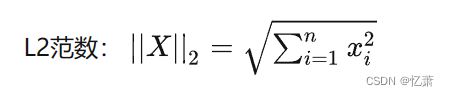李沐深度学习-04.03权重衰减
1.解释范数
范数分很多种,但是目前深度学习中常用到的就是L1范数和L2范数
L1范数:即为

几何意义就是所有元素绝对值之和,在停车场问题中,即为从初始点到终点的最短距离。
一般用在提高模型的稀疏性。
2.权重衰减
权重衰减是广泛使用的正则化方法之一,技术是通过函数与零的距离来衡量函数的复杂度;
做权重衰减的意义是为了让模型参数都偏小,因为这样可以让模型变的简单。
公式为 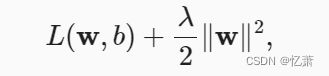
λ 是使用L2范数约束损失函数的强烈程度 λ=0时,为禁用权重衰减;λ较小时,对于w的约束就较小,λ越大,则对w的约束就越大。
当λ太大时,train_loss和 test_loss都会比较大;
当λ较小时,train_loss会很小,但是test_loss会很大。
 |
 |
|---|
2.从零开始代码实现
%matplotlib inline
import torch
from torch import nn
from d2l import torch as d2l
n_train, n_test, num_inputs, batch_size = 20, 100, 200, 5 #维度是200,此处200是为了更容易过拟合,从而使效果更明显
true_w, true_b = torch.ones((num_inputs, 1)) * 0.01, 0.05
train_data = d2l.synthetic_data(true_w, true_b, n_train)
train_iter = d2l.load_array(train_data, batch_size)
test_data = d2l.synthetic_data(true_w, true_b, n_test)
test_iter = d2l.load_array(test_data, batch_size, is_train=False)
#初始化模型参数
def init_params():
w = torch.normal(0, 1, size=(num_inputs, 1), requires_grad=True)
b = torch.zeros(1, requires_grad=True)
return [w, b]
#定义L2范数 为平方和,除以2是为了求导美观
def l2_penalty(w):
return torch.sum(w.pow(2)) / 2
#训练函数
def train(lambd):
w, b = init_params()
# lambda是赋予函数 例如 add = lambda x,y:x+y 意思就是定义add(x,y)函数,为x+y
net, loss = lambda X: d2l.linreg(X, w, b), d2l.squared_loss #均方差损失
num_epochs, lr = 100, 0.003
#画图
animator = d2l.Animator(xlabel='epochs', ylabel='loss', yscale='log',
xlim=[5, num_epochs], legend=['train', 'test'])
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
for X, y in train_iter:
# 增加了L2范数惩罚项,
# 广播机制使l2_penalty(w)成为一个长度为batch_size的向量
l = loss(net(X), y) + lambd * l2_penalty(w)
l.sum().backward()
d2l.sgd([w, b], lr, batch_size) # 优化参数
if (epoch + 1) % 5 == 0:
animator.add(epoch + 1, (d2l.evaluate_loss(net, train_iter, loss),
d2l.evaluate_loss(net, test_iter, loss)))
print('w的L2范数是:', torch.norm(w).item())
train(lambd=0)
train(lambd=3)
3.简洁代码实现
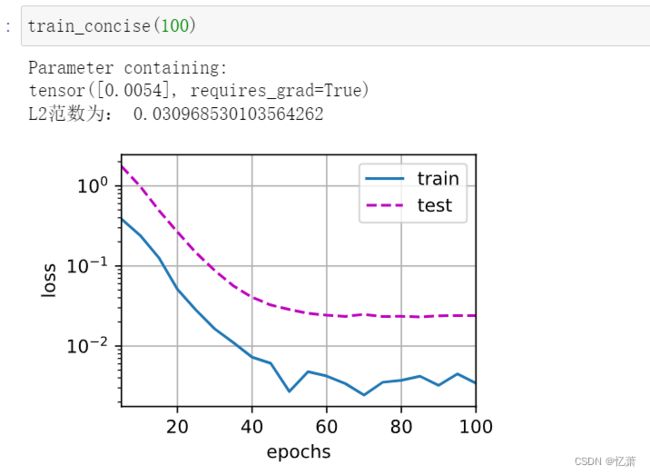
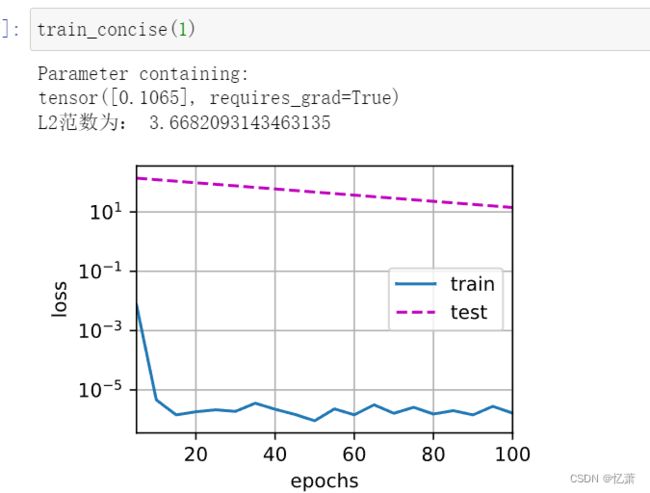
def train_concise(wd):
net = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(num_inputs, 1)) # 定义模型
for param in net.parameters():#初始化参数
param.data.normal_()
loss = nn.MSELoss(reduction='none')#损失函数
num_epochs, lr = 100, 0.003
# 偏置参数没有衰减
trainer = torch.optim.SGD([
{"params":net[0].weight,'weight_decay': wd},
{"params":net[0].bias}], lr=lr)
animator = d2l.Animator(xlabel='epochs', ylabel='loss', yscale='log',
xlim=[5, num_epochs], legend=['train', 'test'])
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
for X, y in train_iter:
trainer.zero_grad()
l = loss(net(X), y)
l.mean().backward()#此处mean和sum意义不一样
trainer.step()
if (epoch + 1) % 5 == 0:
animator.add(epoch + 1,
(d2l.evaluate_loss(net, train_iter, loss),
d2l.evaluate_loss(net, test_iter, loss)))
print('w的L2范数:', net[0].weight.norm().item())