Netty权威指南之NIO入门
本章学习目标:
1、传统的同步阻塞式IO编程
2、基于NIO非阻塞式编程
3、基于NIO2.0异步非阻塞式编程
4、为什么使用NIO编程
5、为什么选择Netty
传统BIO编程
网络编程的基本模式是C/S模式,也就是两个进程之间的相互通信,其中服务端提供位置信息(绑定IP地址和监听端口),客户端通过连接操作向服务端监听的地址发起连接请求,通过三次握手建立连接,如果连接成功,双方通过网络套接字(Socket)进行通信。
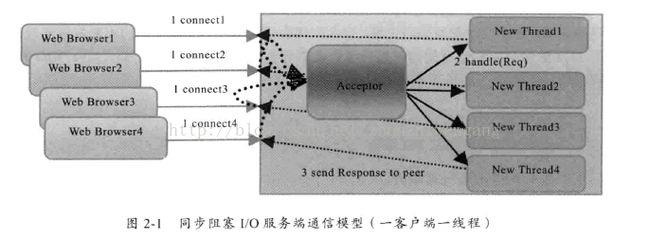
在基于传统同步阻塞开发模式中,ServerSocket负责绑定IP地址,启动监听端口:Socket负责发起连接操作。连接成功之后,双方通过输入和输出流进行同步阻塞式通信。
BIO通信模型图
BIO演示代码
服务端程序代码:
package com.nio.server;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
import com.nio.thread.ServerThread;
public class TimeServer {
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
//监听端口
int port=1666;
//创建ServerSocket 对象
ServerSocket server=null;
try{
server=new ServerSocket(port);
System.out.println("Serverocket启动对:"+port+"端口监听");
Socket socket=null;
while(true){
socket=server.accept();
new Thread(new ServerThread(socket)).start();
}
}finally{
if(server!=null){
System.out.println("ServerSocket 服务正在关闭");
server.close();
server=null;
}
}
}
}
package com.nio.thread;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.net.Socket;
public class ServerThread implements Runnable {
// 套接字
private Socket socket;
// 构造函数
public ServerThread(Socket socket) {
super();
this.socket = socket;
}
public void run() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
BufferedReader in = null;
PrintWriter out = null;
try {
in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(
this.socket.getInputStream()));
out = new PrintWriter(this.socket.getOutputStream(), true);
String currentTime = null;
String body = null;
while (true) {
body = in.readLine();
if (body == null) {
break;
}
System.out.println("this ServerSocket receiver message is:"
+ body);
currentTime = "time".equalsIgnoreCase(body) ? new java.util.Date(
System.currentTimeMillis()).toString() : "bad time";
out.println("current is:" + currentTime);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
if (in != null) {
try {
in.close();
in = null;
} catch (IOException el) {
el.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (out != null) {
out.close();
out = null;
}
if (this.socket != null) {
try {
this.socket.close();
} catch (IOException el) {
el.printStackTrace();
}
this.socket = null;
}
}
}
}
客户端程序代码:
package com.nio.client;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.net.Socket;
public class TimeClient {
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
int port=1666;
Socket socket=null;
BufferedReader in = null;
PrintWriter out = null;
try{
socket=new Socket("127.0.0.1",port);
in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(
socket.getInputStream()));
out = new PrintWriter(socket.getOutputStream(), true);
out.println("123");
System.out.println("this client has send message");
String resp=in.readLine();
System.out.println("response message is:"+resp);
}catch(Exception e){
}finally{
if (in != null) {
try {
in.close();
in = null;
} catch (IOException el) {
el.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (out != null) {
out.close();
out = null;
}
if (socket != null) {
try {
socket.close();
} catch (IOException el) {
el.printStackTrace();
}
socket = null;
}
}
}
}
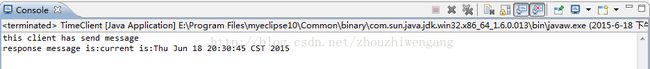
结果展示:
客户端发送信息为:"123"
服务端返回结果为:
客户端发送信息为:"time"
服务端返回信息为:
第二节:伪异步IO编程
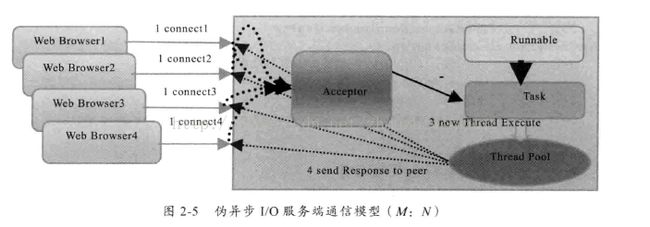
为了解决同步阻塞IO面临的一个链路需要一个线程处理的问题,后来有人对它的线程模式进行了优化,后端通过一个线程池来处理多个客户端的请求接入,形成客户端个数M:线程池最大线程数N的比例关系,其中M可以远远大于N,通过线程池可以灵活的调配线程资源,设置线程的最大值,防止由于海量并发导致线程耗尽。
伪异步IO模型图
采用线程池和任务队列可以实现一种叫做伪异步的IO通信框架,它的模型如上图。
当有新的客户端接入的时候,将客户端的Socket封装成一个Task()该任务实现java.lang.Runnable 接口投递到后端的线程池进行处理,JDK维护一个消息队列和N个活跃的线程对消息队列中的任务进行处理。由于线程池可以设置消息队列的大小和最大线程数,因此,它的资源是可控的,无论多少个客户端并发访问,都不会导致资源耗尽和宕机。
伪异步IO演示代码
服务端代码
package com.nio.server;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
import com.nio.executepool.TimeServerHandlerExcutePool;
import com.nio.thread.ServerThread;
public class TimeServer {
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
//监听端口
int port=1667;
//创建ServerSocket 对象
ServerSocket server=null;
try{
server=new ServerSocket(port);
System.out.println("Serverocket启动对:"+port+"端口监听");
Socket socket=null;
TimeServerHandlerExcutePool pool=new TimeServerHandlerExcutePool(50,1000);
while(true){
socket=server.accept();
pool.execute(new ServerThread(socket));
}
}finally{
if(server!=null){
System.out.println("ServerSocket 服务正在关闭");
server.close();
server=null;
}
}
}
}
线程池
package com.nio.executepool;
import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class TimeServerHandlerExcutePool {
private ExecutorService executor;
public TimeServerHandlerExcutePool(int maxPoolSize,int queueSize) {
executor=new ThreadPoolExecutor(Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors(),maxPoolSize,120L,TimeUnit.SECONDS,new ArrayBlockingQueue(queueSize));
}
public void execute(java.lang.Runnable command){
executor.execute(command);
}
}
package com.nio.thread;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.net.Socket;
public class ServerThread implements Runnable {
// 套接字
private Socket socket;
// 构造函数
public ServerThread(Socket socket) {
super();
this.socket = socket;
}
public void run() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
BufferedReader in = null;
PrintWriter out = null;
try {
in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(
this.socket.getInputStream()));
out = new PrintWriter(this.socket.getOutputStream(), true);
String currentTime = null;
String body = null;
while (true) {
body = in.readLine();
if (body == null) {
break;
}
System.out.println("this ServerSocket receiver message is:"
+ body);
currentTime = "time".equalsIgnoreCase(body) ? new java.util.Date(
System.currentTimeMillis()).toString() : "bad time";
out.println("current is:" + currentTime);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
if (in != null) {
try {
in.close();
in = null;
} catch (IOException el) {
el.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (out != null) {
out.close();
out = null;
}
if (this.socket != null) {
try {
this.socket.close();
} catch (IOException el) {
el.printStackTrace();
}
this.socket = null;
}
}
}
}
客户端代码
客户端代码未做任何修改。
第三节 NIO编程
在介绍NIO编程之前,我们首先澄清一个概念:NIO到底是什么的简称?有人称之为New IO,因为它是相对之前的IO库新增的,所以称之为New IO。这是它的官方叫法。但是,由于之前的IO类库是阻塞IO,New IO类库的目标就是让IO支持非阻塞,所以,人们更喜欢称之为非阻塞IO,由于非阻塞IO更能体现NIO的特点。
与Socket和ServerSocket类相对应,NIO也提供了SocketChannel和ServerSocketChannel两种不同的套接字通道实现。这两种新增的通道都支持阻塞和非阻塞两种模式。阻塞模式使用非常简单,但是性能和可靠性都不好,非阻塞模式正好相反。一般来说低负载、低并发的应用程序可以选择阻塞式IO来降低开发的编程复杂度,但是对于高负载、高并发的网络应用,需要使用NIO非阻塞模式进行开发。
NIO演示代码
服务端代码
package com.nio.server;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.util.Iterator;
/**
* NIO服务端
* @author 小路
*/
public class NIOServer {
//通道管理器
private Selector selector;
/**
* 获得一个ServerSocket通道,并对该通道做一些初始化的工作
* @param port 绑定的端口号
* @throws IOException
*/
public void initServer(int port) throws IOException {
// 获得一个ServerSocket通道
ServerSocketChannel serverChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
// 设置通道为非阻塞
serverChannel.configureBlocking(false);
// 将该通道对应的ServerSocket绑定到port端口
serverChannel.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(port));
// 获得一个通道管理器
this.selector = Selector.open();
//将通道管理器和该通道绑定,并为该通道注册SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT事件,注册该事件后,
//当该事件到达时,selector.select()会返回,如果该事件没到达selector.select()会一直阻塞。
serverChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
}
/**
* 采用轮询的方式监听selector上是否有需要处理的事件,如果有,则进行处理
* @throws IOException
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public void listen() throws IOException {
System.out.println("服务端启动成功!");
// 轮询访问selector
while (true) {
//当注册的事件到达时,方法返回;否则,该方法会一直阻塞
selector.select();
// 获得selector中选中的项的迭代器,选中的项为注册的事件
Iterator ite = this.selector.selectedKeys().iterator();
while (ite.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey key = (SelectionKey) ite.next();
// 删除已选的key,以防重复处理
ite.remove();
// 客户端请求连接事件
if (key.isAcceptable()) {
ServerSocketChannel server = (ServerSocketChannel) key
.channel();
// 获得和客户端连接的通道
SocketChannel channel = server.accept();
// 设置成非阻塞
channel.configureBlocking(false);
//在这里可以给客户端发送信息哦
channel.write(ByteBuffer.wrap(new String("server").getBytes()));
//在和客户端连接成功之后,为了可以接收到客户端的信息,需要给通道设置读的权限。
channel.register(this.selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
// 获得了可读的事件
} else if (key.isReadable()) {
read(key);
}
}
}
}
/**
* 处理读取客户端发来的信息 的事件
* @param key
* @throws IOException
*/
public void read(SelectionKey key) throws IOException{
// 服务器可读取消息:得到事件发生的Socket通道
SocketChannel channel = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
// 创建读取的缓冲区
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(10);
channel.read(buffer);
byte[] data = buffer.array();
String msg = new String(data).trim();
System.out.println("服务端收到信息:"+msg);
ByteBuffer outBuffer = ByteBuffer.wrap(msg.getBytes());
channel.write(outBuffer);// 将消息回送给客户端
}
/**
* 启动服务端测试
* @throws IOException
*/
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
NIOServer server = new NIOServer();
server.initServer(8000);
server.listen();
}
}
客户端代码
package com.nio.client;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.util.Iterator;
/**
* NIO客户端
* @author 小路
*/
public class NIOClient {
//通道管理器
private Selector selector;
/**
* 获得一个Socket通道,并对该通道做一些初始化的工作
* @param ip 连接的服务器的ip
* @param port 连接的服务器的端口号
* @throws IOException
*/
public void initClient(String ip,int port) throws IOException {
// 获得一个Socket通道
SocketChannel channel = SocketChannel.open();
// 设置通道为非阻塞
channel.configureBlocking(false);
// 获得一个通道管理器
this.selector = Selector.open();
// 客户端连接服务器,其实方法执行并没有实现连接,需要在listen()方法中调
//用channel.finishConnect();才能完成连接
channel.connect(new InetSocketAddress(ip,port));
//将通道管理器和该通道绑定,并为该通道注册SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT事件。
channel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT);
}
/**
* 采用轮询的方式监听selector上是否有需要处理的事件,如果有,则进行处理
* @throws IOException
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public void listen() throws IOException {
// 轮询访问selector
while (true) {
selector.select();
// 获得selector中选中的项的迭代器
Iterator ite = this.selector.selectedKeys().iterator();
while (ite.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey key = (SelectionKey) ite.next();
// 删除已选的key,以防重复处理
ite.remove();
// 连接事件发生
if (key.isConnectable()) {
SocketChannel channel = (SocketChannel) key
.channel();
// 如果正在连接,则完成连接
if(channel.isConnectionPending()){
channel.finishConnect();
}
// 设置成非阻塞
channel.configureBlocking(false);
//在这里可以给服务端发送信息哦
channel.write(ByteBuffer.wrap(new String("client").getBytes()));
//在和服务端连接成功之后,为了可以接收到服务端的信息,需要给通道设置读的权限。
channel.register(this.selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
// 获得了可读的事件
} else if (key.isReadable()) {
read(key);
}
}
}
}
/**
* 处理读取服务端发来的信息 的事件
* @param key
* @throws IOException
*/
public void read(SelectionKey key) throws IOException{
// 客户端可读取消息:得到事件发生的Socket通道
SocketChannel channel = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
// 创建读取的缓冲区
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(10);
channel.read(buffer);
byte[] data = buffer.array();
String msg = new String(data).trim();
System.out.println("客户端收到信息:"+msg);
ByteBuffer outBuffer = ByteBuffer.wrap(msg.getBytes());
channel.write(outBuffer);// 将消息回送给服务器
}
/**
* 启动客户端测试
* @throws IOException
*/
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
NIOClient client = new NIOClient();
client.initClient("localhost",8000);
client.listen();
}
}