Pytorch(五):神经网络之 torch.nn——Convolution Layers
上一篇文章记录了 Pytorch 用于构建神经网络的容器,并且提到 一个神经网络模块是由其他子模块嵌套而成的结构,常用的就是卷积、池化等等,所以这篇简单介绍下 torch.nn 中的卷积类。
目录
-
- 一、卷积-Convolution
-
- 1 nn.Conv1d
-
- 1.1 原型&参数
- 1.2 输入&输出的shape
- 1.3 属性
- 1.4 示例
- 2 nn.Conv2d
-
- 2.1 原型&参数
- 2.2 输入&输出的shape
- 2.3 属性
- 2.4 示例
- 3 nn.Conv3d
-
- 3.1 原型&参数
- 3.2 输入&输出的shape
- 3.3 属性
- 3.4 示例
- 二、转置卷积-Transposed Convolution
-
- 1 nn.ConvTranspose1d
-
- 1.1 原型及参数
- 1.2 输入&输出的shape
- 1.3 属性
- 1.4 示例
- 2 nn.ConvTranspose2d
-
- 2.1 原型及参数
- 2.2 输入&输出的shape
- 2.3 属性
- 2.4 示例
- 3 nn.ConvTranspose3d
-
- 3.1 原型及参数
- 3.2 输入&输出的shape
- 3.3 属性
- 3.4 示例
- 三、延迟卷积-Lazy Convolution
-
- 1 nn.LazyConv1d
- 2 nn.LazyConv2d
- 3 nn.LazyConv3d
- 四、延迟转置卷积-LazyConvTransposed
-
- 1 nn.LazyConvTransposed1d
- 2 nn.LazyConvTransposed2d
- 3 nn.LazyConvTransposed3d
- 五、其他
-
- 1 nn.Unfold
- 2 nn.Fold
- 六、参考
一、卷积-Convolution
1 nn.Conv1d
1.1 原型&参数
torch.nn.Conv1d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride=1, padding=0, dilation=1, groups=1, bias=True, padding_mode='zeros')
Conv1d 的作用就是对输入数据执行 一维卷积,所谓的一维卷积以数学形式可以这么表达:设输入为 ( N , C i n , L i n ) (N, C_{in}, L_{in}) (N,Cin,Lin),输出为 ( N , C o u t , L o u t ) (N, C_{out}, L_{out}) (N,Cout,Lout)。
- N , C i n , C o u t N, C_{in}, C_{out} N,Cin,Cout 分别表示批大小、输入通道数、输出通道数;
- L i n , L o u t L_{in}, L_{out} Lin,Lout 分别表示输入数据和输出数据的长度;
- ⋆ \star ⋆ 表示 互相关算子(valid cross-correlation operator)。
那么 第 i i i 批第 j j j 个通道的输出 可以精确描述为:
o u t ( N i , C o u t j ) = b i a s ( C o u t j ) + ∑ k = 0 C i n − 1 w e i g h t ( C o u t j , k ) ⋆ i n p u t ( N i , k ) out(N_i, C_{out_{j}})=bias(C_{out_{j}})+\sum_{k=0}^{C_{in}-1}{weight(C_{out_{j}},k){\star}\ input(N_i,k)} out(Ni,Coutj)=bias(Coutj)+k=0∑Cin−1weight(Coutj,k)⋆ input(Ni,k)
注:前两天在朋友圈看到一个对卷积超好玩的理解:什么是卷积?你在过去不同时刻惹女朋友生气的叠加,对女朋友现在坏心情的贡献就是卷积。
参数:
in_channels:类型为int,表示输入数据的通道数;out_channels:类型为int,表示经过一维卷积操作后输出数据的通道数;kernel_size:类型为int、tuple,表示卷积核的大小;stride:可选参数,类型为int、tuple,控制进行卷积的步长,默认stride=1;padding:可选参数,类型为int、tuple,可对输入的两侧进行零填充,即控制输入两侧的隐式填充量,默认padding=0;padding_mode:可选参数,类型为string,控制填充模式zeros-零填充, reflect-镜像填充, replicate-复制填充, circular,默认为padding_mode=zeros;dilation:可选参数,类型为int、tuple,控制卷积核元素的间距,默认dilation=1就是标准卷积,更改该参数的话标准卷积就变成了 膨胀卷积(空洞卷积),也被称为à trous算法,文字描述很困难,但是用图就很容易理解,参考 [1];groups:可选参数,类型为int,控制从输入到输出之间的连接数,该参数必须满足能够整除input_channels & output_channels,默认为groups=1,例如:- 当
groups=1时,所有的输入都会被卷积到输出; - 当
groups=2时,相当于并排放置两个conv1d层,每个层会传入一半的input_channels并产生一半的output_channels,然后将两者连接起来; - 当
groups=input_channels时,每个input_channels只会与该通道的大小为 o u t p u t _ c h a n n e l s i n p u t _ c h a n n e l s \frac{output{\_}channels}{input{\_}channels} input_channelsoutput_channels 的滤波器进行卷积; - 注:当
groups == in_channels和out_channels == K * in_channels时(其中 K 是正整数),此操作也称为 深度卷积,换句话说,对于输入 ( N , C i n , L i n ) (N, C_{in}, L_{in}) (N,Cin,Lin),可以使用参数 ( C i n = C i n , C o u t = C i n ∗ K , ⋯ , g r o u p s = C i n ) (C_{in}=C_{in}, C_{out}=C_{in}*K, \cdots, groups=C_{in}) (Cin=Cin,Cout=Cin∗K,⋯,groups=Cin) 实现depth=K的深度卷积。下同。
- 当
bias:可选参数,类型为bool,若bias=True,则会添加可学习的偏差参数,默认值为bias=True。
1.2 输入&输出的shape
假设:
- 输入的 shape 为 ( N , C i n , L i n ) (N, C_{in}, L_{in}) (N,Cin,Lin);
- 输出的 shape 为 ( N , C o u t , L o u t ) (N, C_{out}, L_{out}) (N,Cout,Lout)
- 满足:
L o u t = [ L i n + 2 × p a d d i n g − d i l a t i o n × ( k e r n e l _ s i z e − 1 ) − 1 s t r i d e + 1 ] L_{out}=[\frac{L_{in} + 2{\times}padding-dilation{\times}(kernel{\_}size-1)-1}{stride}+1] Lout=[strideLin+2×padding−dilation×(kernel_size−1)−1+1]
1.3 属性
在卷积的过程中,可以学习的
Conv1d.weight:类型为Tensor,代表模型中可学习的权重,shape 为 ( o u t _ c h a n n e l s , i n _ c h a n n e l s g r o u p s , k e r n e l _ s i z e ) (out{\_}channels, \frac{in{\_}channels}{groups}, kernel{\_}size) (out_channels,groupsin_channels,kernel_size),这些值是从 μ ( − k , k ) , k = g r o u p s C _ i n ∗ k e r n e l _ s i z e \mu(-\sqrt{k}, \sqrt{k}),{\ }k=\frac{groups}{C{\_}{in}*kernel{\_}size} μ(−k,k), k=C_in∗kernel_sizegroups 取样得到;Conv1d.bias:类型为Tensor,代表模型中可学习的偏差,shape 为 ( o u t _ c h a n n e l s ) (out{\_}channels) (out_channels)。如果参数bias=True,那么这些值是从 μ ( − k , k ) , k = g r o u p s C _ i n ∗ k e r n e l _ s i z e \mu(-\sqrt{k}, \sqrt{k}),{\ }k=\frac{groups}{C{\_}{in}*kernel{\_}size} μ(−k,k), k=C_in∗kernel_sizegroups 取样得到。
1.4 示例
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
conv_layers = [nn.Conv1d(16, 33, 3, stride=2),
nn.Conv1d(16, 33, 5, stride=2),
nn.Conv1d(16, 33, 3, stride=3),
nn.Conv1d(16, 33, 3, stride=2, padding=2),
nn.Conv1d(16, 33, 3, stride=2, dilation=3),
nn.Conv1d(16, 33, 3, stride=2, bias=True),
nn.Conv1d(16, 24, 3, stride=2),
nn.Conv1d(16, 24, 3, stride=2, groups=2)]
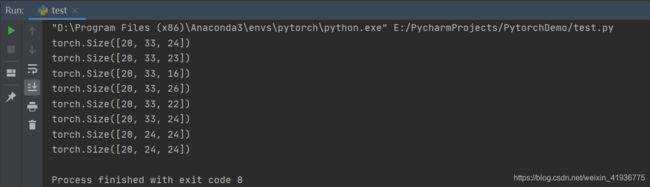
input_data = torch.randn(20, 16, 50)
for i in range(len(conv_layers)):
output_data = conv_layers[i](input_data)
print(output_data.shape)
可以按照 1.3 中的公式验证下结果:
- o u t 1 = [ 50 + 2 × 0 − 1 × ( 3 − 1 ) − 1 2 + 1 ] = 24 out_1=[\frac{50 + 2{\times}0-1{\times}(3-1)-1}{2}+1]=24 out1=[250+2×0−1×(3−1)−1+1]=24
- o u t 2 = [ 50 + 2 × 0 − 1 × ( 5 − 1 ) − 1 2 + 1 ] = 23 out_2=[\frac{50 + 2{\times}0-1{\times}(5-1)-1}{2}+1]=23 out2=[250+2×0−1×(5−1)−1+1]=23
- o u t 3 = [ 50 + 2 × 0 − 1 × ( 3 − 1 ) − 1 3 + 1 ] = 16 out_3=[\frac{50 + 2{\times}0-1{\times}(3-1)-1}{3}+1]=16 out3=[350+2×0−1×(3−1)−1+1]=16
- o u t 4 = [ 50 + 2 × 2 − 1 × ( 3 − 1 ) − 1 2 + 1 ] = 26 out_4=[\frac{50 + 2{\times}2-1{\times}(3-1)-1}{2}+1]=26 out4=[250+2×2−1×(3−1)−1+1]=26
- o u t 5 = [ 50 + 2 × 0 − 3 × ( 3 − 1 ) − 1 2 + 1 ] = 22 out_5=[\frac{50 + 2{\times}0-3{\times}(3-1)-1}{2}+1]=22 out5=[250+2×0−3×(3−1)−1+1]=22
- o u t 6 = [ 50 + 2 × 0 − 1 × ( 3 − 1 ) − 1 2 + 1 ] = 24 out_6=[\frac{50 + 2{\times}0-1{\times}(3-1)-1}{2}+1]=24 out6=[250+2×0−1×(3−1)−1+1]=24
最后两个测试改变了输入通道数和分组,可以发现采用参数 groups 并不会改变结果:
- o u t 7 = [ 50 + 2 × 0 − 1 × ( 3 − 1 ) − 1 2 + 1 ] = 24 out_7=[\frac{50 + 2{\times}0-1{\times}(3-1)-1}{2}+1]=24 out7=[250+2×0−1×(3−1)−1+1]=24
- o u t 8 = [ 50 + 2 × 0 − 1 × ( 3 − 1 ) − 1 2 + 1 ] = 24 out_8=[\frac{50 + 2{\times}0-1{\times}(3-1)-1}{2}+1]=24 out8=[250+2×0−1×(3−1)−1+1]=24
2 nn.Conv2d
2.1 原型&参数
torch.nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride=1, padding=0, dilation=1, groups=1, bias=True, padding_mode='zeros')
Conv2d 的作用就是对输入数据执行 二维卷积,二维卷积以数学形式可以这么表达:设输入为 ( N , C i n , H i n , W i n ) (N, C_{in}, H_{in}, W_{in}) (N,Cin,Hin,Win),输出为 ( N , C o u t , H o u t , W o u t ) (N, C_{out}, H_{out}, W_{out}) (N,Cout,Hout,Wout)。
- N , C i n , C o u t N, C_{in}, C_{out} N,Cin,Cout 分别表示批大小、输入通道数、输出通道数;
- H i n , W i n , H o u t , W o u t H_{in}, W_{in}, H_{out}, W_{out} Hin,Win,Hout,Wout 分别表示输入数据和输出数据的宽和高;
- ⋆ \star ⋆ 表示 二维互相关算子(valid cross-correlation operator)。
那么 第 i i i 批第 j j j 个通道的输出 可以精确描述为:
o u t ( N i , C o u t j ) = b i a s ( C o u t j ) + ∑ k = 0 C i n − 1 w e i g h t ( C o u t j , k ) ⋆ i n p u t ( N i , k ) out(N_i, C_{out_{j}})=bias(C_{out_{j}})+\sum_{k=0}^{C_{in}-1}{weight(C_{out_{j}},k){\star}\ input(N_i,k)} out(Ni,Coutj)=bias(Coutj)+k=0∑Cin−1weight(Coutj,k)⋆ input(Ni,k)
参数:
in_channels:类型为int,表示输入数据的通道数;out_channels:类型为int,表示经过二维卷积操作后输出数据的通道数;kernel_size:类型为int、tuple of two ints,表示卷积核的大小:- 当类型为单个
int时,宽高将使用同样的尺寸值; - 当类型为
tuple of two ints时,第一个int用于高度尺寸,第二个int用于宽度尺寸。下同。
- 当类型为单个
stride:可选参数,类型为int、tuple of two ints,控制进行卷积的步长,默认stride=1;padding:可选参数,类型为int、tuple of two ints,可对输入的两侧进行零填充,即控制输入两侧的隐式填充量,默认padding=0;padding_mode:可选参数,类型为string,控制填充模式zeros-零填充, reflect-镜像填充, replicate-复制填充, circular,默认为padding_mode=zeros;dilation:可选参数,类型为int、tuple of two ints,控制卷积核元素的间距,默认dilation=1是标准卷积,膨胀卷积(空洞卷积) 参考 [1];groups:可选参数,类型为int,控制从输入到输出之间的连接数,该参数必须满足能够整除input_channels & output_channels,默认为groups=1,例如:- 当
groups=1时,所有的输入都会被卷积到输出; - 当
groups=2时,相当于并排放置两个conv1d层,每个层会传入一半的input_channels并产生一半的output_channels,然后将两者连接起来; - 当
groups=input_channels时,每个input_channels只会与该通道的大小为 o u t p u t _ c h a n n e l s i n p u t _ c h a n n e l s \frac{output{\_}channels}{input{\_}channels} input_channelsoutput_channels 的滤波器进行卷积;
- 当
bias:可选参数,类型为bool,若bias=True,则会添加可学习的偏差参数,默认值为bias=True。
2.2 输入&输出的shape
假设:
- 输入的 shape 为 ( N , C i n , H i n , W i n ) (N, C_{in}, H_{in}, W_{in}) (N,Cin,Hin,Win);
- 输出的 shape为 ( N , C o u t , H o u t , W o u t ) (N, C_{out}, H_{out}, W_{out}) (N,Cout,Hout,Wout)
- 满足:
H o u t = [ H i n + 2 × p a d d i n g [ 0 ] − d i l a t i o n [ 0 ] × ( k e r n e l _ s i z e [ 0 ] − 1 ) − 1 s t r i d e [ 0 ] + 1 ] H_{out}=[\frac{H_{in} + 2{\times}padding[0]-dilation[0]{\times}(kernel{\_}size[0]-1)-1}{stride[0]}+1] Hout=[stride[0]Hin+2×padding[0]−dilation[0]×(kernel_size[0]−1)−1+1]
W o u t = [ W i n + 2 × p a d d i n g [ 1 ] − d i l a t i o n [ 1 ] × ( k e r n e l _ s i z e [ 1 ] − 1 ) − 1 s t r i d e [ 1 ] + 1 ] W_{out}=[\frac{W_{in} + 2{\times}padding[1]-dilation[1]{\times}(kernel{\_}size[1]-1)-1}{stride[1]}+1] Wout=[stride[1]Win+2×padding[1]−dilation[1]×(kernel_size[1]−1)−1+1]
2.3 属性
在卷积的过程中,可以学习权重和偏差:
Conv2d.weight:类型为Tensor,代表模型中可学习的权重,shape 为 ( o u t _ c h a n n e l s , i n _ c h a n n e l s g r o u p s , k e r n e l _ s i z e [ 0 ] , k e r n e l _ s i z e [ 1 ] ) (out{\_}channels, \frac{in{\_}channels}{groups}, kernel{\_}size[0], kernel{\_}size[1]) (out_channels,groupsin_channels,kernel_size[0],kernel_size[1]),这些值是从 μ ( − k , k ) , k = g r o u p s C _ i n ∗ k e r n e l _ s i z e [ 0 ] ∗ k e r n e l _ s i z e [ 1 ] \mu(-\sqrt{k}, \sqrt{k}),{\ }k=\frac{groups}{C{\_}{in}*kernel{\_}size[0]*kernel{\_}size[1]} μ(−k,k), k=C_in∗kernel_size[0]∗kernel_size[1]groups 取样得到;Conv2d.bias:类型为Tensor,代表模型中可学习的偏差,shape 为 ( o u t _ c h a n n e l s ) (out{\_}channels) (out_channels)。如果参数bias=True,那么这些值是从 μ ( − k , k ) , k = g r o u p s C _ i n ∗ k e r n e l _ s i z e [ 0 ] ∗ k e r n e l _ s i z e [ 1 ] \mu(-\sqrt{k}, \sqrt{k}),{\ }k=\frac{groups}{C{\_}{in}*kernel{\_}size[0]*kernel{\_}size[1]} μ(−k,k), k=C_in∗kernel_size[0]∗kernel_size[1]groups 取样得到。
2.4 示例
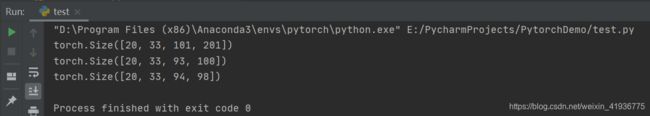
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
conv_layers = [nn.Conv2d(16, 33, 3, stride=2), # square kernels and equal stride
# non-square kernels and unequal stride and padding
nn.Conv2d(16, 33, (3, 5), stride=(2, 1), padding=(4, 2)),
# non-square kernels and unequal stride and padding
nn.Conv2d(16, 33, (3, 5), stride=(2, 1), padding=(4, 2), dilation=(3, 1))
]
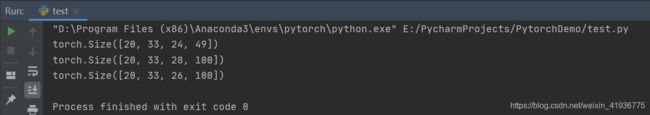
input_data = torch.randn(20, 16, 50, 100)
for i in range(len(conv_layers)):
output_data = conv_layers[i](input_data)
print(output_data.shape)
-
H o u t 1 = [ 50 + 2 × 0 − 1 × ( 3 − 1 ) − 1 2 + 1 ] = 24 H_{out1}=[\frac{50 + 2{\times}0-1{\times}(3-1)-1}{2}+1]=24 Hout1=[250+2×0−1×(3−1)−1+1]=24
W o u t 1 = [ 100 + 2 × 0 − 1 × ( 3 − 1 ) − 1 2 + 1 ] = 49 W_{out1}=[\frac{100 + 2{\times}0-1{\times}(3-1)-1}{2}+1]=49 Wout1=[2100+2×0−1×(3−1)−1+1]=49 -
H o u t 2 = [ 50 + 2 × 4 − 1 × ( 3 − 1 ) − 1 2 + 1 ] = 28 H_{out2}=[\frac{50 + 2{\times}4-1{\times}(3-1)-1}{2}+1]=28 Hout2=[250+2×4−1×(3−1)−1+1]=28
W o u t 2 = [ 100 + 2 × 2 − 1 × ( 5 − 1 ) − 1 1 + 1 ] = 100 W_{out2}=[\frac{100 + 2{\times}2-1{\times}(5-1)-1}{1}+1]=100 Wout2=[1100+2×2−1×(5−1)−1+1]=100 -
H o u t 3 = [ 50 + 2 × 4 − 3 × ( 3 − 1 ) − 1 2 + 1 ] = 26 H_{out3}=[\frac{50 + 2{\times}4-3{\times}(3-1)-1}{2}+1]=26 Hout3=[250+2×4−3×(3−1)−1+1]=26
W o u t 3 = [ 100 + 2 × 2 − 1 × ( 5 − 1 ) − 1 1 + 1 ] = 100 W_{out3}=[\frac{100 + 2{\times}2-1{\times}(5-1)-1}{1}+1]=100 Wout3=[1100+2×2−1×(5−1)−1+1]=100
3 nn.Conv3d
3.1 原型&参数
torch.nn.Conv3d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride=1, padding=0, dilation=1, groups=1, bias=True, padding_mode='zeros')
Conv3d 的作用就是对输入数据执行 三维卷积,三维卷积以数学形式可以表达为:设输入为 ( N , C i n , D i n , H i n , W i n ) (N, C_{in}, D_{in}, H_{in}, W_{in}) (N,Cin,Din,Hin,Win),输出为 ( N , C o u t , D o u t , H o u t , W o u t ) (N, C_{out}, D_{out}, H_{out}, W_{out}) (N,Cout,Dout,Hout,Wout)。
- N , C i n , C o u t N, C_{in}, C_{out} N,Cin,Cout 分别表示批大小、输入通道数、输出通道数;
- H i n , W i n , H o u t , W o u t H_{in}, W_{in}, H_{out}, W_{out} Hin,Win,Hout,Wout 分别表示输入数据和输出数据的宽和高;
- ⋆ \star ⋆ 表示 三维互相关算子(valid cross-correlation operator)。
那么 第 i i i 批第 j j j 个通道的输出 可以精确描述为:
o u t ( N i , C o u t j ) = b i a s ( C o u t j ) + ∑ k = 0 C i n − 1 w e i g h t ( C o u t j , k ) ⋆ i n p u t ( N i , k ) out(N_i, C_{out_{j}})=bias(C_{out_{j}})+\sum_{k=0}^{C_{in}-1}{weight(C_{out_{j}},k){\star}\ input(N_i,k)} out(Ni,Coutj)=bias(Coutj)+k=0∑Cin−1weight(Coutj,k)⋆ input(Ni,k)
参数:
in_channels:类型为int,表示输入数据的通道数;out_channels:类型为int,表示经过三维卷积操作后输出数据的通道数;kernel_size:类型为int、tuple of three ints,表示卷积核的大小:- 当类型为单个
int时,宽高将使用同样的尺寸值; - 当类型为
tuple of three ints时,第一个int用于深度尺寸,第二个int用于高度,第三个int用于宽度。下同。
- 当类型为单个
stride:可选参数,类型为int、tuple of three ints,控制进行卷积的步长,默认stride=1;padding:可选参数,类型为int、tuple of three ints,可对输入的三边均进行零填充,即控制输入两侧的隐式填充量,默认padding=0;padding_mode:可选参数,类型为string,控制填充模式zeros-零填充, reflect-镜像填充, replicate-复制填充, circular,默认为padding_mode=zeros;dilation:可选参数,类型为int、tuple of three ints,控制卷积核元素的间距,默认dilation=1是标准卷积,膨胀卷积(空洞卷积) 参考 [1];groups:可选参数,类型为int,控制从输入到输出之间的连接数,该参数必须满足能够整除input_channels & output_channels,默认为groups=1,例如:- 当
groups=1时,所有的输入都会被卷积到输出; - 当
groups=2时,相当于并排放置两个conv1d层,每个层会传入一半的input_channels并产生一半的output_channels,然后将两者连接起来; - 当
groups=input_channels时,每个input_channels只会与该通道的大小为 o u t p u t _ c h a n n e l s i n p u t _ c h a n n e l s \frac{output{\_}channels}{input{\_}channels} input_channelsoutput_channels 的滤波器进行卷积;
- 当
bias:可选参数,类型为bool,若bias=True,则会添加可学习的偏差参数,默认值为bias=True。
3.2 输入&输出的shape
假设:
- 输入的 shape 为 ( N , C i n , D i n , H i n , W i n ) (N, C_{in}, D_{in}, H_{in}, W_{in}) (N,Cin,Din,Hin,Win);
- 输出的 shape为 ( N , C o u t , D o u t , H o u t , W o u t ) (N, C_{out}, D_{out}, H_{out}, W_{out}) (N,Cout,Dout,Hout,Wout)
- 满足: D o u t = [ D i n + 2 × p a d d i n g [ 0 ] − d i l a t i o n [ 0 ] × ( k e r n e l _ s i z e [ 0 ] − 1 ) − 1 s t r i d e [ 0 ] + 1 ] D_{out}=[\frac{D_{in} + 2{\times}padding[0]-dilation[0]{\times}(kernel{\_}size[0]-1)-1}{stride[0]}+1] Dout=[stride[0]Din+2×padding[0]−dilation[0]×(kernel_size[0]−1)−1+1]
H o u t = [ H i n + 2 × p a d d i n g [ 1 ] − d i l a t i o n [ 1 ] × ( k e r n e l _ s i z e [ 1 ] − 1 ) − 1 s t r i d e [ 1 ] + 1 ] H_{out}=[\frac{H_{in} + 2{\times}padding[1]-dilation[1]{\times}(kernel{\_}size[1]-1)-1}{stride[1]}+1] Hout=[stride[1]Hin+2×padding[1]−dilation[1]×(kernel_size[1]−1)−1+1]
W o u t = [ W i n + 2 × p a d d i n g [ 2 ] − d i l a t i o n [ 2 ] × ( k e r n e l _ s i z e [ 2 ] − 1 ) − 1 s t r i d e [ 2 ] + 1 ] W_{out}=[\frac{W_{in} + 2{\times}padding[2]-dilation[2]{\times}(kernel{\_}size[2]-1)-1}{stride[2]}+1] Wout=[stride[2]Win+2×padding[2]−dilation[2]×(kernel_size[2]−1)−1+1]
3.3 属性
在卷积的过程中,可以学习权重和偏差:
Conv3d.weight:类型为Tensor,代表模型中可学习的权重,shape 为 ( o u t _ c h a n n e l s , i n _ c h a n n e l s g r o u p s , k e r n e l _ s i z e [ 0 ] , k e r n e l _ s i z e [ 1 ] , k e r n e l _ s i z e [ ] ) (out{\_}channels, \frac{in{\_}channels}{groups}, kernel{\_}size[0], kernel{\_}size[1], kernel{\_}size[]) (out_channels,groupsin_channels,kernel_size[0],kernel_size[1],kernel_size[]),这些值是从 μ ( − k , k ) , k = g r o u p s C _ i n ∗ k e r n e l _ s i z e [ 0 ] ∗ k e r n e l _ s i z e [ 1 ] ∗ k e r n e l _ s i z e [ 2 ] \mu(-\sqrt{k}, \sqrt{k}),{\ }k=\frac{groups}{C{\_}{in}*kernel{\_}size[0]*kernel{\_}size[1]*kernel{\_}size[2]} μ(−k,k), k=C_in∗kernel_size[0]∗kernel_size[1]∗kernel_size[2]groups 取样得到;Conv3d.bias:类型为Tensor,代表模型中可学习的偏差,shape 为 ( o u t _ c h a n n e l s ) (out{\_}channels) (out_channels)。如果参数bias=True,那么这些值是从 μ ( − k , k ) , k = g r o u p s C _ i n ∗ k e r n e l _ s i z e [ 0 ] ∗ k e r n e l _ s i z e [ 1 ] ∗ k e r n e l _ s i z e [ 2 ] \mu(-\sqrt{k}, \sqrt{k}),{\ }k=\frac{groups}{C{\_}{in}*kernel{\_}size[0]*kernel{\_}size[1]*kernel{\_}size[2]} μ(−k,k), k=C_in∗kernel_size[0]∗kernel_size[1]∗kernel_size[2]groups 取样得到。
3.4 示例
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
conv_layers = [nn.Conv3d(16, 33, 3, stride=2), # square kernels and equal stride
# non-square kernels and unequal stride with padding
nn.Conv3d(16, 33, (3, 5, 2), stride=(2, 1, 1), padding=(4, 2, 0)),
]
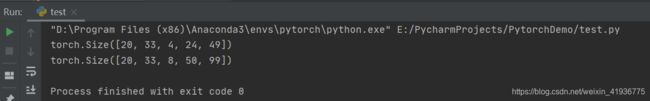
input_data = torch.randn(20, 16, 10, 50, 100)
for i in range(len(conv_layers)):
output_data = conv_layers[i](input_data)
print(output_data.shape)
-
D o u t 1 = [ 10 + 2 × 0 − 1 × ( 3 − 1 ) − 1 2 + 1 ] = 4 D_{out1}=[\frac{10 + 2{\times}0-1{\times}(3-1)-1}{2}+1]=4 Dout1=[210+2×0−1×(3−1)−1+1]=4
H o u t 1 = [ 50 + 2 × 0 − 1 × ( 3 − 1 ) − 1 2 + 1 ] = 24 H_{out1}=[\frac{50 + 2{\times}0-1{\times}(3-1)-1}{2}+1]=24 Hout1=[250+2×0−1×(3−1)−1+1]=24
W o u t 1 = [ 100 + 2 × 0 − 1 × ( 3 − 1 ) − 1 2 + 1 ] = 49 W_{out1}=[\frac{100 + 2{\times}0-1{\times}(3-1)-1}{2}+1]=49 Wout1=[2100+2×0−1×(3−1)−1+1]=49 -
D o u t 2 = [ 10 + 2 × 4 − 1 × ( 3 − 1 ) − 1 2 + 1 ] = 8 D_{out2}=[\frac{10 + 2{\times}4-1{\times}(3-1)-1}{2}+1]=8 Dout2=[210+2×4−1×(3−1)−1+1]=8
H o u t 2 = [ 50 + 2 × 2 − 1 × ( 5 − 1 ) − 1 1 + 1 ] = 50 H_{out2}=[\frac{50 + 2{\times}2-1{\times}(5-1)-1}{1}+1]=50 Hout2=[150+2×2−1×(5−1)−1+1]=50
W o u t 2 = [ 100 + 2 × 0 − 1 × ( 2 − 1 ) − 1 1 + 1 ] = 99 W_{out2}=[\frac{100 + 2{\times}0-1{\times}(2-1)-1}{1}+1]=99 Wout2=[1100+2×0−1×(2−1)−1+1]=99
二、转置卷积-Transposed Convolution
转置卷积(Transposed Convolution) 是卷积的逆过程,也被称为反卷积。在卷积神经网络中,属于 上采样(up-sampling) 的一种方式,常用于提升图像的分辨率,恢复图像的尺寸而不是像素值喔!图解分析可以参考 [1]。
和标准卷积类似,转置卷积也分为三种维度。
1 nn.ConvTranspose1d
1.1 原型及参数
torch.nn.ConvTranspose1d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride=1, padding=0, output_padding=0, groups=1, bias=True, dilation=1, padding_mode='zeros')
ConvTranspose1d 的作用就是对输入数据执行 一维转置卷积,可以看作是 Conv1d 相对于其输入的梯度,它也称为 fractionally-strided convolution 或 deconvolution (尽管它不是实际的反卷积操作)。
参数:
in_channels:类型为int,表示输入数据的通道数;out_channels:类型为int,表示经过一维转置卷积操作后输出数据的通道数;kernel_size:类型为int、tuple of one int,表示卷积核的大小;stride:可选参数,类型为int、tuple of one int,控制进行卷积的步长,默认stride=1;padding:可选参数,类型为int、tuple of one int,可对输入的两侧进行dilation * (kernel_size-1) - padding数量的零填充,默认padding=0。之所以进行固定熟练的填充点数,是为了遵循当Conv1d和ConvTranspose1d使用相同的参数初始化时,它们在输入和输出形状方面互为倒数 。output_padding:可选参数,类型为int、tuple of one int,控制添加到输出形状一侧的附加尺寸,默认为output_padding=0。该参数的作用是处理当stride>1时的情况:Conv1d将多个输入形状映射到相同的输出形状,output_padding通过有效增加一侧计算后的输出形状来解决这种歧义。注:output_padding仅用于查找输出形状,但实际上并未向输出执行零填充。padding_mode:可选参数,类型为string,控制填充模式zeros-零填充, reflect-镜像填充, replicate-复制填充, circular,默认为padding_mode=zeros;dilation:可选参数,类型为int、tuple,控制卷积核元素的间距,默认dilation=1就是标准卷积,更改该参数的话标准卷积就变成了 膨胀卷积(空洞卷积),参考 [1];groups:可选参数,类型为int,控制从输入到输出之间的连接数,该参数必须满足能够整除input_channels & output_channels,默认为groups=1,例如:- 当
groups=1时,所有的输入都会被卷积到输出; - 当
groups=2时,相当于并排放置两个conv1d层,每个层会传入一半的input_channels并产生一半的output_channels,然后将两者连接起来; - 当
groups=input_channels时,每个input_channels只会与该通道的大小为 o u t p u t _ c h a n n e l s i n p u t _ c h a n n e l s \frac{output{\_}channels}{input{\_}channels} input_channelsoutput_channels 的滤波器进行卷积;
- 当
bias:可选参数,类型为bool,若bias=True,则会添加可学习的偏差参数,默认值为bias=True。
1.2 输入&输出的shape
input shape: ( N , C i n , L i n ) (N, C_{in}, L_{in}) (N,Cin,Lin)output shape: ( N , C o u t , L o u t ) (N, C_{out}, L_{out}) (N,Cout,Lout)- 满足:
L o u t = ( L i n − 1 ) × s t r i d e − 2 × p a d d i n g + d i l a t i o n × ( k e r n e l _ s i z e − 1 ) + o u t p u t _ p a d d i n g + 1 L_{out}=(L_{in}-1){\times}stride-2{\times}padding+dilation×(kernel{\_}size−1)+output{\_}padding+1 Lout=(Lin−1)×stride−2×padding+dilation×(kernel_size−1)+output_padding+1
1.3 属性
在卷积的过程中,可以学习的
ConvTranspose1d.weight:类型为Tensor,代表模型中可学习的权重,shape 为 ( o u t _ c h a n n e l s , i n _ c h a n n e l s g r o u p s , k e r n e l _ s i z e ) (out{\_}channels, \frac{in{\_}channels}{groups}, kernel{\_}size) (out_channels,groupsin_channels,kernel_size),这些值是从 μ ( − k , k ) , k = g r o u p s C _ o u t ∗ k e r n e l _ s i z e \mu(-\sqrt{k}, \sqrt{k}),{\ }k=\frac{groups}{C{\_}{out}*kernel{\_}size} μ(−k,k), k=C_out∗kernel_sizegroups 取样得到;ConvTranspose1d.bias:类型为Tensor,代表模型中可学习的偏差,shape 为 ( o u t _ c h a n n e l s ) (out{\_}channels) (out_channels)。如果参数bias=True,那么这些值是从 μ ( − k , k ) , k = g r o u p s C _ o u t ∗ k e r n e l _ s i z e \mu(-\sqrt{k}, \sqrt{k}),{\ }k=\frac{groups}{C{\_}{out}*kernel{\_}size} μ(−k,k), k=C_out∗kernel_sizegroups 取样得到。
1.4 示例
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
conv_layers = [nn.ConvTranspose1d(16, 33, 3, stride=2),
nn.ConvTranspose1d(16, 33, 3, stride=2, padding=2),
nn.ConvTranspose1d(16, 33, 3, stride=2, padding=2, output_padding=1),
nn.ConvTranspose1d(16, 33, 3, stride=2, padding=2, output_padding=1, dilation=3)
]
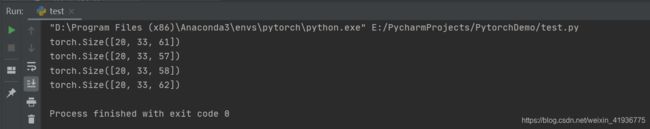
input_data = torch.randn(20, 16, 30)
for i in range(len(conv_layers)):
output_data = conv_layers[i](input_data)
print(output_data.shape)
- o u t 1 = ( 30 − 1 ) × 2 − 2 × 0 + 1 × ( 3 − 1 ) + 0 + 1 = 61 out_1=(30-1){\times}2-2{\times}0+1{\times}(3-1)+0+1=61 out1=(30−1)×2−2×0+1×(3−1)+0+1=61
- o u t 2 = ( 30 − 1 ) × 2 − 2 × 2 + 1 × ( 3 − 1 ) + 0 + 1 = 57 out_2=(30-1){\times}2-2{\times}2+1{\times}(3-1)+0+1=57 out2=(30−1)×2−2×2+1×(3−1)+0+1=57
- o u t 2 = ( 30 − 1 ) × 2 − 2 × 2 + 1 × ( 3 − 1 ) + 1 + 1 = 58 out_2=(30-1){\times}2-2{\times}2+1{\times}(3-1)+1+1=58 out2=(30−1)×2−2×2+1×(3−1)+1+1=58
- o u t 2 = ( 30 − 1 ) × 2 − 2 × 2 + 3 × ( 3 − 1 ) + 1 + 1 = 62 out_2=(30-1){\times}2-2{\times}2+3{\times}(3-1)+1+1=62 out2=(30−1)×2−2×2+3×(3−1)+1+1=62
2 nn.ConvTranspose2d
2.1 原型及参数
torch.nn.ConvTranspose2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride=1, padding=0, output_padding=0, groups=1, bias=True, dilation=1, padding_mode='zeros')
ConvTranspose2d 的作用就是对输入数据执行 二维转置卷积,可以看作是 Conv2d 相对于其输入的梯度。
参数:
in_channels:类型为int,表示输入数据的通道数;out_channels:类型为int,表示经过二维转置卷积操作后输出数据的通道数;kernel_size:类型为int、tuple of two ints,表示卷积核的大小;- 当类型为单个
int时,宽高将使用同样的尺寸值; - 当类型为
tuple of two ints时,第一个int用于高度尺寸,第二个int用于宽度尺寸。下同。
- 当类型为单个
stride:可选参数,类型为int、tuple of two ints,控制进行卷积的步长,默认stride=1;padding:可选参数,类型为int、tuple of two ints,可对输入进行dilation * (kernel_size-1) - padding数量的零填充,默认padding=0。之所以进行固定熟练的填充点数,是为了遵循当Conv2d和ConvTranspose2d使用相同的参数初始化时,它们在输入和输出形状方面互为倒数 。output_padding:可选参数,类型为int、tuple of two ints,控制添加到输出形状一侧的附加尺寸,默认为output_padding=0。该参数的作用是处理当stride>1时的情况:Conv2d将多个输入形状映射到相同的输出形状,output_padding通过有效增加一侧计算后的输出形状来解决这种歧义。注:output_padding仅用于查找输出形状,但实际上并未向输出执行零填充。padding_mode:可选参数,类型为string,控制填充模式zeros-零填充, reflect-镜像填充, replicate-复制填充, circular,默认为padding_mode=zeros;dilation:可选参数,类型为int、tuple of two ints,控制卷积核元素的间距,默认dilation=1就是标准卷积,更改该参数的话标准卷积就变成了 膨胀卷积(空洞卷积),参考 [1];groups:可选参数,类型为int,控制从输入到输出之间的连接数,该参数必须满足能够整除input_channels & output_channels,默认为groups=1,例如:- 当
groups=1时,所有的输入都会被卷积到输出; - 当
groups=2时,相当于并排放置两个conv1d层,每个层会传入一半的input_channels并产生一半的output_channels,然后将两者连接起来; - 当
groups=input_channels时,每个input_channels只会与该通道的大小为 o u t p u t _ c h a n n e l s i n p u t _ c h a n n e l s \frac{output{\_}channels}{input{\_}channels} input_channelsoutput_channels 的滤波器进行卷积;
- 当
bias:可选参数,类型为bool,若bias=True,则会添加可学习的偏差参数,默认值为bias=True。
2.2 输入&输出的shape
input shape: ( N , C i n , H i n , W i n ) (N, C_{in}, H_{in}, W_{in}) (N,Cin,Hin,Win)output shape: ( N , C o u t , H o u t , W o u t ) (N, C_{out}, H_{out}, W_{out}) (N,Cout,Hout,Wout)- 满足:
H o u t = ( H i n − 1 ) × s t r i d e [ 0 ] − 2 × p a d d i n g [ 0 ] + d i l a t i o n [ 0 ] × ( k e r n e l _ s i z e [ 0 ] − 1 ) + o u t p u t _ p a d d i n g [ 0 ] + 1 H_{out}=(H_{in}−1){\times}stride[0]−2{\times}padding[0]+dilation[0]{\times}(kernel{\_}size[0]−1)+output{\_}padding[0]+1 Hout=(Hin−1)×stride[0]−2×padding[0]+dilation[0]×(kernel_size[0]−1)+output_padding[0]+1
W o u t = ( W i n − 1 ) × s t r i d e [ 1 ] − 2 × p a d d i n g [ 1 ] + d i l a t i o n [ 1 ] × ( k e r n e l _ s i z e [ 1 ] − 1 ) + o u t p u t _ p a d d i n g [ 1 ] + 1 W_{out}=(W_{in}−1){\times}stride[1]−2{\times}padding[1]+dilation[1]{\times}(kernel{\_}size[1]−1)+output{\_}padding[1]+1 Wout=(Win−1)×stride[1]−2×padding[1]+dilation[1]×(kernel_size[1]−1)+output_padding[1]+1
2.3 属性
ConvTranspose2d.weight:类型为Tensor,代表模型中可学习的权重,shape 为 ( o u t _ c h a n n e l s , i n _ c h a n n e l s g r o u p s , k e r n e l _ s i z e [ 0 ] , k e r n e l _ s i z e [ 1 ] ) (out{\_}channels, \frac{in{\_}channels}{groups}, kernel{\_}size[0], kernel{\_}size[1]) (out_channels,groupsin_channels,kernel_size[0],kernel_size[1]),这些值是从 μ ( − k , k ) , k = g r o u p s C _ o u t ∗ k e r n e l _ s i z e [ 0 ] ∗ k e r n e l _ s i z e [ 1 ] \mu(-\sqrt{k}, \sqrt{k}),{\ }k=\frac{groups}{C{\_}{out}*kernel{\_}size[0]*kernel{\_}size[1]} μ(−k,k), k=C_out∗kernel_size[0]∗kernel_size[1]groups 取样得到;ConvTranspose2d.bias:类型为Tensor,代表模型中可学习的偏差,shape 为 ( o u t _ c h a n n e l s ) (out{\_}channels) (out_channels)。如果参数bias=True,那么这些值是从 μ ( − k , k ) , k = g r o u p s C _ o u t ∗ k e r n e l _ s i z e [ 0 ] ∗ k e r n e l _ s i z e [ 1 ] \mu(-\sqrt{k}, \sqrt{k}),{\ }k=\frac{groups}{C{\_}{out}*kernel{\_}size[0]*kernel{\_}size[1]} μ(−k,k), k=C_out∗kernel_size[0]∗kernel_size[1]groups 取样得到。
2.4 示例
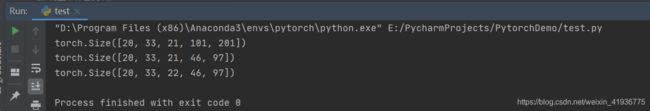
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
conv_layers = [nn.ConvTranspose2d(16, 33, 3, stride=2), # With square kernels and equal stride
# non-square kernels and unequal stride and with padding
nn.ConvTranspose2d(16, 33, (3, 5), stride=(2, 1), padding=(4, 2)),
# non-square kernels and unequal stride and with padding & output_padding
nn.ConvTranspose2d(16, 33, 3, stride=(2, 1), padding=(4, 2), output_padding=(1, 0)),
]
input_data = torch.randn(20, 16, 50, 100)
for i in range(len(conv_layers)):
output_data = conv_layers[i](input_data)
print(output_data.shape)
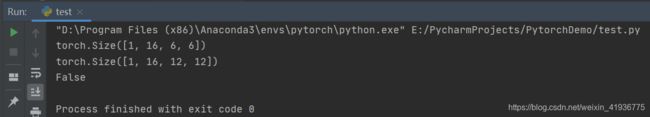
官网还给了另外一种应用形式,即用给定的数据进行转置卷积。通过下面的例子可以发现转置卷积和卷积是互为逆过程的。需要注意的地方是,转置卷积只可以恢复尺寸并不能保证数据也是和原始值是一样的。
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
input_data = torch.randn(1, 16, 12, 12)
down_sample = nn.Conv2d(16, 16, 3, stride=2, padding=1)
up_sample = nn.ConvTranspose2d(16, 16, 3, stride=2, padding=1)
# 计算正向卷积的输出
pe_output = down_sample(input_data)
print(pe_output.size())
# 将上述输出作为转置卷积的输入
# 可以发现最终的输出和原始输入的尺寸是一致的
output = up_sample(pe_output, output_size=input_data.size())
print(output.size())
# 检验输入和输出的值是否相同,显然是不同的
print(input_data.equal(output))
3 nn.ConvTranspose3d
3.1 原型及参数
原型:torch.nn.ConvTranspose3d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride=1, padding=0, output_padding=0, groups=1, bias=True, dilation=1, padding_mode='zeros')
ConvTranspose3d 的作用就是对输入数据执行 三维转置卷积,可描述为:在由多个输入平面组成的输入图像上应用 ConvTranspose3d,会将每个输入值逐个乘以一个可学习的内核,并对所有输入特征平面的输出求和。该模块可以看作是 Conv3d 相对于其输入的梯度。
参数:
in_channels:类型为int,表示输入数据的通道数;out_channels:类型为int,表示经过三维转置卷积操作后输出数据的通道数;kernel_size:类型为int、tuple of three ints,表示卷积核的大小;- 当类型为单个
int时,宽高将使用同样的尺寸值; - 当类型为
tuple of three ints时,第一个int用于深度尺寸,第二个int用于高度尺寸,第二个int用于宽度尺寸。下同。
- 当类型为单个
stride:可选参数,类型为int、tuple of three ints,控制进行卷积的步长,默认stride=1;padding:可选参数,类型为int、tuple of three ints,可对输入进行dilation * (kernel_size-1) - padding数量的零填充,默认padding=0。output_padding:可选参数,类型为int、tuple of two ints,控制添加到输出形状一侧的附加尺寸,默认为output_padding=0。该参数的作用是处理当stride>1时的情况:Conv3d将多个输入形状映射到相同的输出形状,output_padding通过有效增加一侧计算后的输出形状来解决这种歧义。注:output_padding仅用于查找输出形状,但实际上并未向输出执行零填充。padding_mode:可选参数,类型为string,控制填充模式zeros-零填充, reflect-镜像填充, replicate-复制填充, circular,默认为padding_mode=zeros;dilation:可选参数,类型为int、tuple of two ints,控制卷积核元素的间距,默认dilation=1就是标准卷积,更改该参数的话标准卷积就变成了 膨胀卷积(空洞卷积),参考 [1];groups:可选参数,类型为int,控制从输入到输出之间的连接数,该参数必须满足能够整除input_channels & output_channels,默认为groups=1,例如:- 当
groups=1时,所有的输入都会被卷积到输出; - 当
groups=2时,相当于并排放置两个conv1d层,每个层会传入一半的input_channels并产生一半的output_channels,然后将两者连接起来; - 当
groups=input_channels时,每个input_channels只会与该通道的大小为 o u t p u t _ c h a n n e l s i n p u t _ c h a n n e l s \frac{output{\_}channels}{input{\_}channels} input_channelsoutput_channels 的滤波器进行卷积;
- 当
bias:可选参数,类型为bool,若bias=True,则会添加可学习的偏差参数,默认值为bias=True。
3.2 输入&输出的shape
input shape: ( N , C i n , D i n , H i n , W i n ) (N, C_{in}, D_{in}, H_{in}, W_{in}) (N,Cin,Din,Hin,Win)output shape: ( N , C o u t , D o u t , H o u t , W o u t ) (N, C_{out}, D_{out}, H_{out}, W_{out}) (N,Cout,Dout,Hout,Wout)- 满足:
D o u t = ( D i n − 1 ) × s t r i d e [ 0 ] − 2 × p a d d i n g [ 0 ] + d i l a t i o n [ 0 ] × ( k e r n e l _ s i z e [ 0 ] − 1 ) + o u t p u t _ p a d d i n g [ 0 ] + 1 D_{out}=(D_{in}−1){\times}stride[0]−2{\times}padding[0]+dilation[0]{\times}(kernel{\_}size[0]−1)+output{\_}padding[0]+1 Dout=(Din−1)×stride[0]−2×padding[0]+dilation[0]×(kernel_size[0]−1)+output_padding[0]+1
H o u t = ( H i n − 1 ) × s t r i d e [ 1 ] − 2 × p a d d i n g [ 1 ] + d i l a t i o n [ 1 ] × ( k e r n e l _ s i z e [ 1 ] − 1 ) + o u t p u t _ p a d d i n g [ 1 ] + 1 H_{out}=(H_{in}−1){\times}stride[1]−2{\times}padding[1]+dilation[1]{\times}(kernel{\_}size[1]−1)+output{\_}padding[1]+1 Hout=(Hin−1)×stride[1]−2×padding[1]+dilation[1]×(kernel_size[1]−1)+output_padding[1]+1
W o u t = ( W i n − 1 ) × s t r i d e [ 2 ] − 2 × p a d d i n g [ 2 ] + d i l a t i o n [ 2 ] × ( k e r n e l _ s i z e [ 2 ] − 1 ) + o u t p u t _ p a d d i n g [ 2 ] + 1 W_{out}=(W_{in}−1){\times}stride[2]−2{\times}padding[2]+dilation[2]{\times}(kernel{\_}size[2]−1)+output{\_}padding[2]+1 Wout=(Win−1)×stride[2]−2×padding[2]+dilation[2]×(kernel_size[2]−1)+output_padding[2]+1
3.3 属性
在转置卷积的过程中,可以学习权重和偏差:
ConvTranspose3d.weight:类型为Tensor,代表模型中可学习的权重,shape 为 ( o u t _ c h a n n e l s , i n _ c h a n n e l s g r o u p s , k e r n e l _ s i z e [ 0 ] , k e r n e l _ s i z e [ 1 ] , k e r n e l _ s i z e [ 2 ] ) (out{\_}channels, \frac{in{\_}channels}{groups}, kernel{\_}size[0], kernel{\_}size[1], kernel{\_}size[2]) (out_channels,groupsin_channels,kernel_size[0],kernel_size[1],kernel_size[2]),这些值是从 μ ( − k , k ) , k = g r o u p s C _ o u t ∗ k e r n e l _ s i z e [ 0 ] ∗ k e r n e l _ s i z e [ 1 ] ∗ k e r n e l _ s i z e [ 2 ] \mu(-\sqrt{k}, \sqrt{k}),{\ }k=\frac{groups}{C{\_}{out}*kernel{\_}size[0]*kernel{\_}size[1]*kernel{\_}size[2]} μ(−k,k), k=C_out∗kernel_size[0]∗kernel_size[1]∗kernel_size[2]groups 取样得到;ConvTranspose3d.bias:类型为Tensor,代表模型中可学习的偏差,shape 为 ( o u t _ c h a n n e l s ) (out{\_}channels) (out_channels)。如果参数bias=True,那么这些值是从 μ ( − k , k ) , k = g r o u p s C _ o u t ∗ k e r n e l _ s i z e [ 0 ] ∗ k e r n e l _ s i z e [ 1 ] ∗ k e r n e l _ s i z e [ 2 ] \mu(-\sqrt{k}, \sqrt{k}),{\ }k=\frac{groups}{C{\_}{out}*kernel{\_}size[0]*kernel{\_}size[1]*kernel{\_}size[2]} μ(−k,k), k=C_out∗kernel_size[0]∗kernel_size[1]∗kernel_size[2]groups 取样得到。
3.4 示例
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
conv_layers = [nn.ConvTranspose3d(16, 33, 3, stride=2), # With square kernels and equal stride
# non-square kernels and unequal stride and with padding
nn.ConvTranspose3d(16, 33, (3, 5, 2), stride=(2, 1, 1), padding=(0, 4, 2)),
# non-square kernels and unequal stride and with padding & output_padding
nn.ConvTranspose3d(16, 33, (3, 5, 2), stride=(2, 1, 1), padding=(0, 4, 2), output_padding=(1, 0, 0)),
]
input_data = torch.randn(20, 16, 10, 50, 100)
for i in range(len(conv_layers)):
output_data = conv_layers[i](input_data)
print(output_data.shape)
三、延迟卷积-Lazy Convolution
1 nn.LazyConv1d
torch.nn.LazyConv1d(out_channels, kernel_size, stride=1, padding=0, dilation=1, groups=1, bias=True, padding_mode='zeros')
LazyConv1d 本质上就是 Conv1d,只不过是使用了延迟初始化的卷积,也就是利用 input.size(1) = Conv1d的参数in_channels 进行延迟初始化。
参数:
out_channels:类型为int,表示经过延迟卷积后的输出通道数;kernel_size:类型为int、tuple of one int,控制卷积核的大小;stride:可选参数,类型为int、tuple of one int,控制卷积的步长,默认为stride=1;padding:可选参数,类型为int、tuple of one int,控制对输入两侧进行填充点的数量,默认为stride=0表示不进行填充;padding_mode:可选参数,类型为string,控制填充模式zeros-零填充, reflect-镜像填充, replicate-复制填充, circular,默认为padding_mode=zeros;dilation:可选参数,类型为int、tuple of one int,控制卷积核元素的间距,默认dilation=1就是标准卷积;groups:可选参数,类型为int,控制从输入到输出之间的连接数,该参数必须满足能够整除input_channels & output_channels,默认为groups=1;bias:可选参数,类型为bool,若bias=True,则会添加可学习的偏差参数,默认值为bias=True。
2 nn.LazyConv2d
torch.nn.LazyConv2d(out_channels, kernel_size, stride=1, padding=0, dilation=1, groups=1, bias=True, padding_mode='zeros')
LazyConv2d 是使用了延迟初始化的 Conv2d,也就是利用 input.size(1) = Conv2d 的参数 in_channels 进行延迟初始化。
参数:
out_channels:类型为int,表示经过延迟卷积后的输出通道数;kernel_size:类型为int、tuple of two ints,控制卷积核的大小;stride:可选参数,类型为int、tuple of two ints,控制卷积的步长,默认为stride=1;padding:可选参数,类型为int、tuple of two ints,控制对输入两侧进行填充点的数量,默认为stride=0表示不进行填充;padding_mode:可选参数,类型为string,控制填充模式zeros-零填充, reflect-镜像填充, replicate-复制填充, circular,默认为padding_mode=zeros;dilation:可选参数,类型为int、tuple of two ints,控制卷积核元素的间距,默认dilation=1就是标准卷积;groups:可选参数,类型为int,控制从输入到输出之间的连接数,该参数必须满足能够整除input_channels & output_channels,默认为groups=1;bias:可选参数,类型为bool,若bias=True,则会添加可学习的偏差参数,默认值为bias=True。
3 nn.LazyConv3d
torch.nn.LazyConv3d(out_channels, kernel_size, stride=1, padding=0, dilation=1, groups=1, bias=True, padding_mode='zeros')
LazyConv3d 是使用了延迟初始化的 Conv3d,即利用 input.size(1) = Conv3d 的参数 in_channels 进行延迟初始化。
参数:
out_channels:类型为int,表示经过延迟卷积后的输出通道数;kernel_size:类型为int、tuple of three ints,控制卷积核的大小;stride:可选参数,类型为int、tuple of three ints,控制卷积的步长,默认为stride=1;padding:可选参数,类型为int、tuple of three ints,控制对输入两侧进行填充点的数量,默认为stride=0表示不进行填充;padding_mode:可选参数,类型为string,控制填充模式zeros-零填充, reflect-镜像填充, replicate-复制填充, circular,默认为padding_mode=zeros;dilation:可选参数,类型为int、tuple of three ints,控制卷积核元素的间距,默认dilation=1就是标准卷积;groups:可选参数,类型为int,控制从输入到输出之间的连接数,该参数必须满足能够整除input_channels & output_channels,默认为groups=1;bias:可选参数,类型为bool,若bias=True,则会添加可学习的偏差参数,默认值为bias=True。
四、延迟转置卷积-LazyConvTransposed
1 nn.LazyConvTransposed1d
torch.nn.LazyConvTranspose1d(out_channels, kernel_size, stride=1, padding=0, output_padding=0, groups=1, bias=True, dilation=1, padding_mode='zeros')
torch.nn.LazyConvTranspose1d 本质上是使用了延迟初始化 ConvTranspose1d,利用 input.size(1) = ConvTranspose1d 的参数 in_channels 进行延迟初始化。
参数:
out_channels:类型为int,表示输出通道数;kernel_size:类型为int、tuple of one int,表示卷积核的大小;stride:可选参数,类型为int、tuple of one int,控制进行卷积的步长,默认stride=1;padding:可选参数,类型为int、tuple of one int,可对输入的两侧进行dilation * (kernel_size-1) - padding数量的零填充,默认padding=0。之所以进行固定熟练的填充点数,是为了遵循当Conv1d和ConvTranspose1d使用相同的参数初始化时,它们在输入和输出形状方面互为倒数 。output_padding:可选参数,类型为int、tuple of one int,控制添加到输出形状一侧的附加尺寸,默认为output_padding=0。padding_mode:可选参数,类型为string,控制填充模式zeros-零填充, reflect-镜像填充, replicate-复制填充, circular,默认为padding_mode=zeros;dilation:可选参数,类型为int、tuple,控制卷积核元素的间距,默认dilation=1就是标准卷积,更改该参数的话标准卷积就变成了 膨胀卷积(空洞卷积),参考 [1];groups:可选参数,类型为int,控制从输入到输出之间的连接数,该参数必须满足能够整除input_channels & output_channels,默认为groups=1;bias:可选参数,类型为bool,若bias=True,则会添加可学习的偏差参数,默认值为bias=True。
2 nn.LazyConvTransposed2d
torch.nn.LazyConvTranspose2d(out_channels, kernel_size, stride=1, padding=0, output_padding=0, groups=1, bias=True, dilation=1, padding_mode='zeros')')
LazyConvTransposed2d 是使用了延迟初始化的 ConvTransposed2d,也就是利用 input.size(1) = ConvTransposed2d 的参数 in_channels 进行延迟初始化。
参数:
out_channels:类型为int,表示输出通道数;kernel_size:类型为int、tuple of two ints,表示卷积核的大小;stride:可选参数,类型为int、tuple of two ints,控制进行卷积的步长,默认stride=1;padding:可选参数,类型为int、tuple of two ints,可对输入的两侧进行dilation * (kernel_size-1) - padding数量的零填充,默认padding=0。之所以进行固定熟练的填充点数,是为了遵循当Conv1d和ConvTranspose1d使用相同的参数初始化时,它们在输入和输出形状方面互为倒数 。output_padding:可选参数,类型为int、tuple of two ints,控制添加到输出形状一侧的附加尺寸,默认为output_padding=0。padding_mode:可选参数,类型为string,控制填充模式zeros-零填充, reflect-镜像填充, replicate-复制填充, circular,默认为padding_mode=zeros;dilation:可选参数,类型为int、tuple of two ints,控制卷积核元素的间距,默认dilation=1就是标准卷积,更改该参数的话标准卷积就变成了 膨胀卷积(空洞卷积),参考 [1];groups:可选参数,类型为int、tuple of two ints,控制从输入到输出之间的连接数,该参数必须满足能够整除input_channels & output_channels,默认为groups=1;bias:可选参数,类型为bool,若bias=True,则会添加可学习的偏差参数,默认值为bias=True。
3 nn.LazyConvTransposed3d
torch.nn.LazyConvTranspose3d(out_channels, kernel_size, stride=1, padding=0, output_padding=0, groups=1, bias=True, dilation=1, padding_mode='zeros')
LazyConvTransposed3d 是使用了延迟初始化的 ConvTransposed3d,也就是利用 input.size(1) = ConvTransposed3d 的参数 in_channels 进行延迟初始化。
参数:
out_channels:类型为int,表示输出通道数;kernel_size:类型为int、tuple of three ints,表示卷积核的大小;stride:可选参数,类型为int、tuple of three ints,控制进行卷积的步长,默认stride=1;padding:可选参数,类型为int、tuple of three ints,可对输入的两侧进行dilation * (kernel_size-1) - padding数量的零填充,默认padding=0。之所以进行固定熟练的填充点数,是为了遵循当Conv1d和ConvTranspose1d使用相同的参数初始化时,它们在输入和输出形状方面互为倒数 。output_padding:可选参数,类型为int、tuple of three ints,控制添加到输出形状一侧的附加尺寸,默认为output_padding=0。padding_mode:可选参数,类型为string,控制填充模式zeros-零填充, reflect-镜像填充, replicate-复制填充, circular,默认为padding_mode=zeros;dilation:可选参数,类型为int、tuple of two ints,控制卷积核元素的间距,默认dilation=1就是标准卷积,更改该参数的话标准卷积就变成了 膨胀卷积(空洞卷积),参考 [1];groups:可选参数,类型为int、tuple of three ints,控制从输入到输出之间的连接数,该参数必须满足能够整除input_channels & output_channels,默认为groups=1;bias:可选参数,类型为bool,若bias=True,则会添加可学习的偏差参数,默认值为bias=True。
五、其他
1 nn.Unfold
该方法 torch.nn.Unfold(kernel_size, dilation=1, padding=0, stride=1) 可以从批量输入张量中提取滑动局部块。目前没有怎么用到这块所以就先不记录了。
2 nn.Fold
与上面的方法相反的是 torch.nn.Fold(output_size, kernel_size, dilation=1, padding=0, stride=1) 可以将一组滑动局部块组合成一个大的组合张量。
六、参考
[1]. 膨胀卷积