Java的练习2
今天练习的是图书馆系统的用户管理模块,紧接昨天的用户登陆模块。
首先是JDBC连接数据库,继续熟悉代码,尽量是自己不看书不看之前的代码敲
package 用户管理;
import java.sql.Statement;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public class DBUtil {
private static String driverName="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver";
private static String URL="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/amis";
private static String user="root";
private static String password="y888888";
public static Connection getConnection(){
Connection conn=null;
try {
Class.forName(driverName);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
conn=DriverManager.getConnection(URL, user, password);
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return conn;
}
public static void closeConn(Connection c) {
if (c!=null){
try {
c.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static void closeSm(Statement sm) {
if (sm!=null){
try {
sm.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static void closeRs(ResultSet rs) {
if (rs!=null){
try {
rs.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static boolean insertBysql() {
return true;
}
public static boolean deleteBysql() {
return true;
}
public static boolean editBysql() {
return true;
}
public static boolean updateTable() {
return true;
}
}
getConnection里面就是开启驱动建立连接。然后可以看到哦,下面多了四个增删改查的操作。
书上是说在昨天那个DBUtil类的基础上,再添加四个增删改查,然而我还是不知道这四个到底在哪里用?当然前提是都不知道到底里面的内容写什么。
然后用户类是和昨天的一样,可以直接调用,但是我还是在这个包里面自己又建了一个。对哦!其实是不用写的,直接用昨天的是可以的。
package 用户管理;
public class Users {
private int user_id;
private String user_name;
private String user_pass;
private String user_type;
private String startdate;
private boolean vaild;
public Users(){
}
public Users(int i,String n,String p,String t,String d,boolean v){
this.user_id=i;
this.user_name=n;
this.user_pass=p;
this.user_type=t;
this.startdate=d;
this.vaild=v;
}
public int getUser_id() {
return user_id;
}
public void setUser_id(int user_id) {
this.user_id = user_id;
}
public String getUser_name() {
return user_name;
}
public void setUser_name(String user_name) {
this.user_name = user_name;
}
public String getUser_pass() {
return user_pass;
}
public void setUser_pass(String user_pass) {
this.user_pass = user_pass;
}
public String getUser_type() {
return user_type;
}
public void setUser_type(String user_type) {
this.user_type = user_type;
}
public String getStartdate() {
return startdate;
}
public void setStartdate(String startdate) {
this.startdate = startdate;
}
public boolean isVaild() {
return vaild;
}
public void setVaild(boolean vaild) {
this.vaild = vaild;
}
}
package 用户管理;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
import javax.swing.JOptionPane;
public class UserManage {
JOptionPane jop;
public boolean addUsers(String name,String word,String type,String date,int flag) {
int row=0;
Connection con=DBUtil.getConnection();
if (!new UserManage().isExist(name)){
try {
Statement sm=con.createStatement();
String sql="insert into userInfo(user_name,user_pass,user_type,startdate,valid,) "
+ "values ('"+name+"','"+word+"','"+type+"','"+date+"',"+flag+")";
row=sm.executeUpdate(sql);
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
else{
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(jop,"该用户已存在!!!");
return false;
}
if (row>0){
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(jop, "添加成功");
return true;
}
else{
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(jop, "添加失败");
return false;
}
}
public boolean updateUser(String name,String word,String type,String date,int flag){
int row=0;
Connection con=DBUtil.getConnection();
if (!new UserManage().isExist(name)){
try {
Statement sm=con.createStatement();
String sql="update userInfo set user_name='"+name+"',user_pass='"+word+"',user_type='"+type+"',startdate='"+date+"',valid="+flag+" where user_name='"+name+"'";
row=sm.executeUpdate(sql);
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
else {
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(jop, "用户名不存在,请注册一个!!");
return false;
}
if (row>0){
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(jop, "修改成功");
return true;
}
else{
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(jop, "修改失败");
return false;
}
}
public boolean deleteUser(String name) {
int row=0;
Connection con=DBUtil.getConnection();
try {
Statement sm=con.createStatement();
String sql="delete from userInfo where user_name='"+name+"'";
row=sm.executeUpdate(sql);
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
con.close();
} catch (SQLException e2) {
e2.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (row>0){
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(jop, "删除成功");
return true;
}
else {
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(jop, "删除失败");
return false;
}
}
public boolean isExist(String name) {
Connection con=DBUtil.getConnection();
try {
String sql="select user_name from userInfo where user_name='"+name+"'";
Statement sm=con.createStatement();
ResultSet rs=sm.executeQuery(sql);
if (rs.next()){
return true;
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
con.close();
} catch (Exception e2) {
e2.printStackTrace();
}
}
return false;
}
//浏览数据库中的用户信息
public ResultSet view(){
Connection con=DBUtil.getConnection();
ResultSet rs=null;
Statement sm;
String sql="select user_name,user_type,startdate,valid from userInfo";
try {
sm=con.createStatement();
rs=sm.executeQuery(sql);
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return rs;
}
}
row=sm.executeUpdate(sql);说一下isExist(),是用到了昨天的Statement和ResultSet的结合,最后Result遍历方式next看是否有内容。
最后的view()也是返回ResultSet。
最后今天的界面,里面用到了Jtable,因为上学期课设是在这上面费了好大功夫,今天对这个特别感触深。
public class UserManageJPanel extends JFrame implements ActionListener{
JLabel name,pass,ptype,startdate;
JButton regis,delete,cancel,exit,view,edit;
JTextField tl1,tl2,tl6,ts1,ts2,ts3;
JPanel p,p1,p2,c1;
JScrollPane js;
JComboBox type;
JRadioButton start,stop;
ButtonGroup bg;
public static String u_name,u_password,u_type,date,valid;
int flag;
JTable table;
public static int i=0,ii=0;
public UserManageJPanel(){
name=new JLabel("姓名");
pass=new JLabel("密码");
ptype=new JLabel("用户类型");
type=new JComboBox();
type.addItem("系统管理员");
type.addItem("图书管理员");
startdate=new JLabel("启用日期");
start=new JRadioButton("启用");
stop=new JRadioButton("停用");
bg=new ButtonGroup();
bg.add(start);
bg.add(stop);
regis=new JButton("注册");
regis.addActionListener(this);
delete=new JButton("删除");
delete.addActionListener(this);
edit=new JButton("修改");
edit.addActionListener(this);
view=new JButton("浏览");
view.addActionListener(this);
cancel=new JButton("取消");
cancel.addActionListener(this);
exit=new JButton("退出");
exit.addActionListener(this);
tl1=new JTextField(10);
tl2=new JTextField(10);
tl6=new JTextField(10);
JPanel pp1=new JPanel();
ts1=new JTextField(20);
ts1.setEditable(false);
ts2=new JTextField(10);
ts3=new JTextField(10);
p=new JPanel(new FlowLayout());
c1=new JPanel(new BorderLayout());
p2=new JPanel();
Container con=getContentPane();
con.setLayout(new FlowLayout());
p2.add(name);
p2.add(tl1);
p2.add(pass);
p2.add(tl2);
p2.add(startdate);
p2.add(tl6);
p2.add(ptype);
p2.add(type);
p2.add(start);
p2.add(stop);
pp1.add(p2);
p.add(regis);
p.add(edit);
p.add(view);
p.add(delete);
p.add(cancel);
p.add(exit);
String ta[]={"用户名","用户类型","启用日期","状态"};
Object a[][]=new Object[30][4];
for (int i=0;i<30;i++)
for (int j=0;j<4;j++){
a[i][j]="";
}
table=new JTable(a, ta);
js=new JScrollPane(table);
JPanel pjs=new JPanel();
pjs.add(js);
con.add(pp1);
con.add(p);
con.add(pjs);
}
}Jcombobox这次是基础的用法,没有昨天的难度那么大。
Jtable的初始化,书上吧,
for (int i=0;i<=1;i++)
for (int j=0;j<=1;j++){
a[i][j]="";
}最后就是给按钮添加监听事件。之前添加的监听事件,原来都是麻烦的操作,一个btn写一个事件。
像类似下面的操作,用e.getSource()监听对应等于的按钮即可。
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
u_name=tl1.getText();
u_password=tl2.getText();
date=tl6.getText();
u_type=type.getSelectedItem().toString();
flag=0;
Enumeration radioBtns=bg.getElements();
while (radioBtns.hasMoreElements()){
AbstractButton btn=radioBtns.nextElement();
if (btn.isSelected()){
valid=btn.getText();
if (valid.equals("启用")){
flag=1;
}
break;
}
}
if (e.getSource()==regis){
if (new UserManage().addUsers(u_name, u_password, u_type, date, flag)){
int j=0;
table.setValueAt(u_name, i, j++);
table.setValueAt(u_type, i, j++);
table.setValueAt(date, i, j++);
table.setValueAt(valid, i, j++);
}
}
if (e.getSource()==edit){
if (u_name.equals("")){
u_name=(String)table.getValueAt(table.getSelectedRow(), 0);
}
if (new UserManage().updateUser(u_name, u_password, u_type, date, flag)){
int j=0;
table.setValueAt(u_name, i, j++);
table.setValueAt(u_type, i, j++);
table.setValueAt(date, i, j++);
table.setValueAt(valid, i, j++);
}
}
if (e.getSource()==delete){
int k=0;
int r=table.getSelectedRow();
String ss=(String)table.getValueAt(r, 0);
if (new UserManage().deleteUser(ss)){
ResultSet rs=null;
String v;
rs=new UserManage().view();
try {
while (rs.next()){
table.setValueAt(rs.getString("user_name"), k, 0);
table.setValueAt(rs.getString("user_type"), k, 1);
table.setValueAt(rs.getString("startdate"), k, 2);
if (rs.getBoolean("valid")==true)
v="启用";
else
v="停用";
table.setValueAt(v, ii, 3);
k++;
}
} catch (SQLException e2) {
e2.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
if (e.getSource()==view){
ResultSet rs=null;
String v;
rs=new UserManage().view();
try {
while (rs.next()){
table.setValueAt(rs.getString("user_name"), ii, 0);
table.setValueAt(rs.getString("user_type"), ii, 1);
table.setValueAt(rs.getString("startdate"), ii, 2);
if (rs.getBoolean("valid")==true)
v="启用";
else
v="停用";
table.setValueAt(v, ii, 3);
ii++;
}
} catch (SQLException e2) {
e2.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (e.getSource()==cancel){
dispose();
}
if (e.getSource()==exit){
System.exit(0);
}
} 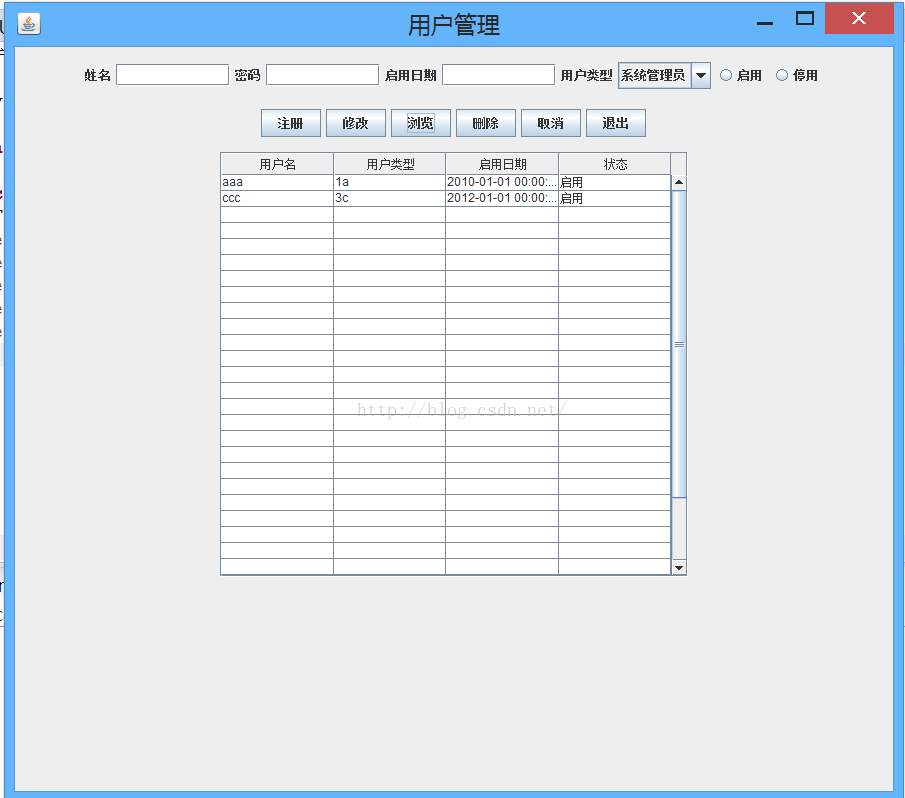
点击浏览,数据库中的信息就出现在表单中,没问题。删除,数据库内容会删除掉,表单显示是有问题。
注册的话,在上面输入选择信息后,点击注册会添加失败,原因是
values ('aaa','aaa','?????','20100101',0)' at line 1:言下之意就是添加的不全,type那里没有添加进去
修改会失败。返回看代码,修改有修改密码一说,然而我怎么修改这个呢?
未完待续。