这款国产化大模型应用开发平台太好用了!
本文首发于博客LLM 应用开发实践
最近看到的一个开源的提示词编排平台bisheng,音同「毕昇」,项目介绍说 「“毕昇”是活字印刷术的发明人,活字印刷术为人类知识的传递起到了巨大的推动作用。我们希望“毕昇”同样能够为智能应用的广泛落地提供有力的支撑」。看了下团队团队前身为国内人工智能独角兽企业第四范式的智能文档产品事业部,后根据发展需要进行业务独立拆分与运营,专注于非结构化数据的价值挖掘、信息处理自动化与数据即服务,第四范式在 AI 行业深耕多年,我比较期待能在这个项目里看到一些企业落地实践,所以阅读了毕昇平台的源码,写篇文章分享下。
项目演示里可以看到一些很不错的演示案例,比较贴合实际需求:
- 合同审核报告生成
- 信贷调查报告生成
- 招股书分析报告生成
- 智能投顾报告生成
- 等等
技能模块源码
技能创建
这部分比较简单,就是序列化后入库
@router.post('/', response_model=FlowRead, status_code=201)
def create_flow(*, session: Session = Depends(get_session), flow: FlowCreate, Authorize: AuthJWT = Depends()):
"""Create a new flow."""
Authorize.jwt_required()
payload = json.loads(Authorize.get_jwt_subject())
flow.user_id = payload.get('user_id')
db_flow = Flow.from_orm(flow)
session.add(db_flow)
session.commit()
session.refresh(db_flow)
return db_flow
技能上线
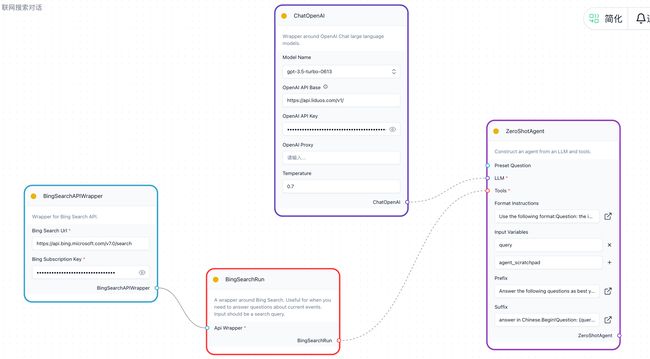
技能上线时会触发编译动作,下面是一个具体步骤,以联网搜索技能为例:
- 权限和状态校验,进入
build_flow_no_yield开始编译(注:编译实际上就是将参数传入相应节点后进行验证节点是否正常,比如向量数据库连通性,搜索工具连通性,大模型端点是否可达)
@router.patch('/{flow_id}', response_model=FlowRead, status_code=200)
def update_flow(*,
session: Session = Depends(get_session),
flow_id: UUID,
flow: FlowUpdate,
Authorize: AuthJWT = Depends()):
...
db_flow = session.get(Flow, flow_id)
if not db_flow:
raise HTTPException(status_code=404, detail='Flow not found')
if 'admin' != payload.get('role') and db_flow.user_id != payload.get('user_id'):
raise HTTPException(status_code=500, detail='没有权限编辑此技能')
flow_data = flow.dict(exclude_unset=True)
if 'status' in flow_data and flow_data['status'] == 2 and db_flow.status == 1:
# 上线校验
try:
art = {}
build_flow_no_yield(graph_data=db_flow.data, artifacts=art, process_file=False)
except Exception as exc:
raise HTTPException(status_code=500, detail='Flow 编译不通过') from exc
...
return db_flow
- 遍历技能模板的节点(根结点默认在节点列表第一个,序号为 0),进行编译。
vertex.artifacts用作提示词变量,这些变量将传递给build_input_keys_response函数以设置输入键值;向量数据库节点未配置集合名称时需要自动生成。
def build_flow_no_yield(graph_data: dict,
artifacts,
process_file=False,
flow_id=None,
chat_id=None):
try:
graph = Graph.from_payload(graph_data)
except Exception as exc:
logger.exception(exc)
raise exc
for i, vertex in enumerate(graph.generator_build(), 1):
try:
if vertex.base_type == 'vectorstores':
if 'collection_name' in vertex.params and not vertex.params.get('collection_name'):
vertex.params['collection_name'] = f'tmp_{flow_id}_{chat_id}'
logger.info(f"rename_vector_col col={vertex.params['collection_name']}")
vertex.build()
params = vertex._built_object_repr()
if vertex.artifacts:
artifacts.update(vertex.artifacts)
except Exception as exc:
raise exc
return graph
-
所有的节点都继承自
Vertex对象,但是只有部分节点实现了自己的build方法,编译过程实际上就是逐次执行节点的build方法class ToolVertex(Vertex) class ToolkitVertex(Vertex) class FileToolVertex(ToolVertex) class OutputParserVertex(Vertex) class DocumentLoaderVertex(Vertex) class EmbeddingVertex(Vertex) class VectorStoreVertex(Vertex) class MemoryVertex(Vertex) class RetrieverVertex(Vertex) class TextSplitterVertex(Vertex) # Agent 节点 class AgentVertex(Vertex): ... def build(self, force: bool = False) -> Any: if not self._built or force: self._set_tools_and_chains() for tool_node in self.tools: tool_node.build() for chain_node in self.chains: chain_node.build(tools=self.tools) self._build() return self._built_object # 大模型节点 class LLMVertex(Vertex): ... def build(self, force: bool = False) -> Any: # 因为有些模型可能会占用太多内存,选择懒加载(只在需要的时候加载它们) if self.vertex_type == self.built_node_type: return self.class_built_object if not self._built or force: self._build() self.built_node_type = self.vertex_type self.class_built_object = self._built_object # 避免直接复制从文件中加载的 LLM return self._built_object # 通用工具节点 class WrapperVertex(Vertex): ... def build(self, force: bool = False) -> Any: # 主要处理 header 参数,比如这里联网搜索的例子中 bing_subscription_key 字段。 if not self._built or force: if 'headers' in self.params: self.params['headers'] = ast.literal_eval(self.params['headers']) self._build() return self._built_object # 链节点 class ChainVertex(Vertex): ... def build( self, force: bool = False, tools: Optional[List[Union[ToolkitVertex, ToolVertex]]] = None, ) -> Any: if not self._built or force: for key, value in self.params.items(): if isinstance(value, PromptVertex): # 构建PromptVertex,如果有工具则传递 self.params[key] = value.build(tools=tools, force=force) self._build() return self._built_object # 提示词编辑节点 class PromptVertex(Vertex): ... def build( self, force: bool = False, tools: Optional[List[Union[ToolkitVertex, ToolVertex]]] = None, ) -> Any: if not self._built or force: if ( 'input_variables' not in self.params or self.params['input_variables'] is None ): self.params['input_variables'] = [] # 检查是否为ZeroShotPrompt并需要工具 if 'ShotPrompt' in self.vertex_type: tools = ( [tool_node.build() for tool_node in tools] if tools is not None else [] ) # 展开工具嵌套列表 if tools and isinstance(tools, list) and isinstance(tools[0], list): tools = flatten_list(tools) self.params['tools'] = tools prompt_params = [ key for key, value in self.params.items() if isinstance(value, str) and key != 'format_instructions' ] else: prompt_params = ['template'] if 'prompt' not in self.params and 'messages' not in self.params: for param in prompt_params: prompt_text = self.params[param] variables = extract_input_variables_from_prompt(prompt_text) self.params['input_variables'].extend(variables) self.params['input_variables'] = list( set(self.params['input_variables']) ) else: self.params.pop('input_variables', None) self._build() return self._built_object def _built_object_repr(self): if ( not self.artifacts or self._built_object is None or not hasattr(self._built_object, 'format') ): return super()._built_object_repr() # 构建提示,以向用户展示带有填充变量的提示内容 artifacts = self.artifacts.copy() artifacts.pop('handle_keys', None) try: template = self._built_object.format(**artifacts) return ( template if isinstance(template, str) else f'{self.vertex_type}({template})' ) except KeyError: return str(self._built_object) -
以上即为技能模板首次创建时,各个节点的编译过程。
应用(新建会话)模块源码
应用创建
对话聊天接口采用websocket协议,应用创建应用时会关联一个技能模板,会判断技能是否存在,上线状态以及是否编译成功。
@router.websocket('/chat/{client_id}')
async def chat(client_id: str,
websocket: WebSocket,
chat_id: Optional[str] = None,
type: Optional[str] = None,
Authorize: AuthJWT = Depends()):
...
if type and type == 'L1':
with next(get_session()) as session:
db_flow = session.get(Flow, client_id)
if not db_flow:
await websocket.accept()
message = '该技能已被删除'
await websocket.close(code=status.WS_1008_POLICY_VIOLATION, reason=message)
if db_flow.status != 2:
await websocket.accept()
message = '当前技能未上线,无法直接对话'
await websocket.close(code=status.WS_1008_POLICY_VIOLATION, reason=message)
graph_data = db_flow.data
else:
flow_data_key = 'flow_data_' + client_id
if str(flow_data_store.hget(flow_data_key, 'status'), 'utf-8') != BuildStatus.SUCCESS.value:
await websocket.accept()
message = '当前编译没通过'
await websocket.close(code=status.WS_1013_TRY_AGAIN_LATER, reason=message)
graph_data = json.loads(flow_data_store.hget(flow_data_key, 'graph_data'))
try:
graph = build_flow_no_yield(graph_data=graph_data,
artifacts={},
process_file=False,
flow_id=UUID(client_id).hex,
chat_id=chat_id)
langchain_object = graph.build()
for node in langchain_object:
key_node = get_cache_key(client_id, chat_id, node.id)
chat_manager.set_cache(key_node, node._built_object)
chat_manager.set_cache(get_cache_key(client_id, chat_id), node._built_object)
await chat_manager.handle_websocket(client_id, chat_id, websocket, user_id)
except WebSocketException as exc:
logger.error(exc)
await websocket.close(code=status.WS_1011_INTERNAL_ERROR, reason=str(exc))
except Exception as e:
logger.error(str(e))
技能编译
可以看到,执行build_flow_no_yield子节点的编译后,最后会通过langchain_object = graph.build()对技能模板整体进行编译,最后返回一个 Chain 对象,其实就和 langchain 里的 Chain 对象概念一样(比较讨巧的做法,Chain 的执行可以直接使用 langchain 的逻辑,不用再二次开发),感兴趣的可以读这篇文章,这里不再赘述。
class Graph:
...
def build(self) -> Chain:
# 获取跟节点
root_node = payload.get_root_node(self)
if root_node is None:
raise ValueError('No root node found')
[node.build() for node in root_node]
return root_node
最后将编译后的结果写入缓存,后续对话读入技能模板内容都是从缓存读取,不需要每次全量编译。
消息处理
消息处理环节,文字消息的处理时使用输入节点 InputNode,填充内容后,重新编译生成 Chain;文件消息的处理时输入节点 InputFileNode,将文件上传,嵌入后,重新编译生成 Chain,这个技能执行过程其实就是 langchian 的 Chains 执行过程,可以看相关代码解读,也可看我历史文章。
async def handle_websocket(self, client_id: str, chat_id: str, websocket: WebSocket,
user_id: int):
await self.connect(client_id, chat_id, websocket)
try:
chat_history = self.chat_history.get_history(client_id, chat_id)
# iterate and make BaseModel into dict
chat_history = [chat.dict() for chat in chat_history]
await websocket.send_json(chat_history)
while True:
json_payload = await websocket.receive_json()
try:
payload = json.loads(json_payload)
except TypeError:
payload = json_payload
if 'clear_history' in payload:
self.chat_history.history[client_id] = []
continue
if 'clear_cache' in payload:
self.in_memory_cache
if 'file_path' in payload:
# 上传文件,需要处理文件逻辑
file_path = payload.get('file_path')
node_id = payload.get('id')
with self.cache_manager.set_client_id(client_id, chat_id):
logger.info(f'client_id={client_id} act=process_message user_id={chat_id}')
await self.process_file(file_path=file_path,
chat_id=chat_id,
client_id=client_id,
id=node_id,
user_id=user_id)
continue
with self.cache_manager.set_client_id(client_id, chat_id):
logger.info(f'client_id={client_id} act=process_message user_id={chat_id}')
await self.process_message(client_id, chat_id, payload, None, False, user_id)
后台引擎
前后端整体交互部分的逻辑没啥太多亮点,自研的文本处理引擎是我比较感兴趣的,但是实际看到开源出来的内容也不多,主要包括下面几部分。
.
├── __init__.py
├── chains
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── combine_documents
│ ├── loader_output.py
│ └── question_answering
├── chat_models
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── host_llm.py
│ ├── interface
│ ├── minimax.py
│ ├── proxy_llm.py
│ ├── wenxin.py
│ ├── xunfeiai.py
│ └── zhipuai.py
├── document_loaders
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── elem_html.py
│ ├── elem_image.py
│ ├── elem_pdf.py
│ ├── parsers
│ └── universal_kv.py
├── embeddings
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── host_embedding.py
│ ├── interface
│ └── wenxin.py
├── retrievers
│ ├── __init__.py
│ └── mix_es_vector.py
└── vectorstores
├── __init__.py
└── elastic_keywords_search.py
- chains 工作链模块实现了文件合并的链
StuffDocumentsChain和打印加载器输出的链LoaderOutputChain - chat_models 模块主要国产模型和自托管模型的对接接口
- document_loaders 文档加载模块,文档解析的 LayoutParser,CRClient,ELLMClient,加载 PDF 的 PDFWithSemanticLoader,以及 UniversalKVLoader
- embeddings 嵌入模型接入了’WenxinEmbeddings’, ‘ME5Embedding’, ‘BGEZhEmbedding’, ‘GTEEmbedding’
- retrievers 检索模块实现了
MixEsVectorRetriever,Elasticsearch 和向量数据库结合的查询方式,但当前应该只是 demo 状态,技能创建页面看不到。 - vectorstores 向量数据库模块实现了 Elasticsearch 关键字搜索接口 ElasticKeywordsSearch
后续会持续关注 document_loaders 模块的内容更新,毕竟在当前嵌入模型效果相差不大的情况下,非结构化的数据预处理对一个 RAG 引擎的作用很大。
官方的演示环境可能因为使用人数较多,老是出现意外错误。为了调试代码,我自己也搭建了一套环境,公号后台回复「bisheng」,获取体验地址。
更多内容在公号:LLM 应用全栈开发