_ref['flags']
data_labelme['shapes'] = labelme_shapes(data,data_ref)
data_labelme['lineColor'] = data_ref['lineColor']
data_labelme['fillColor'] = data_ref['fillColor']
data_labelme['imagePath'] = data['images'][0]['file_name']
data_labelme['imageData'] = None
# ~ data_labelme['imageData'] = data_ref['imageData']
data_labelme['imageHeight'] = data['images'][0]['height']
data_labelme['imageWidth'] = data['images'][0]['width']
return data_labelme
if __name__ == '__main__':
root_dir = './ROOT DIR'
json_list = os.listdir(root_dir)
#参考的json
data_ref = reference_labelme_json()
for json_path in json_list:
if json_path.split('.')[-1] == 'json':
print('当前文件: ', json_path)
data_labelme= Coco2labelme(os.path.join(root_dir,json_path), data_ref)
file_name = data_labelme['imagePath']
# 保存json文件
json.dump(data_labelme,open('./PATH/%s.json' % file_name.split('.')[0],'w'),indent=4)
![]()
用2中的可视化代码检验是否正确转换。
4.labelme格式的json转coco格式的json
直接上代码:
![]()
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""Created on Thu Aug 15 15:05:56 2019
@author: Taoting
将用labeime标注的json转化成coco格式的json
"""
import json
import cv2
import numpy as np
import os
#用闭包实现计数器
def counter():
cnt = 1000000
def increce():
nonlocal cnt
x = cnt
cnt += 1
return x
return increce
def p_images(data,data_coco):
images=[]
image={}
file_name=data['imagePath'].split('\\')[-1]
image['file_name']=file_name
image['id']=int(file_name.split('.')[0])
image['height']=data['imageHeight']
image['width']=data['imageWidth']
img=None
images.append(image)
data_coco['images']=images
return file_name
#用一个coco格式的json做参考
def modify_categories():
ref_json_path = 'reference.json'
data=json.load(open(ref_json_path))
modified_categories = []
catNms=['person','bicycle','car','motorcycle','truck','bus']#根据你的数据修改
for i,cat in enumerate(data['categories']):
if cat['name'] in catNms:
modified_categories.append(cat)
else:
pass
return modified_categories,data['info'],data['licenses']
def p_annotation(data,data_coco,cnt):
# annotations
annotations=[]
for i in range(len(data['shapes'])):
annotation={}
annotation['segmentation']=[list(np.asarray(data['shapes'][i]['points']).flatten())] # data['shapes'][0]['points']
annotation['iscrowd']=0
annotation['image_id']=data_coco['images'][0]['id']
#找出标注点中的外接矩形的四个点
x = annotation['segmentation'][0][::2]#奇数个是x的坐标
y = annotation['segmentation'][0][1::2]#偶数个是y的坐标
print(x,y)
x_left = min(x)-1#往外扩展1个像素,也可以不扩展
y_left = min(y)-1
w = max(x) - min(x)+1
h = max(y) - min(y)+1
annotation['bbox']=[x_left,y_left,w,h] # [左上角x,y以及宽和高]
cat_list_dict = [cat for cat in data_coco['categories'] if cat['name'] == data['shapes'][i]['label'].split('_')[1]]#注意这里是跟标注时填类别的方式有关
annotation['category_id']=cat_list_dict[0]['id']
annotation['id'] = cnt() # 第一个对象 这个ID也不能重复,如果下一张图,id不能取1,需从1 开始往下取
#print('cnt', annotation['id'])
#print('annotation',annotation)
annotations.append(annotation)
#print('annotations',annotations)
data_coco['annotations']=annotations
#print(data_coco['annotations'])
#return data_coco
def Labelme2coco(json_path,cnt):
with open(json_path,'r') as fp:
data = json.load(fp) # 加载json文件
data_coco={}
# images
file_name = p_images(data,data_coco)
# categories
modified_categories, info, p_license = modify_categories()
data_coco['categories'] = modified_categories
#print(data_coco['categories'])
# info
data_coco['info'] = info
# license
data_coco['license'] = p_license
# annotations
p_annotation(data,data_coco,cnt)
#print(data_coco['annotations'])
return data_coco,file_name
if __name__ == '__main__':
root_dir = './ROOT DIR'
json_list = os.listdir(root_dir)
cnt = counter()
for json_path in json_list:
if json_path.split('.')[-1] == 'json':
data_coco,file_name = Labelme2coco(os.path.join(root_dir,json_path),cnt)
# 保存json文件
json.dump(data_coco,open('./PATH/%s.json' % file_name.split('.')[0],'w'),indent=4)
![]()
用1中的可视化代码检验是否正确转换。