【Spring】Spring ioc源码学习以及关于阅读源码方式的一些小笔记
Spring ioc源码学习以及关于阅读源码方式的一些小笔记
学习源码的方式
最好的方法是带着问题去学习。
如果拿到的是一个新的框架源码,首先应当去搞懂如何使用,这个框架能做什么事。接下来可以采取两种方式:
第一种:
- 第一步了解它的核心概念有哪些,确定你要学习的目标
- 由整体到局部的分析,先拆分目标,这个框架为了达到这个效果做了哪些步骤
- 找到每个步骤对应的入口,先理清楚主干流程,再详细看具体细节
- 理清楚之后针对其可扩展的部分,自己编写一些代码去验证是否能实现(多折腾)
第二种:
- 第一步了解它的核心概念有哪些,确定你要学习的目标
- 自己动手去实现
- 自己实现完之后再对比框架源码,思考为什么源码此处要这么写
由于本人自认为水平欠佳,在阅读过程中采取的是第一种方式。
做了些什么
ioc容器最核心的功能就是帮助用户管理bean,把用户自己创建的模式改成由容器创建的模式,所以至少需要两个步骤:创建bean和获取bean。
实现的步骤
主要有如下几个步骤:
- 用户配置bean定义
- 容器读取用户配置的bean定义
- 容器创建bean定义
- 用户从容器中读取bean
首先找到加载的入口,此处以xml配置方式为例,注解方式后续补充:
xml配置方式的入口为:ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("lalala.xml");
把握整体
ApplicationContext是Spring中的高级容器,它内嵌了一个BeanFactory, ClassPathXmlApplicationContext也是ApplicaitonContext的实现类。下面是ApplicationContext的类图。
这里采用了设计模式中的装饰模式(有疑问,算装饰模式吗):
public interface ApplicationContext extends EnvironmentCapable, ListableBeanFactory, HierarchicalBeanFactory, MessageSource, ApplicationEventPublisher, ResourcePatternResolver {
@Nullable
String getId();
String getApplicationName();
String getDisplayName();
long getStartupDate();
@Nullable
ApplicationContext getParent();
AutowireCapableBeanFactory getAutowireCapableBeanFactory() throws IllegalStateException;
}
可以看到ApplicationContext 继承的功能有:
EnvironmentCapable: 获取环境相关变量ListableBeanFactory: 提供BeanFactory容器HierarchicalBeanFactory: 提供父子容器相关的内容MessageSource: 提供国际化的内容ApplicationEventPublisher: 提供事件发布机制ResourcePatternResolver: 提供资源解析器
具体实现
第一次读源码的时候首先要找准一个你熟悉的过程,debug打断点,获取到它的调用栈并截图保存。 需要关注的重点是入参在这些方法中是如何变化的,从而知道每一个类是干什么用的。
接下来再将步骤拆分的细一点:
- 读取用户配置的xml文件
- 将xml树解析为
beanDefinition - 创建
beanFactory - 将
beanDefinition注册到beanFactory
首先我们观察到启动时候的入参只有一个xml文件的地址:
/**
* xml文件配置方式
*/
private static void testClassPathXmlApplicationContext() {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("lalala.xml");
for (String beanName : context.getBeanDefinitionNames()) {
System.out.println(beanName);
}
System.out.println(context.getBean(Bean2.class).getBean1());
}
那第一步就要先将这个xml文件配置的内容解析成beanDefinition。上面提到过ResourcePatternResolver 是用来解析资源的,点开ClassPathXmlApplicationContext的类图,找到上层哪个类持有这个解析器->AbstractApplicationContext。

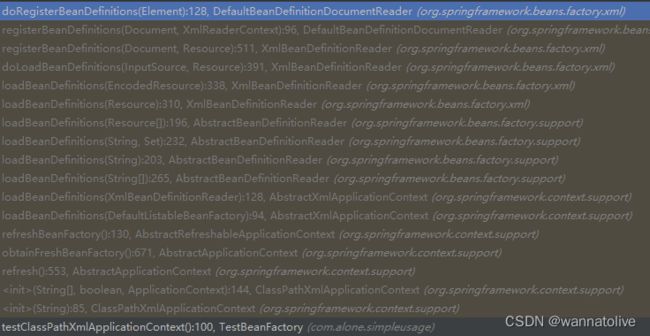
然后定位到对应的方法,再一步一步往下跟踪,能够得到如下的调用栈:
- 在
org.springframework.context.support.AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext#refreshBeanFactory()方法中新建了一个BeanFactory.
它的默认类型是DefaultListableBeanFactory。

- 在
org.springframework.context.support.AbstractXmlApplicationContext#loadBeanDefinitions(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory)中新建了一个XmlBeanDefinitionReader,容器在此处将xml文件的解析过程委托给了这个XmlBeanDefinitionReader进行下一步的解析:
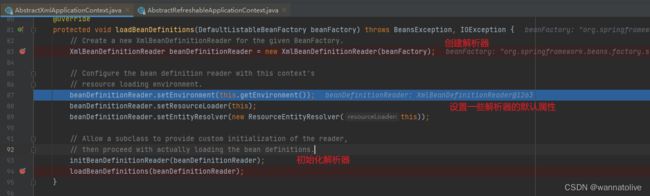
3. 在org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanDefinitionReader 中读取xml的内容并将其转换为Resource 对象。对于多个配置文件是进行循环读取。

- 在
org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanDefinitionReader中有一处转换是将Resource转化为EncodedResource
@Override
public int loadBeanDefinitions(Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
return loadBeanDefinitions(new EncodedResource(resource));
}
- 在
org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanDefinitionReader中开始进行注册beanDefinition的行为
protected int doLoadBeanDefinitions(InputSource inputSource, Resource resource)
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
try {
Document doc = doLoadDocument(inputSource, resource);
int count = registerBeanDefinitions(doc, resource);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Loaded " + count + " bean definitions from " + resource);
}
return count;
}
catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) {
throw ex;
}
catch (SAXParseException ex) {
throw new XmlBeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"Line " + ex.getLineNumber() + " in XML document from " + resource + " is invalid", ex);
}
catch (SAXException ex) {
throw new XmlBeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"XML document from " + resource + " is invalid", ex);
}
catch (ParserConfigurationException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"Parser configuration exception parsing XML from " + resource, ex);
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"IOException parsing XML document from " + resource, ex);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"Unexpected exception parsing XML document from " + resource, ex);
}
}
注册BeanDefinition的行为实际是被委托给了BeanDefinitionDocumentReader 去完成。
- 在
org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader中进行实际的BeanDefinition注册过程。
protected void doRegisterBeanDefinitions(Element root) {
BeanDefinitionParserDelegate parent = this.delegate;
// 处理嵌套的标签
this.delegate = createDelegate(getReaderContext(), root, parent);
// 判断是否是默认命名空间 http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
if (this.delegate.isDefaultNamespace(root)) {
// 判断运行的环境 profile属性
String profileSpec = root.getAttribute(PROFILE_ATTRIBUTE);
if (StringUtils.hasText(profileSpec)) {
String[] specifiedProfiles = StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(
profileSpec, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate.MULTI_VALUE_ATTRIBUTE_DELIMITERS);
if (!getReaderContext().getEnvironment().acceptsProfiles(specifiedProfiles)) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Skipped XML bean definition file due to specified profiles [" + profileSpec +
"] not matching: " + getReaderContext().getResource());
}
return;
}
}
}
// xml的前置处理
preProcessXml(root);
// 处理BeanDefinition
parseBeanDefinitions(root, this.delegate);
// xml的后置处理
postProcessXml(root);
this.delegate = parent;
}
进入parseBeanDefinitions方法:
protected void parseBeanDefinitions(Element root, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) {
if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(root)) {
// 遍历默认命名空间下的每一个节点
NodeList nl = root.getChildNodes();
for (int i = 0; i < nl.getLength(); i++) {
Node node = nl.item(i);
if (node instanceof Element) {
Element ele = (Element) node;
// 是否是默认空间下的
if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(ele)) {
// 处理默认元素 import alias bean beans
parseDefaultElement(ele, delegate);
}
else {
delegate.parseCustomElement(ele);
}
}
}
}
else {
delegate.parseCustomElement(root);
}
}
下面来看看它怎么解析bean标签的:
protected void processBeanDefinition(Element ele, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) {
BeanDefinitionHolder bdHolder = delegate.parseBeanDefinitionElement(ele);
if (bdHolder != null) {
bdHolder = delegate.decorateBeanDefinitionIfRequired(ele, bdHolder);
try {
BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.registerBeanDefinition(bdHolder, getReaderContext().getRegistry());
}
catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) {
getReaderContext().error("Failed to register bean definition with name '" +
bdHolder.getBeanName() + "'", ele, ex);
}
getReaderContext().fireComponentRegistered(new BeanComponentDefinition(bdHolder));
}
}
public BeanDefinitionHolder parseBeanDefinitionElement(Element ele, @Nullable BeanDefinition containingBean) {
// 获取id属性的值
String id = ele.getAttribute(ID_ATTRIBUTE);
// 获取name属性的值
String nameAttr = ele.getAttribute(NAME_ATTRIBUTE);
// 获取别名
List<String> aliases = new ArrayList<>();
if (StringUtils.hasLength(nameAttr)) {
String[] nameArr = StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(nameAttr, MULTI_VALUE_ATTRIBUTE_DELIMITERS);
aliases.addAll(Arrays.asList(nameArr));
}
String beanName = id;
if (!StringUtils.hasText(beanName) && !aliases.isEmpty()) {
beanName = aliases.remove(0);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No XML 'id' specified - using '" + beanName +
"' as bean name and " + aliases + " as aliases");
}
}
// 校验名称的唯一性
if (containingBean == null) {
checkNameUniqueness(beanName, aliases, ele);
}
AbstractBeanDefinition beanDefinition = parseBeanDefinitionElement(ele, beanName, containingBean);
if (beanDefinition != null) {
if (!StringUtils.hasText(beanName)) {
try {
if (containingBean != null) {
beanName = BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.generateBeanName(
beanDefinition, this.readerContext.getRegistry(), true);
}
else {
beanName = this.readerContext.generateBeanName(beanDefinition);
String beanClassName = beanDefinition.getBeanClassName();
if (beanClassName != null &&
beanName.startsWith(beanClassName) && beanName.length() > beanClassName.length() &&
!this.readerContext.getRegistry().isBeanNameInUse(beanClassName)) {
aliases.add(beanClassName);
}
}
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Neither XML 'id' nor 'name' specified - " +
"using generated bean name [" + beanName + "]");
}
}
catch (Exception ex) {
error(ex.getMessage(), ele);
return null;
}
}
String[] aliasesArray = StringUtils.toStringArray(aliases);
return new BeanDefinitionHolder(beanDefinition, beanName, aliasesArray);
}
return null;
}
@Nullable
public AbstractBeanDefinition parseBeanDefinitionElement(
Element ele, String beanName, @Nullable BeanDefinition containingBean) {
this.parseState.push(new BeanEntry(beanName));
String className = null;
// 获取class属性的值
if (ele.hasAttribute(CLASS_ATTRIBUTE)) {
className = ele.getAttribute(CLASS_ATTRIBUTE).trim();
}
String parent = null;
// 获取parent属性的值
if (ele.hasAttribute(PARENT_ATTRIBUTE)) {
parent = ele.getAttribute(PARENT_ATTRIBUTE);
}
try {
// 创建beanDefinition 默认的beanDefinition类型是GenericBeanDefinition
AbstractBeanDefinition bd = createBeanDefinition(className, parent);
// 解析scope abstract lazy-init(默认为false) autowire depends-on autowire-candidate primary init-method destory-method factory-method factory-bean 属性 这里有部分属性会在populateDefaults中设置一遍
parseBeanDefinitionAttributes(ele, beanName, containingBean, bd);
bd.setDescription(DomUtils.getChildElementValueByTagName(ele, DESCRIPTION_ELEMENT));
// 解析meta标签
parseMetaElements(ele, bd);
// 解析lookup-method
parseLookupOverrideSubElements(ele, bd.getMethodOverrides());
// 解析replaced-method
parseReplacedMethodSubElements(ele, bd.getMethodOverrides());
// 解析constructor-arg
parseConstructorArgElements(ele, bd);
// 解析property
parsePropertyElements(ele, bd);
// 解析qualifier
parseQualifierElements(ele, bd);
bd.setResource(this.readerContext.getResource());
bd.setSource(extractSource(ele));
return bd;
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
error("Bean class [" + className + "] not found", ele, ex);
}
catch (NoClassDefFoundError err) {
error("Class that bean class [" + className + "] depends on not found", ele, err);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
error("Unexpected failure during bean definition parsing", ele, ex);
}
finally {
this.parseState.pop();
}
return null;
}
在org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.BeanDefinitionParserDelegate.populateDefaults方法中会先处理如下属性内容:
protected void populateDefaults(DocumentDefaultsDefinition defaults, @Nullable DocumentDefaultsDefinition parentDefaults, Element root) {
String lazyInit = root.getAttribute(DEFAULT_LAZY_INIT_ATTRIBUTE);
if (isDefaultValue(lazyInit)) {
lazyInit = (parentDefaults != null ? parentDefaults.getLazyInit() : FALSE_VALUE);
}
defaults.setLazyInit(lazyInit);
String merge = root.getAttribute(DEFAULT_MERGE_ATTRIBUTE);
if (isDefaultValue(merge)) {
merge = (parentDefaults != null ? parentDefaults.getMerge() : FALSE_VALUE);
}
defaults.setMerge(merge);
String autowire = root.getAttribute(DEFAULT_AUTOWIRE_ATTRIBUTE);
if (isDefaultValue(autowire)) {
autowire = (parentDefaults != null ? parentDefaults.getAutowire() : AUTOWIRE_NO_VALUE);
}
defaults.setAutowire(autowire);
if (root.hasAttribute(DEFAULT_AUTOWIRE_CANDIDATES_ATTRIBUTE)) {
defaults.setAutowireCandidates(root.getAttribute(DEFAULT_AUTOWIRE_CANDIDATES_ATTRIBUTE));
}
else if (parentDefaults != null) {
defaults.setAutowireCandidates(parentDefaults.getAutowireCandidates());
}
if (root.hasAttribute(DEFAULT_INIT_METHOD_ATTRIBUTE)) {
defaults.setInitMethod(root.getAttribute(DEFAULT_INIT_METHOD_ATTRIBUTE));
}
else if (parentDefaults != null) {
defaults.setInitMethod(parentDefaults.getInitMethod());
}
if (root.hasAttribute(DEFAULT_DESTROY_METHOD_ATTRIBUTE)) {
defaults.setDestroyMethod(root.getAttribute(DEFAULT_DESTROY_METHOD_ATTRIBUTE));
}
else if (parentDefaults != null) {
defaults.setDestroyMethod(parentDefaults.getDestroyMethod());
}
defaults.setSource(this.readerContext.extractSource(root));
}
补充一部分:
上面的parseBeanDefinitionElement 有这么两行
// 解析constructor-arg标签
parseConstructorArgElements(ele, bd);
// 解析property标签
parsePropertyElements(ele, bd);
这两个方法再继续往下调用会进入parsePropertyValue(Element ele, BeanDefinition bd, @Nullable String propertyName)方法
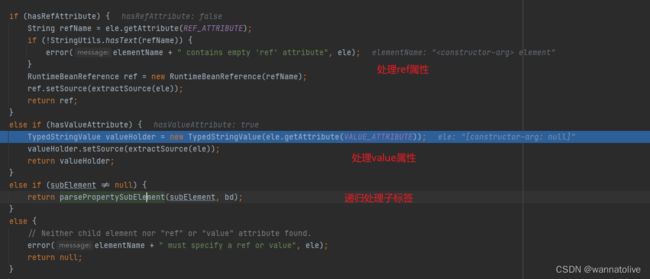
在此处这两类标签ref属性里的值会被初始化成为RuntimeBeanReference对象,value属性里的值会被初始化为TypedStringValue对象,如果里面还有子标签,则递归处理。
然后把处理好的
处理好的
接下来回到: BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.registerBeanDefinition 方法,它内层是这样的:
public void registerBeanDefinition(String beanName, BeanDefinition beanDefinition)
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
Assert.hasText(beanName, "Bean name must not be empty");
Assert.notNull(beanDefinition, "BeanDefinition must not be null");
if (beanDefinition instanceof AbstractBeanDefinition) {
try {
// 验证beanDefinition的完整性
((AbstractBeanDefinition) beanDefinition).validate();
}
catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(beanDefinition.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Validation of bean definition failed", ex);
}
}
BeanDefinition existingDefinition = this.beanDefinitionMap.get(beanName);
// 判断容器中是否已经存在当前beanDefinition
if (existingDefinition != null) {
if (!isAllowBeanDefinitionOverriding()) {
throw new BeanDefinitionOverrideException(beanName, beanDefinition, existingDefinition);
}
else if (existingDefinition.getRole() < beanDefinition.getRole()) {
}
else if (!beanDefinition.equals(existingDefinition)) {
}
else {
}
this.beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition);
}
else {
if (hasBeanCreationStarted()) {
synchronized (this.beanDefinitionMap) {
this.beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition);
List<String> updatedDefinitions = new ArrayList<>(this.beanDefinitionNames.size() + 1);
updatedDefinitions.addAll(this.beanDefinitionNames);
updatedDefinitions.add(beanName);
this.beanDefinitionNames = updatedDefinitions;
removeManualSingletonName(beanName);
}
}
else {
this.beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition);
this.beanDefinitionNames.add(beanName);
removeManualSingletonName(beanName);
}
this.frozenBeanDefinitionNames = null;
}
if (existingDefinition != null || containsSingleton(beanName)) {
resetBeanDefinition(beanName);
}
else if (isConfigurationFrozen()) {
clearByTypeCache();
}
}
从此看出ioc容器中的BeanDefinition都存放在beanDefinitionMap中。
此时beanDefinition已经加载完成。
ps: 嵌套bean标签注入的用法:
如果某个Bean所依赖的Bean不想被Spring容器直接访问,可以使用嵌套Bean。
<beans xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.2.xsd"
>
<bean id="chinese" class="DependencyInjection.Chinese">
<property name="axe">
<bean class="DependencyInjection.StoneAxe"/>
property>
bean>
beans>
时序图如下:
遗留的问题
- EncodedResource 的作用?
- BeanDefinitionHolder 的作用?
- 解析自定义标签的时候,readContext里面的内容是从哪里来的?
public BeanDefinition parseCustomElement(Element ele, @Nullable BeanDefinition containingBd) {
String namespaceUri = getNamespaceURI(ele);
if (namespaceUri == null) {
return null;
}
// 这里
NamespaceHandler handler = this.readerContext.getNamespaceHandlerResolver().resolve(namespaceUri);
if (handler == null) {
error("Unable to locate Spring NamespaceHandler for XML schema namespace [" + namespaceUri + "]", ele);
return null;
}
return handler.parse(ele, new ParserContext(this.readerContext, this, containingBd));
}
参考资料
1.小不点啊的spring源码阅读系列文
2.注入嵌套bean的用法