pytorch基础知识四【索引与切片】
索引与切片
- 1. 索引
- 2. 切片
-
- 2.1 根据首项/尾项切片
- 2.2 根据步长切片
- 2.3 根据特定索引切片
- 2.4 根据掩码切片
- 2.5 根据索引返回指定索引上的数据集合
- 3. torch.ge()、torch.gt()、torch.le()、torch.lt()
-
- 3.1 torch.ge()
- 3.2 torch.gt()
- 3.3 torch.le()
- 3.4 torch.lt()
1. 索引
import torch
a = torch.rand(4,3,28,28) # 建立维度为4的张量
print(a[0].shape) # 获取第一维度的shape
print(a[0,0].shape) # 获取第二维度的shape
print(a[0,0,2,4]) # 打印某个元素
执行结果:
torch.Size([3, 28, 28])
torch.Size([28, 28])
tensor(0.8019)
2. 切片
2.1 根据首项/尾项切片
import torch
a = torch.rand(4,3,28,28) # 建立维度为4的张量
print(a.shape)
print(a[:2].shape)
print(a[:2,:1,:,:].shape)
print(a[:2,1:,:,:].shape)
print(a[:2,-1:,:,:].shape)
print(a[:2,:-1,:,:].shape)
执行结果:
torch.Size([4, 3, 28, 28])
torch.Size([2, 3, 28, 28])
torch.Size([2, 1, 28, 28])
torch.Size([2, 2, 28, 28])
torch.Size([2, 1, 28, 28])
torch.Size([2, 2, 28, 28])
2.2 根据步长切片
import torch
a = torch.rand(4,3,28,28)
print(a[:,:,0:28:2,0:28:2].shape)
print(a[:,:,::2,::2].shape)
print(a[:,:,::5,::5].shape)
执行结果:
torch.Size([4, 3, 14, 14])
torch.Size([4, 3, 14, 14])
torch.Size([4, 3, 6, 6])
2.3 根据特定索引切片
import torch
a = torch.rand(4,3,28,28)
# index_select(dim,index)中的dim代表张量的某个维度,以a为例
# 0 -> 4
# 1 -> 3
# 2 -> 28
# 3 -> 28
# index代表索引,表示取第index个元素
print(a.index_select(0,torch.tensor([0,2])).shape)
print(a.index_select(1,torch.tensor([0,1,2])).shape)
print(a.index_select(2,torch.tensor([0,2,3,4,5])).shape)
print(a.index_select(3,torch.tensor([0,1,2,3,4,5,6])).shape)
# ...表示索引全部取到
print(a[0,...].shape)
print(a[:,1,...].shape)
print(a[...,:2].shape)
执行结果:
torch.Size([2, 3, 28, 28])
torch.Size([4, 3, 28, 28])
torch.Size([4, 3, 5, 28])
torch.Size([4, 3, 28, 7])
torch.Size([3, 28, 28])
torch.Size([4, 28, 28])
torch.Size([4, 3, 28, 2])
2.4 根据掩码切片
x = torch.randn(3,4)
print(x)
mask = x.ge(0.5) # 大于0.5的赋为True,反之为False
print(mask)
print(torch.masked_select(x,mask)) # 输出mask为True的元素
print(torch.masked_select(x,mask).shape)
执行结果:
tensor([[ 0.9910, -1.2207, -0.3169, 2.3048],
[-0.3671, -0.8469, -0.6350, 0.2997],
[-0.6556, 1.1191, 0.5445, -0.5113]])
tensor([[ True, False, False, True],
[False, False, False, False],
[False, True, True, False]])
tensor([0.9910, 2.3048, 1.1191, 0.5445])
torch.Size([4])
2.5 根据索引返回指定索引上的数据集合
src = torch.tensor([[4,3,5],[6,7,8]])
print(src)
print(torch.take(src,torch.tensor([0,2,5])))
执行结果:
tensor([[4, 3, 5],
[6, 7, 8]])
tensor([4, 5, 8])
3. torch.ge()、torch.gt()、torch.le()、torch.lt()
3.1 torch.ge()
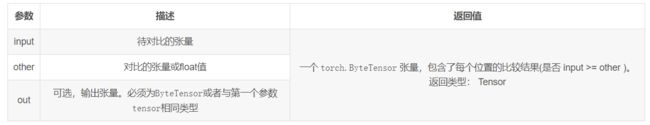
(1)逐元素比较input和other,即是否 ( input >= other )。
(2)如果两个张量有相同的形状和元素值,则返回True ,否则 False。 第二个参数可以为一个数或与第一个参数相同形状和类型的张量。
torch.ge(input, other, out=None) → Tensor
print(torch.ge(torch.Tensor([[1, 2], [3, 4]]), torch.Tensor([[1, 1], [4, 4]])))
执行结果:
tensor([[ True, True],
[False, True]])
3.2 torch.gt()
(1)逐元素比较input和other , 即是否( input > other ) 如果两个张量有相同的形状和元素值,则返回True ,否则 False。
(2)第二个参数可以为一个数或与第一个参数相同形状和类型的张量。
torch.gt(input, other, out=None) → Tensor
print(torch.gt(torch.Tensor([[1, 2], [3, 4]]), torch.Tensor([[1, 1], [4, 4]])))
执行结果:
tensor([[False, True],
[False, False]])
3.3 torch.le()
逐元素比较input和other , 即是否input<=other 第二个参数可以为一个数或与第一个参数相同形状和类型的张量。
print(torch.le(torch.Tensor([[1, 2], [3, 4]]), torch.Tensor([[1, 1], [4, 4]])))
执行结果:
tensor([[ True, False],
[ True, True]])
3.4 torch.lt()
逐元素比较input和other , 即是否 inputprint(torch.lt(torch.Tensor([[1, 2], [3, 4]]), torch.Tensor([[1, 1], [4, 4]])))
执行结果:
tensor([[False, False],
[ True, False]])