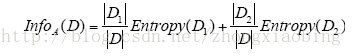《程序员的第一年》---------- 数据挖掘之数据处理(C#基于熵的离散化算法代码)
熵(entropy)是最常用的离散化度量之一。它由Claude Shannon在信息论和信息增益概念的开创性工作中首次引进。基于熵的离散化是一种监督的、自顶向下的分裂技术。它在计算和确定分裂点(划分属性区间的数据值)时利用类分布信息。为了离散数值属性A,该方法选择A的具有最小熵的值作为分裂点,并递归地划分结果区间,得到分层离散化。这种离散化形成A的概念分层。
设D由属性集和类标号属性定义的数据元组组成。类标号属性提供每个元组的类信息。该集合中属性A的基于熵的离散化基本方法如下:
(1)A的每个值都可以看作一个划分A的值域的潜在的区间边界或分裂点(记作split_ point)。也就是说,A的分裂点可以将D中的元组划分成分别满足条件A≤split_point和A > split_point的两个子集,这样就创建了一个二元离散化。
(2)正如上面提到的,基于熵的离散化使用元组的类标号信息。为了解释基于熵的离散化的基本思想,必须考察一下分类。假定要根据属性A和某分裂点上的划分将D中的元组分类。理想地,希望该划分导致元组的准确分类。例如,如果有两个类,希望类C1的所有元组落入一个划分,而类C2的所有元组落入另一个划分。然而,这不大可能。例如,第一个划分可能包含许多C1的元组,但也包含某些C2的元组。在该划分之后,为了得到完全的分类,我们还需要多少信息?这个量称作基于A的划分对D的元组分类的期望信息需求,由下式给出
其中,D1和D2分别对应于D中满足条件A≤split_point和A > split_point的元组,|D|是D中元组的个数,如此等等。给定集合的熵函数Entropy根据集合中元组的类分布来计算。例如,给定
m个类C1, C2, ., Cm,D1的熵是m
其中,pi是D1中类Ci的概率,由D1中Ci类的元组数除以D1中的元组总数|D1|确定。这样,在选择属性A的分裂点时,我们希望选择产生最小期望信息需求(即min(InfoA(D)))的属性值。这将导致在用A≤split_point和A > split_point划分之后,对元组完全分类(还)需要的期望信息量最小。这等价于具有最大信息增益的属性-值对(这方面的进一步细节在第6章讨论分类时给出)。注意,Entropy(D2)的值可以类似于式(2-16)计算。
你可能会说,“但是我们的任务是离散化,而不是分类!”是这样。我们使用分裂点将A的值域划分成两个区间,对应于A≤split_point和A > split_point。
(3)确定分裂点的过程递归地用于所得到的每个分划,直到满足某个终止标准,如当所有候选分裂点上的最小信息需求小于一个小阈值ε,或者当区间的个数大于阈值max_interval 时终止。
基于熵的离散化可以减少数据量。与迄今为止提到的其他方法不同,基于熵的离散化使用类信息。这使得它更有可能将区间边界(分裂点)定义在准确位置,有助于提高分类的准确性。这里介绍的熵和信息增益度量也用于决策树归纳
C#代码实现如下:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Windows.Forms;
using System.Data.OleDb;
using Excel = Microsoft.Office.Interop.Excel;
namespace 连续值离散化
{
///
/// 连续型数据离散化。
/// 要求:
///
/// 输入:两个序列,一个是待离散化的数据序列(如支付延迟时间)
/// 一个是数据对应的分类(如是否复购);
///
/// 操作:基于熵做有监督离散化操作;
///
/// 输出:分割点
///
///
public partial class Form1 : Form
{
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void Form1_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
}
private List dataAll = new List();
private List SaveTi ;
private void btnOk_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
SaveTi = new List();
this.listBox2.Items.Clear();
//步骤
//1 根据属性A值大小对数据集进行升序排序
//数据集
List datas = new List();
for (int j = 0, l = dataAll.Count ; j < l; j++)
{
Data tempData = new Data();
tempData.id = j;
tempData.myClass = dataAll[j].myClass;
tempData.value = dataAll[j].value;
datas.Add(tempData);
}
#region 添加 测试 数据
//for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
//{
// Data tempData = new Data();
// Random rd = new Random();
// string Myclass = "T";
// if (i % 3 == 0)
// {
// Myclass = "F";
// }
// tempData.id = i;
// tempData.myClass = Myclass;
// tempData.value = i + 1;
// //tempData.value = rd.Next(10) * (i + 1);
// //if (i < 2)
// //{
// // tempData.value = 1;//rd.Next(10) * (i + 1)
// //}
// listBox1.Items.Add(tempData.value);
// datas.Add(tempData);
//}
#endregion
int counts = datas.Count;//样本总数
try
{
this.Print(GetTiByRecursionData(datas));
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
MessageBox.Show(ex.ToString());
}
}
private List Sort(List datas)
{
listBox1.Items.Clear();
//升序排序 ,对datas类数据集中的属性A的所有取值从小到大进行排序,不妨设得到的序列为:a1 ,a2,...
for (int i = 0,l=datas.Count; i < l; i++)
{
for (int j = l - 1; i < j; j--)
{
if (datas[i].value > datas[j].value)
{
Data tempData = new Data();
tempData = datas[j];
datas[j] = datas[i];
datas[i] = tempData;
}
}
}
for (int j = 0, l = datas.Count; j < l; j++)
{
listBox1.Items.Add(datas[j].value);
}
return datas;
}
///
/// 取得Ti并做递归操作
///
///
private string GetTiByRecursionData(List datas)
{
int counts = datas.Count;//样本总数
if (counts < 1 )
{
return "";
}
//dataTi 为Ti为候选分割点 数据集
List dataTi = new List();
for (int i = 0; i < counts; i++)
{
if (i < counts - 1)
{
dataTi.Add((double)(datas[i].value + datas[i + 1].value) / 2);
}
}
计算每次划分的信息增益 Gain(A,T)=I(S1,S2,...Sm)-Ent(A,T)
//List gainList = new List();
#region 选择Ti,使得将其作为分割点划分S后的熵最小
//最小熵值
double minEnt = -1;
//最小熵值时的Ti
double isMinEntTi = -1;
for (int i = 0, l = dataTi.Count; i < l; i++)
{
double tempTi = dataTi[i];
//熵的计算
double tempMinEnt= Ent(datas, tempTi);
if (minEnt > tempMinEnt || i==0)
{
minEnt = tempMinEnt;
isMinEntTi = tempTi;
}
}
if (SaveTi.Contains(isMinEntTi))
{
return "";
}
else
{
SaveTi.Add(isMinEntTi);
}
Dictionary classDtAll = new Dictionary();
//取得两个划分
List dataTiLeft = new List();
List dataTiRight = new List();
#region 取两个划分 数据集,所有样本都在这两个划分中
for (int i = 0; i < counts; i++)
{
if (datas[i].value <= isMinEntTi)
{
dataTiLeft.Add(datas[i]);
}
else
{
dataTiRight.Add(datas[i]);
}
this.AddDictionaryValue(classDtAll, datas[i].myClass);
}
#endregion
if (classDtAll.Count<=1)
{
return datas[counts-1].value.ToString()+" ";
}
//计算D(I)= f(I)/L(I) , f(I)=|S|
double L_Left=0;
double L_Right = 0;
double D_I_Left = 0;
double D_I_Right = 0;
if (dataTiLeft.Count > 0)
{
L_Left = dataTiLeft[dataTiLeft.Count - 1].value - dataTiLeft[0].value + 1;
D_I_Left = (double)dataTiLeft.Count / L_Left;
}
if (dataTiRight.Count > 0)
{
L_Right = dataTiRight[dataTiRight.Count - 1].value - dataTiRight[0].value + 1;
D_I_Right = (double)dataTiRight.Count / L_Right;
}
//定thresholdValue0 =E(S)
double thresholdValue0 = this.E(classDtAll, counts);
//自动计算阀值
double thresholdValueLeft = D_I_Left * thresholdValue0;
double thresholdValueRight = D_I_Right * thresholdValue0;
string temp=string.Empty;
//手动设置阈值
double thresholdValue = Convert.ToDouble(this.txt_gz.Text);
if (!this.checkBox1.Checked)
{
thresholdValue = thresholdValueLeft;
}
if (minEnt > thresholdValue)
{
temp += this.GetTiByRecursionData(dataTiLeft) + " ";
}
if (!this.checkBox1.Checked)
{
thresholdValue = thresholdValueRight;
}
if (minEnt > thresholdValue)
{
temp += this.GetTiByRecursionData(dataTiRight) + " ";
}
if (temp!=string.Empty)
{
return temp;
}
else
{
return isMinEntTi.ToString() + " ";
//Ent 为1时两划分中的属性属于各个不同类 ,为0时两划分中的属性属于相同类
}
#endregion
}
///
/// 打印排序好的分割点
///
///
private void Print(string Ti)
{
string[] arr = Ti.Split(new char[] { ' ' }, StringSplitOptions.RemoveEmptyEntries);
for (int i = 0, l = arr.Length; i < l; i++)
{
for (int j = arr.Length-1; j >= i; j--)
{
if (Convert.ToDouble(arr[i]) > Convert.ToDouble(arr[j]))
{
string temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = temp;
}
}
}
foreach (string item in arr)
{
listBox2.Items.Add(item);
}
}
///
/// 熵的计算
///
///
///
private double Ent(List datas, double T)
{
//取得分类数据集 与 当前分类包涵的属性A的样本个数
Dictionary classDtLeft = new Dictionary();
Dictionary classDtRight = new Dictionary();
//Dictionary classDtAll = new Dictionary();
int counts = datas.Count;
//取得两个划分
List dataTiLeft = new List();
List dataTiRight = new List();
#region 取两个划分 数据集,所有样本都在这两个划分中
for (int i = 0; i < counts; i++)
{
if (datas[i].value <= T)
{
dataTiLeft.Add(datas[i]);
this.AddDictionaryValue(classDtLeft, datas[i].myClass);
}
else
{
dataTiRight.Add(datas[i]);
this.AddDictionaryValue(classDtRight, datas[i].myClass);
}
//this.AddDictionaryValue(classDtAll, datas[i].myClass);
}
#endregion
//取得两划分的样本个数
int countLeft = dataTiLeft.Count;
int countRight = dataTiRight.Count;
//计算两划分的期望值
//P_k_l为类别l在子集S_k中的概率 (k为参数 如 S_1 =左划分,S_2 =右划分)
double expectLeft = this.E(classDtLeft, countLeft);
double expectRight = this.E(classDtRight, countRight);
double returnEnt = ((double)countLeft / counts) * expectLeft + ((double)countRight / counts) * expectRight;
return returnEnt;
}
///
/// 添加值到Dictionary数据集内
///
///
///
private void AddDictionaryValue(Dictionary classDt, string myClass)
{
if (classDt.ContainsKey(myClass))
{
classDt[myClass] = classDt[myClass] + 1;
}
else
{
classDt.Add(myClass, 1);
}
}
///
/// 计算集合内的期望值
///
/// 样本内部类别 数据集
/// 划分后的单个划分样本总数
/// 当前划分的期望值
private double E(Dictionary classDt, int sampleCount)
{
//计算两划分的期望值
//P_k_l为类别l在子集S_k中的概率 (k为参数 如 S_1 =左划分)
double expect = 0;
foreach (KeyValuePair item in classDt)
{
//概率
double tempProbability = item.Value / sampleCount;
double tempExpect = tempProbability * Math.Log(tempProbability, 2);
expect += tempExpect;
}
return -expect;
}
private void btn_InputExecel_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
System.Windows.Forms.OpenFileDialog ofp = new OpenFileDialog();
ofp.DefaultExt = "xls";
ofp.Filter = "Excel文件 (*.xlsx)|*.xlsx|(*.xls)|*.xls";
if (ofp.ShowDialog()==System.Windows.Forms.DialogResult.OK)
{
this.txt_InputExecel.Text=ofp.FileName;
}
}
private void Import(string fileName)
{
List columns = new List(20);
columns.Add(this.txt_Class.Text);
columns.Add(this.txt_Number.Text);
Excel.Application app = new Excel.Application();
Excel.Workbook book = app.Workbooks.Open(fileName);
Excel.Worksheet srcSheet = (Excel.Worksheet)book.Sheets[this.txt_Sheet.Text];
int rows = Convert.ToInt32( this.txt_rows.Text);
for (int i = 2; i <= rows+1; i++)
{
Data tempData = new Data();
Excel.Range srcRange = srcSheet.get_Range(columns[0] + i, Type.Missing);
Excel.Range srcRange1 = srcSheet.get_Range(columns[1] + i, Type.Missing);
tempData.myClass = Convert.ToString(srcRange.Value);
tempData.value = Convert.ToDouble(srcRange1.Value);
tempData.id = i;
if (tempData.myClass==null)
{
break;
}
dataAll.Add(tempData);
}
app.ActiveWorkbook.Close();
}
///
/// 导入数据并排序
///
///
///
private void btn_inputE_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
this.listBox1.Items.Clear();
dataAll.Clear();
if (this.txt_Class.Text != "" && this.txt_InputExecel.Text != "" && this.txt_Number.Text != "" && this.txt_rows.Text != "" && this.txt_Sheet.Text != "")
{
try
{
Import(this.txt_InputExecel.Text);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
MessageBox.Show(ex.ToString());
return;
}
dataAll = this.Sort(dataAll);
//for (int j = 0, l = dataAll.Count; j < l; j++)
//{
// listBox1.Items.Add(dataAll[j].value);
//}
}
else
{
MessageBox.Show("请设置完参数再导入");
return;
}
}
private void btn_sort_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
dataAll = this.Sort(dataAll);
}
private void checkBox1_CheckedChanged(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
CheckBox cb = (CheckBox)sender;
if (cb.Checked)
{
this.txt_gz.Enabled = true;
}
else
{
this.txt_gz.Enabled = false;
}
}
}
}
还要优化,请读者多加说说看法。小弟在此谢过
来自无忧返利网数据挖掘编者:http://www.5ufanli.net